A Quantitative HILIC–MS/MS Assay of the Metabolic Response of Huh-7 Cells Exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
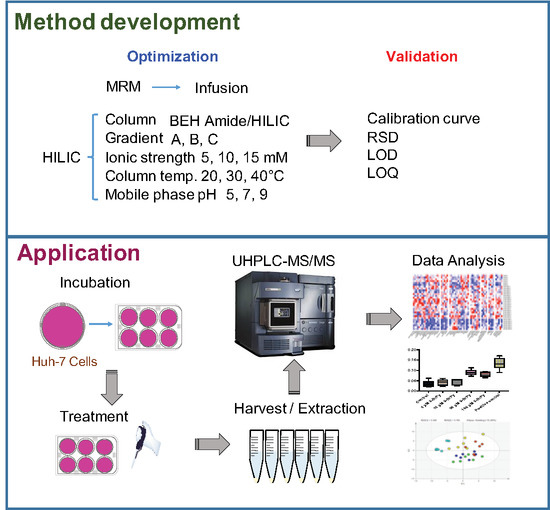
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. MRM Transitions and Validation of the HILIC-UHPLC-MS/MS Method
2.2. HILIC Method Development
2.3. Validation of Method with Huh-7 Cells for Glycolysis Pathway
2.4. Application of Method on TCDD Toxicology with Huh-7 Cells
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. HILIC-UHPLC-MS/MS Analysis
4.3. Cell Experiment
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.5. Metabolite Extraction for LC-MS/MS
4.6. Metabolite Extraction for 1H NMR
4.7. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramautar, R.; Berger, R.; van der Greef, J.; Hankemeier, T. Human Metabolomics: Strategies to Understand Biology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deidda, M.; Piras, C.; Bassareo, P.P.; Cadeddu Dessalvi, C.; Mercuro, G. Metabolomics, a Promising Approach to Translational Research in Cardiology. IJC Metab. Endocr. 2015, 9, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Ye, W.; Zu, X.; Xie, H.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Integrative Metabolic and Microbial Profiling on Patients with Spleen-Yang-Deficiency Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchione, M.B.; Eiras, J.; Suarez, G.V.; Angerami, M.T.; Marquez, C.; Sued, O.; Ben, G.; Pérez, H.M.; Gonzalez, D.; Maidana, P.; et al. Determination of Dehydroepiandrosterone and Its Biologically Active Oxygenated Metabolites in Human Plasma Evinces a Hormonal Imbalance during HIV-TB Coinfection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.H.; Kumar, S. Caspases in Metabolic Disease and Their Therapeutic Potential. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metabolomic Profiles Delineate Potential Role for Sarcosineh in Prostate Cancer Progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravenzwaay, V.B.; Cunha, G.C.-P.; Leibold, E.; Looser, R.; Mellert, W.; Prokoudine, A.; Walk, T.; Wiemer, J. The Use of Metabolomics for the Discovery of New Biomarkers of Effect. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 172, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghotbaddini, M.; Powell, J.B. The AhR Ligand, TCDD, Regulates Androgen Receptor Activity Differently in Androgen-Sensitive versus Castration-Resistant Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7506–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, C.C.; Hattemer-Frey, H.A. Human Exposure to Dioxin. Sci. Total Environ. 1991, 104, 97–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luster, M.I.; Faith, R.E.; Clark, G. Laboratory Studies on the Immune Effects of Halogenated Aromatics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1979, 320, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, J.; Yamashita, K.; Nakamura, K.; Morita, M.; Takagi, T.N.; Nakao, K.; Ema, M.; Sogawa, K.; Yasuda, M.; Katsuki, M.; et al. Loss of Teratogenic Response to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin (TCDD) in Mice Lacking the Ah (Dioxin) Receptor. Genes Cells 2003, 2, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe, S.H. Comparative Toxicology and Mechanism of Action of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-P-Dioxins and Dibenzofurans. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1986, 26, 371–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Salguero, P.M.; Hilbert, D.M.; Rudikoff, S.; Ward, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J. Aryl-Hydrocarbon Receptor-Deficient Mice Are Resistant to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin-Induced Toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1996, 140, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poland, A.; Glover, E. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin: Segregation of Toxicity with the Ah Locus. Mol. Pharmacol. 1980, 17, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beger, R.D.; Sun, J.; Schnackenberg, L.K. Metabolomics Approaches for Discovering Biomarkers of Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 243, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coen, M.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling and Metabonomic Approaches to Problems in Molecular Toxicology. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vliet, E.; Morath, S.; Eskes, C.; Linge, J.; Neurotoxicology, J.R. A Novel in Vitro Metabolomics Approach for Neurotoxicity Testing, Proof of Principle for Methyl Mercury Chloride and Caffeine. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.K.; Chan, P.H.; Doktorova, T.; Athersuch, T.J.; Cavill, R.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V.; Vinken, M.; Nicholson, J.K.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; et al. Effect of the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Trichostatin A on the Metabolome of Cultured Primary Hepatocytes. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.E.; Miao, Z.F.; Lee, W.J.; Chao, H.R.; Li, L.A.; Wang, Y.F.; Ko, Y.C.; Tsai, F.Y.; Yeh, S.C.; Tsou, T.C. Arecoline Inhibits the 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin-Induced Cytochrome P450 1A1 Activation in Human Hepatoma Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yan, K.; Chen, Q.; Cheddah, S.; Shen, L.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, C. Preparation of Silica Colloidal Crystal Column and Its Application in Pressurized Capillary Electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1587, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Noga, S. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC)—A Powerful Separation Technique. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedo, F. Adsorption from Liquid Mixtures and Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 1982, 238, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Duda, J.; Radke, C.J. Solution Adsorption from Liquid Chromatography. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1978, 66, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, D.; Rhoades, S.; Weljie, A.M. Extraction and Analysis of Pan-Metabolome Polar Metabolites by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Bio-Protocol 2018, 8, e2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaceau, J.P.; Chambers, E.E.; Fountain, K.J. Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) for LC-MS/MS Analysis of Monoamine Neurotransmitters. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoshan, M.C. 3-Bromopyruvate: Targets and Outcomes. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2012, 44, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy-Kanniappan, S.; Geschwind, J.F.H.; Kunjithapatham, R.; Buijs, M.; Vossen, J.A.; Tchernyshyov, I.; Cole, R.N.; Syed, L.H.; Rao, P.P.; Ota, S.; et al. Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH) Is Pyruvylated during 3-Bromopyruvate Mediated Cancer Cell Death. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 4909–4918. [Google Scholar]
- Arendt, T.; Schugens, M.M.; Marchbanks, R.M. Reversible Inhibition of Acetylcholine Synthesis and Behavioural Effects Caused by 3-Bromopyruvate. J. Neurochem. 1990, 55, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardaci, S.; Desideri, E.; Ciriolo, M.R. Targeting Aerobic Glycolysis: 3-Bromopyruvate as a Promising Anticancer Drug. J. Bioenerg. 2012, 44, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Agnihotri, S.; Micallef, J.; Mukherjee, J.; Sabha, N.; Cairns, R.; Hawkins, C.; Guha, A. Hexokinase 2 Is a Key Mediator of Aerobic Glycolysis and Promotes Tumor Growth in Human Glioblastoma Multiforme. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy-Kanniappan, S.; Kunjithapatham, R.; Torbenson, M.S.; Rao, P.P.; Carson, K.A.; Buijs, M.; Vali, M.; Geschwind, J.F.H. Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Mouse Model: Assessment of Tumor Response to Percutaneous Ablation by Using Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Antagonists. Radiology 2012, 262, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, M.; Chen, S.; Lao, T.; Liang, D.; Sang, N. Nitrogen Anabolism Underlies the Importance of Glutaminolysis in Proliferating Cells. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3921–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrke, E.; Arend, C.; Dringen, R. 3-Bromopyruvate Inhibits Glycolysis, Depletes Cellular Glutathione, and Compromises the Viability of Cultured Primary Rat Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 93, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofk, H.R.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Harris, M.H.; Ramanathan, A.; Gerszten, R.E.; Wei, R.; Fleming, M.D.; Schreiber, S.L.; Cantley, L.C. The M2 Splice Isoform of Pyruvate Kinase Is Important for Cancer Metabolism and Tumour Growth. Nature 2008, 452, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qie, S.; Liang, D.; Yin, C.; Gu, W.; Meng, M.; Wang, C.; Sang, N. Glutamine Depletion and Glucose Depletion Trigger Growth Inhibition via Distinctive Gene Expression Reprogramming. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkalainen, M.; Huumonen, K.; Naarala, J.; Viluksela, M.; Juutilainen, J. Dioxin Induces Genomic Instability in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Hankinson, O. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin Suppresses the Growth of Human Liver Cancer HepG2 Cells in Vitro: Involvement of Cell Signaling Factors. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeilinger, K.; Freyer, N.; Damm, G.; Seehofer, D.; Knöspel, F. Cell Sources for in Vitro Human Liver Cell Culture Models. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 1684–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkening, S.; Stahl, F.; Bader, A. Comparison of Primary Human Hepatocytes and Hepatoma Cell Line HEPG2 with Regard to their Biotransformation Properties. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, M.T.; Jover, R.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J. Hepatic Cell Lines for Drug Hepatotoxicity Testing: Limitations and Strategies to Upgrade Their Metabolic Competence by Gene Engineering. Curr. Drug Metab. 2013, 14, 946–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwosu, Z.C.; Battello, N.; Rothley, M.; Piorońska, W.; Sitek, B.; Ebert, M.P.; Hofmann, U.; Sleeman, J.; Wölfl, S.; Meyer, C. Liver Cancer Cell Lines Distinctly Mimic the Metabolic Gene Expression Pattern of the Corresponding Human Tumours. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Sirota, M.; Fan-Minogue, H.; Hadley, D.; Butte, A.J. Relating Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumor Samples and Cell Lines Using Gene Expression Data in Translational Research. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denison, M.; Nagy, S.R. Activation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor by Structurally Diverse Exogenous and Endogenous Chemicals. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 2003, 43, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, A.; Bindesbøll, C.; Satheesh, S.V.; Grimaldi, G.; Hutin, D.; MacPherson, L.; Ahmed, S.; Tamblyn, L.; Cho, T.; Nebb, H.I.; et al. Characterization of TCDD-Inducible Poly-ADP-Ribose Polymerase (TIPARP/ARTD14) Catalytic Activity. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 3827–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, H.-R.; Tsou, T.-C.; Li, L.-A.; Tsai, F.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chang, E.E.; Miao, Z.-F.; Wu, C.-H.; Lee, W.-J. Arsenic Inhibits Induction of Cytochrome P450 1A1 by 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin in Human Hepatoma Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.W. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin (TCDD) Inhibits Growth Factor Withdrawal-Induced Apoptosis in the Human Mammary Epithelial Cell Line, MCF-10A. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.W.; Lauer, F.T.; Burdick, A.D.; Hudson, L.G.; Burchiel, S.W. Prevention of Apoptosis by 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin (TCDD) in the MCF-10A Cell Line: Correlation with Increased Transforming Growth Factor Alpha Production. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3314–3320. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Chen, H.; Su, H.; Lee, C.; Shen, K.; Ho, W.; Ho, S.; Ho, Y.; Wang, Y. The Topical Application of 2, 3, 7, 8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin Lacks Skin Tumor-Promoting Potency but Induces Hepatic Injury and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Expression in ICR Male Mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 8, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, D.B.; Partensky, C.; Wilbourn, J.; Rice, J.M. An IARC Evaluation of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans as Risk Factors in Human Carcinogenesis. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 755–760. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.J.; Siao, S.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Chang, L.W.; Wu, C.H.; Lin, P.; Wang, Y.J. TCDD Promotes Lung Tumors via Attenuation of Apoptosis through Activation of the Akt and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.M.; Feugang, J.M.; Pfeiffer, K.E.; Stokes, J.V.; Bowers, S.D.; Ryan, P.L. L-Arginine Enhances Cell Proliferation and Reduces Apoptosis in Human Endometrial RL95-2 Cells. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2013, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Shukla, G.; Wahi, A.K. Protective Effect of L-Arginine against Necrosis and Apoptosis Induced by Experimental Ischemic and Reperfusion in Rat Liver. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Aracama, A.; Peijnenburg, A.; Kleinjans, J.; Jennen, D.; van Delft, J.; Hellfrisch, C.; Lommen, A. An Untargeted Multi-Technique Metabolomics Approach to Studying Intracellular Metabolites of HepG2 Cells Exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, H.; Park, K.K.; Kim, H.W.; Park, T. Taurine-Responsive Genes Related to Signal Transduction as Identified by CDNA Microarray Analyses of HepG2 Cells. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, L.H.; Sutter, C.H.; Leon Carrion, S.; Tran, Q.T.; Bodreddigari, S.; Kensicki, E.; Mohney, R.P.; Sutter, T.R. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin-Mediated Production of Reactive Oxygen Species Is an Essential Step in the Mechanism of Action to Accelerate Human Keratinocyte Differentiation. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 132, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Bergmeier, S.; Qian, Y.; Akbar, H.; Colvin, R.; Ding, J.; Tong, L.; Wu, S.; et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of glucose transporter 1 downregulates glycolysis, induces cell-cycle arrest, and inhibits cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Cai, J.; Nichols, R.G.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Smith, P.B.; Wang, Y.; Yan, C.; Patterson, A.D. A Quantitative HILIC–MS/MS Assay of the Metabolic Response of Huh-7 Cells Exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin. Metabolites 2019, 9, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9060118
Liu Q, Cai J, Nichols RG, Tian Y, Zhang J, Smith PB, Wang Y, Yan C, Patterson AD. A Quantitative HILIC–MS/MS Assay of the Metabolic Response of Huh-7 Cells Exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin. Metabolites. 2019; 9(6):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9060118
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qing, Jingwei Cai, Robert G. Nichols, Yuan Tian, Jintao Zhang, Philip B. Smith, Yan Wang, Chao Yan, and Andrew D. Patterson. 2019. "A Quantitative HILIC–MS/MS Assay of the Metabolic Response of Huh-7 Cells Exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin" Metabolites 9, no. 6: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9060118
APA StyleLiu, Q., Cai, J., Nichols, R. G., Tian, Y., Zhang, J., Smith, P. B., Wang, Y., Yan, C., & Patterson, A. D. (2019). A Quantitative HILIC–MS/MS Assay of the Metabolic Response of Huh-7 Cells Exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin. Metabolites, 9(6), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9060118