The Formation of a Rubble Pile Asteroid: Insights from the Asteroid Ryugu
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Nature of Ryugu Particles
3. Formation of a Progenitor Planetesimal
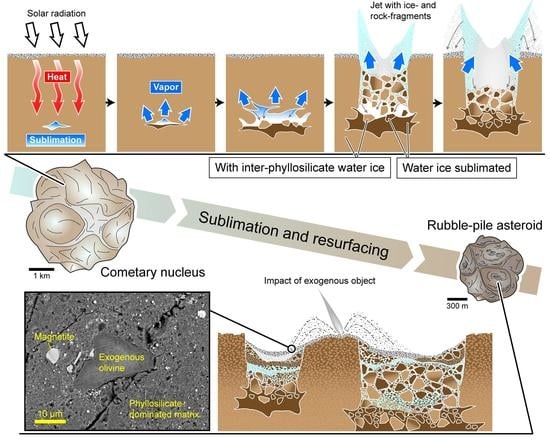
4. Evolution to a Rubble Pile Asteroid
5. Implications for Near-Earth Objects
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Systematics of Highly Siderophile Elements and Their Isotopes in the Ryugu Particles

References
- Bus, S.J.; Binzel, R.P. Phase II of the Small Main-Belt Asteroid Spectroscopic Survey: A feature-based taxonomy. Icarus 2002, 158, 146–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.I.; Tsuda, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Tanaka, S.; Saiki, T.; Nakazawa, S. Hayabusa2 mission overview. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 208, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Hirabayashi, M.; Hirata, N.; Hirata, N.; Noguchi, R.; Shimaki, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Tatsumi, E.; Yoshikawa, M.; Kikuchi, S.; et al. Hayabusa2 arrives at the carbonaceous asteroid 162173 Ryugu—A spinning top-shaped rubble pile. Science 2019, 364, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, S.; Honda, R.; Morota, T.; Kameda, S.; Sawada, H.; Tatsumi, E.; Yamada, M.; Honda, C.; Yokota, Y.; Kouyama, T.; et al. The geomorphology, color, and thermal properties of Ryugu: Implications for parent-body processes. Science 2019, 364, eaaw0422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitazato, K.; Milliken, R.E.; Iwata, T.; Abe, M.; Ohtake, M.; Matsuura, S.; Arai, T.; Nakauchi, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Matsuoka, M.; et al. The surface composition of asteroid 162173 Ryugu from Hayabusa2 near-infrared spectroscopy. Science 2019, 364, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potiszil, C.; Tanaka, R.; Kobayashi, K.; Kunihiro, T.; Nakamura, E. The albedo of Ryugu: Evidence for a high organic abundance, as inferred from the Hayabusa2 touchdown maneuver. Astrobiology 2020, 20, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Nakamura, E.; Kunihiro, T. The asteroid 162173 Ryugu: A cometary origin. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 925, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, F.; Timms, N.E.; Nakamura, T.; Rickard, W.D.A.; Mayers, C.; Reddy, S.M.; Saxey, D.; Daly, L.; Bland, P.A.; Eroglu, E.; et al. Rubble pile asteroids are forever. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2214353120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.J. Rubble Pile Asteroids. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 56, 593–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grott, M.; Knollenberg, J.; Hamm, M.; Ogawa, K.; Jaumann, R.; Otto, K.A.; Delbo, M.; Michel, P.; Biele, J.; Neumann, W.; et al. Low thermal conductivity boulder with high porosity identified on C-type asteroid (162173) Ryugu. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Tanaka, S.; Taguchi, M.; Arai, T.; Senshu, H.; Sakatani, N.; Shimaki, Y.; Demura, H.; Ogawa, Y.; et al. Highly porous nature of a primitive asteroid revealed by thermal imaging. Nature 2020, 579, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakatani, N.; Tanaka, S.; Okada, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Riu, L.; Sugita, S.; Honda, R.; Morota, T.; Kameda, S.; Yokota, Y.; et al. Anomalously porous boulders on (162173) Ryugu as primordial materials from its parent body. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottke, W.F.; Durda, D.D.; Nesvorný, D.; Jedicke, R.; Morbidelli, A.; Vokrouhlický, D.; Levison, H. The fossilized size distribution of the main asteroid belt. Icarus 2005, 175, 111–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deller, J.F.; Lowry, S.C.; Snodgrass, C.; Price, M.C.; Sierks, H. A new approach to modelling impacts on rubble pile asteroid simulants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 455, 3752–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arakawa, M.; Saiki, T.; Wada, K.; Ogawa, K.; Kadono, T.; Shirai, K.; Sawada, H.; Ishibashi, K.; Honda, R.; Sakatani, N.; et al. An artificial impact on the asteroid (162173) Ryugu formed a crater in the gravity-dominated regime. Science 2020, 368, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morota, T.; Sugita, S.; Cho, Y.; Kanamaru, M.; Tatsumi, E.; Sakatani, N.; Honda, R.; Kikuchi, H.; Yamada, M.; Yokota, Y.; et al. Sample collection from asteroid (162173) Ryugu by Hayabusa2: Implications for surface evolution. Science 2020, 368, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, S.; Sawada, H.; Okazaki, R.; Takano, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Miura, Y.N.; Okamoto, C.; Yano, H.; Yamanouchi, S.; Michel, P.; et al. Pebbles and sand on asteroid (162173) Ryugu: In situ observation and particles returned to Earth. Science 2022, 375, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yada, T.; Abe, M.; Okada, T.; Nakato, A.; Yogata, K.; Miyazaki, A.; Hatakeda, K.; Kumagai, K.; Nishimura, M.; Hitomi, Y.; et al. Preliminary analysis of the Hayabusa2 samples returned from C-type asteroid Ryugu. Nat. Astron. 2021, 6, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, E.; Kobayashi, K.; Tanaka, R.; Kunihiro, T.; Kitagawa, H.; Potiszil, C.; Ota, T.; Sakaguchi, C.; Yamanaka, M.; Ratnayake, D.M.; et al. On the origin and evolution of the asteroid Ryugu: A comprehensive geochemical perspective. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2022, 98, 227–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Amano, K.; Enokido, Y.; Zolensky, M.E.; Mikouchi, T.; Genda, H.; Tanaka, S.; Zolotov, M.Y.; Kurosawa, K.; et al. Formation and evolution of carbonaceous asteroid Ryugu: Direct evidence from returned samples. Science 2022, 379, eabn8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barucci, M.A.; Perna, D.; Popescu, M.; Fornasier, S.; Doressoundiram, A.; Lantz, C.; Merlin, F.; Fulchignoni, M.; Dotto, E.; Kanuchova, S. Small D-type asteroids in the NEO population: New targets for space missions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 4481–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiya, W.; Hoppe, P.; Ushikubo, T.; Fukuda, K.; Lindgren, P.; Lee, M.R.; Koike, M.; Shirai, K.; Sano, Y. Migration of D-type asteroids from the outer Solar System inferred from carbonate in meteorites. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokoyama, T.; Nagashima, K.; Nakai, I.; Young, E.D.; Abe, Y.; Aléon, J.; Alexander, C.M.O.; Amari, S.; Amelin, Y.; Bajo, K.i.; et al. Samples returned from the asteroid Ryugu are similar to Ivuna-type carbonaceous meteorites. Science 2022, 379, eabn7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, R.C.; Franchi, I.A.; Findlay, R.; Malley, J.A.; Ito, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kimura, M.; Tomioka, N.; Uesugi, M.; Imae, N.; et al. Oxygen isotope evidence from Ryugu samples for early water delivery to Earth by CI chondrites. Nat. Astron. 2023, 7, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraoka, H.; Takano, Y.; Dworkin, J.P.; Oba, Y.; Hamase, K.; Furusho, A.; Ogawa, N.O.; Hashiguchi, M.; Fukushima, K.; Aoki, D.; et al. Soluble organic molecules in samples of the carbonaceous asteroid (162173) Ryugu. Science 2023, 379, eabn9033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piani, L.; Nagashima, K.; Kawasaki, N.; Sakamoto, N.; Bajo, K.i.; Abe, Y.; Aléon, J.; Alexander, C.M.O.; Amari, S.; Amelin, Y.; et al. Hydrogen Isotopic Composition of Hydrous Minerals in Asteroid Ryugu. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 946, L43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Tomioka, N.; Uesugi, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Shirai, N.; Ohigashi, T.; Liu, M.C.; Greenwood, R.C.; Kimura, M.; Imae, N.; et al. A pristine record of outer Solar System materials from asteroid Ryugu’s returned sample. Nat. Astron. 2022, 6, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, T.; Dauphas, N.; Abe, Y.; Aléon, J.; Alexander, C.M.O.; Amari, S.; Amelin, Y.; Bajo, K.I.; Bizzarro, M.; Bouvier, A.; et al. Ryugu’s nucleosynthetic heritage from the outskirts of the Solar System. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, R.; Marty, B.; Busemann, H.; Hashizume, K.; Gilmour, J.D.; Meshik, A.; Yada, T.; Kitajima, F.; Broadley, M.W.; Byrne, D.; et al. Noble gases and nitrogen in samples of asteroid Ryugu record its volatile sources and recent surface evolution. Science 2022, 379, eabo0431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuta, H.; Cody, G.D.; Engrand, C.; Kebukawa, Y.; Gregorio, B.D.; Bonal, L.; Remusat, L.; Stroud, R.; Quirico, E.; Nittler, L.; et al. Macromolecular organic matter in samples of the asteroid (162173) Ryugu. Science 2023, 379, eabn9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aléon, J. Multiple origins of nitrogen isotopic anomalies in meteorites and comets. Astrophys. J. 2010, 722, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herd, C.D.K.; Blinova, A.; Simkus, D.N.; Huang, Y.; Tarozo, R.; Alexander, C.M.O.; Gyngard, F.; Nittler, L.R.; Cody, G.D.; Fogel, M.L.; et al. Origin and Evolution of Prebiotic Organic Matter As Inferred from the Tagish Lake Meteorite. Science 2011, 332, 1304–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregorio, B.T.D.; Stroud, R.M.; Nittler, L.R.; Alexander, C.M.; Kilcoyne, A.D.; Zega, T.J. Isotopic anomalies in organic nanoglobules from Comet 81P/Wild 2: Comparison to Murchison nanoglobules and isotopic anomalies induced in terrestrial organics by electron irradiation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 4454–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartois, E.; Engrand, C.; Brunetto, R.; Duprat, J.; Pino, T.; Quirico, E.; Remusat, L.; Bardin, N.; Briani, G.; Mostefaoui, S.; et al. UltraCarbonaceous Antarctic micrometeorites, probing the Solar System beyond the nitrogen snow-line. Icarus 2013, 224, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fray, N.; Bardyn, A.; Cottin, H.; Baklouti, D.; Briois, C.; Engrand, C.; Fischer, H.; Hornung, K.; Isnard, R.; Langevin, Y.; et al. Nitrogen-to-carbon atomic ratio measured by COSIMA in the particles of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, S506–S516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poch, O.; Istiqomah, I.; Quirico, E.; Beck, P.; Schmitt, B.; Theulé, P.; Faure, A.; Hily-Blant, P.; Bonal, L.; Raponi, A.; et al. Ammonium salts are a reservoir of nitrogen on a cometary nucleus and possibly on some asteroids. Science 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilorget, C.; Okada, T.; Hamm, V.; Brunetto, R.; Yada, T.; Loizeau, D.; Riu, L.; Usui, T.; Moussi-Soffys, A.; Hatakeda, K.; et al. First compositional analysis of Ryugu samples by the MicrOmega hyperspectral microscope. Nat. Astron. 2021, 6, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potiszil, C.; Ota, T.; Yamanaka, M.; Sakaguchi, C.; Kobayashi, K.; Tanaka, R.; Kunihiro, T.; Kitagawa, H.; Abe, M.; Miyazaki, A.; et al. Insights into the formation and evolution of extraterrestrial amino acids from the asteroid Ryugu. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.T.; McLain, H.L.; Glavin, D.P.; Dworkin, J.P.; Elsila, J.E.; Aponte, J.C.; Naraoka, H.; Takano, Y.; Tachibana, S.; Yabuta, H.; et al. Extraterrestrial amino acids and amines identified in asteroid Ryugu samples returned by the Hayabusa2 mission. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 347, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potiszil, C.; Tanaka, R.; Ota, T.; Kunihiro, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Nakamura, E. Concentration of meteoritic free organic matter by fluid transport and adsorption. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 2020, 13, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, Y.; Koga, T.; Takano, Y.; Ogawa, N.O.; Ohkouchi, N.; Sasaki, K.; Sato, H.; Glavin, D.P.; Dworkin, J.P.; Naraoka, H.; et al. Uracil in the carbonaceous asteroid (162173) Ryugu. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, J.C.; Dworkin, J.P.; Glavin, D.P.; Elsila, J.E.; Parker, E.T.; McLain, H.L.; Naraoka, H.; Okazaki, R.; Takano, Y.; Tachibana, S.; et al. PAHs, hydrocarbons, and dimethylsulfides in Asteroid Ryugu samples A0106 and C0107 and the Orgueil (CI1) meteorite. Earth Planets Space 2023, 75, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, M.; Aoki, D.; Fukushima, K.; Naraoka, H.; Takano, Y.; Dworkin, J.P.; Dworkin, K.E.; Aponte, J.C.; Elsila, J.E.; Eiler, J.M.; et al. The spatial distribution of soluble organic matter and their relationship to minerals in the asteroid (162173) Ryugu. Earth Planets Space 2023, 75, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.C.; McCain, K.A.; Matsuda, N.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kimura, M.; Tomioka, N.; Ito, M.; Uesugi, M.; Imae, N.; Shirai, N.; et al. Incorporation of 16O-rich anhydrous silicates in the protolith of highly hydrated asteroid Ryugu. Nat. Astron. 2022, 6, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunihiro, T.; Ota, T.; Nakamura, E. Lithium- and oxygen-isotope compositions of chondrule constituents in the Allende meteorite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 252, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krot, A.N.; Nagashima, K.; Fintor, K.; Pál-Molnár, E. Evidence for oxygen-isotope exchange in refractory inclusions from Kaba (CV3.1) carbonaceous chondrite during fluid-rock interaction on the CV parent asteroid. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 246, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, N.; Nagashima, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Bajo, K.i.; Wada, S.; Igami, Y.; Miyake, A.; Noguchi, T.; Yamamoto, D.; et al. Oxygen isotopes of anhydrous primary minerals show kinship between asteroid Ryugu and comet 81P/Wild2. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eade2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, D.; Nakamura, T.; Zhang, M.; Kita, N.T.; Mikouchi, T.; Yoshida, H.; Enokido, Y.; Morita, T.; Kikuiri, M.; Amano, K.; et al. Chondrule-like objects and Ca-Al-rich inclusions in Ryugu may potentially be the oldest Solar System materials. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.P.; Ishii, H.A.; Bustillo, K.; Ciston, J.; Ogliore, R.; Stephan, T.; Brownlee, D.E.; Joswiak, D.J. On the provenance of GEMS, a quarter century post discovery. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 335, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCain, K.A.; Matsuda, N.; Liu, M.C.; McKeegan, K.D.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kimura, M.; Tomioka, N.; Ito, M.; Imae, N.; Uesugi, M.; et al. Early fluid activity on Ryugu inferred by isotopic analyses of carbonates and magnetite. Nat. Astron. 2023, 7, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, S.; Sekiya, M. Thermal evolution of icy planetesimals in the solar nebula. Earth Planets Space 2011, 63, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, H.H. Asteroid-comet continuum objects in the solar system. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 375, 20160259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, P.; Ballouz, R.L.; Barnouin, O.S.; Jutzi, M.; Walsh, K.J.; May, B.H.; Manzoni, C.; Richardson, D.C.; Schwartz, S.R.; Sugita, S.; et al. Collisional formation of top-shaped asteroids and implications for the origins of Ryugu and Bennu. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomioka, N.; Yamaguchi, A.; Ito, M.; Uesugi, M.; Imae, N.; Shirai, N.; Ohigashi, T.; Kimura, M.; Liu, M.C.; Greenwood, R.C.; et al. A history of mild shocks experienced by the regolith particles on hydrated asteroid Ryugu. Nat. Astron. 2023, 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.; Levison, H.F.; Tsiganis, K.; Morbidelli, A. Origin of the cataclysmic Late Heavy Bombardment period of the terrestrial planets. Nature 2005, 435, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morbidelli, A.; Levison, H.F.; Tsiganis, K.; Gomes, R. Chaotic capture of Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids in the early Solar System. Nature 2005, 435, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiganis, K.; Gomes, R.; Morbidelli, A.; Levison, H.F. Origin of the orbital architecture of the giant planets of the Solar System. Nature 2005, 435, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierks, H.; Barbieri, C.; Lamy, P.L.; Rodrigo, R.; Koschny, D.; Rickman, H.; Keller, H.U.; Agarwal, J.; A’Hearn, M.F.; Angrilli, F.; et al. On the nucleus structure and activity of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Science 2015, 347, aaa1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.B.; Bodewits, D.; Besse, S.; Sierks, H.; Barbieri, C.; Lamy, P.; Rodrigo, R.; Koschny, D.; Rickman, H.; Keller, H.U.; et al. Large heterogeneities in comet 67P as revealed by active pits from sinkhole collapse. Nature 2015, 523, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.; Bekaert, D.V.; Broadley, M.W.; Drozdovskaya, M.N.; Wampfler, S.F. Volatile Species in Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko: Investigating the Link from the ISM to the Terrestrial Planets. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 1792–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phelan, N.; Day, J.M.; Dhaliwal, J.K.; Liu, Y.; Corder, C.A.; Strom, C.; Pringle, E.; Assayag, N.; Cartigny, P.; Marti, K.; et al. A 187Re-187Os, 87Rb-86Sr, highly siderophile and incompatible trace element study of some carbonaceous, ordinary and enstatite chondrite meteorites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 318, 19–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, P.; Morbidelli, A.; Davidsson, B.; Blum, J. Origin and Evolution of Cometary Nuclei. Space Sci. Rev. 2020, 216, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, P.; Bottke, W.; Levison, H. Evolution of Comets into Asteroids. Asteroids III 2002, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, H.; Potiszil, C.; Tanaka, R.; Nakamura, E. The ice-organic-silicate contents of small solar system bodies: Indicators for a comet to asteroid evolutionary pathway. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 3734–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.; Bischoff, D.; Gundlach, B. Formation of Comets. Universe 2022, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounelle, M.; Spurný, P.; Bland, P.A. The orbit and atmospheric trajectory of the Orgueil meteorite from historical records. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2006, 41, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, E.; Kunihiro, T.; Ota, T.; Sakaguchi, C.; Tanaka, R.; Kitagawa, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamanaka, M.; Shimaki, Y.; Bebout, G.E.; et al. Hypervelocity collision and water-rock interaction in space preserved in the Chelyabinsk ordinary chondrite. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2019, 95, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lauretta, D.S.; Balram-Knutson, S.S.; Beshore, E.; Boynton, W.V.; d’Aubigny, C.D.; DellaGiustina, D.N.; Enos, H.L.; Golish, D.R.; Hergenrother, C.W.; Howell, E.S.; et al. OSIRIS-REx: Sample Return from Asteroid (101955) Bennu. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 925–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnouin, O.S.; Daly, M.G.; Palmer, E.E.; Gaskell, R.W.; Weirich, J.R.; Johnson, C.L.; Asad, M.M.A.; Roberts, J.H.; Perry, M.E.; Susorney, H.C.M.; et al. Shape of (101955) Bennu indicative of a rubble pile with internal stiffness. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DellaGiustina, D.N.; Emery, J.P.; Golish, D.R.; Rozitis, B.; Bennett, C.A.; Burke, K.N.; Ballouz, R.L.; Becker, K.J.; Christensen, P.R.; d’Aubigny, C.Y.D.; et al. Properties of rubble-pile asteroid (101955) Bennu from OSIRIS-REx imaging and thermal analysis. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuth, J.A.; Abreu, N.; Ferguson, F.T.; Glavin, D.P.; Hergenrother, C.; Hill, H.G.M.; Johnson, N.M.; Pajola, M.; Walsh, K. Volatile-rich Asteroids in the Inner Solar System. Planet. Sci. J. 2020, 1, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.F.; Rivkin, A.S.; Michel, P.; Atchison, J.; Barnouin, O.; Benner, L.; Chabot, N.L.; Ernst, C.; Fahnestock, E.G.; Kueppers, M.; et al. AIDA DART asteroid deflection test: Planetary defense and science objectives. Planet. Space Sci. 2018, 157, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. DART’s Final Images Prior to Impact. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/dart-s-final-images-prior-to-impact, (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Daly, R.T.; Ernst, C.M.; Barnouin, O.S.; Chabot, N.L.; Rivkin, A.S.; Cheng, A.F.; Adams, E.Y.; Agrusa, H.F.; Abel, E.D.; Alford, A.L.; et al. Successful kinetic impact into an asteroid for planetary defence. Nature 2023, 616, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NASA. NASA’s Hubble Spots Twin Tails in New Image after DART Impact. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-s-hubble-spots-twin-tails-in-new-image-after-dart-impact (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Li, J.Y.; Hirabayashi, M.; Farnham, T.L.; Sunshine, J.M.; Knight, M.M.; Tancredi, G.; Moreno, F.; Murphy, B.; Opitom, C.; Chesley, S.; et al. Ejecta from the DART-produced active asteroid Dimorphos. Nature 2023, 616, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graykowski, A.; Lambert, R.A.; Marchis, F.; Cazeneuve, D.; Dalba, P.A.; Esposito, T.M.; Peluso, D.O.; Sgro, L.A.; Blaclard, G.; Borot, A.; et al. Light curves and colours of the ejecta from Dimorphos after the DART impact. Nature 2023, 616, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.E.; Schaller, E.L.; Fraser, W.C. A hypothesis for the color diversity of the Kuiper belt. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 739, L60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filacchione, G.; Capaccioni, F.; Ciarniello, M.; Raponi, A.; Rinaldi, G.; Sanctis, M.C.D.; Bockelèe-Morvan, D.; Erard, S.; Arnold, G.; Mennella, V.; et al. An orbital water-ice cycle on comet 67P from colour changes. Nature 2020, 578, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de León, J.; Licandro, J.; Serra-Ricart, M.; Pinilla-Alonso, N.; Campins, H. Observations, compositional, and physical characterization of near-Earth and Mars-crosser asteroids from a spectroscopic survey. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 517, A23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, T.L.; Burbine, T.H.; Bottke, W.F.; Clark, J.P. Mineralogies and source regions of near-Earth asteroids. Icarus 2013, 222, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieva, S.; Epifani, E.M.; Perna, D.; Dall’Ora, M.; Petropoulou, V.; Deshapriya, J.D.P.; Hasselmann, P.H.; Rossi, A.; Poggiali, G.; Brucato, J.R.; et al. Spectral Rotational Characterization of the Didymos System prior to the DART Impact. Planet. Sci. J. 2022, 3, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, P.; Küppers, M.; Bagatin, A.C.; Carry, B.; Charnoz, S.; Leon, J.d.; Fitzsimmons, A.; Gordo, P.; Green, S.F.; Hérique, A.; et al. The ESA Hera Mission: Detailed Characterization of the DART Impact Outcome and of the Binary Asteroid (65803) Didymos. Planet. Sci. J. 2022, 3, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoliar, M.I.; Walker, R.J.; Morgan, J.W. Re-Os Ages of Group IIA, IIIA, IVA, and IVB Iron Meteorites. Science 1996, 271, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ota, T.; Potiszil, C.; Kobayashi, K.; Tanaka, R.; Kitagawa, H.; Kunihiro, T.; Sakaguchi, C.; Yamanaka, M.; Nakamura, E. The Formation of a Rubble Pile Asteroid: Insights from the Asteroid Ryugu. Universe 2023, 9, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9060293
Ota T, Potiszil C, Kobayashi K, Tanaka R, Kitagawa H, Kunihiro T, Sakaguchi C, Yamanaka M, Nakamura E. The Formation of a Rubble Pile Asteroid: Insights from the Asteroid Ryugu. Universe. 2023; 9(6):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9060293
Chicago/Turabian StyleOta, Tsutomu, Christian Potiszil, Katsura Kobayashi, Ryoji Tanaka, Hiroshi Kitagawa, Tak Kunihiro, Chie Sakaguchi, Masahiro Yamanaka, and Eizo Nakamura. 2023. "The Formation of a Rubble Pile Asteroid: Insights from the Asteroid Ryugu" Universe 9, no. 6: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9060293
APA StyleOta, T., Potiszil, C., Kobayashi, K., Tanaka, R., Kitagawa, H., Kunihiro, T., Sakaguchi, C., Yamanaka, M., & Nakamura, E. (2023). The Formation of a Rubble Pile Asteroid: Insights from the Asteroid Ryugu. Universe, 9(6), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9060293