Ginsenoside Compound K Induces Adult Hippocampal Proliferation and Survival of Newly Generated Cells in Young and Elderly Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Compound K Administration
2.3. EdU Administration
2.4. Perfusion
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Immunoblotting
2.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CK Increases the Number of Newly Born Cells in the Dentate Gyrus
3.2. CK Enhances the Proliferation of Newly Born Cells in the Dentate Gyrus
3.3. CK Improves Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis by Increasing Neuronal Survival
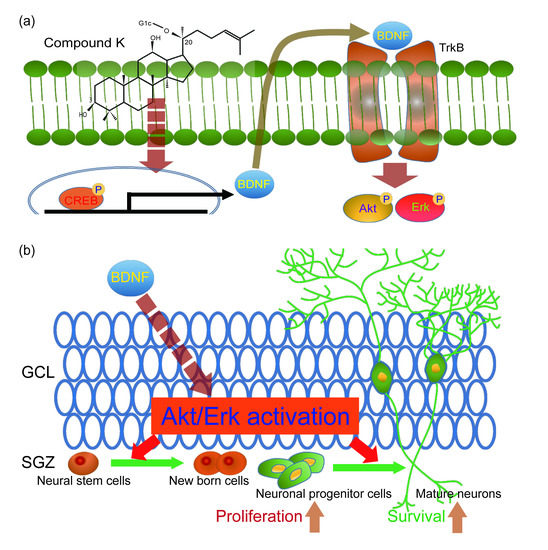
3.4. Adult Neurogenesis by CK is Mediated via BDNF Signaling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altman, J.; Das, G.D. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1965, 124, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, T.; Parylak, S.L.; Linker, S.B.; Gage, F.H. The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braskie, M.N.; Thompson, P.M. Understanding cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease based on neuroimaging findings. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffman, J.D.; Parikh, I.; Green, S.J.; Chlipala, G.; Mohney, R.P.; Keaton, M.; Bauer, B.; Hartz, A.M.S.; Lin, A.L. Age Drives Distortion of Brain Metabolic, Vascular and Cognitive Functions, and the Gut Microbiome. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, H.G.; Dickinson-Anson, H.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathews, K.J.; Allen, K.M.; Boerrigter, D.; Ball, H.; Shannon Weickert, C.; Double, K.L. Evidence for reduced neurogenesis in the aging human hippocampus despite stable stem cell markers. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, B.; Kohl, Z.; Gage, F.H. Neurodegenerative disease and adult neurogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-Nallar, L.; Aranguiz, F.C.; Abbott, A.C.; Slater, P.G.; Inestrosa, N.C. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Birth Defects Res. 2010, 90, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgusluoglu, E.; Nudelman, K.; Nho, K.; Saykin, A.J. Adult neurogenesis and neurodegenerative diseases: A systems biology perspective. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 174, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Encinas, J.M.; Michurina, T.V.; Peunova, N.; Park, J.H.; Tordo, J.; Peterson, D.A.; Fishell, G.; Koulakov, A.; Enikolopov, G. Division-coupled astrocytic differentiation and age-related depletion of neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebara, E.; Sultan, S.; Kocher-Braissant, J.; Toni, N. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis inversely correlates with microglia in conditions of voluntary running and aging. Front. Neurosci 2013, 7, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gil-Mohapel, J.; Brocardo, P.S.; Choquette, W.; Gothard, R.; Simpson, J.M.; Christie, B.R. Hippocampal neurogenesis levels predict WATERMAZE search strategies in the aging brain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, H.; Sung, J.H.; Matsumiya, S.; Uchiyama, M. Main ginseng saponin metabolites formed by intestinal bacteria. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.H.; Han, E.J.; Sung, J.H.; Chung, S.H. Anti-diabetic effects of compound K versus metformin versus compound K-metformin combination therapy in diabetic db/db mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 2196–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Si, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, A.; Wei, W. Ginsenoside metabolite compound K exerts anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects via downregulating COX2. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.M.; Kim, E.; Chun, S. Ginsenoside Compound K Induces Ros-Mediated Apoptosis and Autophagic Inhibition in Human Neuroblastoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Kim, D.; Yoo, S.; Hong, Y.H.; Han, S.Y.; Jeong, S.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y.; Park, J. The skin protective effects of compound K, a metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Shin, J.A.; Jung, J.S.; Hyun, J.W.; Van Le, T.K.; Kim, D.H.; Park, E.M.; Kim, H.S. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of compound K in activated microglia and its neuroprotective effect on experimental stroke in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.G.; Xue, J.J.; Lee, M.R.; Sun, M.Q.; Zhao, X.H.; Zheng, Y.N.; Sung, C.K. Compound K is able to ameliorate the impaired cognitive function and hippocampal neurogenesis following chemotherapy treatment. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 436, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Zeng, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Zeng, G.; Hu, K.; Ouyang, D. Ginsenoside compound K attenuates cognitive deficits in vascular dementia rats by reducing the Abeta deposition. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 139, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Ju, S.H.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.S. Neuroprotective and Cognition-Enhancing Effects of Compound K Isolated from Red Ginseng. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bologna-Molina, R.; Mosqueda-Taylor, A.; Molina-Frechero, N.; Mori-Estevez, A.D.; Sanchez-Acuna, G. Comparison of the value of PCNA and Ki-67 as markers of cell proliferation in ameloblastic tumors. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2013, 18, e174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shohayeb, B.; Diab, M.; Ahmed, M.; Ng, D.C.H. Factors that influence adult neurogenesis as potential therapy. Transl. Neurodegener. 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 677–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilar, M.; Mira, H. Regulation of Neurogenesis by Neurotrophins during Adulthood: Expected and Unexpected Roles. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazarov, O.; Mattson, M.P.; Peterson, D.A.; Pimplikar, S.W.; van Praag, H. When neurogenesis encounters aging and disease. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Jimenez, E.P.; Flor-Garcia, M.; Terreros-Roncal, J.; Rabano, A.; Cafini, F.; Pallas-Bazarra, N.; Avila, J.; Llorens-Martin, M. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.M.; Pallas-Bazarra, N.; Bolos, M.; Terreros-Roncal, J.; Avila, J.; Llorens-Martin, M. Untold New Beginnings: Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, S497–S505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Praag, H.; Christie, B.R.; Sejnowski, T.J.; Gage, F.H. Running enhances neurogenesis, learning, and long-term potentiation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13427–13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Seroogy, K.B.; Mattson, M.P. Dietary restriction enhances neurotrophin expression and neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. J. Neurochem. 2002, 80, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, H.; Goodman, J.; Macleod, A.; Phani, S.; Antonelli, C.; Croll, S. Increased neurogenesis and the ectopic granule cells after intrahippocampal BDNF infusion in adult rats. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 192, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesseveur, G.; David, D.J.; Gaillard, M.C.; Pla, P.; Wu, M.V.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nicolas, V.; Auregan, G.; David, I.; Dranovsky, A.; et al. BDNF overexpression in mouse hippocampal astrocytes promotes local neurogenesis and elicits anxiolytic-like activities. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockel, M.; Lewin, G.R.; Barde, Y.A. In vivo effects of neurotrophin-3 during sensory neurogenesis. Development 1996, 122, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimazu, K.; Zhao, M.; Sakata, K.; Akbarian, S.; Bates, B.; Jaenisch, R.; Lu, B. NT-3 facilitates hippocampal plasticity and learning and memory by regulating neurogenesis. Learn. Mem. 2006, 13, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blurton-Jones, M.; Kitazawa, M.; Martinez-Coria, H.; Castello, N.A.; Muller, F.J.; Loring, J.F.; Yamasaki, T.R.; Poon, W.W.; Green, K.N.; LaFerla, F.M. Neural stem cells improve cognition via BDNF in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13594–13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Merrill, D.A.; Coppola, G.; Tsukada, S.; Schroeder, B.E.; Shaked, G.M.; Wang, L.; Blesch, A.; Kim, A.; Conner, J.M.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent and primate models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Luikart, B.W.; Birnbaum, S.; Chen, J.; Kwon, C.H.; Kernie, S.G.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Parada, L.F. TrkB regulates hippocampal neurogenesis and governs sensitivity to antidepressive treatment. Neuron 2008, 59, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruel-Jungerman, E.; Veyrac, A.; Dufour, F.; Horwood, J.; Laroche, S.; Davis, S. Inhibition of PI3K-Akt signaling blocks exercise-mediated enhancement of adult neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, P.; Zhu, T.; Xia, Z.; Gao, F.; Gu, W.; Chen, X.; Yuan, T.; Yu, H. Inhibition of MAPK/ERK signaling blocks hippocampal neurogenesis and impairs cognitive performance in prenatally infected neonatal rats. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 265, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Dong, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, X.J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Ye, W.C.; Shi, L. A natural diarylheptanoid promotes neuronal differentiation via activating ERK and PI3K-Akt dependent pathways. Neuroscience 2015, 303, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, J.-M.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; Chun, S. Ginsenoside Compound K Induces Adult Hippocampal Proliferation and Survival of Newly Generated Cells in Young and Elderly Mice. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030484
Oh J-M, Jeong JH, Park SY, Chun S. Ginsenoside Compound K Induces Adult Hippocampal Proliferation and Survival of Newly Generated Cells in Young and Elderly Mice. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(3):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030484
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Jung-Mi, Jae Hoon Jeong, Sun Young Park, and Sungkun Chun. 2020. "Ginsenoside Compound K Induces Adult Hippocampal Proliferation and Survival of Newly Generated Cells in Young and Elderly Mice" Biomolecules 10, no. 3: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030484
APA StyleOh, J. -M., Jeong, J. H., Park, S. Y., & Chun, S. (2020). Ginsenoside Compound K Induces Adult Hippocampal Proliferation and Survival of Newly Generated Cells in Young and Elderly Mice. Biomolecules, 10(3), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030484