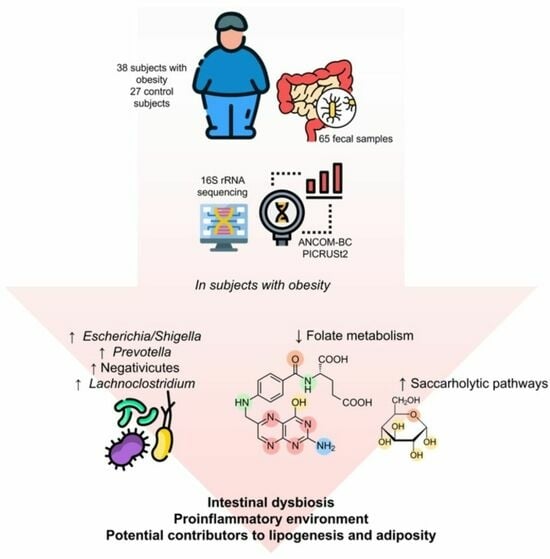
Intestinal Dysbiosis in Subjects with Obesity from Western Mexico and Its Association with a Proinflammatory Profile and Disturbances of Folate (B9) and Carbohydrate Metabolism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Anthropometric Evaluation and Biochemical Parameters
2.3. Blood Pressure
2.4. Extraction of Nucleic Acids and 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis of 16S Amplicon Sequencing
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Cross-Sectional Study and Clinical Assessments
3.2. Microbiota Diversity between Groups
3.3. Relative Abundances
3.4. Differential Abundances (LEfSe and ANCOM-BC)
3.5. Functional Prediction of Metabolic Pathways (PICRUSt2)
3.6. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Instituto de Seguridad y Servicios Sociales de los Trabajadores del Estado La Obesidad En México. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/issste/articulos/la-obesidad-en-mexico (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Rubio, M.A.; Barbany, M.; Moreno, B. Consenso SEEDO 2007 Para La Evaluación Del Sobrepeso y La Obesidad y El Establecimiento de Criterios de Intervención Terapéutica. Med. Clin. 2007, 128, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.D. The Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Obesity. Nutr. Today 2016, 51, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.; Yang, H. Factors Affecting the Composition of the Gut Microbiota, and Its Modulation. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Han, R.; Cao, Y.; Hua, W.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, X.; Wei, C.; et al. Interactions between Gut Microbiota, Host Genetics and Diet Relevant to Development of Metabolic Syndromes in Mice. ISME J. 2010, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mantrana, I.; Selma-Royo, M.; Alcantara, C.; Collado, M.C. Shifts on Gut Microbiota Associated to Mediterranean Diet Adherence and Specific Dietary Intakes on General Adult Population. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Vannini, L.; Jeffery, I.B.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Di Cagno, R.; Ferrocino, I.; Lazzi, C.; et al. High-Level Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet Beneficially Impacts the Gut Microbiota and Associated Metabolome. Gut 2016, 65, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Dutta, A.; Bose, T.; Mande, S.S. A Compendium of Predicted Growths and Derived Symbiotic Relationships between 803 Gut Microbes in 13 Different Diets. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merra, G.; Noce, A.; Marrone, G.; Cintoni, M.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Capacci, A.; De Lorenzo, A. Influence of Mediterranean Diet on Human Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2020, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañer, O.; Schröder, H. Response to: Comment on “The Gut Microbiome Profile in Obesity: A Systematic Review”. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 9109451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farías, N.M.M.; Silva, B.C.; Rozowski, N.J. Microbiota Intestinal: Rol En Obesidad. Rev. Chil. Nutr. 2011, 38, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinart, M.; Dötsch, A.; Schlicht, K.; Laudes, M.; Bouwman, J.; Forslund, S.K.; Pischon, T.; Nimptsch, K. Gut Microbiome Composition in Obese and Non-Obese Persons: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovesy, L.; Masterson, D.; Rosado, E.L. Profile of the Gut Microbiota of Adults with Obesity: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jinag, W.; Huang, W.; Lin, Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; Ng, S.C. Gut Microbiota in Patients with Obesity and Metabolic Disorders—A Systematic Review. Genes. Nutr. 2022, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina Inc. Illumina 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/downloads/16s_metagenomic_sequencing_library_preparation.html (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.I.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A Novel Method for Rapid Multiple Sequence Alignment Based on Fast Fourier Transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robeson, M.S.; O’Rourke, D.R.; Kaehler, B.D.; Ziemski, M.; Dillon, M.R.; Foster, J.T.; Bokulich, N.A. RESCRIPt: Reproducible Sequence Taxonomy Reference Database Management. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing Taxonomic Classification of Marker-Gene Amplicon Sequences with QIIME 2′s Q2-Feature-Classifier Plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric Estimation of the Number of Classes in a Population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Kelley, S.T.; Knight, R. Quantitative and Qualitative β Diversity Measures Lead to Different Insights into Factors That Structure Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afgan, E.; Baker, D.; Batut, B.; van den Beek, M.; Bouvier, D.; Čech, M.; Chilton, J.; Clements, D.; Coraor, N.; Grüning, B.A.; et al. The Galaxy Platform for Accessible, Reproducible and Collaborative Biomedical Analyses: 2018 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W537–W544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for Prediction of Metagenome Functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, P.; Kozlov, A.M.; Czech, L.; Morel, B.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. EPA-Ng: Massively Parallel Evolutionary Placement of Genetic Sequences. Syst. Biol. 2019, 68, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, L.; Barbera, P.; Stamatakis, A. Genesis and Gappa: Processing, Analyzing and Visualizing Phylogenetic (Placement) Data. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3263–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Doebeli, M. Efficient Comparative Phylogenetics on Large Trees. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1053–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Doak, T.G. A Parsimony Approach to Biological Pathway Reconstruction/Inference for Genomes and Metagenomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, R.; Altman, T.; Billington, R.; Dreher, K.; Foerster, H.; Fulcher, C.A.; Holland, T.A.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Kubo, A.; et al. The MetaCyc Database of Metabolic Pathways and Enzymes and the BioCyc Collection of Pathway/Genome Databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D459–D471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S. Das Analysis of Compositions of Microbiomes with Bias Correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for Comprehensive Statistical, Functional, and Meta-Analysis of Microbiome Data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Díaz, T.A.; Amador-Lara, F.; Andrade-Villanueva, J.F.; González-Hernández, L.A.; Cabrera-Silva, R.I.; Sánchez-Reyes, K.; Álvarez-Zavala, M.; Valenzuela-Ramírez, A.; Del Toro-Arreola, S.; Bueno-Topete, M.R. Gut Bacterial Communities in HIV-Infected Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome: Effects of the Therapy with Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor-Based and Protease Inhibitor-Based Regimens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, L.C.; Sardà Carbasse, J.; Koblitz, J.; Ebeling, C.; Podstawka, A.; Overmann, J. BacDive in 2022: The Knowledge Base for Standardized Bacterial and Archaeal Data. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, D741–D746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubourg, G.; Lagier, J.C.; Hüe, S.; Surenaud, M.; Bachar, D.; Robert, C.; Michelle, C.; Ravaux, I.; Mokhtari, S.; Million, M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Associated with HIV Infection Is Significantly Enriched in Bacteria Tolerant to Oxygen. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2016, 3, e000080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, M.K.; Kaliaperumal, V.; Akella, A.; Venugopal, G.; Ramadass, B. Mapping Microbiome-Redox Spectrum and Evaluating Microbial-Redox Index in Chronic Gastritis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.-B.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Huang, H.-H.; Lin, J. Prospects for Clinical Applications of Butyrate-Producing Bacteria. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Gut Microbiota: Role in Pathogen Colonization, Immune Responses, and Inflammatory Disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez-Carbajal, A.; Nirmalkar, K.; Pérez-Lizaur, A.; Hernández-Quiroz, F.; Ramírez-del-Alto, S.; García-Mena, J.; Hernández-Guerrero, C. Gut Microbiota and Predicted Metabolic Pathways in a Sample of Mexican Women Affected by Obesity and Obesity Plus Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Qin, Q.; Chen, J.; Yan, S.; Li, T.; Gao, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, A.; Ding, S. Gut Microbiome Alterations in Patients With Visceral Obesity Based on Quantitative Computed Tomography. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 823262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Guo, P.; Mao, R.; Ren, Z.; Wen, J.; Yang, Q.; Yan, T.; Yu, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. Gut Microbiota Signature of Obese Adults Across Different Classifications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 3933–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Yang, W.; Chen, G.; Shafiq, M.; Javed, S.; Ali Zaidi, S.S.; Shahid, R.; Liu, C.; Bokhari, H. Analysis of Gut Microbiota of Obese Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and Healthy Individuals. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz Pedrogo, D.A.; Jensen, M.D.; Van Dyke, C.T.; Murray, J.A.; Woods, J.A.; Chen, J.; Kashyap, P.C.; Nehra, V. Gut Microbial Carbohydrate Metabolism Hinders Weight Loss in Overweight Adults Undergoing Lifestyle Intervention With a Volumetric Diet. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luca, C.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Mei, M.; Yang, S.; Li, Q. Roles of Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation in the Development of Ectopic Fat Deposition. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 418185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, V.; Scaldaferri, F.; Putignani, L.; Del Chierico, F. The Role of Enterobacteriaceae in Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anhê, F.F.; Jensen, B.A.H.; Varin, T.V.; Servant, F.; Van Blerk, S.; Richard, D.; Marceau, S.; Surette, M.; Biertho, L.; Lelouvier, B.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes Influences Bacterial Tissue Compartmentalisation in Human Obesity. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.S.; Luu, K.; Lagishetty, V.; Sedighian, F.; Woo, S.-L.; Dreskin, B.W.; Katzka, W.; Chang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Arias-Jayo, N.; et al. The Intestinal Microbiome Predicts Weight Loss on a Calorie-Restricted Diet and Is Associated with Improved Hepatic Steatosis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.M. The Immune Response to Prevotella Bacteria in Chronic Inflammatory Disease. Immunology 2017, 151, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z. The Relationship of Megamonas Species with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents Revealed by Metagenomics of Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmas, V.; Pisanu, S.; Madau, V.; Casula, E.; Deledda, A.; Cusano, R.; Uva, P.; Vascellari, S.; Loviselli, A.; Manzin, A.; et al. Gut Microbiota Markers Associated with Obesity and Overweight in Italian Adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, A.; Louca, P.; Zhang, X.; Wells, P.M.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; Falchi, M.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. Circulating Levels of the Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate Mediate the Effect of the Gut Microbiome on Visceral Fat. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 711359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, J.L.; Ley, R.E. The Human Gut Bacteria Christensenellaceae Are Widespread, Heritable, and Associated with Health. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansaldo, E.; Slayden, L.C.; Ching, K.L.; Koch, M.A.; Wolf, N.K.; Plichta, D.R.; Brown, E.M.; Graham, D.B.; Xavier, R.J.; Moon, J.J.; et al. Akkermansia Muciniphila Induces Intestinal Adaptive Immune Responses during Homeostasis. Science 2019, 364, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia Muciniphila in Overweight and Obese Human Volunteers: A Proof-of-Concept Exploratory Study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete-Muñoz, E.-M.; Vioque, J.; Toledo, E.; Oncina-Canovas, A.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Romaguera, D.; Alonso-Gómez, Á.M.; et al. Dietary Folate Intake and Metabolic Syndrome in Participants of PREDIMED-Plus Study: A Cross-Sectional Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, S.; Sözlü, S.; Bölükbaşi, H.; Ünsal, N.; Gezmen-Karadağ, M. Obesity Is Associated with Folate Metabolism. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2020, 90, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belda, E.; Voland, L.; Tremaroli, V.; Falony, G.; Adriouch, S.; Assmann, K.E.; Prifti, E.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Debédat, J.; Le Roy, T.; et al. Impairment of Gut Microbial Biotin Metabolism and Host Biotin Status in Severe Obesity: Effect of Biotin and Prebiotic Supplementation on Improved Metabolism. Gut 2022, 71, 2463–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Mejia, C. Pharmacological Effects of Biotin. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, R.; Guo, M.; Zheng, H. Characteristics of Gut Microbiota in People with Obesity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Characteristics | Ob Group (n = 38) | Control Group (n = 27) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 37.7 ± 12.0 | 44.2 ± 12.4 | 0.088 a |
| Sex | |||
| Men, n (%) | 17 (44.7%) | 14 (51.9%) | 0.571 c |
| Women, n (%) | 21 (55.3%) | 13 (48.1%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 35.6 (32.8–42.7) | 24.9 (23.1–26.9) | <0.001 *b |
| Body fat % | 45.0 ± 7.9 | 29.3 ± 7.9 | <0.001 *a |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 97.0 (92.0–105.3) | 90.0 (85.5–94.5) | 0.001 *b |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 213.2 ± 77.1 | 126.6 ± 78.3 | 0.001 *a |
| TC (mg/dL) | 192.9 ± 28.6 | 158.6 ± 26.4 | 0.005 *a |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 92.0 (88.5–115.5) | 100.0 (59.0–113.0) | 0.540 b |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 35.0 (28.0–46.0) | 44.0 (40.0–59.0) | 0.002 *b |
| SBP (mmHg) | 135.9 ± 19.9 | 110.4 ± 20.0 | 0.002 *a |
| DBP (mmHg) | 92.5 ± 11.0 | 77.3 ± 11.5 | 0.001 *a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riggen-Bueno, V.; Del Toro-Arreola, S.; Baltazar-Díaz, T.A.; Vega-Magaña, A.N.; Peña-Rodríguez, M.; Castaño-Jiménez, P.A.; Sánchez-Orozco, L.V.; Vera-Cruz, J.M.; Bueno-Topete, M.R. Intestinal Dysbiosis in Subjects with Obesity from Western Mexico and Its Association with a Proinflammatory Profile and Disturbances of Folate (B9) and Carbohydrate Metabolism. Metabolites 2024, 14, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020121
Riggen-Bueno V, Del Toro-Arreola S, Baltazar-Díaz TA, Vega-Magaña AN, Peña-Rodríguez M, Castaño-Jiménez PA, Sánchez-Orozco LV, Vera-Cruz JM, Bueno-Topete MR. Intestinal Dysbiosis in Subjects with Obesity from Western Mexico and Its Association with a Proinflammatory Profile and Disturbances of Folate (B9) and Carbohydrate Metabolism. Metabolites. 2024; 14(2):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020121
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiggen-Bueno, Verónica, Susana Del Toro-Arreola, Tonatiuh Abimael Baltazar-Díaz, Alejandra N. Vega-Magaña, Marcela Peña-Rodríguez, Paula Alejandra Castaño-Jiménez, Laura Verónica Sánchez-Orozco, José María Vera-Cruz, and Miriam Ruth Bueno-Topete. 2024. "Intestinal Dysbiosis in Subjects with Obesity from Western Mexico and Its Association with a Proinflammatory Profile and Disturbances of Folate (B9) and Carbohydrate Metabolism" Metabolites 14, no. 2: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020121
APA StyleRiggen-Bueno, V., Del Toro-Arreola, S., Baltazar-Díaz, T. A., Vega-Magaña, A. N., Peña-Rodríguez, M., Castaño-Jiménez, P. A., Sánchez-Orozco, L. V., Vera-Cruz, J. M., & Bueno-Topete, M. R. (2024). Intestinal Dysbiosis in Subjects with Obesity from Western Mexico and Its Association with a Proinflammatory Profile and Disturbances of Folate (B9) and Carbohydrate Metabolism. Metabolites, 14(2), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14020121