Cloning and Characterization of Aedes aegypti Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor (TMOF) Gut Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects, Bacterial Strains, and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Gut Membrane Proteins
2.3. Cross Linking of TMOF to Its Soluble Gut Receptor
2.4. Cloning and Sequencing of AeaABC-TMOF Gut Receptor cDNA
2.5. Synthesis of AeaABC-TMOF Receptor dsRNA
2.6. Feeding Female Ae. aegypti with dsRNA
2.7. Molecular Modeling of AeaABC-TMOF Receptor
2.8. Cloning and Expression of AeaABC-TMOF Receptor
2.9. AeaABC-TMOF Receptor Binding Assay and Kinetics
2.10. Transport of AeaTMOF-FITC into E. coli Cells Expressing AeaABC-TMOF Receptor in the Presence of Inhibitors
2.11. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Purification and Identification of AeaABC-TMOF Receptor
3.2. Sequencing and Characterization of AeaABC-TMOF Receptor cDNA
3.3. Effect of AeaABC-TMOF Receptor dsRNA on Trypsin Activity in the Gut
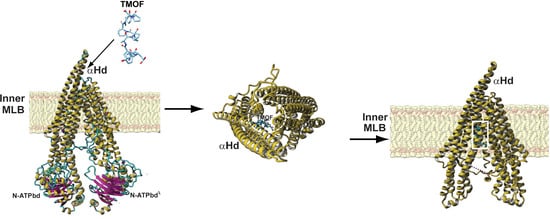
3.4. Three-Dimensional Structure Analysis
3.5. Binding Kinetics of TMOF to AeaABC-TMOF Receptor
3.6. TMOF Transport into E. coli Cells Expressing ABC-TMOF Receptor Is ATP Driven
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iwanov, P.P.; Mescherskaya, K.A. Die physiologischen Besonderheiten der geschlechtlich unreifen Insektenovarien und die zyklischen Veränderungen ihrer Eigenschaften. Zool. Jb. Physiol. 1935, 55, 281–348. [Google Scholar]
- Carlisle, D.B.; Knowles, F. Endocrine control in crustaceans. Camb. Monogr. Exp. Biol. 1959, 10, 10–120. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, T.S.; Hintz, A.M.; Pomonis, J.G. Oostatic hormone production in houseflies, Musca domestica, with developing ovaries. J. Insect Physiol. 1968, 14, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.J.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Woods, C.W.; Borkovec, A.B. Effects of housefly oostatic hormone on egg development neurosecretory hormone action in Aedes atropalpus. J. Exp. Zool. 1984, 229, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meola, R.; Lea, A.O. Humoral inhibition of egg development in mosquitoes. J. Med. Entomol. 1972, 9, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Else, J.G.; Judson, C.L. Enforced egg-retention and its effect on vitellogenesis in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. J. Med. Entomol. 1972, 9, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.P.; Davey, K.G. Partial characterization of a proposed antigonadotropin from the ovaries of the insect Rhodnius prolixus Stal. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1974, 24, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, K.G. Hormonal stimulation and inhibition in the ovary of an insect, Rhodnius prolixus. In Comparative Endocrinology; Gaillard, P.J., Boer, H.H., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Davey, K.G.; Kunster, J.E. The source of an antigonadotropin in the female of Rhodnius prolixus Stal. Can. J. Zool. 1981, 59, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.S. The role of ovarian hormone in maintaining cyclical egg production in insects. In Advances in Invertebrate Reproduction; Clark, W.H., Jr., Adams, T.S., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Borovsky, D. Oostatic hormone inhibits biosynthesis of midgut proteolytic enzymes and egg development in mosquitoes. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1988, 7, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovsky, D.; Carlson, D.A.; Griffin, P.R.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F. Mosquito oostatic factor a novel decapeptide modulating trypsin-like enzyme biosynthesis in the midgut. FASEB J. 1990, 4, 3015–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hamblin, M.T.; Edwards, M.J.; Barillas-Mury, C.; Kanost, M.R.; Knipple, D.C.; Wolfner, M.F.; Hagedorn, H.H. Structure, expression, and hormonal control of genes from the mosquito, Aedes aegypti, which encode proteins similar to the vitelline membrane proteins of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev. Biol. 1993, 155, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Loof, A.; Bylemans, D.; Schoofs, L.; Janssen, I.; Spittaels, K.; Vanden Broeck, J.; Huybrechts, R.; Borovsky, D.; Hua, Y.; Koolman, J.; et al. Folliculostatins, gonadotropins and a model for control of growth in the grey fleshfly, Neobellieria (Sarcophaga) bullata. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 25, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Baggerman, G.; D’Hertog, W.; Verleyen, P.; Schoof, L.; Wets, G. In silico identification of new secretory peptide genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2006, 5, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borovsky, D.; Nauen, R. Biological and biochemical effects of organo-synthetic analogues of Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor (TMOF) on Aedes aegypti, Heliothis virescens and Plutella xylostella. Pestycyde/Pesticides 2007, 3–4, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Borovsky, D.; Carlson, D.A.; Hunt, D.F. Mosquito oostatic hormone a trypsin modulating oostatic factor. In Insect Neuropeptides Chemistry, Biology and Action; Menn, J.J., Kelly, T.J., Masler, E.P., Eds.; ACS Symposium Series; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; Volume 453, pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Borovsky, D.; Carlson, D.A.; Griffin, P.R.; Shabanowiz, J.; Hunt, D.F. Sequence analysis, synthesis and characterization of Aedes aegypti trypsin modulating oostatic factor (TMOF) and its analogs. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1993, 23, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovsky, D.; Meola, S.M. Biochemical and cytoimmunological evidence for the control of Aedes aegypti larval trypsin with Aea-TMOF. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2004, 55, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curto, E.V.; Jarpe, M.A.; Blalock, J.B.; Borovsky, D.; Krishna, N.R. Solution structure of trypsin modulating oostatic factor is a left-handed helix. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 193, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovsky, D.; Song, Q.; Ma, M.; Carlson, D.A. Biosynthesis, secretion and cytoimmunochemistry of trypsin modulating oostatic factor of Aedes aegypti. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1994, 27, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovsky, D.; Janssen, I.; Vanden Broeck, J.; Huybrechts, R.; Verhaert, P.; DeBondt, H.L.; Bylemans, D.; DeLoof, A. Molecular sequencing and modeling of Neobellieria bullata trypsin: Evidence for translational control with Neb TMOF. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 237, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovsky, D.; Rabindran, S.; Dawson, W.O.; Powell, C.R.; Iannotti, D.; Morris, T.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F.; De Bondt, H.L.; De Loof, A. Expression of Aedes TMOF on the virion of TMV: Potential larvicide. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18963–18968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borovsky, D. Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor (TMOF) and insect biotechnology. In Insect Molecular Biology and Ecology; Hoffmann, K.H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2015; Chapter 11; pp. 319–349. [Google Scholar]
- Borovsky, D.; Powell, C.A.; Nayar, J.K.; Blalock, J.E.; Hayes, T.K. Characterization and localization of mosquito-gut receptors for trypsin modulating oostatic factor (TMOF) using a complementary peptide and immunocytochemistry. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbalan, N.; Runti, G.; Adler, C.; Covaceuszach, S.; Ford, R.C.; Lamba, D.; Beis, K.; Scocchi, M.; Vincenta, P.A. Functional and Structural Study of the Dimeric Inner Membrane Protein SbmA. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 5352–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Runti, G.; del Carmen Lopez Ruitz, M.; Stoilova, T.; Hussain, R.; Jennions, M.; Choudhury, H.G.; Benincasa, M.; Gennaro, R.; Beis, K.; Scocchi, M. Functional characterization of SbmA, a bacterial inner membrane transporter required for importing the antimicrobial peptide Bac7(1-35). J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 5343–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkens, F. Structure and mechanism of ABC transporters. F1000Prime Rep. 2015, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Cho, Y.; Burla, B.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Jeon, B.; Maeshima, M.; Yoo, J.-Y.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y. The ABC transporter AtABCB14 is a malate importer and modulates stomatal response to CO2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barany, G.; Merrifield, R.B.; Gross, E. The Peptides; Gross, E., Meienhofer, J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 2, pp. 1–284. [Google Scholar]
- Borovsky, D. Trypsin modulating oostatic factor for developing resistant crops. In Insectidices Design Using Advanced Technologies; Ishaaya, I., Nauen, R., Horowitz, A.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Chapter 6; pp. 135–149. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttemann, M. Partial heat denaturation step during reverse transcription and PCR screening yields full-length 50-cDNAs. Biotechniques 2002, 32, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borovsky, D.; Schlein, Y. Quantitative determination of trypsin like a chymotrypsin like enzymes in insects. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1988, 8, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, E.; Koraimann, G.; Vriend, G. Increasing the precision of comparative models with YASARA NOVA—A self-parameterizing force field. Proteins 2002, 47, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.S.; Oldham, M.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J. Crystal structure of the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein from Cænorhabditis erlegans. Nature 2012, 490, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Jaimes, K.F.; Aller, S.G. Refined structures of mouse P-glycoprotein. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.; Tao, H.; McGrath, A.P.; Villaluz, M.; Rees, S.D.; Lee, S.C.; Doshi, R.; Urbatsch, I.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, G. Snapshots of ligand entry, malleable binding and induced helical movement in P-glycoproytein. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esser, L.; Zhou, F.; Pluchino, K.M.; Shiloach, J.; Ma, J.; Tang, W.K.; Gutierrez, C.; Zhang, A.; Shukla, S.; Madigan, J.P.; et al. Structures of the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein reveal asymmetric ATP binding and the mechanism of polyspecificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemistry of protein structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.; Feytmans, E. Assessing protein structures with a non-local atomic interaction energy. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 277, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkert, P.; Biasini, M.; Schwede, T. Toward the estimation of the absolute quality of individual protein structure models. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis, J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tovchigrechko, A.; Vakser, I.A. Development and testing of an automated approach to protein docking. Proteins 2005, 60, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovchigrechko, A.; Vakser, I.A. GRAMM-X public web server for protein-protein docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W310–W314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajda, S.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Bohnuud, T.; Mottarella, S.E.; Xia, B.; Hall, D.R.; Kozakov, D. New additions to the ClusPro server motivated by CAPRI. Proteins 2017, 85, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozakov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Xia, B.; Porter, K.A.; Padhorny, D.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro web server for protein-protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakov, D.; Beglov, D.; Bohnuud, T.; Mottarella, S.; Xia, B.; Hall, D.R.; Vajda, S. How good is automated protein docking? Proteins 2013, 81, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar]
- Mattiuzzo, M.; Bandlera, A.; Gennaro, R.; Benincasa, M.; Scocchi, M. Role of the Escherichia coli SbmA in the antimicrobial activity of proline-rich peptides. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, P.C.; Kashket, E.R.; Wilson, T.H. Protonmotive force drives ATP synthesis in bacteria. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3896–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, M.; Rzhetsky, A.; Allikmets, R. The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassa, E.; Bouige, P. The ABC of ABCS: A phylogenetic and functional classification of ABC systems in living organisms. Res. Microbiol. 2001, 152, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, I.B.; Cole, S.P.; Kuchler, K.; Higgins, C.F. ABC Proteins—From Bacteria to Man; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; p. 647. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, D.C.; Johnson, E.; Lewinson, O. ABC transporters: The power to change. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, C.F. ABC transporters: From microorganisms to man. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1991, 8, 67–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermauw, W.; Van Leeuwen, T. The ABC gene family in arthropods: Comparative genomics and role in insecticide transport and resistance. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 45, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-López, L.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal three-domain Cry toxins: Mode of action, insect resistance and consequences for crop protection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 37, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C.; Heckel, D.G.; Li, X.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Wu, K. Mis-splicing of the ABCC2 gene linked with Bt toxin resistance in Helicoverpa armigera. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wei, J.Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.N.; Wang, B.J.; Niu, L.L.; Liang, G.M. Specific binding protein ABCC1 Is associated with Cry2Ab toxicity in Helicoverpa armigera. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chakrabarty, S.; Jin, M.; Liu, K.; Xiao, Y. Insect ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) Transporters: Role in Xenobiotic detoxification and Bt insecticidal activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Ekert, E.; Powell, C.A.; Shatters, R.G., Jr.; Borovsky, D. Control of larval and egg development in Aedes aegypti with RNA interference against juvenile hormone acid methyl transferase. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 70, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Sheng, Z.; Sui, Y.; Palli, S.R. Steroid Receptor Co-activator Is Required for Juvenile Hormone Signal Transduction through a bHLH-PAS Transcription Factor, Methoprene Tolerant. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8437–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregoriou, M.-E.; Mathiopoulos, K.D. Knocking down the sex peptide receptor by dsRNA feeding results in reduced oviposition rate in olive fruit flies. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 104, e21665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, K.M.; Boldbaatar, D.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Liao, M.; Xuenan, X.; Suzuki, H.; Galay, R.L.; Tanaka, T.; Fujisaki, K. Scavenger Receptor Mediates Systemic RNA Interference in Ticks. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, R.N.; Lomakin, I.B.; Gagnon, M.G.; Steitz, T.A. The mechanism of inhibition of protein synthesis by the proline-rich peptide oncocin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| Primers | Primer Sequence (5’-3’) | Position (5’-3’) | Amplicon (nt) | tm (C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB 2000 (forward) | ATGACCAAACAAAGACTTTCCTCA | 64 | ||
| DB 2001(reverse) | CAGGTCGTACCAGGTCATATCCTGG | 1–600 | 600 | 69 |
| DB 2002 (forward | AATAAGTAGAATACGGAAGTTGTTC | 60 | ||
| DB 2003 (reverse) | CCAGAATGCAAGCGCGTAGCAACAGT | 534–1010 | 516 | 72 |
| DB 2004 (forward) | GGGAACGTAAGGAGCTCGATAGAT | 66 | ||
| DB 2005 (reverse) | ATTTTTGGATTGCGAACTAACGCTC | 911–1755 | 864 | 66 |
| DB 2006 (forward) | AACTATCGGGAGGTCAGAAACAACG | 67 | ||
| DB 2007 (reverse) | CGATGCTCCTACAACCATGGCT | 1712–2603 | 891 | 68 |
| DB 2008 (forward) | GAATTCTCCTGAATGGCCTTATATTT | 63 | ||
| DB 2009 (reverse) | GGATATTTGAAATGGCTTCAACTGCA | 2199–2800 | 601 | 66 |
| DB 2010 (forward) | CAATAGTAGCCATTCCTATTGTATTGG | 63 | ||
| DB 2011 (reverse) | CCGCAACCTGAAGGCCCTACTAGA | 2669–3315 | 646 | 70 |
| DB 2012 (forward) | ACCCAACGCGACCAACAATTCCAAT | 70 | ||
| DB 2013 (reverse) | TCCAAGGCGGATGTTGCTTCG | 3221–3710 | 489 | 68 |
| DB 2014 (forward) | ACATTGACGGGATCACGACAACTG | 68 | ||
| DB 2015 (reverse) | CTATGCCACTTGTTGCATGGAGTAAA | 3374–3924 | 550 | 67 |
| 3’ End | ||||
| DB 2016 (forward) | GTCCAGAATGCTTTGGACCCAT | 57 | ||
| 3’End (reverse) | CGCGCAGCCTAAG | 3730–3944 | 214 | 60 |
| 5’ RACE: | ||||
| dT17 adapter (forward) | GACTCGAGTCGACATCGA(T)17 | 74 | ||
| DB 2017 (reverse) | TGAAGTACGATACGGGTTGGG | 12–190 | 202 | 57 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borovsky, D.; Deckers, K.; Vanhove, A.C.; Verstraete, M.; Rougé, P.; Shatters, R.G., Jr.; Powell, C.A. Cloning and Characterization of Aedes aegypti Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor (TMOF) Gut Receptor. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11070934
Borovsky D, Deckers K, Vanhove AC, Verstraete M, Rougé P, Shatters RG Jr., Powell CA. Cloning and Characterization of Aedes aegypti Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor (TMOF) Gut Receptor. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(7):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11070934
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorovsky, Dov, Kato Deckers, Anne Catherine Vanhove, Maud Verstraete, Pierre Rougé, Robert G. Shatters, Jr., and Charles A. Powell. 2021. "Cloning and Characterization of Aedes aegypti Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor (TMOF) Gut Receptor" Biomolecules 11, no. 7: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11070934
APA StyleBorovsky, D., Deckers, K., Vanhove, A. C., Verstraete, M., Rougé, P., Shatters, R. G., Jr., & Powell, C. A. (2021). Cloning and Characterization of Aedes aegypti Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor (TMOF) Gut Receptor. Biomolecules, 11(7), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11070934