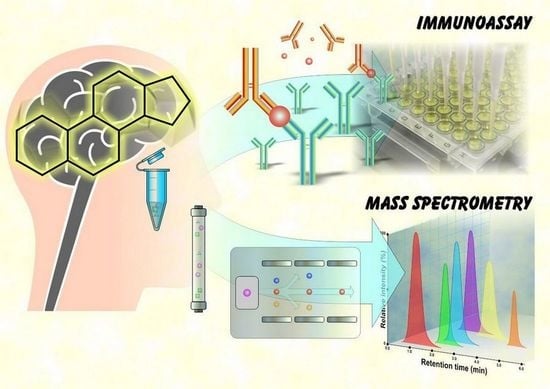
Analytical Methods for the Determination of Neuroactive Steroids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Determination of Neuroactive Steroids
2.1. Types of Biological Matrices
2.2. Factors Affecting Steroid Hormone Levels
3. Analysis of Neuroactive Steroids by Immunoassays
3.1. History of Immunoassays
3.2. Preparation of Antibodies
3.3. Enzyme and Direct Immunoassay
3.4. Antibody Specificity
3.5. High-Dose Hook Effect
3.6. Positives of Immunoassays
3.7. Limitations of Immunoassays
4. Analysis of Neuroactive Steroids by Mass Spectrometry
4.1. Internal Standards
4.2. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
4.2.1. Introduction and History of GC–MS
4.2.2. Gas Chromatography
4.2.3. GC–MS Sample Preparation: Hydrolysis and Derivatization
4.2.4. GC–MS Ionization Techniques
4.2.5. GC–MS and Their Applications
4.3. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
4.3.1. Introduction and History of LC–MS
4.3.2. Liquid Chromatography
4.3.3. Ionization Techniques Used in LC–MS
4.3.4. Matrix Effects
4.3.5. Sample Preparation for LC–MS
4.3.6. LC–MS Applications in Steroid Analysis
4.3.7. SFC–MS Applications in Steroid Analysis
4.3.8. Ion Mobility
4.4. Metabolomics, Targeted and Untargeted Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.5. Validation of Bioanalytical Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melcangi, R.C.; Giatti, S.; Garcia-Segura, L.M. Levels and actions of neuroactive steroids in the nervous system under physiological and pathological conditions: Sex-specific features. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 67, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giatti, S.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Barreto, G.E.; Melcangi, R.C. Neuroactive steroids, neurosteroidogenesis and sex. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 176, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, R.F.; Jevalikar, G.; Hewitt, J.K.; Zacharin, M.R. A guide to understanding the steroid pathway: New insights and diagnostic implications. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belvederi Murri, M.; Fanelli, F.; Pagotto, U.; Bonora, E.; Triolo, F.; Chiri, L.; Allegri, F.; Mezzullo, M.; Menchetti, M.; Mondelli, V.; et al. Neuroactive steroids in first-episode psychosis: A role for progesterone? Schizophr. Res. Treat. 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melcangi, R.C.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Mensah-Nyagan, A.G. Neuroactive steroids: State of the art and new perspectives. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 777–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baulieu, E.-E. Steroid hormones in the brain: Several mechanisms? In Steroid Hormone Regulation of the Brain; Pergamon, Press: Oxford, UK, 1981; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tuem, K.B.; Atey, T.M. Neuroactive steroids: Receptor interactions and responses. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M. Neurosteroids and GABA-A Receptor function. Front. Endocrinol. 2011, 2, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, D.S. Neurosteroids: Endogenous role in the human brain and therapeutic potentials. Prog. Brain Res. 2010, 186, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.P.; Soldin, O.P.; Guo, T.; Soldin, S.J. Steroid hormones: Relevance and measurement in the clinical laboratory. Clin. Lab. Med. 2004, 24, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, P. Neuroactive steroid regulation of neurotransmitter release in the CNS: Action, mechanism and possible significance. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 89, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, D.; Melis, M.; Fenu, G.; Giatti, S.; Romano, S.; Grimoldi, M.; Crippa, D.; Marrosu, M.G.; Cavaletti, G.; Melcangi, R.C. Neuroactive steroid levels in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of male multiple sclerosis patients. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.L.; Marrian, G.F. The application of the Kober test to the quantitative estimation of oestrone and oestriol in human pregnancy urine. Biochem. J. 1934, 28, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, H.; Bates, R.W. A simple quantitative colorimetric method for estrogenic steroids. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1947, 7, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, G.; Wheeler, G.; Young, G.; Zahl, P.A. The colorimetric determination of urinary estrin. J. Biol. Chem. 1936, 116, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auchus, R.J. Steroid assays and endocrinology: Best practices for basic scientists. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 2049–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handelsman, D.J. Mass spectrometry, immunoassay and valid steroid measurements in reproductive medicine and science. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 32, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wudy, S.A.; Schuler, G.; Sánchez-Guijo, A.; Hartmann, M.F. The art of measuring steroids: Principles and practice of current hormonal steroid analysis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 179, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conklin, S.E.; Knezevic, C.E. Advancements in the gold standard: Measuring steroid sex hormones by mass spectrometry. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 82, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröschl, M. Current status of salivary hormone analysis. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.S.; Li, S.; Kellermann, G. Simultaneous determination of three estrogens in human saliva without derivatization or liquid-liquid extraction for routine testing via miniaturized solid phase extraction with LC-MS/MS detection. Talanta 2018, 178, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, E.; Persi, G.; González, N.; Tumilasci, O.; Arregger, A.; Burgos, M.; Rodríguez, V.; Molina, A.; Contreras, L.N. Assessment of adrenal function by measurement of salivary steroids in response to corticotrophin in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Steroids 2007, 72, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P. Salivary steroid assays-research or routine? Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keevil, B.G.; Clifton, S.; Tanton, C.; Macdowall, W.; Copas, A.J.; Lee, D.; Field, N.; Mitchell, K.R.; Sonnenberg, P.; Bancroft, J.; et al. Distribution of salivary testosterone in men and women in a british general population-based sample: The third national survey of sexual attitudes and lifestyles (Natsal-3). J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prokai-Tatrai, K.; Bonds, D.; Prokai, L. Simultaneous measurement of 17β-estradiol, 17α-estradiol and estrone by GC–isotope dilution MS–MS. Chromatographia 2010, 71, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noppe, G.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Dorst, K.; van den Akker, E.L.T.; van Rossum, E.F.C. LC-MS/MS-based method for long-term steroid profiling in human scalp hair. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 83, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafigullina, Z.R.; Velikanova, L.I.; Vorokhobina, N.V.; Shustov, S.B.; Lisitsin, A.A.; Malevanaia, E.V.; Buinova, M.O.; Bessonova, E.A.; Kirsanov, D.O. Urinary steroid profiling by gas chromatography mass spectrometry: Early features of malignancy in patients with adrenal incidentalomas. Steroids 2018, 135, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voegel, C.D.; La Marca-Ghaemmaghami, P.; Ehlert, U.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Kraemer, T.; Binz, T.M. Steroid profiling in nails using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Steroids 2018, 140, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naldi, A.C.; Fayad, P.B.; Prévost, M.; Sauvé, S. Analysis of steroid hormones and their conjugated forms in water and urine by on-line solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Chem. Cent. J. 2016, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wozniak, B.; Matraszek-Zuchowska, I.; Zmudzki, J. LC-MS/MS fast analysis of androgenic steroids in urine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2965–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borts, D.J.; Bowers, L.D. Direct measurement of urinary testosterone and epitestosterone conjugates using high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 35, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosvorova, L.; Vitku, J.; Chlupacova, T.; Mohapl, M.; Hampl, R. Determination of seven selected neuro- and immunomodulatory steroids in human cerebrospinal fluid and plasma using LC-MS/MS. Steroids 2015, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krone, N.; Hughes, B.A.; Lavery, G.G.; Stewart, P.M.; Arlt, W.; Shackleton, C.H.L. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) remains a pre-eminent discovery tool in clinical steroid investigations even in the era of fast liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teubel, J.; Parr, M.K. Determination of neurosteroids in human cerebrospinal fluid in the 21st century: A review. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 204, 105753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.; Plank, E.; Jungwirth, B.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Podtschaske, A.; Kagerbauer, S.M. Weak correlations between serum and cerebrospinal fluid levels of estradiol, progesterone and testosterone in males. BMC Neurosci. 2019, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Li, L.; Gatson, J.W.; Maass, D.; Wigginton, J.G.; Simpkins, J.W.; Schug, K.A. Simultaneous quantification of four native estrogen hormones at trace levels in human cerebrospinal fluid using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, T.P.; Stolze, B.; Ozarda, Y.; Jonklaas, J.; Welsh, K.; Masika, L.; Hill, M.; DeCherney, A.; Soldin, S.J. Diurnal variation of steroid hormones and their reference intervals using mass spectrometric analysis. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stolze, B.R.; Gounden, V.; Gu, J.; Abel, B.S.; Merke, D.P.; Skarulis, M.C.; Soldin, S.J. Use of Micro-HPLC-MS/MS Method to Assess Diurnal Effects on Steroid Hormones. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyce, M.J.; Baisley, K.J.; Clark, E.V.; Warrington, S.J. Are published normal ranges of serum testosterone too high? Results of a cross-sectional survey of serum testosterone and luteinizing hormone in healthy men. BJU Int. 2004, 94, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, W.; Auchus, R.J.; Azziz, R.; Sluss, P.M.; Raff, H. Utility, Limitations, and pitfalls in measuring testosterone: An endocrine society position statement. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalow, R.S.; Berson, S.A. Assay of plasma insulin in human subjects by immunological methods. Nature 1959, 184, 1648–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, S. Rosalyn Sussman Yalow (1921–2011). Nature 2011, 474, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalow, R.S. Radioimmunoassay: A probe for the fine structure of biologic systems. Science 1978, 200, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, G.E. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of estradiol-17β. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1969, 29, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendjabil, M.; Chellouai, Z.; Abbou, O. Role of mass spectrometry in steroid assays. Ann. Endocrinol. 2016, 77, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, L.; Lei, H.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, Z. Antibody production and application for immunoassay development of environmental hormones: A review. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lequin, R.M. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Karu, K.; Griffiths, W.J. Analysis of neurosterols and neurosteroids by mass spectrometry. Biochimie 2007, 89, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratty, G. Immune hemolytic anemia associated with drug therapy. Blood Rev. 2010, 24, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelsman, D.J.; Wartofsky, L. Requirement for mass spectrometry sex steroid assays in the journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 3971–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, A.E.; Keevil, B.; Huhtaniemi, I.T. Mass spectrometry and immunoassay: How to measure steroid hormones today and tomorrow. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, D1–D12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berzofsky, J.A.; Berkower, I.J.; Epstein, S.L. Antigen–antibody interactions and monoclonal antibodies. In Fundamental Immunology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 152–191. ISBN 978-0-7817-6519-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Stalder, T.; Kirschbaum, C. Quantitative analysis of estradiol and six other steroid hormones in human saliva using a high throughput liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry assay. Talanta 2015, 143, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowski, M.D.; Drees, D.; Morris, C.S.; Maakestad, J.; Blau, J.L.; Ekins, S. Cross-reactivity of steroid hormone immunoassays: Clinical significance and two-dimensional molecular similarity prediction. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2014, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Middle, J.G. Dehydroepiandrostenedione sulphate interferes in many direct immunoassays for testosterone. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 44, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, M.H.; Kane, J.W.; Atkin, S.L.; Kilpatrick, E.S. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate interferes with the Abbott Architect direct immunoassay for testosterone. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 43, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, F.; Cremades, A.; Monserrat, F.; Peñafiel, R. Interference of the antihormone RU486 in the determination of testosterone and estradiol by enzyme-immunoassay. Clin. Chim. Acta 1998, 275, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoofnagle, A.N.; Wener, M.H. The fundamental flaws of immunoassays and potential solutions using tandem mass spectrometry. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 347, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akın, L.; Kurtoglu, S.; Kendirci, M.; Akın, M.A.; Hartmann, M.F.; Wudy, S.A. Hook Effect: A pitfall leading to misdiagnosis of hypoaldosteronism in an infant with pseudohypoaldosteronism. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2010, 74, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güran, T.; Yeşil, G.; Güran, Ö.; Cesur, S.; Bosnalı, O.; Celayir, A.; Topçuoğlu, S.; Bereket, A. A giant ovarian cyst in a neonate with classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency with very high testosterone levels demonstrating a high-dose hook effect. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2012, 4, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak, M.; Ellidağ, H.Y.; Türkkahraman, D. High-dose hook effect in 17-hydroxyprogesterone assay in a patient with 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2015, 7, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtaniemi, I.T.; Tajar, A.; Lee, D.M.; O’Neill, T.W.; Finn, J.D.; Bartfai, G.; Boonen, S.; Casanueva, F.F.; Giwercman, A.; Han, T.S.; et al. Comparison of serum testosterone and estradiol measurements in 3174 European men using platform immunoassay and mass spectrometry; relevance for the diagnostics in aging men. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faupel-Badger, J.M.; Fuhrman, B.J.; Xu, X.; Falk, R.T.; Keefer, L.K.; Veenstra, T.D.; Hoover, R.N.; Ziegler, R.G. Comparison of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, RIA, and ELISA methods for measurement of urinary estrogens. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanczyk, F.Z.; Cho, M.M.; Endres, D.B.; Morrison, J.L.; Patel, S.; Paulson, R.J. Limitations of direct estradiol and testosterone immunoassay kits. Steroids 2003, 68, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.G.; Matthew, S.; Auchus, R.J. steroid profiling by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and high performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry for adrenal diseases. Horm. Cancer 2011, 2, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, M.E.; Vandenput, L.; Tivesten, Å.; Norlén, A.-K.; Lagerquist, M.K.; Windahl, S.H.; Börjesson, A.E.; Farman, H.H.; Poutanen, M.; Benrick, A.; et al. Measurement of a comprehensive sex steroid profile in rodent serum by high-sensitive gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taieb, J.; Mathian, B.; Millot, F.; Patricot, M.C.; Mathieu, E.; Queyrel, N.; Lacroix, I.; Somma-Delpero, C.; Boudou, P. Testosterone measured by 10 immunoassays and by isotope-dilution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in sera from 116 men, women, and children. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picó, Y. Chromatography–mass spectrometry: Recent evolution and current trends in environmental science. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 18, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokvis, E.; Rosing, H.; Beijnen, J.H. Stable isotopically labeled internal standards in quantitative bioanalysis using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry: Necessity or not? Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.R. Stable labeled isotopes as internal standards: A critical review. Mod. Appl. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.M.; Ghassabian, S. Linearity of calibration curves for analytical methods: A review of criteria for assessment of method reliability. In Calibration and Validation of Analytical Methods-A Sampling of Current Approaches; InTech Open: London, UK, 2018; pp. 109–127. [Google Scholar]
- Khodadadi, M.; Pourfarzam, M. A review of strategies for untargeted urinary metabolomic analysis using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuoka, S.M.; Yasumoto, A.; Kita, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Yatomi, Y.; Oda, Y. Limitations of deuterium-labeled internal standards for quantitative electrospray ionization mass spectrometry analysis of fatty acid metabolites. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieling, J. LC-MS-MS experiences with internal standards. Chromatographia 2002, 55, S107–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VandenHeuvel, W.J.A.; Horning, E.C. Gas chromatography of adrenal cortical steroid hormones. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1960, 3, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eneroth, P.; Hellstroem, K.; Ryhage, R. Identification and quantification of neutral fecal steroids by gas-liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry: Studies of human excretion during two dietary regimens. J. Lipid Res. 1964, 5, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, O. Separation techniques: Chromatography. N. Clin. Istanb. 2016, 3, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Bukhaiti, W.Q.; Noman, A.; Qasim, A.S.; Al-Farga, A. Gas chromatography: Principles, advantages and applications in food analysis. Int. J. Agric. Innov. Res. 2017, 6, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Makin, H.L.J.; Honour, J.W.; Shackleton, C.H.L.; Griffiths, W.J. General methods for the extraction, purification, and measurement of steroids by chromatography and mass spectrometry. In Steroid Analysis; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 163–282. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, B.; David, F.; Sandra, P. Capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: Current trends and perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.J.; Pinu, F.R.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Poojary, M.M.; Narayana, V.K.; Boughton, B.A.; Kanojia, K.; Dayalan, S.; Jones, O.A.H.; Dias, D.A. Review of recent developments in GC–MS approaches to metabolomics-based research. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, C.S.; David, V. Derivatization methods in GC and GC/MS. In Gas Chromatography-Derivatization, Sample Preparation, Application; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Volume I, pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Poojary, M.M.; Passamonti, P. Improved conventional and microwave-assisted silylation protocols for simultaneous gas chromatographic determination of tocopherols and sterols: Method development and multi-response optimization. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1476, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dury, A.Y.; Ke, Y.; Gonthier, R.; Isabelle, M.; Simard, J.; Labrie, F. Validated LC–MS/MS simultaneous assay of five sex steroid/neurosteroid-related sulfates in human serum. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 149, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Guijo, A.; Oji, V.; Hartmann, M.F.; Traupe, H.; Wudy, S.A. Simultaneous quantification of cholesterol sulfate, androgen sulfates, and progestagen sulfates in human serum by LC-MS/MS. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsugawa, H.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Arita, M.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E. GC/MS based metabolomics: Development of a data mining system for metabolite identification by using soft independent modeling of class analogy (SIMCA). BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry: Combined targeted and untargeted profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanceva, R.; Stárka, L.; Kancheva, L.; Hill, M.; Veliková, M.; Havrdová, E. Increased serum levels of C21 steroids in female patients with multiple sclerosis. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, S247–S254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancheva, R.; Hill, M.; Novák, Z.; Chrastina, J.; Velíková, M.; Kancheva, L.; Říha, I.; Stárka, L. Peripheral neuroactive steroids may be as good as the steroids in the cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnostics of CNS disturbances. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 119, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polet, M.; Van Gansbeke, W.; Van Eenoo, P.; Deventer, K. Gas chromatography/chemical ionization triple quadrupole mass spectrometry analysis of anabolic steroids: Ionization and collision-induced dissociation behavior. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Jacobsen, N.W.; Nielsen, F.K.; Björklund, E.; Styrishave, B.; Halling-Sørensen, B. Determination of steroid hormones in blood by GC–MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3409–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysik, S.; Schmitz, G. Determination of steroid hormones in human plasma by GC–triple quadrupole MS. Steroids 2015, 99, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakoudi, S.; Cowan, D.A.; Taylor, N.F. Steroids excreted in urine by neonates with 21-hydroxylase deficiency: Characterization, using GC–MS and GC–MS/MS, of the D-ring and side chain structure of pregnanes and pregnenes. Steroids 2010, 75, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.; Pařízek, A.; Kancheva, R.; Dušková, M.M.; Velíková, M.; Kříž, L.; Klímková, M.; Pašková, A.; Žižka, Z.; Matucha, P.; et al. Steroid metabolome in plasma from the umbilical artery, umbilical vein, maternal cubital vein and in amniotic fluid in normal and preterm labor. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 594–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.; Hána, V.; Velíková, M.; Pařízek, A.; Kolátorová, L.; Vítků, J.; Škodová, T.; Šimková, M.; Šimják, P.; Kancheva, R.; et al. A method for determination of one hundred endogenous steroids in human serum by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, 179–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, C. Clinical steroid mass spectrometry: A 45-year history culminating in HPLC–MS/MS becoming an essential tool for patient diagnosis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackleton, C. Genetic disorders of steroid metabolism diagnosed by mass spectrometry. In Laboratory Guide to the Methods in Biochemical Genetics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 549–605. ISBN 9783540766971. [Google Scholar]
- Storbeck, K.H.; Gilligan, L.; Jenkinson, C.; Baranowski, E.S.; Quanson, J.L.; Arlt, W.; Taylor, A.E. The utility of ultra-high performance supercritical fluid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UHPSFC-MS/MS) for clinically relevant steroid analysis. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1085, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilařová, V.; Plachká, K.; Khalikova, M.A.; Svec, F.; Nováková, L. Recent developments in supercritical fluid chromatography–mass spectrometry: Is it a viable option for analysis of complex samples? TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kock, N.; Acharya, S.R.; Ubhayasekera, S.J.K.A.; Bergquist, J. A novel targeted analysis of peripheral steroids by ultra-performance supercritical fluid chromatography hyphenated to tandem mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verplaetse, R.; Tytgat, J. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry in forensic toxicology: What about matrix effects? TIAFT Bull. 2011, 41, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Keevil, B.G. Novel liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) methods for measuring steroids. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 27, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J. Matrix effects: The Achilles heel of quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray–tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachniuk, A.; Fornal, E. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in the analysis of pesticide residues in food. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1654–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.G. Matrix effects and application of matrix effect factor. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antignac, J.-P.; de Wasch, K.; Monteau, F.; De Brabander, H.; Andre, F.; Le Bizec, B. The ion suppression phenomenon in liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and its consequences in the field of residue analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 529, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooding, K.M.; Auchus, R.J. Mass spectrometry theory and application to adrenal diseases. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 371, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Márta, Z.; Bobály, B.; Fekete, J.; Magda, B.; Imre, T.; Mészáros, K.V.; Bálint, M.; Szabó, P.T. Simultaneous determination of thirteen different steroid hormones using micro UHPLC-MS/MS with on-line SPE system. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 150, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Yin, W.; Chen, J.; Leng, T.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, P.; Yang, X.; et al. Simultaneous determination of seven neuroactive steroids associated with depression in rat plasma and brain by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuomola, M.; Hakala, M.; Manninen, P. Determination of androstenone in pig fat using packed column supercritical fluid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1998, 719, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Roman, J.M.; Veenstra, T.D.; Van Anda, J.; Ziegler, R.G.; Issaq, H.J. Analysis of fifteen estrogen metabolites using packed column supercritical fluid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doué, M.; Dervilly-Pinel, G.; Pouponneau, K.; Monteau, F.; Le Bizec, B. Analysis of glucuronide and sulfate steroids in urine by ultra-high-performance supercritical-fluid chromatography hyphenated tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 4473–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teubel, J.; Wüst, B.; Schipke, C.G.; Peters, O.; Parr, M.K. Methods in endogenous steroid profiling–A comparison of gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC–MS) with supercritical fluid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (SFC-MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1554, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, L.; Desfontaine, V.; Ponzetto, F.; Nicoli, R.; Saugy, M.; Veuthey, J.L.; Guillarme, D. Fast and sensitive supercritical fluid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry multi-class screening method for the determination of doping agents in urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 915, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rister, A.L.; Dodds, E.D. Liquid chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry analysis of multiple classes of steroid hormone isomers in a mixture. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1137, 121941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, C.D.; Beekman, C.R.; Kemperman, R.H.J.; King, H.M.; Yost, R.A. Ion mobility-mass spectrometry separation of steroid structural isomers and epimers. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 2017, 20, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rister, A.L.; Dodds, E.D. Steroid analysis by ion mobility spectrometry. Steroids 2020, 153, 108531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.A.; Kushnir, M.M.; Yost, R.A.; Rockwood, A.L.; Wayne Meikle, A. Performance enhancement in the measurement of 5 endogenous steroids by LC–MS/MS combined with differential ion mobility spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 438, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Hinzman, A.A.; Kang, E.L.; Szczesniak, R.D.; Lu, L.J. Computational and statistical analysis of metabolomics data. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1492–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Bailey, N.J.C.; Johnson, H.E. Measuring the metabolome: Current analytical technologies. Analyst 2005, 130, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesti, E.; Boccard, J.; Visconti, G.; González-Ruiz, V.; Rudaz, S. From a single steroid to the steroidome: Trends and analytical challenges. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athimulam, S.; Grebe, S.; Bancos, I. Steroid profiling in the diagnosis of mild and overt Cushing’s syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 101488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Qin, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Pan, B.; et al. A liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)-based assay to profile 20 plasma steroids in endocrine disorders. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Li, N.N.; Cai, H.L. Candidate metabolic biomarkers for schizophrenia in CNS and periphery: Do any possible associations exist? Schizophr. Res. 2020, 226, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicikova, M.; Hill, M.; Ripova, D.; Mohr, P.; Hampl, R. Determination of steroid metabolome as a possible tool for laboratory diagnosis of schizophrenia. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 133, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dušková, M.; Hill, M.; Bičíková, M.; Šrámková, M.; Řípová, D.; Mohr, P.; Stárka, L. The steroid metabolome in men with mood and anxiety disorders. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, S275–S282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humer, E.; Pieh, C.; Probst, T. Metabolomic biomarkers in anxiety disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, A.; Botrè, F.; de la Torre, X.; Zamboni, N. Non-targeted LC-MS based metabolomics analysis of the urinary steroidal profile. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 964, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharp, S.; Mitchell, S.J.; Vallée, M.; Kuzmanova, E.; Cooper, M.; Belelli, D.; Lambert, J.J.; Huang, J.T.J. Isotope dilution-based targeted and nontargeted carbonyl neurosteroid/steroid profiling. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5247–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeanneret, F.; Tonoli, D.; Rossier, M.F.; Saugy, M.; Boccard, J.; Rudaz, S. Evaluation of steroidomics by liquid chromatography hyphenated to mass spectrometry as a powerful analytical strategy for measuring human steroid perturbations. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1430, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, C.; Pozo, O.J.; Marcos, J. GC/MS in recent years has defined the normal and clinically disordered steroidome: Will it soon be surpassed by LC/Tandem MS in this role? J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 2, 974–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation; European Medicines Agency: Parma, Italy, 2012; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration. Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]



| Analytical Method | Sample Type | Class of Analytes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| IA | saliva, serum | glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids | [22] |
| serum, CSF | androgens, progestins, estrogens | [35] | |
| serum | androgens | [39] | |
| plasma | estrogens | [44] | |
| plasma, serum | androgens, progestins, estrogens, glucocorticoids | [54] | |
| serum | androgens | [55] | |
| serum | androgens | [56] | |
| plasma | androgens, estrogens | [57] | |
| serum | androgens, estrogens | [62] | |
| urine | estrogens | [63] | |
| serum | androgens, estrogens | [64] | |
| serum | androgens | [67] | |
| serum, CSF | progestins, glucocorticoids | [89] | |
| plasma | progestins, estrogens, glucocorticoids | [126] | |
| GC–MS(/MS) | serum | estrogens | [25] |
| urine | androgens, progestins, glucocorticoids | [27] | |
| serum | androgens, estrogens | [62] | |
| serum | androgens, progestins, estrogens | [66] | |
| serum | androgens | [67] | |
| feces | neutral fecal steroids | [76] | |
| serum | androgens, progestins, estrogens | [88] | |
| serum, CSF | androgens, progestins | [89] | |
| plasma, serum | androgens, progestins, estrogens | [91] | |
| plasma | androgens, progestins | [92] | |
| plasma | androgens, progestins, estrogens | [94] | |
| serum | androgens, progestins, estrogens, glucocorticoids | [95] | |
| serum | androgens, progestins, glucocorticoids | [125] | |
| plasma | androgens, progestins, estrogens | [126] | |
| LC–MS(/MS) | serum | androgens, progestins, glucocorticoids | [4] |
| plasma, CSF | androgens, progestins, estrogens | [12] | |
| saliva | estrogens | [21] | |
| saliva | androgens | [24] | |
| scalp hair | androgens, progestins, glucocorticoids | [26] | |
| finger nails | androgens, progestins, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids | [28] | |
| water matrices, urine | estrogens | [29] | |
| urine | androgens | [30] | |
| urine | androgens | [31] | |
| plasma, CSF | androgens, glucocorticoids | [32] | |
| CSF | estrogens | [36] | |
| serum | androgens, progestins, glucocorticoids | [37] | |
| plasma | androgens, progestins, glucocorticoids | [38] | |
| saliva | androgens, progestins, estrogens, glucocorticoids | [53] | |
| urine | estrogens | [63] | |
| serum | androgens, progestins, estrogens | [84] | |
| serum | progestins, androgens | [85] | |
| serum | androgens, progestins, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids | [108] | |
| plasma, brain tissue | androgens, progestins, estrogens, glucocorticoids | [109] | |
| plasma | androgens, progestins, estrogens, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids | [123] | |
| urine | >3000 individual metabolic features | [128] | |
| brain tissue | carbonyl steroids | [129] | |
| SFC–MS(/MS) | plasma | androgens, progestins, estrogens, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids | [100] |
| fat | androgens | [110] | |
| urine, serum | estrogens | [111] | |
| urine | androgens, estrogens | [112] | |
| CSF | androgens, progestins, estrogens, glucocorticoids | [113] | |
| urine | androgens | [114] | |
| (LC–)IMS–MS(/MS) | standard solutions | androgens, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids | [115] |
| standard solutions | androgens, progestins, estrogens, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids | [116] | |
| serum, plasma | progestins, glucocorticoids | [118] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaleta, M.; Oklestkova, J.; Novák, O.; Strnad, M. Analytical Methods for the Determination of Neuroactive Steroids. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040553
Kaleta M, Oklestkova J, Novák O, Strnad M. Analytical Methods for the Determination of Neuroactive Steroids. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(4):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040553
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaleta, Michal, Jana Oklestkova, Ondřej Novák, and Miroslav Strnad. 2021. "Analytical Methods for the Determination of Neuroactive Steroids" Biomolecules 11, no. 4: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040553
APA StyleKaleta, M., Oklestkova, J., Novák, O., & Strnad, M. (2021). Analytical Methods for the Determination of Neuroactive Steroids. Biomolecules, 11(4), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040553