Therapeutic Potential of αS Evolvability for Neuropathic Gaucher Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Conventional View of the Relationship between GD and αS Pathology
2.1. Association of PD with GBA1 Mutations
2.2. Proposed Mechanism of Association between GD and PD
3. Comorbidity of GD1 with PD from Viewpoint of αS Evolvability
3.1. Physiological Functions of αS
3.2. Evolvability of αS
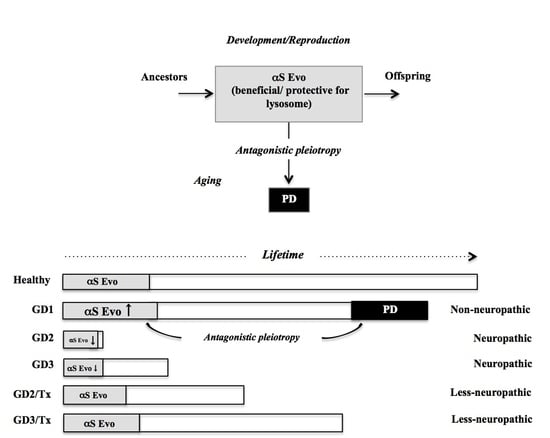
3.3. Possible Relevance of αS Evolvability to Pathogenesis of GD
3.4. βS as Buffer against αS Evolvability
3.5. Experimental Support of Pleiotropic Effects of αS in Terms of Lysosomal Activity
4. Application of Evolvability Hypothesis to Other LSDs
4.1. Niemann-Pick Type C (NPC)
4.2. NPC and Amyloidogenic Evolvability
5. βS as Therapeutic Target
5.1. Conventional Therapy
5.2. Evolvability-Based Novel Therapy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, C.R.; Gahl, W.A. Lysosomal storage diseases. Transl. Sci. Rare Dis. 2017, 2, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabowski, G.A. Phenotype, diagnosis, and treatment of Gaucher’s disease. Lancet 2008, 372, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, B.E.; Weinreb, N.J. Gaucher disease: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2013, 18, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, P.; Liang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Hashimoto, M.; Wei, J. Gaucher-Associated Parkinsonism. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayebi, N.; Walker, J.; Stubblefield, B.; Orvisky, E.; La Marca, M.E.; Wong, K.; Rosenbaum, H.; Schiffmann, R.; Bembi, B.; Sindransky, E. Gaucher disease with parkinsonian manifestations: Does glucocerebrosidase deficiency contribute to a vulnerability to parkinsonism? Mol. Genet. Metab. 2003, 79, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Fujita, M.; Nakai, M.; Waragai, M.; Sekigawa, A.; Sugama, S.; Takenouchi, T.; Masliah, E.; Hashimoto, M. Protective role of endogenous gangliosides for lysosomal pathology in a cellular model of synucleinopathies. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1891–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Sintes, G.R. Boya, Lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cell death. Traffic 2018, 19, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkovska, I.; Krainc, D.; Mazzulli, J.R. Molecular mechanisms of alpha-synuclein and GBA1 in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, J.; McKinney, C.; Sharma, P.; Sidransky, E. Glucocerebrosidase and its relevance to Parkinson disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regan, O.G.; de Souza, R.M.; Balestrino, R.; Schapira, A.H. Glucocerebrosidase Mutations in Parkinson Disease. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2017, 7, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sidransky, E.; Lopez, G. The link between the GBA gene and parkinsonism. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bultron, G.; Kacena, K.; Pearson, D.; Boxer, M.; Yang, R.; Sathe, S.; Pastores, G.; Mistry, P.K. The risk of Parkinson’s disease in type 1 Gaucher disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sidransky, E.; Nalls, M.A.; Aasly, J.O.; Peretz, A.J.; Barbosa, E.R.; Shira, B.A.; Berg, D.; Bras, J.; Brice, A.; Chen, C.M.; et al. Multicenter analysis of glucocerebrosidase mutations in Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maor, G.; Rapaport, D.; Horowitz, M. The effect of mutant GBA1 on accumulation and aggregation of alpha-synuclein. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 1768–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.; Patnaik, S.; Schoenen, F.; Zheng, W.; Choi, J.; Motabar, O.; Southall, N.; Westbroek, W.; Goldin, E.; Sidranksy, E.; et al. Discovery, SAR, Biological Evaluation of Non-Inhibitory Chaperones of Glucocerebrosidase, Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program, Bethesda (MD); Europe PubMed Central: Cambridgeshire, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vitner, E.B.; Becker, T.; Ferreira, F.N.S.; Leshkowitz, D.; Sharma, P.; Lang, K.S.; Futerman, A.H. Induction of the type I interferon response in neurological forms of Gaucher disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzulli, J.R.; Xu, Y.H.; Sun, Y.; Knight, A.L.; McLean, P.J.; Caldwell, G.A.; Sidransky, E.; Grabowski, G.A.; Krainc, D. Gaucher disease glucocerebrosidase and alpha-synuclein form a bidirectional pathogenic loop in synucleinopathies. Cell 2011, 146, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cookson, M.R. A feedforward loop links Gaucher and Parkinson’s diseases? Cell 2011, 146, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, J.M.; Jin, H.; Woods, W.S.; Clayton, D.F. Characterization of a novel protein regulated during the critical period for song learning in the zebra finch. Neuron 1995, 15, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandra, S.; Gallardo, G.; Chacon, F.R.; Schluter, O.M.; Sudhof, T.C. Alpha-synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell 2005, 123, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Hsu, L.J.; Rockenstein, E.; Takenouchi, T.; Mallory, M.; Masliah, E. Alpha-Synuclein protects against oxidative stress via inactivation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase stress-signaling pathway in neuronal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11465–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musgrove, R.E.; King, A.E.; Dickson, T.C. Alpha-Synuclein protects neurons from apoptosis downstream of free-radical production through modulation of the MAPK signalling pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 23, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menges, S.; Minakaki, G.; Schaefer, P.M.; Meixner, H.; Prots, I.; Schrehardt, U.S.; Friedland, K.; Winner, B.; Outeiro, T.F.; Winklhofer, K.F.; et al. Alpha-synuclein prevents the formation of spherical mitochondria and apoptosis under oxidative stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y. Like father like son. A fresh review of the inheritance of acquired characteristics. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, M.; Ho, G.; Sugama, S.; Takamatsu, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Takenouchi, T.; Waragai, M.; Masliah, E. Evolvability of Amyloidogenic Proteins in Human Brain. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirschner, M.; Gerhart, J. Evolvabilit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8420–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically disordered proteins in overcrowded milieu: Membrane-less organelles, phase separation, and intrinsic disorder. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 44, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Ho, G.; Takamatsu, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Sugama, S.; Takenouchi, T.; Waragai, M.; Masliah, E. Evolvability and Neurodegenerative Disease: Antagonistic Pleiotropy Phenomena Derived from Amyloid Aggregates. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2018, 8, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitsui, J.; Matsukawa, T.; Sasaki, H.; Yabe, I.; Matsushima, M.; Durr, A.; Brice, A.; Takashima, H.; Kikuchi, A.; Aoki, M.; et al. Variants associated with Gaucher disease in multiple system atrophy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueda, K.; Fukushima, H.; Masliah, E.; Xia, Y.; Iwai, A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Otero, D.A.; Kondo, J.; Ihara, Y.; Saitoh, T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11282–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, M.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Mallory, M.; Masliah, E. Beta-Synuclein inhibits alpha-synuclein aggregation: A possible role as an anti-parkinsonian factor. Neuron 2001, 32, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Souillac, P.; Millett, I.S.; Doniach, S.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M.; Fink, A.L. Biophysical properties of the synucleins and their propensities to fibrillate: Inhibition of alpha-synuclein assembly by beta- and gamma-synucleins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11970–11978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Fujita, M.; Nakai, M.; Waragai, M.; Watabe, K.; Akatsu, H.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E.; Hashimoto, M. Enhanced lysosomal pathology caused by beta-synuclein mutants linked to dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28904–28914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crews, L.; Spencer, B.; Desplats, P.; Patrick, C.; Paulino, A.; Rockenstein, E.; Hansen, L.; Adame, A.; Galasko, D.; Masliah, E. Selective molecular alterations in the autophagy pathway in patients with Lewy body disease and in models of alpha-synucleinopathy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, M.; Sugama, S.; Sekiyama, K.; Sekigawa, A.; Tsukui, T.; Nakai, M.; Waragai, M.; Takenouchi, T.; Takamatsu, Y.; Wei, J.; et al. A beta-synuclein mutation linked to dementia produces neurodegeneration when expressed in mouse brain. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtake, H.; Limprasert, P.; Fan, Y.; Onodera, O.; Kakita, A.; Takahashi, H.; Bonner, L.T.; Tsuang, D.W.; Murray, I.V.J.; Lee, V.M.Y.; et al. Beta-synuclein gene alterations in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 2004, 63, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Lazzaro, V.; Marano, M.; Florio, L.; de Santis, S. Niemann-Pick type C: Focus on the adolescent/adult onset form. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, B.S.; Baruteau, J.; Rahim, A.A.; Gissen, P. Clinical and Molecular Features of Early Infantile Niemann Pick Type C Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Nanba, E.; Yamamoto, T.; Ohno, K.; Murayama, S. Niemann-Pick type C disease: Accelerated neurofibrillary tangle formation and amyloid beta deposition associated with apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 homozygosity. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 52, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.W.; Shie, F.S.; Maezawa, I.; Vincent, I.; Bird, T. Intracellular accumulation of amyloidogenic fragments of amyloid-beta precursor protein in neurons with Niemann-Pick type C defects is associated with endosomal abnormalities. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.; Pressey, S.N.; Cooper, J.D.; Soriano, S. Loss of amyloid precursor protein in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick type C disease exacerbates its phenotype and disrupts tau homeostasis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 42, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, C.D.; Elrick, M.J.; Lieberman, A.P. Tau normal function influences Niemann-Pick type C disease pathogenesis in mice and modulates autophagy in NPC1-deficient cells. Autophagy 2009, 5, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naughton, B.J.; Duncan, F.J.; Murrey, D.; Ware, T.; Meadows, A.; McCarty, D.M.; Fu, H. Amyloidosis, synucleinopathy, and prion encephalopathy in a neuropathic lysosomal storage disease: The CNS-biomarker potential of peripheral blood. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0080142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rossum, A.; Holsopple, M. Enzyme Replacement or Substrate Reduction? A Review of Gaucher Disease Treatment Options. Hosp. Pharm. 2016, 51, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Concolino, D.; Deodato, F.; Parini, R. Enzyme replacement therapy: Efficacy and limitations. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.J.; Li, J.Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Feng, J.S. Efficacy and safety of anti-amyloid-beta immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2017, 4, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, C.; Wood, M.J.A. Antisense oligonucleotides: The next frontier for treatment of neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, S.; Sframeli, M. New Treatments in Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Positive Results and New Challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.H.; Hojrup, P.; Hager, H.; Nielsen, M.S.; Jacobsen, L.; Olesen, O.F.; Gliemann, J.; Jakes, R. Binding of Abeta to alpha- and beta-synucleins: Identification of segments in alpha-synuclein/NAC precursor that bind Abeta and NAC. Biochem. J. 1997, 323, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasson, B.I.; Forman, M.S.; Higuchi, M.; Golbe, L.I.; Graves, C.L.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuclein. Science 2003, 300, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, F.T.; Vitner, E.B.; Futerman, A.H. Animal models for Gaucher disease research. Dis. Model. Mech. 2011, 4, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fog, C.K.; Kirkegaard, T. Animal models for Niemann-Pick type C: Implications for drug discovery & development. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uemura, N.; Koike, M.; Ansai, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Fujiwara, T.I.; Matsui, H.; Naruse, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Uchiyama, Y.; Todo, T.; et al. Viable neuronopathic Gaucher disease model in Medaka (Oryzias latipes) displays axonal accumulation of alpha-synuclein. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Cai, X.; Wang, G.; Ouyang, G.; Cao, H. Model construction of Niemann-Pick type C disease in zebrafish. Biol. Chem. 2018, 399, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, Y.; Ho, G.; Wada, R.; Inoue, S.; Hashimoto, M. Adiponectin paradox as a therapeutic target of the cancer evolvability in aging. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, Y.; Ho, G.; Hashimoto, M. Amyloid Evolvability and Cancer. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Takamatsu, Y.; Wada, R.; Fujita, M.; Ho, G.; Masliah, E.; Hashimoto, M. Therapeutic Potential of αS Evolvability for Neuropathic Gaucher Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020289
Wei J, Takamatsu Y, Wada R, Fujita M, Ho G, Masliah E, Hashimoto M. Therapeutic Potential of αS Evolvability for Neuropathic Gaucher Disease. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(2):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020289
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jianshe, Yoshiki Takamatsu, Ryoko Wada, Masayo Fujita, Gilbert Ho, Eliezer Masliah, and Makoto Hashimoto. 2021. "Therapeutic Potential of αS Evolvability for Neuropathic Gaucher Disease" Biomolecules 11, no. 2: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020289
APA StyleWei, J., Takamatsu, Y., Wada, R., Fujita, M., Ho, G., Masliah, E., & Hashimoto, M. (2021). Therapeutic Potential of αS Evolvability for Neuropathic Gaucher Disease. Biomolecules, 11(2), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020289