A Lipidomic Perspective of the Action of Group IIA Secreted Phospholipase A2 on Human Monocytes: Lipid Droplet Biogenesis and Activation of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α
Abstract
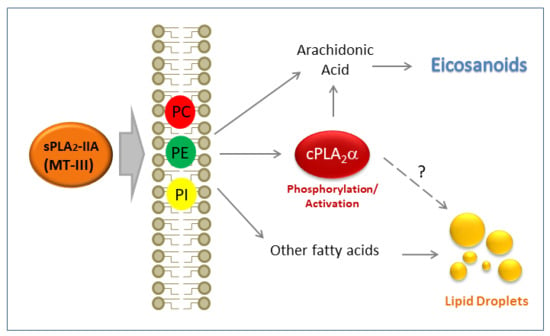
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enzymes
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cellular Staining and Fluorescence Microscopy
2.4. Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) Analysis of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters
2.5. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Free Fatty Acids
2.6. Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS) Analyses of Phospholipids
2.7. Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS) Analyses of Eicosanoids
2.8. Immunoblot
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | arachidonic acid |
| CE | cholesterol esters |
| cPLA2α | group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A2α |
| GC/MS | gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry |
| LC/MS | liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry |
| PC | choline-containing phospholipids |
| PE | ethanolamine-containing phospholipids |
| PI | phosphatidylinositol |
| sPLA2 | secreted phospholipase A2 |
| TAG | triacylglycerol |
References
- Dennis, E.A.; Cao, J.; Hsu, Y.H.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G. Phospholipase A₂ enzymes: Physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, M. Novel functions of phospholipase A₂s: Overview. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2019, 1864, 763–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambeau, G.; Gelb, M.H. Biochemistry and physiology of mammalian secreted phospholipases A₂. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 495–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Triggiani, M.; Granata, F.; Giannattasio, G.; Marone, G. Secretory phospholipases A₂ in inflammatory and allergic diseases: Not just enzymes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Gelb, M.H. Secretory Phospholipase A₂: A multifaceted family of proatherogenic enzymes. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2009, 11, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, J.M.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Guijas, C.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Group V secreted phospholipase A₂ is upregulated by IL-4 in human macrophages and mediates phagocytosis via hydrolysis of ethanolamine phospholipids. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3327–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balestrieri, B.; Maekawa, A.; Xing, W.; Gelb, M.H.; Katz, H.R.; Arm, J.P. Group V secretory phospholipase A₂ modulates phagosome maturation and regulates the innate immune response against Candida albicans. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4891–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boilard, E.; Lai, Y.; Larabee, K.; Balestrieri, B.; Ghomashchi, F.; Fujioka, D.; Gobezie, R.; Coblyn, J.S.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Massarotti, E.M.; et al. A novel anti-inflammatory role for secretory phospholipase A₂ in immune complex-mediated arthritis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, E.A.; Norris, P.C. Eicosanoid storm in infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Astudillo, A.M.; Balgoma, D.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Dynamics of arachidonic acid mobilization by inflammatory cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Astudillo, A.M.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Selectivity of phospholipid hydrolysis by phospholipase A₂ enzymes in activated cells leading to polyunsaturated fatty acid mobilization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2019, 1864, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Chacón, G.; Astudillo, A.M.; Balgoma, D.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Control of free arachidonic acid levels by phospholipases A₂ and lysophospholipid acyltransferases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leslie, C.C. Cytosolic phospholipase A₂: Physiological function and role in disease. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1386–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balsinde, J.; Winstead, M.V.; Dennis, E.A. Phospholipase A₂ regulation of arachidonic acid mobilization. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.K.; Sapirstein, A.; Huang, C.C.; Alessandrini, A.; Bonventre, J.V. Cross-talk between cytosolic phospholipase A₂α (cPLA₂α) and secretory phospholipase A₂ (sPLA₂) in hydrogen peroxide-induced arachidonic acid release in murine mesangial cells: sPLA₂ regulates cPLA₂α activity that is responsible for the arachidonic acid release. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 24153–24163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marshall, J.; Krump, E.; Lindsay, T.; Downey, G.; Ford, D.A.; Zhu, P.; Walker, P.; Rubin, B. Involvement of cytosolic phospholipase A₂ and secretory phospholipase A₂ in arachidonic acid release from human neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Degousee, N.; Ghomashchi, F.; Stefanski, E.; Singer, A.G.; Smart, B.P.; Borregaard, N.; Reithmeier, R.; Lindsay, T.F.; Lichtenberger, C.; Reinisch, W.; et al. Groups IV, V, and X phospholipases A₂s in human neutrophils: Role in eicosanoid production and gram-negative bacterial phospholipid hydrolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5061–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruipérez, V.; Casas, J.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Group V phospholipase A₂-derived lysophosphatidyl-choline mediates cyclooxygenase-2 induction in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruipérez, V.; Astudillo, M.A.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Coordinate regulation of TLR-mediated arachidonic acid mobilization in macrophages by group IVA and group V phospholipase A₂s. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3877–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balboa, M.A.; Pérez, R.; Balsinde, J. Amplification mechanisms of inflammation: Paracrine stimulation of arachidonic acid mobilization by secreted phospholipase A2 is regulated by cytosolic phospholipase A₂-derived hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balgoma, D.; Astudillo, A.M.; Pérez-Chacón, G.; Montero, O.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Markers of monocyte activation revealed by lipidomic profiling of arachidonic acid-containing phospholipids. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3857–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Astudillo, A.M.; Pérez-Chacón, G.; Meana, C.; Balgoma, D.; Pol, A.; del Pozo, M.A.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Altered arachidonate distribution in macrophages from caveolin-1 null mice leading to reduced eicosanoid synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35299–35307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdearcos, M.; Esquinas, E.; Meana, C.; Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Guijas, C.; Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A. Subcellular localization and role of lipin-1 in human macrophages. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6004–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Astudillo, A.M.; Meana, C.; Rubio, J.M.; Guijas, C.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. A phosphatidylinositol species acutely generated by activated macrophages regulates innate immune responses. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5169–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Astudillo, A.M.; Guijas, C.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Cytosolic group IVA and calcium-independent group VIA phospholipase A₂s act on distinct phospholipid pools in zymosan-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Astudillo, A.M.; Lebrero, P.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Essential role for ethanolamine plasmalogen hydrolysis in bacterial lipopolysaccharide priming of macrophages for enhanced arachidonic acid release. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, J.M.; Astudillo, A.M.; Casas, J.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Regulation of phagocytosis in macrophages by membrane ethanolamine plasmalogens. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monge, P.; Garrido, A.; Rubio, J.M.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. The contribution of cytosolic group IVA and calcium-independent group VIA phospholipase A₂s to adrenic acid mobilization in murine macrophages. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dore, E.; Boilard, E. Roles of secreted phospholipase A₂ group IIA in inflammation and host defense. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2019, 1864, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Obando, D.; Fernández, J.; Montecucco, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Synergism between basic Asp49 and Lys49 phospholipase A₂ myotoxins of viperid snake venom in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birts, C.N.; Barton, C.H.; Wilton, D.C. Catalytic and non-catalytic functions of human IIA phospholipase A₂. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koduri, R.S.; Baker, S.F.; Snitko, Y.; Han, S.K.; Cho, W.; Wilton, D.C.; Gelb, M.H. Action of human group IIA secreted phospholipase A₂ on cell membranes. Vesicle but not heparinoid binding determines rate of fatty acid release by exogenously added enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 273, 32142–32153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valentin, E.; Lambeau, G. Increasing molecular diversity of secreted phospholipases A₂ and their receptors and binding proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1488, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Calderón, L. An overview of lysine-49 phospholipase A₂ myotoxins from crotalid snake venoms and their structural determinants of myotoxic action. Toxicon 2003, 42, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Phospholipases A₂: Unveiling the secrets of a functionally versatile group of snake venom toxins. Toxicon 2013, 62, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Obando, D.; Díaz, C.; Angulo, Y.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Role of enzymatic activity in muscle damage and cytotoxicity induced by Bothrops asper Asp49 phospholipase A₂ myotoxins: Are there additional effector mechanisms involved? Peer J. 2014, 2, e569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaiser, I.I.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Plummer, D.; Aird, S.D.; Odell, G.V. The amino acid sequence of a myotoxic phospholipase from the venom of Bothrops asper. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 278, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Caccin, P.; Koster, G.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Montecucco, C.; Postle, A.D. Muscle phospholipid hydrolysis by Bothrops asper Asp49 and Lys49 phospholipase A₂ myotoxins – distinct mechanisms of action. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 3878–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takayama, K.; Mitchell, D.H.; Din, Z.Z.; Mukerjee, P.; Li, C.; Coleman, D.L. Monomeric Re lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli is more active than the aggregated form in the Limulus amebocyte lysate assay and in inducing Egr-1 mRNA in murine peritoneal macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 2241–2244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Chacón, G.; Astudillo, A.M.; Ruipérez, V.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Signaling role for lysophospholipid acyltransferase 3 in receptor-regulated arachidonic acid reacylation reactions in human monocytes. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casas, J.; Meana, C.; Esquinas, E.; Valdearcos, M.; Pindado, J.; Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A. Requirement of JNK-mediated phosphorylation for translocation of group IVA phospholipase A₂ to phagosomes in human macrophages. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2767–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diez, E.; Balsinde, J.; Aracil, M.; Schüller, A. Ethanol induces release of arachidonic acid but not synthesis of eicosanoids in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 921, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, J.B.; Sprecher, H. Unidimensional thin-layer chromatography of phospholipids on boric acid-impregnated plates. J. Lipid Res. 1982, 23, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Astudillo, A.M.; Pérez-Chacón, G.; Balgoma, D.; Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Ruipérez, V.; Guijas, C.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Influence of cellular arachidonic acid levels on phospholipid remodeling and CoA-independent transacylase activity in human monocytes and U937 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1811, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guijas, C.; Pérez-Chacón, G.; Astudillo, A.M.; Rubio, J.M.; Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Simultaneous activation of p38 and JNK by arachidonic acid stimulates the cytosolic phospholipase A₂-dependent synthesis of lipid droplets in human monocytes. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2343–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guijas, C.; Meana, C.; Astudillo, A.M.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Foamy monocytes are enriched in cis-7-hexadecenoic fatty acid (16:1n-9), a possible biomarker for early detection of cardiovascular disease. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, J.P.; Guijas, C.; Astudillo, A.M.; Rubio, J.M.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Sequestration of 9-hydroxystearic acid in FAHFA (fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids) as a protective mechanism for colon carcinoma cells to avoid apoptotic cell death. Cancers 2019, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Astudillo, A.M.; Meana, C.; Guijas, C.; Pereira, L.; Lebrero, R.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Occurrence and biological activity of palmitoleic acid isomers in phagocytic cells. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balgoma, D.; Montero, O.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Calcium-independent phospholipase A₂-mediated formation of 1,2-diarachidonoyl-glycerophosphoinositol in monocytes. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 6180–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guijas, C.; Astudillo, A.M.; Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Rubio, J.M.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Phospholipid sources for adrenic acid mobilization in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Comparison with arachidonic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebrero, P.; Astudillo, A.M.; Rubio, J.M.; Fernández-Caballero, J.; Kokotos, G.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Cellular plasmalogen content does not influence arachidonic acid levels or distribution in macrophages: A role for cytosolic phospholipase A₂γ in phospholipid remodeling. Cells 2019, 8, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindado, J.; Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A. TLR3-dependent induction of nitric oxide synthase in RAW 264.7 macrophage-like cells via a cytosolic phospholipase A₂/cyclooxygenase-2 pathway. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4821–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdearcos, M.; Esquinas, E.; Meana, C.; Peña, L.; Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A. Lipin-2 reduces proinflammatory signaling induced by saturated fatty acids in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10894–10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leiguez, E.; Zuliani, J.P.; Cianciarullo, A.M.; Fernandes, C.M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Teixeira, C. A group IIA-secreted phospholipase A₂ from snake venom induces lipid body formation in macrophages: The roles of intracellular phospholipases A₂ and distinct signaling pathways. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuliani, J.P.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Casais e Silva, L.L.; Sampaio, S.C.; Lomonte, B.; Teixeira, C.F.P. Activation of cellular functions in macrophages by venom secretory Asp-49 and Lys-49 phospholipases A₂. Toxicon 2005, 46, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiguez, E.; Giannotti, K.C.; Moreira, V.; Matsubara, M.H.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Balsinde, J.; Teixeira, C. Critical role of TLR2 and MyD88 for functional response of macrophages to a group IIA-secreted phospholipase A₂ from snake venom. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rouzer, C.A.; Ivanova, P.T.; Byrne, M.O.; Milne, S.B.; Brown, H.A.; Marnett, L.J. Lipid profiling reveals glycerophospholipid remodeling in zymosan-stimulated macrophages. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 6026–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chilton, F.H.; Fonteh, A.N.; Surette, M.E.; Triggiani, M.; Winkler, J.D. Control of arachidonate levels within inflammatory cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1299, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Nemoto-Sasaki, Y.; Koizumi, T.; Inagaki, Y.; Oka, S.; Tanikawa, T.; Sugiura, T. Coenzyme-A-independent transacylation system; possible involvement of phospholipase A₂ in transacylation. Biology 2017, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kennett, F.F.; Schenkein, H.A.; Ellis, T.M.; Rutherford, R.B. Phospholipid composition of human monocytes and alterations occurring due to culture and stimulation by C3b. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 804, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, E.J.; Omura, S.; Laposata, M. Triacsin C: A differential inhibitor of arachidonoyl-CoA synthetase and nonspecific long chain acyl-CoA synthetase. Prostaglandins 1989, 37, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.A.; Lewin, T.M.; Van Horn, C.G.; González-Baró, M.R. Do long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases regulate fatty acid entry into synthetic versus degradative pathways? J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2123–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ono, T.; Yamada, K.; Chikazawa, Y.; Ueno, M.; Nakamoto, S.; Okuno, T.; Seno, K. Characterization of a novel inhibitor of cytosolic phospholipase A₂α, pyrrophenone. Biochem. J. 2002, 363, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Involvement of calcium-independent phospholipase A₂ in hydrogen peroxide-induced accumulation of free fatty acids in human U937 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 40384–40389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghomashchi, F.; Stewart, A.; Hefner, Y.; Ramanadham, S.; Turk, J.; Leslie, C.C.; Gelb, M.H. A pyrrolidine-based specific inhibitor of cytosolic phospholipase A₂α blocks arachidonic acid release in a variety of mammalian cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1513, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balboa, M.A.; Sáez, Y.; Balsinde, J. Calcium-independent phospholipase A₂ is required for lysozyme secretion in U937 promonocytes. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5276–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balestrieri, B.; Hsu, V.W.; Gilbert, H.; Leslie, C.C.; Han, W.K.; Bonventre, J.V.; Arm, J.P. Group V secretory phospholipase A₂ translocates to the phagosome after zymosan stimulation of mouse peritoneal macrophages and regulates phagocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 6691–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casas, J.; Gijón, M.A.; Vigo, A.G.; Crespo, M.S.; Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate anchors cytosolic group IVA phospholipase A₂ to perinuclear membranes and decreases its calcium requirement for translocation in live cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satake, Y.; Diaz, B.L.; Balestrieri, B.; Lam, B.K.; Kanaoka, Y.; Grusby, M.J.; Arm, J.P. Role of group V phospholipase A₂ in zymosan-induced eicosanoid generation and vascular permeability revealed by targeted gene disruption. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16488–16494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balboa, M.A.; Shirai, Y.; Gaietta, G.; Ellisman, M.H.; Balsinde, J.; Dennis, E.A. Localization of group V phospholipase A₂ in caveolin-enriched granules in activated P388D1 macrophage-like cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48059–48065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balsinde, J.; Shinohara, H.; Lefkowitz, L.J.; Johnson, C.A.; Balboa, M.A.; Dennis, E.A. Group V phospholipase A₂-dependent induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25967–25970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A.; Yedgar, S.; Dennis, E.A. Group V phospholipase A₂-mediated oleic acid mobilization in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated P388D1 macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4783–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J.; Dillon, D.A.; Carman, G.M.; Dennis, E.A. Proinflammatory macrophage-activating properties of the novel phospholipid diacylglycerol pyrophosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A.; Dennis, E.A. Inflammatory activation of arachidonic acid signaling in murine P388D1 macrophages via sphingomyelin synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20373–20377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A.; Insel, P.A.; Dennis, E.A. Differential regulation of phospholipase D and phospholipase A₂ by protein kinase C in P388D1 macrophages. Biochem. J. 1997, 321, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffman, T.; Lizzio, E.F.; Suissa, J.; Rotrosen, D.; Sullivan, J.A.; Mandell, G.L.; Bonvini, E. Dual stimulation of phospholipase activity in human monocytes. Role of calcium-dependent and calcium-independent pathways in arachidonic acid release and eicosanoid formation. J. Immunol. 1988, 140, 3912–3918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, T.; Brando, C.; Lizzio, E.F.; Lee, Y.L.; Hansen, M.; Tripathi, A.K.; Taplits, M.; Puri, J.; Bonvini, E.; Abrahamsen, T.G.; et al. Calcium-dependent eicosanoid metabolism by concanavalin A-stimulated human monocytes in vitro. Synergism with phorbol ester indicates separate regulation of leukotriene B4 synthesis and release. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Penglis, P.S.; Cleland, L.G.; Demasi, M.; Caughey, G.E.; James, M.J. Differential regulation of prostaglandin E₂ and thromboxane A₂ production in human monocytes: Implications for the use of cyclooxygenase inhibitors. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, C.; Cury, Y.; Moreira, V.; Picolo, G.; Chaves, F. Inflammation induced by Bothrops asper venom. Toxicon 2009, 54, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.K.; Kim, K.P.; Koduri, R.; Bittova, L.; Muñoz, N.M.; Leff, A.R.; Wilton, D.C.; Gelb, M.H.; Cho, W. Roles of Trp31 in high membrane binding and proinflammatory activity of human group V phospholipase A₂. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11881–11888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melo, R.C.N.; Weller, P.F. Lipid droplets in leukocytes: Organelles linked to inflammatory responses. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 340, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cruz, A.L.S.; Barreto, E.A.; Fazolini, N.P.B.; Viola, J.P.B.; Bozza, P.T. Lipid droplets: Platforms with multiple functions in cancer hallmarks. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jarc, E.; Petan, T. A twist of FATe: Lipid droplets and inflammatory lipid mediators. Biochimie 2020, 169, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guijas, C.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Rubio, J.M.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Phospholipase A₂ regulation of lipid droplet formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapman, K.D.; Aziz, M.; Dyer, J.M.; Mullen, R.T. Mechanisms of lipid droplet biogenesis. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 1929–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guijas, C.; Bermúdez, M.A.; Meana, C.; Astudillo, A.M.; Pereira, L.; Fernández-Caballero, L.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Neutral lipids are not a source of arachidonic acid for lipid mediator signaling in human foamy monocytes. Cells 2019, 8, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dichlberger, A.; Schlager, S.; Maaninka, K.; Schneider, W.J.; Kovanen, P.T. Adipose triglyceride lipase regulates eicosanoid production in activated human mast cells. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2471–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlager, S.; Goeritzer, M.; Jandl, K.; Frei, R.; Vujic, N.; Kolb, D.; Strohmaier, H.; Juliane, J.; Dorow, J.; Eichmann, T.O.; et al. Adipose triglyceride lipase acts on neutrophil lipid droplets to regulate substrate availability for lipid mediator synthesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gubern, A.; Casas, J.; Barceló-Torns, M.; Barneda, D.; de la Rosa, X.; Masgrau, R.; Picatoste, F.; Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A.; Claro, E. Group IVA phospholipase A₂ is necessary for the biogenesis of lipid droplets. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27369–27382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gubern, A.; Barceló-Torns, M.; Barneda, D.; López, J.M.; Masgrau, R.; Picatoste, F.; Chalfant, C.E.; Balsinde, J.; Balboa, M.A.; Claro, E. JNK and ceramide kinase govern the biogenesis of lipid droplets through activation of group IVA phospholipase A₂. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32359–32369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez, J.P.; Leiguez, E.; Guijas, C.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Teixeira, C.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. A Lipidomic Perspective of the Action of Group IIA Secreted Phospholipase A2 on Human Monocytes: Lipid Droplet Biogenesis and Activation of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060891
Rodríguez JP, Leiguez E, Guijas C, Lomonte B, Gutiérrez JM, Teixeira C, Balboa MA, Balsinde J. A Lipidomic Perspective of the Action of Group IIA Secreted Phospholipase A2 on Human Monocytes: Lipid Droplet Biogenesis and Activation of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(6):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060891
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez, Juan P., Elbio Leiguez, Carlos Guijas, Bruno Lomonte, José M. Gutiérrez, Catarina Teixeira, María A. Balboa, and Jesús Balsinde. 2020. "A Lipidomic Perspective of the Action of Group IIA Secreted Phospholipase A2 on Human Monocytes: Lipid Droplet Biogenesis and Activation of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α" Biomolecules 10, no. 6: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060891
APA StyleRodríguez, J. P., Leiguez, E., Guijas, C., Lomonte, B., Gutiérrez, J. M., Teixeira, C., Balboa, M. A., & Balsinde, J. (2020). A Lipidomic Perspective of the Action of Group IIA Secreted Phospholipase A2 on Human Monocytes: Lipid Droplet Biogenesis and Activation of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α. Biomolecules, 10(6), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060891