Evaluation of the Simultaneous Production of Xylitol and Ethanol from Sisal Fiber
Abstract
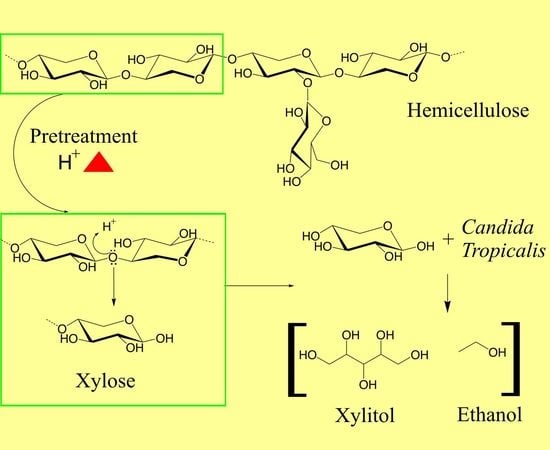
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Acid Pretreatment
2.2. Lignocellulosic Composition
2.3. Infrared Characterization
2.4. Characterization by Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5. Characterization by X-ray Diffraction
2.6. Fermentation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Pretreatment
3.3. High Performance Liquid Chromatography
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.6. X-ray Diffraction
3.7. Preparation of the Inoculum
3.8. Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bezazi, A.; Belaadi, A.; Bourchak, M.; Scarpa, F.; Boba, K. Novel extraction techniques, chemical and mechanical characterization of Agave americana L. natural fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 66, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, C.; Basnet, S.; Otsuka, M.; Sasaki, C.; Nakamura, Y. Epoxy resin synthesis using low molecular weight lignin separated from various lignocellulosic materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loow, Y.; Wu, T.Y.; Tan, K.A.; Lim, Y.S.; Siow, L.F.; Jahim, J.M.; Mohammad, A.W.; Teoh, W.H. Recent Advances in the Application of Inorganic Salt Pretreatment for Transforming Lignocellulosic Biomass into Reducing Sugars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8349–8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiber, J.N. Agricultural and food chemistry contributions to fulfilling the promise of biofuels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12063–12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluiter, J.B.; Ruiz, R.O.; Scarlata, C.J.; Sluiter, A.D.; Templeton, D.W. Compositional Analysis of Lignocellulosic Feedstocks.1. Review and Description of Methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9043–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, M.B.; Beceiro, J.L.; Jiménez, P.E.S.; Cosp, J.P. Comparison of thermal behavior of natural and hot-washed sisal fibers based on their main components: Cellulose, xylan and lignin. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 581, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.S.S.; Conceição, M.M.; Silva, F.L.H.; Lima, E.E.; Conrado, L.S.; Leão, D.A.S. Characterization of acid hydrolysis of sisal. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento. Sisal 2015: Retrospectiva. 2015. Available online: http://www.conab.gov.br/detalhe.php?c=39451&t=2#this (accessed on 6 December 2017).
- Martin, A.R.; Martins, M.A.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Silva, O.R.R.F. Caracterização Química e Estrutural de Fibra de Sisal da Variedade Agave sisalana. Polímeros Ciência e Tecnologia 2009, 19, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalli, S.S.; Patel, M.; Rakshit, S.K. Development and evaluation of poplar hemicellulose prehydrolysate upstream processes for the enhanced fermentative production of xylitol. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 105, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mood, S.H.; Golfeshan, A.H.; Tabatabaei, M.T.; Jouzani, G.S.; Najafi, G.H.; Gholami, M.; Ardjmand, M. Lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol, a comprehensive review with a focus on pretreatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, R.F.; Santos, J.C.; Silva, S.S. A novel use for sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic fraction: Xylitol enzymatic production. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3241–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, P.R.; Kadam, A.A.; Saratale, G.D.; Govindwar, S.P. Enzymatic hydrolysis and characterization of waste lignocellulosic biomass produced after dye bioremediation under solid state fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, Y.; Ling, H.-Z.; Song, G.; Ge, J.-P. Xylitol production from non-detoxified corncob hemicellulose acid hydrolysate by Candida tropicalis. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 75, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, T.M.; Zambon, M.D.; Frollini, E. Effect of acid concentration and pulp properties on hydrolysis reactions of mercerized sisal. Carbohyd. Polym. 2013, 93, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.V.; Goli, J.K.; Gentela, J.; Koti, S. Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass to xylitol: An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 213, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, T.L.; Silva, I.J., Jr.; Macedo, G.R.; Rocha, M.V.P. Biotechnological production of xylitol from lignocellulosic wastes: A review. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenath, K.; Venkatesh, Y.P. Quantification of Xylitol in Foods by an Indirect Competitive Immunoassay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, S.; Qin, W. Microbial and Bioconversion Production of d-xylitol and Its Detection and Application. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 6, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka, P.; Wojdyło, A. Stability of phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and colour through natural sweeteners addition during storage of sour cherry puree. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Dai, L.; Nan, C.; Xiong, L. Effect of heat moisture treatment on physicochemical and morphological properties of wheat starch and xylitol mixture. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orts, W.J.; Holtman, K.M.; Seiber, J.N. Agricultural chemistry and bioenergy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3892–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejos, M.E.; Chade, M.; Mereles, E.B.; Bengoechea, D.I.; Brizuela, J.G.; Felissia, F.E.; Area, M.C. Strategies of detoxification and fermentation for biotechnological production of xylitol from sugarcane bagasse. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 91, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wanga, D.; Gao, X.; Hong, J. Xylitol production at high temperature by engineered Kluyveromycesmarxianus. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiber, J.N.; Finley, J.W. The nexus of food, energy, and water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6255–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, F.C.S.; Silva, F.L.H.; Gomes, J.P.; Muniz, M.B.; Santiago, A.M.; Silva, C.G. Biotechnological Production of Xylitol: Evaluation of Detoxification Process with Residual Lignin Using Response Surface Methodology. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 38, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.; Ghosh, S.K.; Bannerjee, S.; Aikat, K. Bioethanol production from agricultural wastes: An overview. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, E.R.; Nascimento, R.T.; Souto-Maior, A.M.; Rocha, G.J.M. Validação de metodologia para a caracterização química de bagaço de cana-de-açúcar. Quim. Nova 2009, 32, 1500–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Zhao, L.; Chen, C.; Guo, W.; Cao, G. A review on bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass to H2: Key challenges and new insights. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.; Cuevas, M.; García, J.F.; Sánchez, S. Valorization of olive stones for xylitol and ethanol production from dilute acid pretreatment via enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation by Pachysolentannophilus. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 90, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wanga, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Effects of chemical treatments on hemp fibre structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Cheng, G.; Jiang, B. Effect of silane treatment on microstructure of sisal fibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 292, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.K.; Josec, C.; Rohith, K.R.; George, K.E. Sisal nanofibril reinforced polypropylene/polystyrene blends: Morphology, mechanical, dynamic mechanical and water transmission studies. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 71, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binod, P.; Satyanagalakshmi, K.; Sindhu, R.; Rajeev, K.U.J.; Sukumaran, K.; Pandey, A. Short duration microwave assisted pretreatment enhances the enzymatic scarification and fermentable sugar yield from sugarcane bagasse. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Zhang, L. Preparation and characterization of lignin-containing nanofibrillary cellulose. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, N.; Vanderghem, C.; Danthine, S.; Quiévy, N.; Blecker, C.; Devaux, J.; Paquot, M. Influence of steam explosion on physicochemical properties and hydrolysis rate of pure cellulose fibers. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 121, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Kenealy, W.R.; Jeffries, T.W. Xylitol production from DEO hydrolysate of corn stover by Pichiastipitis YS-30. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, T.; Hensirisak, P.; Agblevor, F.A. The influence of aeration and hemicellulosic sugars on xylitol production by Candida tropicalis. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajó, J.C.; Dominguez, H.; Domínguez, J.M. Biotechnological production of xylitol. Part 1: Interest of xylitol and fundamentals of its biosynthesis. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 65, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Saxena, R.K. Evaluation of corncob hemicellulosichydrolysate for xylitol production byadapted strain of Candida tropicalis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickert, L.R.; Souza-Cruz, P.B.; Rosa, C.A.; Ayub, M.A.Z. Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of un-detoxified rice hull hydrolysate by Saccharomyces cerevisiae ICV D254 and Spathasporaarborariae NRRL Y-48658 for the production of ethanol and xylitol. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, J.C.L.; Romero, I.; Cara, C.; Castroa, E.; Mussatto, E.I. Xylitol production by Debaryomyceshansenii and Candida guilliermondii from rapeseed straw hemicellulosichydrolysate. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canilha, L.; Carvalho, W.; Felipe, M.G.A.; Silva, J.B.A. Xylitol production from wheat straw hemicellulosic hydrolysate: Hydrolysate detoxification and carbon source used for inoculum preparation. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2008, 39, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, J.P.S.; Rosa, M.F.; Marconcini, J.M. Documentos 236. Procedimentos para Análise Lignocelulósica, 1st ed.; Embrapa Algodão: Campina Grande, Brazil, 2010; ISSN 0103-0205. Available online: https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/883400/procedimentos-para-analise-lignocelulosica (accessed on 6 December 2017).
- Ruiz, E.; Romero, I.; Moya, M.; Cara, C.; Vidal, J.D.; Castro, E. Dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of sunflower stalks for sugar production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Fu, S.Y.; Zheng, L.M.; Zhan, H.Y. Effect of nanocellulose isolation Techniques on the formation of reinforced poly(vinylalcohol) nanocomposite films. Polym. Lett. 2012, 6, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, L.H.A.; Felipe, M.G.A.; Torres, F.A.G. Reclassification of Candida guilliermondii as Candida tropicalis based on molecular phylogenetic analysis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2003, 34, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.D.V.; Cândido, E.J.; Arruda, P.V.; Silva, S.S.; Felipe, M.G.A. New cultive medium for bioconversion of C5 fraction from sugarcane bagasse using rice bran extract. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| N° | Concentration (%) | Temperature (°C) | Xylose (g·g−1 of Sisal Fiber) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 (−1) | 100 (−1) | 0.030 |
| 2 | 2.5 (+1) | 100 (−1) | 0.110 |
| 3 | 0.5 (−1) | 120 (+1) | 0.124 |
| 4 | 2.5 (+1) | 120 (+1) | 0.132 |
| 5 | 1.5 (0) | 110 (0) | 0.111 |
| 6 | 1.5 (0) | 110 (0) | 0.126 |
| 7 | 1.5 (0) | 110 (0) | 0.111 |
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F-Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression | 3 | 0.6588 | 0.2196 | 1.04 |
| Residual Error | 3 | 0.0678 | 0.0226 | |
| Lack-of-Fit | 1 | 0.0519 | 0.0519 | |
| PureError | 2 | 0.0159 | 0.00798 | |
| Total | 6 | 0.7267 | ||
| % R2 | 90.66 | |||
| Regression Model | Xylose = 0.106 + 0.022 C + 0.029 T | |||
| Analysis | Natura Sisal Fiber/% | * Treated Sisal Fiber/% |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 6.27 | - |
| Ash | 1.20 | - |
| Extractives | 1.75 | - |
| Hemicellulose | 31.81 | 23.70 |
| Lignin | 11.07 | 17.65 |
| Alpha cellulose | 48.20 | 38.87 |
| Components | Concentration in the Liquor (g·g−1 of Sisal Fiber) |
|---|---|
| Glucose | 0.0462 |
| Xylose | 0.1229 |
| Acetic acid | 0.0586 |
| Hydroxymethylfurfural | 0.0010 |
| Furfural | 0.0083 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Damião Xavier, F.; Santos Bezerra, G.; Florentino Melo Santos, S.; Sousa Conrado Oliveira, L.; Luiz Honorato Silva, F.; Joice Oliveira Silva, A.; Maria Conceição, M. Evaluation of the Simultaneous Production of Xylitol and Ethanol from Sisal Fiber. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8010002
Damião Xavier F, Santos Bezerra G, Florentino Melo Santos S, Sousa Conrado Oliveira L, Luiz Honorato Silva F, Joice Oliveira Silva A, Maria Conceição M. Evaluation of the Simultaneous Production of Xylitol and Ethanol from Sisal Fiber. Biomolecules. 2018; 8(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleDamião Xavier, Franklin, Gustavo Santos Bezerra, Sharline Florentino Melo Santos, Líbia Sousa Conrado Oliveira, Flávio Luiz Honorato Silva, Aleir Joice Oliveira Silva, and Marta Maria Conceição. 2018. "Evaluation of the Simultaneous Production of Xylitol and Ethanol from Sisal Fiber" Biomolecules 8, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8010002
APA StyleDamião Xavier, F., Santos Bezerra, G., Florentino Melo Santos, S., Sousa Conrado Oliveira, L., Luiz Honorato Silva, F., Joice Oliveira Silva, A., & Maria Conceição, M. (2018). Evaluation of the Simultaneous Production of Xylitol and Ethanol from Sisal Fiber. Biomolecules, 8(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8010002