Pro-Resolving Effect of Ginsenosides as an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Panax ginseng
Abstract
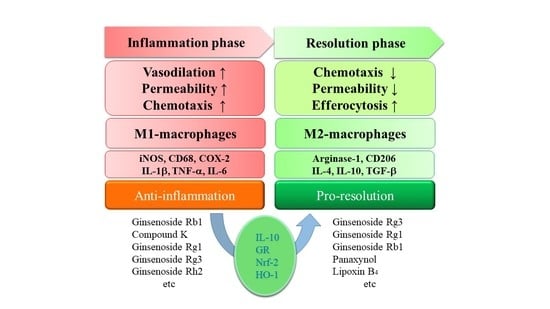
:1. Introduction—Ginseng
2. Ginsenosides in Anti-Inflammation
3. Ginsenosides in Pro-Resolution
4. Perspective
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Im, D.S.; Nah, S.Y. Yin and Yang of ginseng pharmacology: ginsenosides vs. gintonin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nah, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Rhim, H. Ginsenosides: are any of them candidates for drugs acting on the central nervous system? CNS Drug Rev. 2007, 13, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.T. Botanical characteristics, pharmacological effects and medicinal components of Korean Panax ginseng C A Meyer. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H. Pharmacological and medical applications of Panax ginseng and ginsenosides: a review for use in cardiovascular diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Nile, S.H.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Kai, G. Systematic exploration of Astragalus membranaceus and Panax ginseng as immune regulators: Insights from the comparative biological and computational analysis. Phytomedicine 2019, 153077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Q.F.; Xu, Z.R.; Xu, K.Y.; Yang, Y.M. The Efficacy of Ginseng-Related Therapies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.Y.; Farooqui, T.; Koh, H.L.; Farooqui, A.A.; Ling, E.A. Protective effects of ginseng on neurological disorders. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majeed, F.; Malik, F.Z.; Ahmed, Z.; Afreen, A.; Afzal, M.N.; Khalid, N. Ginseng phytochemicals as therapeutics in oncology: Recent perspectives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero-Miliani, L.; Nielsen, O.H.; Andersen, P.S.; Girardin, S.E. Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1b generation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 147, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Ginseng compounds: an update on their molecular mechanisms and medical applications. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 7, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nag, S.A.; Qin, J.J.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Ginsenosides as Anticancer Agents: In vitro and in vivo Activities, Structure-Activity Relationships, and Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Byeon, H.; Im, K.; Min, H. Effects of ginsenosides on regulatory T cell differentiation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Rhee, M.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.H.; Yang, Y.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, Y.; Kim, C.; Kwak, Y.S.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Ginsenoside Rc from Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) Attenuates Inflammatory Symptoms of Gastritis, Hepatitis and Arthritis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Yang, Y.; Kwak, Y.S.; Song, G.G.; Kim, M.Y.; Rhee, M.H.; Cho, J.Y. Ginsenoside Rc from Panax ginseng exerts anti-inflammatory activity by targeting TANK-binding kinase 1/interferon regulatory factor-3 and p38/ATF-2. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Hwang, J.T.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, S.; Kim, M.S.; Yang, H.J.; Kwon, D.Y. Ginsenoside Rc, an active component of Panax ginseng, stimulates glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes through an AMPK-dependent mechanism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, C.H.; Park, D.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, M.H.; Chung, K.W.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, J.S.; Chung, H.Y. Ginsenoside Rc modulates Akt/FoxO1 pathways and suppresses oxidative stress. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Siddiqi, M.H.; Aceituno, V.C.; Simu, S.Y.; Yang, D.C. Suppression of MAPKs/NF-kB Activation Induces Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Action of Ginsenoside Rf in HT-29 and RAW264.7 Cells. Immunol. Investig. 2016, 45, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Lu, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, K.; Zhai, Y.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Attenuation of TNF-a-Induced Inflammatory Injury in Endothelial Cells by Ginsenoside Rb1 via Inhibiting NF-kB, JNK and p38 Signaling Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.K.; Kang, H.; Baek, C.W.; Jung, Y.H.; Woo, Y.C.; Choi, G.J.; Shin, H.Y.; Kim, K.S. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenoside Rf in a rat model of incisional pain. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, Y.T.; Dong, Z. Neuroprotective Effects of Ginsenoside Rf on Amyloid-b-Induced Neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, J. Ginsenoside Rf alleviates dysmenorrhea and inflammation through the BDNF-TrkB-CREB pathway in a rat model of endometriosis. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, S.; Jiang, C. Ginsenoside Rf relieves mechanical hypersensitivity, depression-like behavior, and inflammatory reactions in chronic constriction injury rats. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, S.; Choe, J.H.; Choi, G.E.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.M.; Song, G.Y.; Jo, E.K. Rg6, a rare ginsenoside, inhibits systemic inflammation through the induction of interleukin-10 and microRNA-146a. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Shon, H.J.; Choi, C.S.; Hung, T.M.; Min, B.S.; Bae, K. Ginsenosides from heat processed ginseng. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2009, 57, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenosides Rg5, Rz1, and Rk1: inhibition of TNF-a-induced NF-kB, COX-2, and iNOS transcriptional expression. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1893–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Siddiqi, M.H.; Aceituno, V.C.; Simu, S.Y.; Zhang, J.; Jimenez Perez, Z.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. Ginsenoside Rg5:Rk1 attenuates TNF-a/IFN-g-induced production of thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17) and LPS-induced NO production via downregulation of NF-kB/p38 MAPK/STAT1 signaling in human keratinocytes and macrophages. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2016, 52, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zeng, K.W.; Ma, X.L.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P.F.; Wang, X.M. Ginsenoside Rk1 suppresses pro-inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the Jak2/Stat3 pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 15, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.K.; Lee, J.G.; Park, M.K.; Park, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, S.W. Metabolomic investigation of the anti-platelet aggregation activity of ginsenoside Rk(1) reveals attenuated 12-HETE production. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 4939–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Samukawa, K.; Kubo, M. Anti-inflammatory activity of ginsenoside Ro. Planta Med. 1990, 56, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Samukawa, K.; Kubo, M. Anti-hepatitic activity of ginesenoside ro1. Planta Med. 1991, 57, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.H.; Xu, X.X.; Xu, T. Ginsenoside Ro suppresses interleukin-1b-induced apoptosis and inflammation in rat chondrocytes by inhibiting NF-kB. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Oh, M.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, W.I.; Cho, H.S.; Park, B.Y.; Park, C.; Shin, G.W.; Kwon, J. Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 by ginsenoside Ro attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in macrophage cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, R.; Yu, P.; Qiu, Z. Study on the Structure of Ginseng Glycopeptides with Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, D.; Jiang, R.; Qiu, Z. In vivo and in vitro neuroprotective effects of Panax ginseng glycoproteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, T.T.; Yang, C.S.; Yuk, J.M.; Lee, H.M.; Ko, S.R.; Cho, B.G.; Jo, E.K. Glucocorticoid receptor agonist compound K regulates Dectin-1-dependent inflammatory signaling through inhibition of reactive oxygen species. Life Sci. 2009, 85, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Ko, S.R.; Cho, B.G.; Shin, D.M.; Yuk, J.M.; Li, S.; Kim, J.M.; Evans, R.M.; Jung, J.S.; Song, D.K.; et al. The ginsenoside metabolite compound K, a novel agonist of glucocorticoid receptor, induces tolerance to endotoxin-induced lethal shock. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, K.W.; Cheng, Y.K.; Mak, N.K.; Chan, K.K.; Fan, T.P.; Wong, R.N. Signaling pathway of ginsenoside-Rg1 leading to nitric oxide production in endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 3211–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, K.W.; Leung, F.P.; Huang, Y.; Mak, N.K.; Wong, R.N. Non-genomic effects of ginsenoside-Re in endothelial cells via glucocorticoid receptor. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Jing, G.; Cai, H. Ginsenoside Rg1 suppressed inflammation and neuron apoptosis by activating PPARg/HO-1 in hippocampus in rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, T.; Lian, Y. Ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorates cisplatin-induced learning and memory impairments. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.Y.; Kang, B.; Suh, H.J.; Choi, H.S. Red ginseng-derived saponin fraction suppresses the obesity-induced inflammatory responses via Nrf2-HO-1 pathway in adipocyte-macrophage co-culture system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.A.; Hyam, S.R.; Jang, S.E.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Ginsenoside Re ameliorates inflammation by inhibiting the binding of lipopolysaccharide to TLR4 on macrophages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9595–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W.; Joh, E.H.; Kim, B.; Kim, D.H. Ginsenoside Rg5 ameliorates lung inflammation in mice by inhibiting the binding of LPS to toll-like receptor-4 on macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, H.H.; Guo, G.L.; Lau, J.K.; Cheng, Y.K.; Wang, J.R.; Jiang, Z.H.; Keung, M.H.; Mak, N.K.; Yue, P.Y.; Wong, R.N. Stereoisomers ginsenosides-20(S)-Rg(3) and -20(R)-Rg(3) differentially induce angiogenesis through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-g. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, G.; Su, P.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Liang, Y.; Qin, C.; Zhang, W. Ginsenoside Re reduces Ab production by activating PPARg to inhibit BACE1 in N2a/APP695 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 793, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Fang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Mo, F.; Jiang, G.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Fu, M.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 promotes browning through regulation of PPARg in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 466, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Jin, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, S.; Chen, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 promotes adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells by enhancing PPARg2 and C/EBPa gene expression. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Du, Y.; Duan, S.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Fu, F. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via modulation of PPAR-g/NF-kB signal pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55384–55393. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Park, J.; Choi, K.; Lee, J.; Chen, J.; Park, H.J.; Yu, B.I.; Iida, M.; Rhyu, M.R.; Lee, Y. Ginsenoside Rf inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 induction via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor g in A549 cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.O.; Sica, A.; Mantovani, A.; Locati, M. Macrophage activation and polarization. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, S.; Martinez, F.O. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity 2010, 32, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ariel, A.; Serhan, C.N. New Lives Given by Cell Death: Macrophage Differentiation Following Their Encounter with Apoptotic Leukocytes during the Resolution of Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serhan, C.N. Discovery of specialized pro-resolving mediators marks the dawn of resolution physiology and pharmacology. Mol. Aspects Med. 2017, 58, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Park, S.J.; Lee, A.Y.; Huang, J.; Chung, H.Y.; Im, D.S. Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes inflammation resolution through M2 macrophage polarization. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Choi, Y.R.; Mok, H.J.; Seong, H.A.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, G.S.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, H.D. Characterization of the changes in eicosanoid profiles of activated macrophages treated with 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1065–1066, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Choi, G.; Shim, I.; Chung, Y. Enhanced Rg3 negatively regulates Th1 cell responses. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, E.; Jeong, D.; Irfan, M.; Lee, Y.Y.; Park, S.J.; Park, C.K.; Rhee, M.H. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Rg3-Enriched Korean Red Ginseng Extract in Murine Model of Sepsis. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 6874692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, M.; Xiao, J.; Sheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Tie, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Ji, X. Ginsenoside Rg3 Mitigates Atherosclerosis Progression in Diabetic apoE-/- Mice by Skewing Macrophages to the M2 Phenotype. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, M.H.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Dong, M.; Dai, H.Y.; Ni, M.; Luan, X.R.; Guan, J.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 enhances atherosclerotic plaque stability by skewing macrophages to the M2 phenotype. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, D.D.; Huang, Y.H.; Lai, C.S.W.; Dong, C.M.; Ho, L.C.; Li, X.Y.; Wu, E.X.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, Y.J.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 Prevents Chemotherapy-Induced Cognitive Impairment: Associations with Microglia-Mediated Cytokines, Neuroinflammation, and Neuroplasticity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5626–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, A.; Sun, H.; Ye, Y.; Fang, W. Ginsenoside Rd elicits Th1 and Th2 immune responses to ovalbumin in mice. Vaccine 2007, 25, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Pei, Z.; Hu, S. Ginsenoside Re as an adjuvant to enhance the immune response to the inactivated rabies virus vaccine in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 20, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joh, E.H.; Lee, I.A.; Jung, I.H.; Kim, D.H. Ginsenoside Rb1 and its metabolite compound K inhibit IRAK-1 activation--the key step of inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, J.J.; Eun, S.H.; Kim, D.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and its metabolites ginsenoside Rh1 and 20(S)-protopanaxatriol in mice with TNBS-induced colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 762, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Deng, J.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Huang, G.J. Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, J.; Koo, J.; Kim, S.; Park, T.Y.; Kim, M.Y. Ginsenoside Rp1 Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects via Activation of Dendritic Cells and Regulatory T Cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naito, Y.; Takagi, T.; Higashimura, Y. Heme oxygenase-1 and anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 564, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kensler, T.W.; Wakabayashi, N.; Biswal, S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, M. Stress-sensing mechanisms and the physiological roles of the Keap1-Nrf2 system during cellular stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16817–16824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Abdalrahman, A.; Lai, Y.; Janicki, J.S.; Ward, K.W.; Meyer, C.J.; Wang, X.L.; Tang, D.; Cui, T. Dihydro-CDDO-trifluoroethyl amide suppresses inflammatory responses in macrophages via activation of Nrf2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 444, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Morine, Y.; Ikemoto, T.; Imura, S.; Iwahashi, S.; Saito, Y.; Shimada, M. Nrf2 activation drive macrophages polarization and cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition during interaction. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Chen, G.; Shi, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Feng, D.; Zhang, P.; Wu, L.; Lv, X. Nrf2 activation protects against intratracheal LPS induced mouse/murine acute respiratory distress syndrome by regulating macrophage polarization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Li, B.; Lai, Y.; Li, H.; Windust, A.; Hofseth, L.J.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.; Wang, X.L.; Tang, D.; et al. Identifying panaxynol, a natural activator of nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) from American ginseng as a suppressor of inflamed macrophage-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Ginsenoside Rd mitigates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 14497–14504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Bai, X.; Yu, S.; Zhao, W.; Qiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Ginsenoside Re Inhibits ROS/ASK-1 Dependent Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway and Activation of Nrf2-Antioxidant Response in b-Amyloid-Challenged SH-SY5Y Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Liu, T.; Wu, Y.; Yang, W.; Hu, S.; Sun, Z.; Li, P.; Du, S. Panax notoginseng saponins suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced barrier disruption and monocyte adhesion on bEnd.3 cells via the opposite modulation of Nrf2 antioxidant and NF-kB inflammatory pathways. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 3163–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Im, D.-S. Pro-Resolving Effect of Ginsenosides as an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Panax ginseng. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030444
Im D-S. Pro-Resolving Effect of Ginsenosides as an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Panax ginseng. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(3):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030444
Chicago/Turabian StyleIm, Dong-Soon. 2020. "Pro-Resolving Effect of Ginsenosides as an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Panax ginseng" Biomolecules 10, no. 3: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030444
APA StyleIm, D. -S. (2020). Pro-Resolving Effect of Ginsenosides as an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Panax ginseng. Biomolecules, 10(3), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030444