Chronic Ethanol Exposure: Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Disease and Dysfunction
Abstract
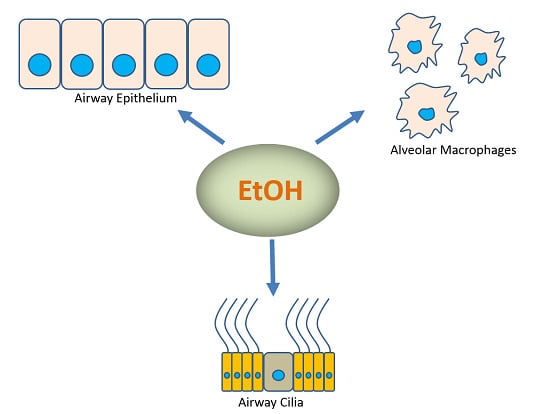
:1. Introduction
2. EtOH Exposure Alters Airway Mucociliary Clearance
2.1. Acute EtOH Exposure Stimulates CBF
2.2. Chronic EtOH Exposure Desensitizes Ciliary Response
3. EtOH Impairs Pulmonary Innate Immune Response
3.1. AMs, NADPH Oxidases and EtOH Exposure
3.2. EtOH Regulates TGF-β Expression
3.3. EtOH Impairs AM Function via Zinc Deficiency
3.4. EtOH Impairs Ability of AMs to Bind Pathogens
4. EtOH Impairs the Adaptive Immune Response
5. EtOH Alters Airway Epithelial Permeability
5.1. EtOH Dysregulates Ion Transporters
5.2. EtOH Disrupts Barrier Function
6. EtOH Exposure Is Implicated in Matrix Remodeling
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasin, D.S.; Stinson, F.S.; Ogburn, E.; Grant, B.F. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-iv alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: Results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happel, K.I.; Nelson, S. Alcohol, immunosuppression, and the lung. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2005, 25, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, J.; Mathers, C.; Popova, S.; Thavorncharoensap, M.; Patra, J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 2009, 373, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchery, E.E.; Harwood, H.J.; Sack, J.J.; Simon, C.J.; Brewer, R.D. Economic costs of excessive alcohol consumption in the U.S., 2006. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 41, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokdad, A.H.; Marks, J.S.; Stoup, D.F.; Gerberding, J.L. Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000. JAMA 2004, 291, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esper, A.; Burnham, E.L.; Moss, M. The effect of alcohol abuse on ARDS and multiple organ dysfunction. Minerva Anestesiol. 2006, 72, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tabak, C.; Smit, H.A.; Räsänen, L.; Fidanza, F.; Menotti, A.; Nissinen, A.; Feskens, E.J.; Heederik, D.; Kromhout, D. Alcohol consumption in relation to 20-year COPD mortality and pulmonary function in middle-aged men from three European countries. Epidemiology 2001, 12, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suadicani, P.; Hein, H.; Meyer, H.; Gyntelberg, F. Exposure to cold and draught, alcohol consumption, and the NS-phenotype are associated with chronic bronchitis: An epidemiological investigation of 3387 men aged 53–75 years: The Copenhagen Male Study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2001, 58, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, S.C.; Hlastala, M.P.; Souders, J.E.; Babb, A.L. Gas exchange in the airways. J. Aerosol Med. 1996, 9, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, C.S. Biochemical factors in alcoholic liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 1993, 13, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaphalia, L.; Calhoun, W.J. Alcoholic lung injury: Metabolic, biochemical and immunological aspects. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 222, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edenberg, H.J. The genetics of alcohol metabolism: Role of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase variants. Alcohol Res. Health 2007, 30, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zerilli, A.; Lucas, D.; Amet, Y.; Beauge, F.; Volant, A.; Floch, H.H.; Berthou, F.; Menez, J.F. Cytochrome P-450 2E1 in rat liver, kidney and lung microsomes after chronic administration of ethanol either orally or by inhalation. Alcohol Alcohol. 1995, 30, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guengerich, F.P.; Kim, D.H.; Iwasaki, M. Role of human cytochrome P-450 IIE1 in the oxidation of many low molecular weight cancer suspects. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1991, 4, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, D.F. Mucociliary dysfunction in COPD: Effect of current pharmacotherapeutic options. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Ward, E.; Hao, Y.; Thun, M. Trends in the leading causes of death in the United States, 1970–2002. JAMA 2005, 294, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samokhvalov, A.V.; Irving, H.M.; Rehm, J. Alcohol consumption as a risk factor for pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, T.A.; Sisson, J.H. Chronic ethanol downregulates PKA activation and ciliary beating in bovine bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 281, L575–L581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Price, M.E.; Pavlik, J.A.; Sisson, J.H.; Wyatt, T.A. Inhibition of protein phosphatase 1 reverses alcohol-induced ciliary dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L577–L585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, E.H.; Green, G.M.; Goldstein, E. Mechanisms of antibacterial action in the respiratory system. Bacteriol. Rev. 1966, 30, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simet, S.M.; Pavlik, J.A.; Sisson, J.H. Proteomic analysis of bovine axonemes exposed to acute alcohol: Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and heat shock protein 90 in cilia stimulation. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cardena, G.; Fan, R.; Shah, V.; Sorrentino, R.; Cirino, G.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Sessa, W.C. Dynamic activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by Hsp90. Nature 1998, 392, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simet, S.M.; Pavlik, J.A.; Sisson, J.H. Dietary antioxidants prevent alcohol-induced ciliary dysfunction. Alcohol 2013, 47, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, S.T.; Udaltsova, N.; Iribarren, C.; Klatsky, A.L. Alcohol and lung airways function. Perm. J. 2010, 14, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, G.M.; Kass, E.H. Factors influencing the clearance of bacteria by the lung. J. Clin. Invest. 1964, 43, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Pavlik, J.; Fox, L.; Scarbrough, C.; Sale, W.S.; Sisson, J.H.; Wirshcell, M. Alcohol-induced ciliary dysfunction targets the outer dynein arm. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L569–L576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambeth, J.D.; Neish, A.S. Nox enzymes and new thinking on reactive oxygen: A double-edged sword revisited. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2014, 9, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, J.M.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase: An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 6049–6055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.-H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeligar, S.M.; Harris, F.L.; Hart, C.M.; Brown, L.A. Ethanol induces oxidative stress in alveolar macrophages via upregulation of NADPH oxidases. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3648–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.A.S.; Ping, X.D.; Harris, F.L.; Gauthier, T.W. Glutathione availability modulates alveolar macrophage function in the chronic ethanol-fed rat. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007, 292, L824–L832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Harris, F.L.; Jones, D.P.; Brown, L.A.S. Alcohol induces mitochondrial redox Imbalance in alveolar macrophages. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 1427–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patenaude, A.; ven Murthy, M.R.; Mirault, M.E. Mitochondrial thioredoxin system: Effects of TrxR2 overexpression on redox balance, cell growth, and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 27302–27314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asplund, M.B.; Coelho, C.; Cordero, R.J.; Martinez, L.R. Alcohol impairs J774.16 macrophage-like cell antimicrobial functions in Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Virulence 2013, 4, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.S.; Fan, X.; Guidot, D.M. Alcohol causes alveolar epithelial oxidative stress by inhibiting the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)—Like 2—Antioxidant response element signaling pathway. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueblinvong, V.; Tseng, V.; Smith, T.; Saghafi, R.; Mills, S.T.; Neujahr, D.C.; Guidot, D.M. TGFβ1 mediates alcohol-induced Nrf2 suppression in lung fibroblasts. Alcohol.Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Staiteh, B.S.; Jensen, J.S.; Mould, K.J.; Greenberg, J.A.; Joshi, P.C.; Koval, M.; Guidot, D.M. Activating the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response element restores barrier function in the alveolar epithelium of HIV-1 transgenic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013, 305, L267–L277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Harris, F.L.; Brown, L.A.S. Alcohol induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and alveolar macrophage dysfunction. BioMed Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.D.; Brown, L.A.S. Ethanol (EtOH)-induced TGF-β1 and reactive oxygen species production are necessary for EtOH-induced alveolar macrophage dysfunction and induction of alternative activation. Alcohol.Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeligar, S.M.; Harris, F.L.; Hart, C.M.; Brown, L.A. Glutathione attenuates ethanol-induced alveolar macrophage oxidative stress and dysfunction by downregulating NADPH oxidases. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L429–L441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trnka, J.; Blaikie, F.H.; Logan, A.; Smith, R.A.; Murphy, M.P. Antioxidant properties of MitoTEMPOL and its hydroxylamine. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, P.C.; Mehta, A.; Jabber, W.S.; Fan, C.; Guidot, D.M. Zinc deficiency mediates alcohol-induced alveolar epithelial and macrophage dysfunction in rats. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 41, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreini, C.; Bertini, I.; Cavallaro, G.; Holliday, G.L.; Thornton, J.M. Metal ions in biological catalysis: From enzyme databases to general principles. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 13, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.J.; Yeligar, S.M.; Elon, L.; Brown, L.A.; Guidot, D.M. Alcoholism causes alveolar macrophage zinc deficiency and immune dysfunction. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Sharma, N.; Kapadia, F.; Zhou, G.; Lu, Y.; Hong, H.; Parachuri, K.; Mahabeleshwar, G.H.; Dalmas, E.; Venteclef, N.; et al. Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 2736–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curry-McCoy, T.V.; Guidot, D.M.; Joshi, P.C. Chronic Alcohol ingestion in rats decreases krüppel-like factor 4 expression and intracellular zinc in the lung. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, Y.; Berclaz, P.Y.; Chroneos, Z.C.; Yoshida, M.; Whitsett, J.A.; Trapnell, B.C. GM-CSF regulates alveolar macrophage differentiation and innate immunity in the lung through PU.1. Immunity 2001, 15, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.C.; Applewhite, L.; Ritzenthaler, J.D.; Roman, J.; Fernandez, A.L.; Eaton, D.C.; Brown, L.A.; Guidot, D.M. Chronic ethanol ingestion in rats decreases granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor expression and downstream signaling in the alveolar macrophage. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 6837–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.J.; Joshi, P.C.; Fan, X.; Brown, L.A.; Ritzenthaler, J.D.; Roman, J.; Guidot, D.M. Zinc supplementation restores PU.1 and Nrf2 nuclear binding in alveolar macrophages and improves redox balance and bacterial clearance in the lungs of alcohol-fed rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, E.; Hall, A. Identification of two distinct mechanisms of phagocytosis controlled by different Rho GTPases. Science 1998, 282, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasch, R.M.; Tomas, M.; Minambres, R.; Valles, S.; Renau-Piqueras, J.; Guerri, C. RhoA and lysophosphatidic acid are involved in the actin cytoskeleton reorganization of astrocytes exposed to ethanol. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 72, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Wang, Y.; Chang, B.; Zhang, D.; Liu, P.; Wang, B. Activation of RhoA in alcohol-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction. Inflammation 2013, 36, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamin, E.; Masclee, A.; Dekker, J.; Jonkers, D. Ethanol disrupts intestinal epithelial tight junction integrity through intracellular calcium-mediated Rho/ROCK activation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G677–G685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgdorff, M.; Veen, J.; Kalisvaart, N.A.; Nagelkerke, N. Mortality among tuberculosis patients in The Netherlands in the period 1993–1995. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 11, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, C.M.; Dobard, E.; Zhang, P.; Nelson, S. Alcohol exacerbates murine pulmonary tuberculosis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2556–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.L.; Chan, J.; Triebold, K.J.; Dalton, D.K.; Stewart, T.A.; Bloom, B.R. An essential role for interferon gamma in resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 178, 2249–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porretta, E.; Happel, K.I.; Teng, X.S.; Ramsay, A.; Mason, C.M. The impact of alcohol on BCG-induced immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, P.; Young, B.M.; Coleman, R.A.; Wiechert, S.; Turner, L.E.; Ray, N.B.; Waldshmidt, T.J.; Legge, K.L.; Cook, R.T. Chronic ethanol induces inhibition of antigen-specific CD8+ but not CD4+ immunodominant T cell responses following Listeria monocytogenes inoculation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, R.; Waltenbaugh, C. Ethanol consumption modifies dendritic cell antigen presentation in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edsen-Moore, M.R.; Fan, J.; Ness, K.J.; Marietta, J.R.; Cook, R.T.; Schlueter, A.J. Effects of chronic ethanol feeding on murine dendritic cell numbers, turnover rate, and dendropoiesis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shellito, J.E.; Zheng, M.Q.; Ye, P.; Ruan, S.; Shean, M.K.; Kolls, J. Effect of alcohol consumption on host release of interleukin-17 during pulmonary infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happel, K.I.; Zheng, M.; Young, E.; Quinton, L.J.; Lockhart, E.; Ramsay, A.J.; Shellito, J.E.; Schurr, J.R.; Bagby, G.J.; Nelson, S.; et al. Cutting edge: Roles of toll-like receptor 4 and IL-23 in IL-17 expression in response to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4432–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisman, D.A.; Strieter, R.M.; Kunkel, S.L.; Tsai, W.C.; Wilkowski, J.M.; Bucknell, K.A.; Standiford, T.J. Ethanol feeding impairs innate immunity and alters the expression of Th1- and Th2-phenotype cytokines in murine Klebsiella pneumonia. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberger, M.J.; Strieter, R.M.; Kunkel, S.L.; Danforth, J.M.; Goodman, R.E.; Standiford, T.J. Neutralization of IL-10 increases survival in a murine model of Klebsiella pneumonia. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matthay, M.A.; Zimmerman, G.A. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 33, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidot, D.M.; Modelska, K.; Lois, M.; Jain, L.; Moss, I.M.; Pittet, J.F.; Brown, L.A. Ethanol ingestion via glutathione depletion impairs alveolar epithelial barrier function in rats. Am. J Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L127–L135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ware, L.B. Pathophysiology of acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 27, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, M.; Bucher, B.; Moore, F.A.; Moore, E.E.; Parsons, P.E. The role of chronic alcohol abuse in the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome in adults. JAMA 1996, 275, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidot, D.M.; Hart, M.C. Alcohol abuse and acute lung injury: Epidemiology and pathophysiology of a recently recognized association. J. Investig. Med. 2005, 53, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, G.M.; Adir, Y.; Jameel, M.; Akhmedov, A.T.; Welch, L.; Dumasius, V.; Meng, F.J.; Zabner, J.; Koenig, C.; Lewis, E.R.; et al. Interdependency of β-adrenergic receptors and CFTR in regulation of alveolar active Na+ transport. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, S.V.; Wang, G. Suppression of adenosine-activated chloride transport by ethanol in airway epithelia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, D.M.; Vadasz, I.; Wujak, L.; Wygrecka, M.; Olschewski, A.; Becker, C.; Herold, S.; Papp, R.; Mayer, K.; Rummel, S.; et al. TGF-β directs trafficking of the epithelial sodium channel ENaC which has implications for ion and fluid transport in acute lung injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E374–E383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilatovskaya, D.V.; Pavlov, T.S.; Levchenko, V.; Staruschenko, A. ROS production as a common mechanism of ENaC regulation by EGF, insulin, and IGF-1. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 304, C102–C111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, C.A.; Trac, D.Q.; Kreiner, L.H.; Eaton, A.F.; Johnson, N.M.; Brown, L.A.; Helms, M.N. Ethanol alters alveolar fluid balance via nadph oxidase (NOX) signaling to epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) in the lung. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koval, M. Claudin heterogeneity and control of lung tight junctions. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Wang, Y.; Chang, B.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B. Evidence for the involvement of RhoA signaling in the ethanol-induced increase in intestinal epithelial barrier permeability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3946–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overgaard, C.E.; Schlingmann, B.; Dorsainvil White, S.; Ward, C.; Fan, X.; Swarnakar, S.; Brown, L.A.; Guidot, D.M.; Koval, M. The relative balance of GM-CSF and TGF-β1 regulates lung epithelial barrier function. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L1212–L1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, S.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-β in progression of liver disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantin, A.M.; Hubbard, R.C.; Crystal, R.G. Glutathione deficiency in the epithelial lining fluid of the lower respiratory tract in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, N.; O’Connor, R.N.; Flanders, K.C.; Unruh, H. TGF-beta 1, but not TGF-beta 2 or TGF-beta 3, is differentially present in epithelial cells of advanced pulmonary fibrosis: An immunohistochemical study. Am. J. Respir.Cell Mol. Biol. 1996, 14, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, M.; Guidot, D.M.; Wong-Lambertina, M.; Ten Hoor, T.; Perez, R.L.; Brown, L.A. The effects of chronic alcohol abuse on pulmonary glutathione homeostasis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechara, R.I.; Brown, L.A.S.; Roman, J.; Joshi, P.C.; Guidot, D.M. Transforming growth factor β1 expression and activation is increased in the alcoholic rat lung. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, W.D.; Glasser, S.W.; Hagood, J.S. Emerging concepts in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, J.; Ritzenthaler, J.D.; Bechara, R.; Brown, L.A.; Guidot, D. Ethanol stimulates the expression of fibronectin in lung fibroblasts via kinase-dependent signals that activate CREB. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 288, L975–L987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueblinvong, V.; Kirchberger, V.E.; Saghafi, R.; Mills, S.T.; Fan, X.; Guidot, D.M. Chronic alcohol ingestion primes the lung for bleomycin-induced fibrosis in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lois, M.; Brown, L.A.; Moss, I.M.; Roman, J.; Guidot, D.M. Ethanol Ingestion increases activation of matrix metalloproteinases in rat lungs during acute endotoxemia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, J.J.; Senior, R.M. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in lung remodeling. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 28, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Traphagen, N.; Tian, Z.; Allen-Gipson, D. Chronic Ethanol Exposure: Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Disease and Dysfunction. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 2840-2853. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042840
Traphagen N, Tian Z, Allen-Gipson D. Chronic Ethanol Exposure: Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Disease and Dysfunction. Biomolecules. 2015; 5(4):2840-2853. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042840
Chicago/Turabian StyleTraphagen, Nicole, Zhi Tian, and Diane Allen-Gipson. 2015. "Chronic Ethanol Exposure: Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Disease and Dysfunction" Biomolecules 5, no. 4: 2840-2853. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042840
APA StyleTraphagen, N., Tian, Z., & Allen-Gipson, D. (2015). Chronic Ethanol Exposure: Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Disease and Dysfunction. Biomolecules, 5(4), 2840-2853. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042840