Is Sotolon Relevant to the Aroma of Madeira Wine Blends?
Abstract
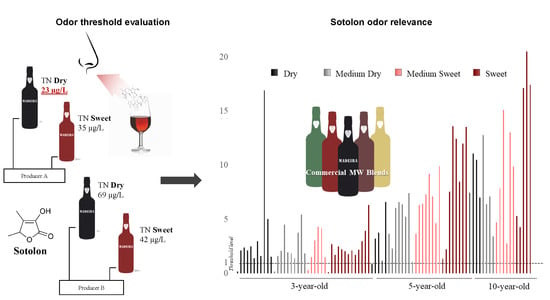
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sotolon Odor Threshold
2.2.1. Panelists
2.2.2. Samples
2.2.3. Sensory Tests
2.3. Sotolon Odor Impact in MW Blends
2.3.1. Wines
2.3.2. Sotolon Extraction and Analysis
2.4. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Odor Threshold Determinations
3.2. Sotolon Odor Impact in MW Blends
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, V.; Pereira, A.C.; Marques, J.C. Emerging trends in fortified wines: A scientific perspective. In Alcoholic Beverages: Volume 7: The Science of Beverages; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2019; pp. 419–470. ISBN 9780128152690. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, V.; Cacho, J.; Marques, J.C. Volatile profile of Madeira wines submitted to traditional accelerated ageing. Food Chem. 2014, 162, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perestrelo, R.; Albuquerque, F.; Rocha, S.M.; Câmara, J.S. Distinctive characteristics of Madeira wine regarding its traditional winemaking and modern analytical methodologies. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Jackson, R.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 63, pp. 207–249. ISBN 9780123849274. [Google Scholar]
- IVBAM Madeira Wine. Available online: http://www.vinhomadeira.pt/ (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Garrafeira Nacional. Available online: https://www.garrafeiranacional.com/ (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- LojaMadeirense.com. Available online: https://www.lojamadeirense.com/pt/ (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Oliveira e Silva, H.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Machado, B.P.; Hogg, T.; Marques, J.C.; Câmara, J.S.; Albuquerque, F.; Silva Ferreira, A.C. Impact of forced-aging process on Madeira wine flavor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11989–11996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, R.F.; Nascimento, A.M.D.; Nogueira, J.M.F. Characterization of the aroma profile of Madeira wine by sorptive extraction techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 546, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, E.; Ferreira, V.; Escudero, A.; Marques, J.C.; Cacho, J. Quantitative gas chromatography-olfactometry and chemical quantitative study of the aroma of four Madeira wines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 563, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, A.; Lavigne, V.; Landais, Y.; Darriet, P.; Dubourdieu, D. Distribution and organoleptic impact of sotolon enantiomers in dry white wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1606–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, E.; Etiévant, P.; Henry, R.; Mosandl, A. Enantiomeric ratios of pantolactone, solerone, 4-carboethoxy-4-hydroxy-butyrolactone and of sotolon, a flavour impact compound of flor-sherry and botrytized wines. Zeitschrift für Leb. und Forsch. 1992, 195, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, C.M.; Capone, D.L.; Pardon, K.H.; Black, C.A.; Pomeroy, D.; Francis, I.L. Quantitative analysis by GC-MS/MS of 18 aroma compounds related to oxidative off-flavor in wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3394–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, A.; Nikolantonaki, M.; Lavigne, V.; Shinoda, K.; Dubourdieu, D.; Darriet, P. New insights into intrinsic and extrinsic factors triggering premature aging in white wines. In Advances in Wine Research; Ebeler, S.B., Sacks, G., Vidal, S., Winterhalter, P., Eds.; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; Volume 1203, pp. 229–251. ISBN 0-8412-3010-2. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, B.; Etiévant, P.; Le Quere, J.L.; Schlich, P. More clues about sensory impact of sotolon in some flor sherry wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Ferreira, A.C.; Barbe, J.-C.; Bertrand, A. 3-Hydroxy-4,5-dimethyl-2(5H)-furanone: A key odorant of the typical aroma of oxidative aged Port wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4356–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Câmara, J.S.; Marques, J.C.; Alves, M.A.; Silva Ferreira, A.C. 3-Hydroxy-4,5-dimethyl-2(5H)-furanone levels in fortified Madeira wines: Relationship to sugar content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6765–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Câmara, J.S.; Alves, M.A.; Marques, J.C. Changes in volatile composition of Madeira wines during their oxidative ageing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 563, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, V.; Santos, M.; Cacho, J.; Marques, J.C. Assessment of the development of browning, antioxidant activity and volatile organic compounds in thermally processed sugar model wines. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.M.; Pereira, V.; Marques, J.C. Odor detection threshold (ODT) and odor rejection threshold (ORT) determination of sotolon in Madeira wine: A preliminary study. AIMS Agric. Food 2018, 3, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIV-Oenology Resolutions. Available online: http://www.oiv.int/en/technical-standards-and-documents/resolutions-of-the-oiv/oenology-resolutions (accessed on 31 October 2019).
- Lane, J.H.; Eynon, L. Determination of reducing sugars by means of Fehling’s solution with methylene blue as internal indicator. J. Soc. Chem. Ind. Trans. 1923, 142, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials. ASTM E679-04. Standard Practice for Determination of Odor and Taste Thresholds by a Forced-Choice Ascending Concentration Series Method of Limits; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011; Volume 04. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, V.; Leça, J.M.; Gaspar, J.M.; Pereira, A.C.; Marques, J.C. Rapid determination of sotolon in fortified wines using a miniaturized liquid-liquid extraction followed by LC-MS/MS analysis. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamor, R.R.; Evans, M.A.; Mattinson, D.S.; Ross, C.F. Effects of ethanol, tannin and fructose on the headspace concentration and potential sensory significance of odorants in a model wine. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ickes, C.M.; Cadwallader, K.R. Effects of ethanol on flavor perception in alcoholic beverages. Chemosens. Percept. 2017, 10, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, D.; Hayes, J. Effects of matrix composition on detection threshold estimates for methyl anthranilate and 2-aminoacetophenone. Foods 2016, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammari, A.; Schroen, K. Flavor Retention and Release from Beverages: A Kinetic and Thermodynamic Perspective. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9869–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food; Food Science Text Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4419-6487-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tempere, S.; de Revel, G.; Sicard, G. Impact of learning and training on wine expertise: A review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 27, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Producer A | Producer B | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry MW | Sweet MW | Dry MW | Sweet MW | |
| alcohol (% ABV) | 18.03 ± 0.01 a | 18.53 ± 0.02 b | 19.23 ± 0.03 c | 19.28 ± 0.03 c |
| density (g/mL) | 1.0033± 0.0001 a | 1.0263 ± 0.0002 b | 1.0049 ± 0.0002 c | 1.0274 ± 0.0003 d |
| volatile acidity (g/L) | 0.39 ± 0.01 a | 0.40 ± 0.00 a | 0.44 ± 0.03 a,b | 0.49 ± 0.04 b |
| titratable acidity (g/L) | 4.46 ± 0.06 a | 4.92 ± 0.01 b | 5.1 ± 0.1 b | 4.95 ± 0.06 b |
| pH | 3.52 ± 0.01 a,b | 3.51 ± 0.01 a | 3.51 ± 0.01 a | 3.54 ± 0.02 b |
| residual sugars (g/L) | 52.1 ± 0.8 a | 112.9 ± 0.5 b | 63 ± 1 c | 120 ± 1 d |
| Age | Style | No. Samples |
|---|---|---|
| 3-year-old | dry | 11 |
| medium dry | 10 | |
| medium sweet | 6 | |
| sweet | 14 | |
| 5-year-old | dry | 5 |
| medium dry | 7 | |
| medium sweet | 9 | |
| sweet | 8 | |
| 10-year-old | dry | 4 |
| medium dry | 4 | |
| medium sweet | 5 | |
| sweet | 6 |
| Producer A | Producer B | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry MW | Sweet MW | Dry MW | Sweet MW | |
| group BET (µg/L) a | 23.3 | 35.3 | 68.7 | 41.7 |
| log10 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| log10 standard deviation | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaspar, J.M.; Freitas, A.I.; Zhao, Q.; Leça, J.M.; Pereira, V.; Marques, J.C. Is Sotolon Relevant to the Aroma of Madeira Wine Blends? Biomolecules 2019, 9, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110720
Gaspar JM, Freitas AI, Zhao Q, Leça JM, Pereira V, Marques JC. Is Sotolon Relevant to the Aroma of Madeira Wine Blends? Biomolecules. 2019; 9(11):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110720
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaspar, João M., Ana I. Freitas, Qianzhu Zhao, João M. Leça, Vanda Pereira, and José C. Marques. 2019. "Is Sotolon Relevant to the Aroma of Madeira Wine Blends?" Biomolecules 9, no. 11: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110720
APA StyleGaspar, J. M., Freitas, A. I., Zhao, Q., Leça, J. M., Pereira, V., & Marques, J. C. (2019). Is Sotolon Relevant to the Aroma of Madeira Wine Blends? Biomolecules, 9(11), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110720