Structure–Activity Relationship of HER2 Receptor Targeting Peptide and Its Derivatives in Targeted Tumor Therapy
Abstract
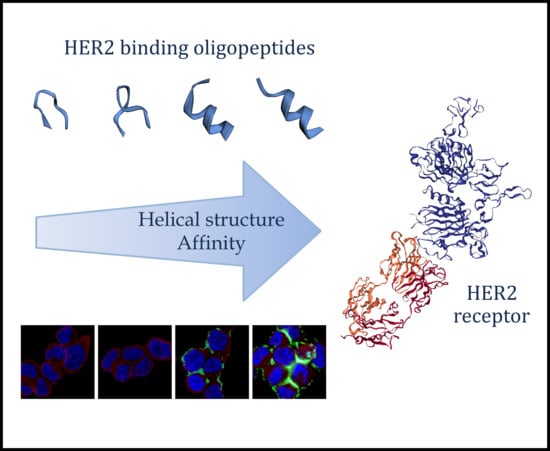
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Peptide Synthesis and Purification
2.3. Cell Culturing
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. In Vitro Flow Cytometry Evaluation and Fluorescent Microscopy
2.6. Immunostaining and Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Secondary Structure Estimation
3. Results
3.1. Peptide Synthesis
3.2. In Vitro Biological Activity
3.3. Cellular Localization
3.4. Cellular Uptake in Cells with Lower HER2 Expression
3.5. Receptor Specificity of HER2-Binding Peptides
3.6. Secondary Structure Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, Q.; Meng, Z.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Guan, D.; Liang, C.; Zhou, J.; Lu, A.; Zhang, G. Molecular Mechanisms and Translational Therapies for Human Epidermal Receptor 2 Positive Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escrivá-De-Romaní, S.; Arumí, M.; Bellet, M.; Saura, C. HER2-positive breast cancer: Current and new therapeutic strategies. Breast 2018, 39, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.L.; Hung, M.-C. The role of HER2, EGFR, and other receptor tyrosine kinases in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirkisoon, S.R.; Carpenter, R.L.; Rimkus, T.; Miller, L.; Metheny-Barlow, L.; Lo, H.-W. EGFR and HER2 signaling in breast cancer brain metastasis. Front. Biosci. 2016, 8, 245–263. [Google Scholar]
- Menard, S.; Pupa, S.M.; Campiglio, M.; Tagliabue, E. Biologic and therapeutic role of HER2 in cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 6570–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moasser, M.M. The oncogene HER2: its signaling and transforming functions and its role in human cancer pathogenesis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6469–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, P.; Presta, L.; Gorman, C.M.; Ridgway, J.B.; Henner, D.; Wong, W.L.; Rowland, A.M.; Kotts, C.; Carver, M.E.; Shepard, H.M. Humanization of an anti-p185HER2 antibody for human cancer therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1992, 89, 4285–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agus, D.B.; Gordon, M.S.; Taylor, C.; Natale, R.B.; Karlan, B.; Mendelson, D.S.; Press, M.F.; Allison, D.E.; Sliwkowski, M.X.; Lieberman, G.; et al. Phase I Clinical Study of Pertuzumab, a Novel HER Dimerization Inhibitor, in Patients With Advanced Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Minckwitz, G.; Procter, M.; De Azambuja, E.; Zardavas, D.; Benyunes, M.; Viale, G.; Suter, T.; Arahmani, A.; Rouchet, N.; Clark, E.; et al. Adjuvant Pertuzumab and Trastuzumab in Early HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nami, N.B.; Maadi, H.; Wang, Z. Mechanisms Underlying the Action and Synergism of Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab in Targeting HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gajria, D.; Chandarlapaty, S. HER2-amplified breast cancer: Mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance and novel targeted therapies. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2011, 11, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston, S.; Leary, A. Lapatinib: A novel EGFR/HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor for cancer. Drugs Today 2006, 42, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Miles, D.; Gianni, L.; Krop, I.E.; Welslau, M.; Baselga, J.; Pegram, M.; Oh, -Y.; Diéras, V.; Guardino, E.; et al. Trastuzumab emtansine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nord, K.; Gunneriusson, E.; Ringdahl, J.; Ståhl, S.; Uhlén, M.; Nygren, P.-Å. Binding proteins selected from combinatorial libraries of an α-helical bacterial receptor domain. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigenbrot, C.; Ultsch, M.; Dubnovitsky, A.; Abrahmsén, L.; Härd, T. Structural basis for high-affinity HER2 receptor binding by an engineered protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 15039–15044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frejd, F.Y.; Kim, K.-T. Affibody molecules as engineered protein drugs. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loibl, S.; Gianni, L. HER2-positive breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 2415–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernas, S.; Tolaney, S.M. HER2-positive breast cancer: new therapeutic frontiers and overcoming resistance. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919833519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapino, A.; Goia, M.; Recupero, D.; Marchio, C. Current Challenges for HER2 Testing in Diagnostic Pathology: State of the Art and Controversial Issues. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, N.; Qin, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Z. Tumor-Targeting Peptides: Ligands for Molecular Imaging and Therapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasseva, N.G.; Glinsky, V.V.; Chen, N.X.; Komatireddy, R.; Quinn, T.P. Identification and characterization of peptides that bind human ErbB-2 selected from a bacteriophage display library. Protein J. 2002, 21, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Wang, Z.; Jia, X.; Han, Q.; Xiang, Z.; Li, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Bu, X.; Wang, W.; et al. HER2 Targeting Peptides Screening and Applications in Tumor Imaging and Drug Delivery. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brinkley, B.R.; Beall, P.T.; Wible, L.J.; Mace, M.L.; Turner, D.S.; Cailleau, R.M. Variations in cell form and cytoskeleton in human breast carcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1980, 40, 3118–3129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cailleau, R.; Reeves, W.J.; Young, R.; Olivé, M. Breast Tumor Cell Lines From Pleural Effusions 2. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1974, 53, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, J.E.; Polyzos, A.; Zhang, R.D.; Daniels, L.M. Tumorigenicity and metastasis of human breast carcinoma cell lines in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.D.; Fidler, I.J.; E Price, J. Relative malignant potential of human breast carcinoma cell lines established from pleural effusions and a brain metastasis. Invasion Metastasis 1991, 11, 204–215. [Google Scholar]
- Sellappan, S. Lineage Infidelity of MDA-MB-435 Cells: Expression of Melanocyte Proteins in a Breast Cancer Cell Line. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3479–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soule, H.D.; Vazquez, J.; Long, A.; Albert, S.; Brennan, M. A Human Cell Line From a Pleural Effusion Derived From a Breast Carcinoma 2. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1973, 51, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, L.J.; Hermonat, M.W. Receptor status and subsequent sensitivity of subclones of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells surviving exposure to diethylstilbestrol. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar]
- Kapus, A.; Grinstein, S.; Wasan, S.; Kandasamy, R.; Orlowski, J. Functional characterization of three isoforms of the Na+/H+ exchanger stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. ATP dependence, osmotic sensitivity, and role in cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23544–23552. [Google Scholar]
- Lamiable, A.; Thévenet, P.; Rey, J.; Vavrusa, M.; Derreumaux, P.; Tufféry, P. PEP-FOLD3: faster de novo structure prediction for linear peptides in solution and in complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W449–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maupetit, J.; Derreumaux, P.; Tuffery, P. A fast method for large-scale de novo peptide and miniprotein structure prediction. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Li, T.; Bai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhan, J.; Shi, B. Breast cancer intrinsic subtype classification, clinical use and future trends. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2929–2943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holliday, D.L.; Speirs, V. Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross, U.T.; Scherf, U.; Eisen, M.B.; Perou, C.M.; Rees, C.; Spellman, P.; Iyer, V.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Van De Rijn, M.; Waltham, M.; et al. Systematic variation in gene expression patterns in human cancer cell lines. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.E.; Mellor, P.; Ward, A.K.; Kendall, S.; McDonald, M.; Vizeacoumar, F.S.; Vizeacoumar, F.J.; Napper, S.; Anderson, D.H. Molecular characterization of breast cancer cell lines through multiple omic approaches. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- RPBS Web Portal. PEP-FOLD 3.5. Available online: http://mobyle.rpbs.univ-paris-diderot.fr/cgi-bin/portal.py#forms::PEP-FOLD3 (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Shen, Y.; Maupetit, J.; Derreumaux, P.; Tufféry, P. Improved PEP-FOLD Approach for Peptide and Miniprotein Structure Prediction. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 4745–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenet, P.; Shen, Y.; Maupetit, J.; Guyon, F.; Derreumaux, P.; Tufféry, P. PEP-FOLD: an updated de novo structure prediction server for both linear and disulfide bonded cyclic peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W288–W293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landgraf, R. HER2 therapy. HER2 (ERBB2): functional diversity from structurally conserved building blocks. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, N. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) in Cancers: Overexpression and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 2014, 852748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larimer, B.M.; Quinn, J.M.; Kramer, K.; Komissarov, A.; Deutscher, S.L. Multiple Bacteriophage Selection Strategies for Improved Affinity of a Peptide Targeting ERBB2. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2015, 21, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boehr, D.D.; Nussinov, R.; Wright, P.E. The role of dynamic conformational ensembles in biomolecular recognition. Nat. Methods 2009, 5, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geng, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Lian, W.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, W.; Bu, X.; Lai, W.; Hu, Z.; et al. Structure-based Design of Peptides with High Affinity and Specificity to HER2 Positive Tumors. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |







| Compound | Code | RP-HPLC Rt (min) 1 | ESI-MS MW (calculated) | ESI-MS MW (measured) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF-KCCYSL-NH2 | P(CC) | 29.9a | 1072.9 | 1072.3 |
| CF-KCGCYSL-NH2 | P(CGC) | 29.4a | 1129.9 | 1129.8 |
| CF-KCGGCYSL-NH2 | P(CGGC) | 31.7a | 1186.0 | 1187.0 |
| CF-KC(Acm)C(Acm)YSL-NH2 | P(C(Acm)C(Acm)) | 28.8a | 1214.5 | 1214.0 |
| CF-KCSYSL-NH2 | P(CS) | 29.7a | 1056.7 | 1056.4 |
| CF-KSCYSL-NH2 | P(SC) | 29.5a | 1056.7 | 1056.4 |
| CF-KSSYSL-NH2 | P(SS) | 27.7a | 1040.8 | 1040.5 |
| CF-KAAYSL-NH2 | P(AA) | 28.8a | 1007.8 | 1008.4 |
| CF-GYYNPT-NH2 | P(YY) | 30.0a | 1070.8 | 1070.4 |
| CF-KAAYSLGYYNPT-NH2 | cP(AA)_P(YY) | 21.4b | 1704.5 | 1704.6 |
| CF-KSCYSLGYYNPT-NH2 | cP(SC)_P(YY) | 21.4b | 1751.8 | 1752.2 |
| CF-YSLGYYNPT-NH2 | P(short)_P(YY) | 22.7b | 1433.8 | 1433.8 |
| CF-TAKLYPGYANYS-NH2 | scr_P(AA_YY) | 21.1b | 1704.5 | 1704.0 |
| CF-GYYNPTKAAYSL-NH2 | cP(YY)_P(AA) | 21.6b | 1704.5 | 1704.6 |
| H-KAAYSLGYYNPT-NH2 | Unlabeled cP(AA)_P(YY) | 19.4b | 1345.7 | 1346.0 |
| H-KSCYSLGYYNPT-NH2 | Unlabeled cP(SC)_P(YY) | 19.4b | 1393.6 | 1394.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biri-Kovács, B.; Adorján, A.; Szabó, I.; Szeder, B.; Bősze, S.; Mező, G. Structure–Activity Relationship of HER2 Receptor Targeting Peptide and Its Derivatives in Targeted Tumor Therapy. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020183
Biri-Kovács B, Adorján A, Szabó I, Szeder B, Bősze S, Mező G. Structure–Activity Relationship of HER2 Receptor Targeting Peptide and Its Derivatives in Targeted Tumor Therapy. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020183
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiri-Kovács, Beáta, Afrodité Adorján, Ildikó Szabó, Bálint Szeder, Szilvia Bősze, and Gábor Mező. 2020. "Structure–Activity Relationship of HER2 Receptor Targeting Peptide and Its Derivatives in Targeted Tumor Therapy" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020183
APA StyleBiri-Kovács, B., Adorján, A., Szabó, I., Szeder, B., Bősze, S., & Mező, G. (2020). Structure–Activity Relationship of HER2 Receptor Targeting Peptide and Its Derivatives in Targeted Tumor Therapy. Biomolecules, 10(2), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020183