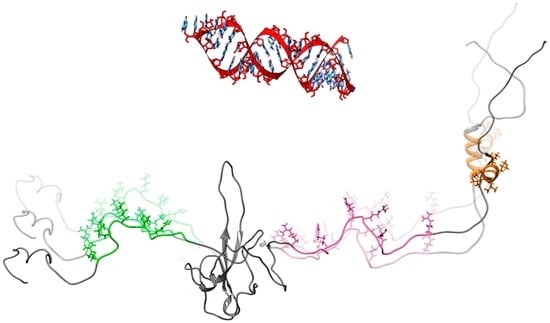
NMR Reveals Specific Tracts within the Intrinsically Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Involved in RNA Encountering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Sample Preparation
2.2. RNA Production
2.3. Spin-Labeling Reaction for PRE Experiments
2.4. Protein NMR Samples
2.5. NMR Experiments
2.6. Protein Visualization
2.7. NMR Spectral Analysis
2.8. Electromobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, C.K.; Hou, M.H.; Chang, C.F.; Hsiao, C.D.; Huang, T.H. The SARS Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein—Forms and Functions. Antivir. Res. 2014, 103, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, R.; Bhardwaj, T.; Shegane, M.; Gehi, B.R.; Kumar, P.; Gadhave, K.; Oldfield, C.J.; Uversky, V.N. Understanding COVID-19 via Comparative Analysis of Dark Proteomes of SARS-CoV-2, Human SARS and Bat SARS-like Coronaviruses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1655–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-K.; Hsu, Y.-L.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chao, F.-A.; Wu, M.-C.; Huang, Y.-S.; Hu, C.-K.; Huang, T.-H. Multiple Nucleic Acid Binding Sites and Intrinsic Disorder of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein: Implications for Ribonucleocapsid Protein Packaging. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rangan, R.; Zheludev, I.N.; Hagey, R.J.; Pham, E.A.; Wayment-Steele, H.K.; Glenn, J.S.; Das, R. RNA Genome Conservation and Secondary Structure in SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-Related Viruses: A First Look. RNA 2020, 26, 937–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacker, A.; Weigand, J.E.; Akabayov, S.R.; Altincekic, N.; Bains, J.K.; Banijamali, E.; Binas, O.; Castillo-Martinez, J.; Cetiner, E.; Ceylan, B.; et al. Secondary Structure Determination of Conserved SARS-CoV-2 RNA Elements by NMR Spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 12415–12435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Cai, Z.; Xiao, X.; Rao, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, N.; Yang, M.; Xing, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; et al. The Architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA Genome inside Virion. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Tavares, R.C.A.; Mahadeshwar, G.; Wan, H.; Huston, N.C.; Pyle, A.M. The Global and Local Distribution of RNA Structure throughout the SARS-CoV-2 Genome. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02190-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J. The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Role in Viral Structure, Biological Functions, and a Potential Target for Drug or Vaccine Mitigation. Viruses 2021, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iserman, C.; Roden, C.A.; Boerneke, M.A.; Sealfon, R.S.G.; McLaughlin, G.A.; Jungreis, I.; Fritch, E.J.; Hou, Y.J.; Ekena, J.; Weidmann, C.A.; et al. Genomic RNA Elements Drive Phase Separation of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 1078–1091.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, D.C.; Chalupska, D.; Silhan, J.; Koutna, E.; Nencka, R.; Veverka, V.; Boura, E. Structural Basis of RNA Recognition by the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Phosphoprotein. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastano, A.; de Opakua, A.I.; Rankovic, M.; Zweckstetter, M. Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Phase Separates into RNA-Rich Polymerase-Containing Condensates. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, H.M.; Rodriguez Galvan, J.; Yu, Z.; Pinckney, S.; Reardon, P.; Cooley, R.B.; Zhu, P.; Rolland, A.D.; Prell, J.S.; Barbar, E. Multivalent Binding of the Partially Disordered SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Phosphoprotein Dimer to RNA. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 2890–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavina, M.; Pontoriero, L.; Uversky, V.N.; Felli, I.C.; Pierattelli, R. The Highly Flexible Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid N Protein within the 1–248 Residue Construct: Sequence-Specific Resonance Assignments through NMR. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2021, 15, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guseva, S.; Perez, L.M.; Camacho-Zarco, A.; Bessa, L.M.; Salvi, N.; Malki, A.; Maurin, D.; Blackledge, M. 1H, 13C and 15N Backbone Chemical Shift Assignments of the N-Terminal and Central Intrinsically Disordered Domains of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2021, 15, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, Í.P.; Sanches, K.; Da Poian, A.T.; Pinheiro, A.S.; Almeida, F.C.L. Dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein N-Terminal Domain Triggers RNA Duplex Destabilization. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 2814–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redzic, J.S.; Lee, E.; Born, A.; Issaian, A.; Henen, M.A.; Nichols, P.J.; Blue, A.; Hansen, K.C.; D’Alessandro, A.; Vögeli, B.; et al. The Inherent Dynamics and Interaction Sites of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid N-Terminal Region. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 167108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, L.M.; Guseva, S.; Camacho-Zarco, A.R.; Salvi, N.; Maurin, D.; Perez, L.M.; Botova, M.; Malki, A.; Nanao, M.; Jensen, M.R.; et al. The Intrinsically Disordered SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein in Dynamic Complex with Its Viral Partner Nsp3a. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felli, I.C.; Pierattelli, R. 13C Direct Detected NMR for Challenging Systems. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 9468–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vögele, J.; Ferner, J.-P.; Altincekic, N.; Bains, J.K.; Ceylan, B.; Fürtig, B.; Grün, J.T.; Hengesbach, M.; Hohmann, K.F.; Hymon, D.; et al. 1H, 13C, 15N and 31P Chemical Shift Assignment for Stem-Loop 4 from the 5′-UTR of SARS-CoV-2. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2021, 15, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeramulu, S.; Richter, C.; Berg, H.; Wirtz Martin, M.A.; Ceylan, B.; Matzel, T.; Adam, J.; Altincekic, N.; Azzaoui, K.; Bains, J.K.; et al. Exploring the Druggability of Conserved RNA Regulatory Elements in the SARS-CoV-2 Genome. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19191–19200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altincekic, N.; Korn, S.M.; Qureshi, N.S.; Dujardin, M.; Ninot-Pedrosa, M.; Abele, R.; Abi Saad, M.J.; Alfano, C.; Almeida, F.C.L.; Alshamleh, I.; et al. Large-Scale Recombinant Production of the SARS-CoV-2 Proteome for High-Throughput and Structural Biology Applications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 653148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marley, J.; Lu, M.; Bracken, C. A Method for Efficient Isotopic Labeling of Recombinant Proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 2001, 20, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A New Coronavirus Associated with Human Respiratory Disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiavina, M.; Murrali, M.G.; Pontoriero, L.; Sainati, V.; Kümmerle, R.; Bermel, W.; Pierattelli, R.; Felli, I.C. Taking Simultaneous Snapshots of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins in Action. Biophys. J. 2019, 117, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermel, W.; Bertini, I.; Csizmok, V.; Felli, I.C.; Pierattelli, R.; Tompa, P. H-Start for Exclusively Heteronuclear NMR Spectroscopy: The Case of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J. Magn. Reson. 2009, 198, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, L.; Bodenhausen, G. Optimization of Shaped Selective Pulses for NMR Using a Quaternion Description of Their Overall Propagators. J. Magn. Reson. 1992, 97, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlen, J.M.; Bodenhausen, G. Experimental Aspects of Chirp NMR Spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. A 1993, 102, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geen, H.; Freeman, R. Band-Selective Radiofrequency Pulses. J. Magn. Reson. 1991, 93, 93–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotto, M.; Saudek, V.; Sklenar, V. Gradient-Tailored Excitation for Single-Quantum NMR Spectroscopy of Aqueous Solutions. J. Biomol. NMR 1992, 2, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felli, I.C.; Pierattelli, R. Spin-State-Selective Methods in Solution- and Solid-State Biomolecular 13C NMR. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2015, 84–85, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Abeygunawardana, C.; Johnson, M.O.; Vanzijl, P.C.M. Improved Sensitivity of HSQC Spectra of Exchanging Protons at Short Interscan Delays Using a New Fast HSQC (FHSQC) Detection Scheme That Avoids Water Saturation. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. B 1995, 108, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A.G.; Cavanagh, J.; Wright, P.E.; Rance, M. Sensitivity Improvement in Proton-Detected Two-Dimensional Heteronuclear Correlation NMR Spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 1991, 93, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera: A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozenne, V.; Bauer, F.; Salmon, L.; Huang, J.R.; Jensen, M.R.; Segard, S.; Bernadó, P.; Charavay, C.; Blackledge, M. Flexible-Meccano: A Tool for the Generation of Explicit Ensemble Descriptions of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Their Associated Experimental Observables. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, J.L.; Bax, A.; Arata, Y.; Hilbers, C.W.; Kaptein, R.; Sykes, B.D.; Wright, P.E.; Wuethrich, K. Recommendations for the Presentation of NMR Structures of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. Pure Appl. Chem. 1998, 70, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R. The Computer Aided Resonance Assignment Tutorial; Cantina Verlag: Goldau, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 1–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bartels, C.; Xia, T.H.; Billeter, M.; Güntert, P.; Wüthrich, K. The Program XEASY for Computer-Supported NMR Spectral Analysis of Biological Macromolecules. J. Biomol. NMR 1995, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, S.P.; Recht, M.I.; Williamson, J.R. Quantitative Analysis of Protein-RNA Interactions by Gel Mobility Shift. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 488, 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Perdikari, T.M.; Murthy, A.C.; Ryan, V.H.; Watters, S.; Naik, M.T.; Fawzi, N.L. SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Phase-separates with RNA and with Human HnRNPs. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e106478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubuk, J.; Alston, J.J.; Incicco, J.J.; Singh, S.; Stuchell-Brereton, M.D.; Ward, M.D.; Zimmerman, M.I.; Vithani, N.; Griffith, D.; Wagoner, J.A.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Is Dynamic, Disordered, and Phase Separates with RNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ye, Q.; Singh, D.; Cao, Y.; Diedrich, J.K.; Yates, J.R.; Villa, E.; Cleveland, D.W.; Corbett, K.D. The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Phosphoprotein Forms Mutually Exclusive Condensates with RNA and the Membrane-Associated M Protein. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompa, P.; Fuxreiter, M. Fuzzy Complexes: Polymorphism and Structural Disorder in Protein-Protein Interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittag, T.; Kay, L.E.; Forman-Kay, J.D. Protein Dynamics and Conformational Disorder in Molecular Recognition. J. Mol. Recognit. 2009, 23, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzbach, D.; Schwarz, T.C.; Platzer, G.; Höfler, S.; Hinderberger, D.; Konrat, R. Compensatory Adaptations of Structural Dynamics in an Intrinsically Disordered Protein Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3840–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habchi, J.; Tompa, P.; Longhi, S.; Uversky, V.N. Introducing Protein Intrinsic Disorder. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6561–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuxreiter, M.; Tóth-Petróczy, Á.; Kraut, D.A.; Matouschek, A.; Matouschek, A.T.; Lim, R.Y.H.; Xue, B.; Kurgan, L.; Uversky, V.N. Disordered Proteinaceous Machines. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6806–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contreras-Martos, S.; Piai, A.; Kosol, S.; Varadi, M.; Bekesi, A.; Lebrun, P.; Volkov, A.N.; Gevaert, K.; Pierattelli, R.; Felli, I.C.; et al. Linking Functions: An Additional Role for an Intrinsically Disordered Linker Domain in the Transcriptional Coactivator CBP. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arbesú, M.; Iruela, G.; Fuentes, H.; Teixeira, J.M.C.; Pons, M. Intramolecular Fuzzy Interactions Involving Intrinsically Disordered Domains. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spreitzer, E.; Usluer, S.; Madl, T. Probing Surfaces in Dynamic Protein Interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 2949–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottini, A.; Borgia, A.; Borgia, M.B.; Bugge, K.; Nettels, D.; Chowdhury, A.; Heidarsson, P.O.; Zosel, F.; Best, R.B.; Kragelund, B.B.; et al. Polyelectrolyte Interactions Enable Rapid Association and Dissociation in High-Affinity Disordered Protein Complexes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrali, M.G.; Felli, I.C.; Pierattelli, R. Adenoviral E1A Exploits Flexibility and Disorder to Target Cellular Proteins. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, M.W.; Lei, M.; Eisenmesser, E.Z.; Labeikovsky, W.; Redfield, A.; Kern, D. Mesodynamics in the SARS Nucleocapsid Measured by NMR Field Cycling. J. Biomol. NMR 2009, 45, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, R.K.; Pappu, R.V. Conformations of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Are Influenced by Linear Sequence Distributions of Oppositely Charged Residues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13392–13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlson, C.R.; Asfaha, J.B.; Ghent, C.M.; Howard, C.J.; Hartooni, N.; Safari, M.; Frankel, A.D.; Morgan, D.O. Phosphoregulation of Phase Separation by the SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Suggests a Biophysical Basis for Its Dual Functions. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 1092–1103.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabretta, S.; Richard, S. Emerging Roles of Disordered Sequences in RNA-Binding Proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järvelin, A.I.; Noerenberg, M.; Davis, I.; Castello, A. The New (Dis)Order in RNA Regulation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popenda, M.; Szachniuk, M.; Antczak, M.; Purzycka, K.J.; Lukasiak, P.; Bartol, N.; Blazewicz, J.; Adamiak, R.W. Automated 3D Structure Composition for Large RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofacker, I.L. Vienna RNA Secondary Structure Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3429–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blom, N.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Gupta, R.; Gammeltoft, S.; Brunak, S. Prediction of Post-Translational Glycosylation and Phosphorylation of Proteins from the Amino Acid Sequence. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1633–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pontoriero, L.; Schiavina, M.; Korn, S.M.; Schlundt, A.; Pierattelli, R.; Felli, I.C. NMR Reveals Specific Tracts within the Intrinsically Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Involved in RNA Encountering. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070929
Pontoriero L, Schiavina M, Korn SM, Schlundt A, Pierattelli R, Felli IC. NMR Reveals Specific Tracts within the Intrinsically Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Involved in RNA Encountering. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(7):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070929
Chicago/Turabian StylePontoriero, Letizia, Marco Schiavina, Sophie M. Korn, Andreas Schlundt, Roberta Pierattelli, and Isabella C. Felli. 2022. "NMR Reveals Specific Tracts within the Intrinsically Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Involved in RNA Encountering" Biomolecules 12, no. 7: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070929
APA StylePontoriero, L., Schiavina, M., Korn, S. M., Schlundt, A., Pierattelli, R., & Felli, I. C. (2022). NMR Reveals Specific Tracts within the Intrinsically Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Involved in RNA Encountering. Biomolecules, 12(7), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070929