Metabolomics Reveals the Effects of Nitrogen/Phosphorus/Potassium (NPK) Fertilizer Levels on Cucumber Fruit Raised in Different Nutrient Soils
Abstract
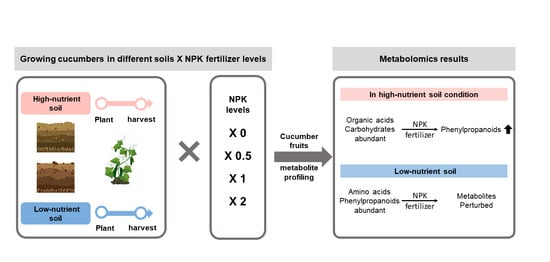
:1. Introduction
- Evaluating the effects of original soil conditions on cucumber fruit yield and quality;
- Assessment of the effects of applied NPK fertilizer levels on the cucumber metabolome in low- and high-nutrient soils;
- Suggesting the necessity for nutrient management based on our results.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Treatments
2.2. Soil Chemical Property Analysis for Two Different Plastic Film Houses
2.3. Sample Preparation for Metabolome Analysis
2.4. Instrumental Analysis
2.5. Data Processing and Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Yields of Cucumber Fruits Cultivated in Two Nutritionally Different Soils
3.2. Soil Chemical Properties of Two Nutritionally Different Soils at Fruit Harvesting
3.3. Non-Targeted Metabolite Profiling and Metabolism Comparison of Cucumber Fruits Cultivated in Two Nutritionally Different Soils
3.4. Effect of NPK Fertilizers on Metabolome of Cucumber Fruits in the Two Different Soils
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shukla, R.; Goyal, A. Novel Dextran from Pediococcus Pentosaceus CRAG3 Isolated from Fermented Cucumber with Anti-Cancer Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Liang, Z.; He, X.; Liu, W.; Jiang, B.; Yan, J.; Sun, P.; Cao, Z.; Peng, Q.; et al. Metabolome and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Chlorophyll and Anthocyanin Metabolism Pathway Associated with Cucumber Fruit Skin Color. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhao, P.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, G.; Cao, L.; Huang, Q. Natural Green-Peel Orange Essential Oil Enhanced the Deposition, Absorption and Permeation of Prochloraz in Cucumber. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 20395–20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, P.C.; Gerber, J.S.; Engstrom, P.M.; Mueller, N.D.; Brauman, K.A.; Carlson, K.M.; Cassidy, E.S.; Johnston, M.; Macdonald, G.K.; Ray, D.K.; et al. Leverage Points for Improving Global Food Security and the Environment. Science 2014, 345, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, C.F.; Tan, C.S.; Gaynor, J.D.; Oloya, T.O.; Welacky, T.W. Influence of Controlled Drainage-Subirrigation on Surface and Tile Drainage Nitrate Loss. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, M.; Lacombe, S.; Bradley, R.L.; Whalen, J.; Cogliastro, A.; Jutras, M.F.; Arp, P. Reduced Soil Nutrient Leaching Following the Establishment of Tree-Based Intercropping Systems in Eastern Canada. Agrofor. Syst. 2011, 83, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.N.; Ac-Pangan, W.O.; Rossi, L. Effects of Soil Salinity on Citrus Rootstock ‘US-942’ physiology and Anatomy. HortScience 2019, 54, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, L. Effect of Optimal Daily Fertigation on Migration of Water and Salt in Soil, Root Growth and Fruit Yield of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) in Solar-Greenhouse. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carranca, C.; Brunetto, G.; Tagliavini, M. Nitrogen Nutrition of Fruit Trees to Reconcile Productivity and Environmental Concerns. Plants 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, F. Crop Responses to Nitrogen Overfertilization: A Review. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 205, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.H.; Lee, F.N.; TeBeest, D.O. Effect of Nitrogen Fertilization on Disease Progress of Rice Blast on Susceptible and Resistant Cultivars. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Soriano, L.; Bundó, M.; Bach-Pages, M.; Chiang, S.F.; Chiou, T.J.; San Segundo, B. Phosphate Excess Increases Susceptibility to Pathogen Infection in Rice. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeijers, S.S.; Pérez-García, A.; Joosten, M.H.A.J.; De Wit, P.J.G.M. The Effect of Nitrogen on Disease Development and Gene Expression in Bacterial and Fungal Plant Pathogens. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2000, 106, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, D.; Goodwin, I.; Jones, R. Minimal Nitrogen and Water Use in Horticulture: Effects on Quality and Content of Selected Nutrients. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Khattak, W.A. Transcriptome Analysis of Sugar and Acid Metabolism in Young Tomato Fruits under High Temperature and Nitrogen Fertilizer Influence. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1197553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, E.A.; Moha, T.; Said, W.; Abdelilahc, M.; Mohammed, R. Use of Metabolomics Data Analysis to Identify Fruit Quality Markers Enhanced by the Application of an Aminopolysaccharide. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 35514–35524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Nie, L.; Zhao, W.; Cui, Q.; Wang, J.; Duan, Y.; Ge, C. Metabolomic Analysis of the Occurrence of Bitter Fruits on Grafted Oriental Melon Plants. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.P.; Singh Bisen, M.; Shukla, R.; Prabha, R.; Maurya, S.; Reddy, Y.S.; Singh, M.; Rai, N.; Chaubey, T.; Chaturvedi, K.K.; et al. Metabolomics-Driven Mining of Metabolite Resources: Applications and Prospects for Improving Vegetable Crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liao, X.; Xia, J.; Xiao, C.; Deng, J.; Xu, Z. Metabolomics: A Promising Technique for Uncovering Quality-Attribute of Fresh and Processed Fruits and Vegetables. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 142, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, G.; Duan, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Tan, S.; Hua, X.; et al. Research Progress and Trends in Metabolomics of Fruit Trees. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 881856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreno-Quintero, N.; Bouwmeester, H.J.; Keurentjes, J.J. Genetic Analysis of Metabolome–Phenotype Interactions: From Model to Crop Species. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katam, R.; Lin, C.; Grant, K.; Katam, C.S.; Chen, S. Advances in Plant Metabolomics and Its Applications in Stress and Single-Cell Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps. World Soil Resour. Rep. 2015, 106, 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Lee, C.-W.; Song, Y.-S.; Lee, Y.-J. Varying Nitrogen Fertigation for Cucumbers Grown in Greenhouses with Soil of Optimal or High Nutrient Status. Korean J. Soil. Sci. Fertil. 2022, 55, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, H.I.; Kwon, M.C.; Lee, N.-R.; Son, S.Y.; Song, D.H.; Lee, C.H. Comparing Metabolites and Functional Properties of Various Tomatoes Using Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Approach. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 659646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.E.; Son, S.Y.; Lee, C.H. Comparison of Metabolome and Functional Properties of Three Korean Cucumber Cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 882120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.M.; Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F. Human Impact on Erodable Phosphorus and Eutrophication: A Global Perspective: Increasing Accumulation of Phosphorus in Soil Threatens Rivers, Lakes, and Coastal. Bioscience 2001, 51, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Xue, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Xue, L.; Yang, L. Fertilization and Global Warming Impact on Paddy CH4 Emissions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turuko, M.; Mohammed, A. Effect of Different Phosphorus Fertilizer Rates on Growth, Dry Matter Yield and Yield Components of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). World J. Agric. Res. 2014, 2, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Sekine-Hayakawa, Y.; Okiyama, A.; Ninomiya, Y. Gustatory Sensation of L-And D-Amino Acids in Humans. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gai, Z.; Gui, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y. Antioxidant Effects of Protocatechuic Acid and Protocatechuic Aldehyde: Old Wine in a New Bottle. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 6139308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Tan, J.; Lou, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhong, Z.; Dai, X.; Sun, Y.; Kuang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Mulberrin Confers Protection against Hepatic Fibrosis by Trim31/Nrf2 Signaling. Redox Biol. 2022, 51, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Niwa, M. Antioxidant Constituents of Radish Sprout (Kaiware-Daikon), Raphanus sativus L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 8061–8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shahzad, B.; Rehman, A.; Bhardwaj, R.; Landi, M.; Zheng, B. Response of Phenylpropanoid Pathway and the Role of Polyphenols in Plants under Abiotic Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Paiva, N.L. Stress-Induced Phenylpropanoid Metabolism. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagin, J.; Sneh, M.; Lowengart-Aycicegi, A. Fertigation. Fertilization through Irrigation. Available online: https://scholar.google.co.kr/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Fertigation.+Fertilization+through+Irrigation&btnG= (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.K. Improving Nutrient and Water Use Efficiency through Fertigation. Available online: https://scholar.google.co.kr/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Improving+nutrient+and+water+use+efficiency+through+fertigation&btnG= (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Hamed, E.; Enrique, P.J. Optimum Management of Furrow Fertigation to Maximize Water and Fertilizer Application Efficiency and Uniformity. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 16, 591–607. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhdary, J.N.; Bakhsh, A.; Arshad, M.; Maqsood, M. Effect of Different Irrigation and Fertigation Strategies on Corn Production under Drip Irrigation. Pak. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 54, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Chemical Properties | NO3-N (mg kg−1) | Av. P2O5 (mg kg−1) | K (cmolc kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-nutrient soil | 32 | 432 | 0.41 |
| High-nutrient soil | 53 | 1147 | 0.85 |
| Recommended * | 70–200 | 350–450 | 0.65–0.80 |
| Chemical Properties | pH (1:5) | EC (1:5; dSm−1) | NO3-N (mg kg−1) | OM (g kg−1) | Av. P2O5 (mg kg−1) | Ex. Cations (cmolc/kg−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | Ca | Mg | Na | ||||||
| Low-nutrient soil | 6.2 a | 1.8 b | 45 b | 22 b | 428 b | 0.91 b | 6.7 b | 2.2 b | 0.23 b |
| High-nutrient soil | 6.4 a | 4.5 a | 99 a | 49 a | 1525 a | 1.88 a | 12.5 a | 2.9 a | 0.74 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, N.-R.; Kim, Y.X.; Lee, Y.; Lee, C.; Song, Y.; Park, H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y. Metabolomics Reveals the Effects of Nitrogen/Phosphorus/Potassium (NPK) Fertilizer Levels on Cucumber Fruit Raised in Different Nutrient Soils. Metabolites 2024, 14, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020102
Lee N-R, Kim YX, Lee Y, Lee C, Song Y, Park H, Lee CH, Lee Y. Metabolomics Reveals the Effects of Nitrogen/Phosphorus/Potassium (NPK) Fertilizer Levels on Cucumber Fruit Raised in Different Nutrient Soils. Metabolites. 2024; 14(2):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020102
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Na-Rae, Yangmin X. Kim, Yerim Lee, Chanwook Lee, Yosung Song, Hyejin Park, Choong Hwan Lee, and Yejin Lee. 2024. "Metabolomics Reveals the Effects of Nitrogen/Phosphorus/Potassium (NPK) Fertilizer Levels on Cucumber Fruit Raised in Different Nutrient Soils" Metabolites 14, no. 2: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020102
APA StyleLee, N. -R., Kim, Y. X., Lee, Y., Lee, C., Song, Y., Park, H., Lee, C. H., & Lee, Y. (2024). Metabolomics Reveals the Effects of Nitrogen/Phosphorus/Potassium (NPK) Fertilizer Levels on Cucumber Fruit Raised in Different Nutrient Soils. Metabolites, 14(2), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020102