Discovery of Sulfated Small Molecule Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinase-8
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chemistry
2.3. Direct Inhibition Studies
2.4. Molecular Modeling Studies
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. GAG Binding Potential of MMP-8
3.2. Structure−Activity Relationships for the Library of NSGMs
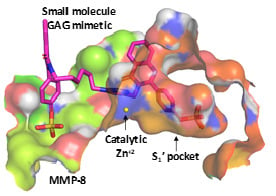
3.3. Computational Analysis of the Preferred Site of NSGMs Binding to MMP-8
3.4. Sulfated Quinazolinones Do Not Inhibit MMP-9
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Lint, P.; Libert, C. Matrix metalloproteinase-8: Cleavage can be decisive. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, H.W.; Defamie, V.; Waterhouse, P.; Khokha, R. TIMPs: Versatile extracellular regulators in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 17, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Tay, F.R.; Yiu, C.K. The past, present and future perspectives of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 207, 107465–107478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S. Putative targeting of matrix metalloproteinase-8 in atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 147, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenglet, S.; Mach, F.; Montecucco, F. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 in Atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 659282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leppert, D.; Leib, S.; Grygar, C.; Miller, K.M.; Schaad, U.B.; Holländer, G.A. Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-8 and MMP-9 in Cerebrospinal Fluid during Bacterial Meningitis: Association with Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Neurological Sequelae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juurikka, K.; Butler, G.; Salo, T.; Nyberg, P.; Åström, P. Salo The Role of MMP8 in Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, H.-K.; Hong, Y.; Lim, M.N.; Yim, J.-J.; Kim, W.J. Relationship between plasma matrix metalloproteinase levels, pulmonary function, bronchodilator response, and emphysema severity. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2016, 11, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, R.; Momiyama, Y.; Ohmori, R.; Taniguchi, H.; Nakamura, H.; Ohsuzu, F. Plasma Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 Concentrations are Associated with the Presence and Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. Circ. J. 2005, 69, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craig, V.J.; Zhang, L.; Hagood, J.S.; Owen, C.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Therapeutic Targets for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Boil. 2015, 53, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lauhio, A.; Färkkilä, E.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Åström, P.; Winkelmann, A.; Tervahartiala, T.; Pirilä, E.; Rissanen, A.; Kaprio, J.; Sorsa, T.; et al. Association of MMP-8 with obesity, smoking and insulin resistance. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 46, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorsa, T.; Gürsoy, U.K.; Nwhator, S.; Hernández, M.; Tervahartiala, T.; Leppilahti, J.; Gursoy, M.; Könönen, E.; Emingil, G.; Pussinen, P.J.; et al. Analysis of matrix metalloproteinases, especially MMP-8, in gingival crevicular fluid, mouthrinse and saliva for monitoring periodontal diseases. Periodontol. 2000 2015, 70, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solan, P.D.; Dunsmore, K.E.; Denenberg, A.G.; Odoms, K.; Zingarelli, B.; Wong, H.R. A novel role for matrix metalloproteinase-8 in sepsis*. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ong, C.W.M.; Elkington, P.T.; Brilha, S.; Ugarte-Gil, C.; Esteban, M.T.T.; Tezera, L.B.; Pabisiak, P.J.; Moores, R.C.; Sathyamoorthy, T.; Patel, V.; et al. Neutrophil-Derived MMP-8 Drives AMPK-Dependent Matrix Destruction in Human Pulmonary Tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danielsen, P.L.; Holst, A.V.; Maltesen, H.R.; Bassi, M.R.; Holst, P.; Heinemeier, K.M.; Olsen, J.; Danielsen, C.C.; Poulsen, S.S.; Jørgensen, L.N.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 overexpression prevents proper tissue repair. Surgery 2011, 150, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, G.B. The Rebirth of Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors: Moving Beyond the Dogma. Cells 2019, 8, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchini, G.; Aschi, M.; Cavicchio, G.; Crucianelli, M.; Preziuso, S.; Gallina, C.; Nastari, A.; Gavuzzo, E.; Mazza, F. Design, modelling, synthesis and biological evaluation of peptidomimetic phosphinates as inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-8. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 4740–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Protease inhibitors: Synthesis of matrix metalloproteinase and bacterial collagenase inhibitors incorporating 5-amino-2-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole zinc binding functions. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 2667–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Shen, F.Q.; Yang, M.R.; You, L.X.; Chen, L.Z.; Zhu, H.L.; Lu, Y.D.; Kong, F.L.; Wang, M.H. Dihydropyrazothiazole derivatives as potential MMP-2/MMP-8 inhibitors for cancer therapy. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3816–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, M.; Tokmina-Roszyk, D.; Onwuha-Ekpete, L.; Harmon, K.; Robichaud, T.; Fuerst, R.; Stawikowska, R.; Steffensen, B.; Roush, W.R.; Wong, H.R.; et al. Second Generation Triple-Helical Peptide Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinases. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3814–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocchi, A.; Parks, W.C. Functional interactions between matrix metalloproteinases and glycosaminoglycans. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2332–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannello, F.; Jung, K.; Tonti, G.A.; Canestrari, F. Heparin affects matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases circulating in peripheral blood. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capila, I.; Linhardt, R.J. Heparin-protein interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2002, 41, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.S.; Mancera, R.L. The Structure of Glycosaminoglycans and their Interactions with Proteins. Chem. Boil. Drug Des. 2008, 72, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ra, H.-J.; Harju-Baker, S.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Wilson, C.L.; Parks, W.C. Control of Promatrilysin (MMP7) Activation and Substrate-specific Activity by Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans. J. Boil. Chem. 2009, 284, 27924–27932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannello, F.; Raffetto, J.D. Matrix metalloproteinase activity and glycosaminoglycans in chronic venous disease: The linkage among cell biology, pathology and translational research. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2010, 3, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Morla, S. Glycosaminoglycans and Glycosaminoglycan Mimetics in Cancer and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagarajan, B.; Sankaranarayanan, N.V.; Patel, B.B.; Desai, U.R. A molecular dynamics-based algorithm for evaluating the glycosaminoglycan mimicking potential of synthetic, homogenous, sulfated small molecules. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morla, S.; Sankaranarayanan, N.V.; Afosah, D.K.; Kumar, M.; Kummarapurugu, A.B.; Voynow, J.A.; Desai, U.R. On the Process of Discovering Leads That Target the Heparin-Binding Site of Neutrophil Elastase in the Sputum of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5501–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Abdelfadiel, E.I.; Afosah, D.K.; Morla, S.; Sistla, J.C.; Mohammed, B.; Martin, E.J.; Sakagami, M.; Brophy, D.F.; Desai, U.R. A synthetic heparin mimetic that allosterically inhibits factor XIa and reduces thrombosis in vivo without enhanced risk of bleeding. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 2110–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afosah, D.K.; Al-Horani, R.A.; Sankaranarayanan, N.V.; Desai, U.R. Potent, Selective, Allosteric Inhibition of Human Plasmin by Sulfated Non-Saccharide Glycosaminoglycan Mimetics. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangji, R.N.; Sankaranarayanan, N.V.; Elste, J.; Al-Horani, R.A.; Afosah, D.K.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, V.; Desai, U.R. Inhibition of Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Entry into Human Cells by Nonsaccharide Glycosaminoglycan Mimetics. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarsson, G.T.; Desai, U.R. Interaction of Designed Sulfated Flavanoids with Antithrombin: Lessons on the Design of Organic Activators. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 4460–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Liang, A.; Desai, U.R. Designing Nonsaccharide, Allosteric Activators of Antithrombin for Accelerated Inhibition of Factor Xa. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6125–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Ponnusamy, P.; Mehta, A.Y.; Gailani, D.; Desai, U.R. Sulfated Pentagalloylglucoside Is a Potent, Allosteric, and Selective Inhibitor of Factor XIa. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boothello, R.S.; Patel, N.J.; Sharon, C.; Abdelfadiel, E.I.; Morla, S.; Brophy, D.F.; Lippman, H.R.; Desai, U.R.; Patel, B.B. A Unique Nonsaccharide Mimetic of Heparin Hexasaccharide Inhibits Colon Cancer Stem Cells via p38 MAP Kinase Activation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 18, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desai, U.R. The promise of sulfated synthetic small molecules as modulators of glycosaminoglycan function. Future Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afosah, D.K.; Verespy, S.; Al-Horani, R.A.; Boothello, R.S.; Karuturi, R.; Desai, U.R. A small group of sulfated benzofurans induces steady-state submaximal inhibition of thrombin. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.J.; Karuturi, R.; Al-Horani, R.A.; Baranwal, S.; Patel, J.; Desai, U.R.; Patel, B.B. Synthetic, Non-saccharide, Glycosaminoglycan Mimetics Selectively Target Colon Cancer Stem Cells. ACS Chem. Boil. 2014, 9, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Desai, U.R. Designing Allosteric Inhibitors of Factor XIa. Lessons from the Interactions of Sulfated Pentagalloylglucopyranosides. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4805–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Karuturi, R.; White, D.T.; Desai, U.R. Plasmin Regulation through Allosteric, Sulfated, Small Molecules. Molecules 2015, 20, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Gailani, D.; Desai, U.R. Allosteric inhibition of factor XIa. Sulfated non-saccharide glycosaminoglycan mimetics as promising anticoagulants. Thromb. Res. 2015, 136, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sankaranarayanan, N.V.; Nagarajan, B.; Desai, U.R. So you think computational approaches to understanding glycosaminoglycan–protein interactions are too dry and too rigid? Think again! Curr. Opin. Struct. Boil. 2018, 50, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimeno, A.; Beltran-Debon, R.; Mulero, M.; Pujadas, G.; Garcia-Vallve, S. Understanding the variability of the S1′ pocket to improve matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor selectivity profiles. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 38–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overall, C.M.; Kleifeld, O. Towards third generation matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iii, S.V.; Mehta, A.Y.; Afosah, D.; Al-Horani, R.A.; Desai, U.R. Allosteric Partial Inhibition of Monomeric Proteases. Sulfated Coumarins Induce Regulation, not just Inhibition, of Thrombin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lira, A.L.; Ferreira, R.S.; Torquato, R.J.S.; Oliva, M.L.V.; Schuck, P.; Sousa, A.A. Allosteric inhibition of alpha-thrombin enzymatic activity with ultrasmall gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agamennone, M.; Campestre, C.; Preziuso, S.; Consalvi, V.; Crucianelli, M.; Mazza, F.; Politi, V.; Ragno, R.; Tortorella, P.; Gallina, C. Synthesis and evaluation of new tripeptide phosphonate inhibitors of MMP-8 and MMP-2. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 40, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, M.; Floyd, C.D.; Brown, P.; Gearing, A.J.H. Design and therapeutic application of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2735–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Disease | Role of MMP-8 |
|---|---|
| Atherosclerosis | High MMP-8 in atheromatous and fibrous plaques promote plaque rupture, leading to vascular and cardiac events, including myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, and abdominal aortic aneurysm [4]. MMP-8 knockdown significantly reduces atherosclerotic events in mouse models [5]. |
| Bacterial meningitis | High MMP-8 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of children with bacterial meningitis are associated with blood–brain barrier damage and neuronal injury [6]. |
| Cancer | MMP-8 displays apparently contradictory roles in both cancer progression and inhibition, depending on the type of cancer, making it both a target and an anti-target for cancer therapy [7]. |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)/emphysema | Increased MMP-8 levels lead to poor pulmonary function and emphysema severity [8]. |
| Coronary artery disease | The plasma MMP-8 levels in patients with coronary artery disease is associated with disease severity [9]. |
| Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) | MMP-8 levels in plasma, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and lung macrophages of IPF patients are noted to be high. MMP-8 knockdown protects mice from bleomycin-mediated lung fibrosis [10]. |
| Obesity | MMP-8, which degrades the human insulin receptor, is increased in the serum of obese individuals, and may contribute to insulin resistance. MMP-8 inhibition restores the insulin receptor [11]. |
| Periodontal diseases | Upregulated MMP-8 levels are observed in gingival cervicular fluid, corresponding to 90–95% of all collagenolytic activity. MMP-8 inhibitors cease the progression of periodontitis [12]. |
| Sepsis | The increased gene expression and activity of MMP-8 correlates with disease severity and a worsening clinical outcome [13]. |
| Tuberculosis | MMP-8 dependent tissue destruction is observed in patient lung biopsies [14]. |
| Wound healing | Increased MMP-8 levels in mice prevent tissue repair, leading to impaired wound healing [15]. |
| NSGM | IC50 (µM)a | ΔY (%)a |
|---|---|---|
| 26 | 13 ± 1b | 75 ± 3 |
| 38 | 11 ± 1 | 99 ± 6 |
| 40 | 25 ± 1 | 100 ± 2 |
| 41 | 15 ± 1 | 97 ± 2 |
| 42 | 34 ± 4 | 98 ± 8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morla, S.; Desai, U.R. Discovery of Sulfated Small Molecule Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinase-8. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081166
Morla S, Desai UR. Discovery of Sulfated Small Molecule Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinase-8. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(8):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081166
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorla, Shravan, and Umesh R. Desai. 2020. "Discovery of Sulfated Small Molecule Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinase-8" Biomolecules 10, no. 8: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081166
APA StyleMorla, S., & Desai, U. R. (2020). Discovery of Sulfated Small Molecule Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinase-8. Biomolecules, 10(8), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081166