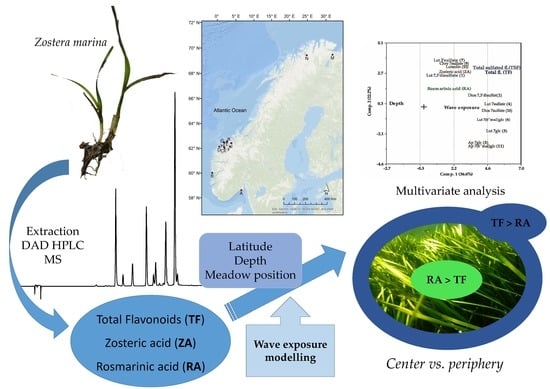
Variation in Phenolic Chemistry in Zostera marina Seagrass along Environmental Gradients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenolic Profiles
2.2. Relative Amount of Sulfated Flavonoids within Regions
2.3. Phenolic Content—Seagrass Meadow Positioning
2.4. Phenolic Content—Variations between Wave Exposure Classes
2.5. Variations in Phenolic Content Explained by Depth and Wave Exposure
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Sites, Plant Collection and Explanatory Variables
4.2. The Wave Exposure Model
4.3. Analytical Instrumentation
4.4. Quantitative Determination
4.5. Multivariate Analysis
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duarte, C.M.; Middelburg, J.J.; Caraco, N. Major Role of Marine Vegetation on the Oceanic Carbon Cycle. Biogeosciences 2005, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Duarte, C.M.; Kennedy, H.; Marbà, N.; Holmer, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Kendrick, G.A.; Krause-Jensen, D.; McGlathery, K.J.; et al. Seagrass Ecosystems as a Globally Significant Carbon Stock. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.P.; Short, F.T. World Atlas of Seagrasses; The UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre, University of California Press: Berkeley, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-520-24047-2. [Google Scholar]
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L.; Hughes, A.R. Accelerating Loss of Seagrasses across the Globe Threatens Coastal Ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, C.; Cui, L.; Huang, X. Macroalgae Bloom Decay Decreases the Sediment Organic Carbon Sequestration Potential in Tropical Seagrass Meadows of the South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, C.M. Allometric Scaling of Seagrass Form and Productivity Malaspina-2010 View Project LIG Sensors View Project. Artic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 77, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, A.Y.; Rotini, A.; Lacasella, F.; Bookman, R.; Thaller, M.C.; Shem-Tov, R.; Winters, G.; Migliore, L. Assessing the Ecological Status of Seagrasses Using Morphology, Biochemical Descriptors and Microbial Community Analyses. A Study in Halophila Stipulacea (Forsk.) Aschers Meadows in the Northern Red Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, D.A. Plant Phenolics: An Ecological Perspective. Am. Nat. 1971, 105, 157–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harborne, J.B.; Williams, C.A. Occurrence of Sulphated Flavones and Caffeic Acid Esters in Members of the Fluviales. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1976, 4, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieg, R.D.; Kubanek, J. Chemical Ecology of Marine Angiosperms: Opportunities at the Interface of Marine and Terrestrial Systems. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 687–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidorn, C. Secondary Metabolites of Seagrasses (Alismatales and Potamogetonales; Alismatidae): Chemical Diversity, Bioactivity, and Ecological Function. Phytochemistry 2016, 124, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, S.; Desjobert, J.-M.; Pergent, G. Distribution of Phenolic Compounds in the Seagrass Posidonia Oceanica. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.R.; Jenkins, K.M.; Porter, D.; Fenical, W. Evidence That a New Antibiotic Flavone Glycoside Chemically Defends the Sea Grass Thalassia Testudinum against Zoosporic Fungi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1490–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vergeer, L.H.T.; Aarts, T.L.; de Groot, J.D. The “Wasting Disease” and the Effect of Abiotic Factors (Light Intensity, Temperature, Salinity) and Infection with Labyrinthula Zosterae on the Phenolic Content of Zostera Marina Shoots. Aquat. Bot. 1995, 52, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergeer, L.H.T.; Develi, A. Phenolic Acids in Healthy and Infected Leaves of Zostera Marina and Their Growth-Limiting Properties towards Labyrinthula Zosterae. Aquat. Bot. 1997, 58, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumay, O.; Costa, J.; Desjobert, J.-M.; Pergent, G. Variations in the Concentration of Phenolic Compounds in the Seagrass Posidonia Oceanica under Conditions of Competition. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliore, L.; Rotini, A.; Randazzo, D.; Albanese, N.N.; Giallongo, A. Phenols Content and 2-D Electrophoresis Protein Pattern: A Promising Tool to Monitor Posidonia Meadows Health State. BMC Ecol. 2007, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Qian, P.Y.; Wang, B.G. Antifeedant, Antibacterial, and Antilarval Compounds from the South China Sea Seagrass Enhalus Acoroides. Bot. Mar. 2008, 51, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazian, S.; Parrot, D.; Burýšková, B.; Weinberger, F.; Tasdemir, D. Surface Chemical Defence of the Eelgrass Zostera Marina against Microbial Foulers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rotini, A.; Belmonte, A.; Barrote, I.; Micheli, C.; Peirano, A.; Santos, R.O.; Silva, J.; Migliore, L. Effectiveness and Consistency of a Suite of Descriptors for Assessing the Ecological Status of Seagrass Meadows (Posidonia Oceanica L. Delile). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pergent, G.; Boudouresque, C.-F.; Dumay, O.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Wyllie-Echeverria, S. Competition between the Invasive Macrophyte Caulerpa Taxifolia and the Seagrass Posidonia Oceanica: Contrasting Strategies. BMC Ecol. 2008, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannino, A.M.; Micheli, C. Ecological Function of Phenolic Compounds from Mediterranean Fucoid Algae and Seagrasses: An Overview on the Genus Cystoseira Sensu Lato and Posidonia Oceanica (L.) Delile. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravn, H.; Pedersen, M.F.; Borum, J.; Andary, C.; Anthoni, U.; Christophersen, C.; Nielsen, P.H. Seasonal Variation and Distribution of Two Phenolic Compounds, Rosmarinic Acid and Caffeic Acid, in Leaves and Roots-Rhizomes of Eelgrass (Zostera Marina L.). Ophelia 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttner, L.; Grabe, V.; Gablenz, S.; Böhme, N.; Appenroth, K.J.; Gershenzon, J.; Huber, M. Differential Localization of Flavonoid Glucosides in an Aquatic Plant Implicates Different Functions under Abiotic Stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, I.; Alegre, L.; Van Breusegem, F.; Munné-Bosch, S. How Relevant Are Flavonoids as Antioxidants in Plants? Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel-Shirley, B. It Takes a Garden. How Work on Diverse Plant Species Has Contributed to an Understanding of Flavonoid Metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, B.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Christensen, P.B. Depth-Related Changes in Reproductive Strategy of a Cold-Temperate Zostera Marina Meadow. Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enerstvedt, K.H. Analysis of Polyphenolic Content in Marine and Aquatic Angiosperms from Norwegian Coastal Waters. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 2018. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1956/17676 (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Enerstvedt, K.H.; Lundberg, A.; Sjøtun, I.K.; Fadnes, P.; Jordheim, M. Characterization and Seasonal Variation of Individual Flavonoids in Zostera Marina and Zostera Noltii from Norwegian Coastal Waters. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2017, 74, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grignon-Dubois, M.; Rezzonico, B. Phenolic Chemistry of the Seagrass Zostera Noltei Hornem. Part 1: First Evidence of Three Infraspecific Flavonoid Chemotypes in Three Distinctive Geographical Regions. Phytochemistry 2018, 146, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laabir, M.; Grignon-Dubois, M.; Masseret, E.; Rezzonico, B.; Soteras, G.; Rouquette, M.; Rieuvilleneuve, F.; Cecchi, P. Algicidal Effects of Zostera Marina L. and Zostera Noltii Hornem. Extracts on the Neuro-Toxic Bloom-Forming Dinoflagellate Alexandrium Catenella. Aquat. Bot. 2013, 111, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noleto-Dias, C.; Harflett, C.; Beale, M.H.; Ward, J.L. Sulfated Flavanones and Dihydroflavonols from Willow. Phytochem. Lett. 2020, 35, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, R.C.; Alberte, R.J.; Todd, S.; Crew, P. Phenolic Acid Sulfate Esters for Prevention of Marine Biofouling. U.S. Patent 5384176, 24 January 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, G.; Ros, G.; Castillo, J. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Rosemary (Rosmarinus Officinalis, L.): A Review. Medicines 2018, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, C.; Parrot, D.; Wiese, J.; Sönnichsen, F.D.; Saha, M.; Tasdemir, D.; Weinberger, F. Identification of Rosmarinic Acid and Sulfated Flavonoids as Inhibitors of Microfouling on the Surface of Eelgrass Zostera Marina. Biofouling 2017, 33, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Rosmarinic Acid. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achamlale, S.; Rezzonico, B.; Grignon-Dubois, M. Rosmarinic Acid from Beach Waste: Isolation and HPLC Quantification in Zostera Detritus from Arcachon Lagoon. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enerstvedt, K.H.; Jordheim, M.; Andersen, Ø.M. Isolation and Identification of Flavonoids Found in Zostera Marina Collected in Norwegian Coastal Waters. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bro, R.; Smilde, A.K. Principal Component Analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-W.; Lin, K.-H.; Kuo, Y.-M. Application of Factor Analysis in the Assessment of Groundwater Quality in a Blackfoot Disease Area in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 313, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.; Coyer, J.; Stam, W.; Moy, F.; Christie, H.; Jørgensen, N. Eelgrass Zostera Marina Populations in Northern Norwegian Fjords Are Genetically Isolated and Diverse. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 486, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albert, A.; Sareedenchai, V.; Heller, W.; Seidlitz, H.K.; Zidorn, C. Temperature Is the Key to Altitudinal Variation of Phenolics in Arnica Montana L. Cv. ARBO. Oecologia 2009, 160, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakola, L.; Hohtola, A. Effect of Latitude on Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Plants: Effect of Latitude on Flavonoid Biosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agati, G.; Brunetti, C.; Di Ferdinando, M.; Ferrini, F.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Functional Roles of Flavonoids in Photoprotection: New Evidence, Lessons from the Past. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 72, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agati, G.; Stefano, G.; Biricolti, S.; Tattini, M. Mesophyll Distribution of ‘antioxidant’ Flavonoid Glycosides in Ligustrum Vulgare Leaves under Contrasting Sunlight Irradiance. Ann. Bot. 2009, 104, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agati, G.; Biricolti, S.; Guidi, L.; Ferrini, F.; Fini, A.; Tattini, M. The Biosynthesis of Flavonoids Is Enhanced Similarly by UV Radiation and Root Zone Salinity in L. Vulgare Leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, T.; Akhtar, T.; Lampi, M.; Tripuranthakam, S.; Dixon, D.; Greenberg, B. Similar Stress Responses Are Elicited by Copper and Ultraviolet Radiation in the Aquatic Plant Lemna Gibba: Implication of Reactive Oxygen Species as Common Signals. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogt, T.; Gülz, P.-G.; Reznik, H. UV Radiation Dependent Flavonoid Accumulation of Cistus Laurifolius L. Z. Nat. C 1991, 46, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkby, T.; Bodvin, T.; Bøe, R.; Moy, F.; Olsen, H.; Rinde, E. Nasjonalt Program for Kartlegging Og Overvåking Av Biologisk Mangfold—Marint. Sluttrapport for Perioden 2007–2010; NIVA Report 6105; Norwegian Institute for Water Research: Oslo, Norway, 2011; ISBN 978-82-577-5840-0. Available online: https://niva.brage.unit.no/niva-xmlui/handle/11250/215287 (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Merces—Marine Ecosystem Restoration in Changing European Seas. Available online: http://www.merces-project.eu/ (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Bekkby, T.; Rinde, E.; Erikstad, L.; Bakkestuen, V.; Longva, O.; Christensen, O.; Isæus, M.; Isachsen, P.E. Spatial Probability Modelling of Eelgrass (Zostera Marina) Distribution on the West Coast of Norway. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinde, E.; Rygg, B.; Bekkby, T.; Isæus, M.; Erikstad, L.; Sloreid, S.-E.; Longva, O. Documentation of Marine Nature Type Models Included in Directorate of Nature Management’s Database Naturbase. First Generation Models for the Municipalities Mapping of Marine Biodiversity 2007; Report LNR 5321-2006; Norwegian Institute for Water Research: Oslo, Norway, 2009; ISBN 82-577-5053-0. Available online: https://niva.brage.unit.no/niva-xmlui/handle/11250/213435 (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Bekkby, T.; Smit, C.; Gundersen, H.; Rinde, E.; Steen, H.; Tveiten, L.; Gitmark, J.K.; Fredriksen, S.; Albretsen, J.; Christie, H. The Abundance of Kelp Is Modified by the Combined Impact of Depth, Waves and Currents. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekkby, T.; Moy, F.E.; Olsen, H.; Rinde, E.; Bodvin, T.; Bøe, R.; Steen, H.; Grefsrud, E.S.; Espeland, S.H.; Pedersen, A.; et al. The Norwegian Programme for Mapping of Marine Habitats—Providing Knowledge and Maps for ICZMP. In Global Challenges in Integrated Coastal Zone Management; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bekkby, T.; Moy, F.E. Developing Spatial Models of Sugar Kelp (Saccharina Latissima) Potential Distribution under Natural Conditions and Areas of Its Disappearance in Skagerrak. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 95, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norderhaug, K.M.; Christie, H.; Rinde, E.; Gundersen, H.; Bekkby, T. Importance of Wave and Current Exposure to Fauna Communities in Laminaria Hyperborea Kelp Forests. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 502, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, M.F.; Nejrup, L.B.; Fredriksen, S.; Christie, H.; Norderhaug, K.M. Effects of Wave Exposure on Population Structure, Demography, Biomass and Productivity of the Kelp Laminaria Hyperborea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 451, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinde, E.; Christie, H.; Fagerli, C.W.; Bekkby, T.; Gundersen, H.; Norderhaug, K.M.; Hjermann, D.Ø. The Influence of Physical Factors on Kelp and Sea Urchin Distribution in Previously and Still Grazed Areas in the NE Atlantic. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eriksson, B.K.; Sandström, A.; Isæus, M.; Schreiber, H.; Karås, P. Effects of Boating Activities on Aquatic Vegetation in the Stockholm Archipelago, Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isæus, M.; Rygg, B. Wave Exposure Calculations for the Finnish Coast; NIVA Report LNR 5075-2005; Norwegian Institute for Water Research: Oslo, Norway, 2005; ISBN 82-577-4780-7. Available online: https://niva.brage.unit.no/niva-xmlui/handle/11250/212934 (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Wijkmark, N.; Isæus, M. Baltic Sea Wave Exposure Calculations for the Baltic Sea; AquaBiota Report 2010:2; AquaBiota Water Research: Stockholm, Sweden, 2010; ISBN 978-91-85975-07-5. Available online: https://www.aquabiota.se/wp-content/uploads/ABWR_Report_2010_02_BaltExp.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2021).








| Location 1 | Compound 2 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZA | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | RA | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Vestfold (A) (59° N 10° E) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||
| Hordaland (B) (60° N 5° E) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||
| Møre and Romsdal (C-L) (~63° N 7° E) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Finnmark (M, N) (~70° N 27° E) | t | + | + | + | + | + | + | t | + | + | + | t | |
| ZA | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | RA | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | TF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 3.12 ± 0.10 | 0.41 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 0.74 ± 0.23 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.83 ± 0.07 | 1.13 ± 0.12 | 3.92 ± 0.42 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 10.23 ± 0.77 | |||
| B | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 3.36 ± 0.11 | 0.59 ± 0.02 | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.51 ± 0.08 | 2.07 ± 0.18 | 2.02 ± 0.20 | 0.75 ± 0.04 | 9.49 ± 0.60 | ||||
| C1 | 0.05 ± 0.001 | 2.21 ± 0.29 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | <0.01 | 0.73 ± 0.12 | 0.76 ± 0.09 | 0.96 ± 0.22 | 0.33 ± 0.05 | 4.58 ± 0.69 | ||||
| C2 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 3.05 ± 0.18 | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 0.58 ± 0.14 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 1.73 ± 0.13 | 1.49 ±0.17 | 2.56 ± 0.4 | 0.88 ± 0.08 | 9.18 ± 1.02 | |||
| C3 | 0.03 ± 0.002 | 1.84 ± 0.14 | 0.19±0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.81 ± 0.08 | 0.67 ± 0.13 | 0.55 ± 0.13 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 3.61 ± 0.51 | ||||
| D1 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 4.73 ± 0.22 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.96 ± 0.14 | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.35 ± 0.05 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 6.03 ± 0.39 | ||||
| D2 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 5.45 ± 0.17 | 0.46 ± 0.02 | 0.74 ± 0.21 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.50 ± 0.06 | 0.38 ± 0.07 | 1.01 ± 0.19 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 8.14 ± 0.67 | ||||
| E1 | 0.05 ± 0.003 | 2.18 ± 0.11 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | <0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.07 | 1.16 ± 0.21 | 0.74 ± 0.21 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | 4.70 ± 0.59 | ||||
| E2 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 2.97 ± 0.11 | 0.38 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | <0.01 | 0.31 ± 0.08 | 0.90 ± 0.14 | 0.78 ± 0.15 | 0.39 ± 0.04 | 5.51 ± 0.51 | ||||
| F1 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 3.25 ± 0.10 | 0.23 ± 0.003 | 0.40 ± 0.09 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 1.24 ± 0.17 | 1.31 ± 0.13 | 0.84 ± 0.09 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 6.61 ± 0.39 | |||
| F2 | 0.08 ± 0.004 | 2.76 ± 0.16 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.05 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.06 | 1.00 ± 0.15 | 0.32 ± 0.08 | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 4.65 ± 0.49 | ||||
| G1 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 3.51 ± 0.17 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 1.28 ± 0.15 | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 0.13 ± 0.003 | 1.41± 0.04 | 2.48 ± 0.07 | 1.63 ± 0.16 | 0.59 ± 0.05 | 10.20 ± 0.35 | ||
| G2 | 0.38 ± 0.02 | 4.25 ± 0.08 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 1.46 ± 0.18 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 4.90 ± 0.11 | |||||
| H | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 4.60 ± 0.04 | 0.16 ± 0.003 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 1.80 ± 0.05 | 0.75 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 5.83 ± 0.07 | ||||
| I | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 4.71 ± 0.07 | 0.27 ± 0.003 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 4.53 ± 0.31 | 0.12 ± 0.005 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 5.84 ± 0.05 | |||||
| J1 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 2.42 ± 0.21 | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.47 ± 0.11 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 1.20 ± 0.06 | 1.36 ± 0.17 | 1.03 ± 0.17 | 0.47 ± 0.06 | 6.08 ± 0.74 | ||||
| J2 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 3.78 ± 0.38 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.06 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.73 ± 0.05 | 1.43 ± 0.22 | 0.40 ± 0.07 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 6.42 ± 0.77 | ||||
| K1 | 0.05 ± 0.002 | 2.87 ± 0.11 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 0.94 ± 0.13 | 0.25 ± 0.05 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 4.69 ± 0.38 | ||||
| K2 | 0.06 ± 0.005 | 3.08 ± 0.24 | 0.54 ± 0.06 | 0.17 ± 0.06 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.79 ± 0.20 | 0.92 ± 0.18 | 0.47 ± 0.11 | 0.31 ± 0.05 | 5.52 ± 0.70 | ||||
| K3 | 0.01 ± 0.002 | 4.87 ± 0.12 | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 0.33 ± 0.08 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.32 ± 0.10 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.87 ± 0.11 | 6.84 ± 0.31 | |||||
| K4 | 0.09 ± 0.002 | 3.13 ± 0.19 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.06 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 1.44 ± 0.11 | 1.14 ± 0.16 | 0.62 ± 0.09 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 6.05 ± 0.56 | |||
| L | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 3.40 ± 0.19 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.08 | 0.41 ± 0.07 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 4.76 ± 0.42 | ||||
| M | <0.01 | 0.84 ± 0.14 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 1.40 ± 0.24 | 2.35 ± 0.41 | ||||||
| N | <0.01 | 1.83 ± 0.09 | 0.06 ± 0.005 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 1.37 ± 0.20 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.31 ± 0.06 | <0.01 | 0.86 ± 0.14 | 3.58 ± 0.35 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | <0.01 | 7.57 ± 0.58 |
| Variables | Depth | Wave Exposure | Rosmarinic Acid (RA) | Zosteric Acid (ZA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth | 1 | −0.11 | 0.52 | −0.47 |
| Wave exposure | 1 | 0.79 | 0.93 | |
| Rosmarinic acid (RA) | 1 | 0.51 | ||
| Zosteric acid (ZA) | 1 |
| Collection Sites | Region, Municipality | Latitude | Longitude | Depth (cm) | Wave Exposure (m2/s) | Wave Exposure Class | Meadow Position | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Ølbergholmen south | Vestfold, Larvik | 59.00681 | 10.13163 | 50 | 34,131 | Sheltered | P |
| B | Espegrend | Hordaland, Bergen | 60.16120 | 5.13203 | 40–100 | 3739 | Extremely sheltered | P |
| C1 | Inner Sykkylvsfjorden | Møre and Romsdal, Sykkylven | 62.34095 | 6.58465 | 580 | 3334 | Extremely sheltered | C |
| C2 | 62.34150 | 6.58665 | 90 | 3357 | Extremely sheltered | P | ||
| C3 | 62.34428 | 6.58472 | 350 | 3333 | Extremely sheltered | P | ||
| D1 | Volsund | Møre and Romsdal, Herøy | 62.36319 | 5.66683 | 280 | 9561 | Very sheltered | C |
| D2 | 62.36387 | 5.66637 | 160 | 6332 | Very sheltered | P | ||
| E1 | Hjartevika, Sykkylvsfjorden | Møre and Romsdal, Sykkylven | 62.37240 | 6.57199 | 300 | 4253 | Very sheltered | C |
| E2 | 62.37267 | 6.57237 | 250 | 4120 | Very sheltered | C | ||
| F1 | Bøleira, Innfjorden | Møre and Romsdal, Vestnes | 62.49767 | 7.55012 | 400 | 6003 | Very sheltered | n.r. |
| F2 | 62.49796 | 7.54864 | 250 | 6237 | Very sheltered | n.r. | ||
| G1 | Stormalen | Møre and Romsdal, Sandøy | 62.75238 | 6.48934 | 570 | 72,851 | Sheltered | C |
| G2 | 62.75089 | 6.48848 | 390 | 63,739 | Sheltered | C | ||
| H | Storholmen | Møre and Romsdal, Sandøy | 62.75439 | 6.40991 | 540 | 21,214 | Sheltered | C |
| I | Malesanden | Møre and Romsdal, Sandøy | 62.77301 | 6.47301 | 230 | 33,657 | Sheltered | C |
| J1 | Fannefjorden | Møre and Romsdal, Molde | 62.78916 | 7.71018 | 360 | 4050 | Very sheltered | n.r. |
| J2 | 62.78957 | 7.70725 | 140 | 4050 | Very sheltered | n.r. | ||
| K1 | Between Nautneset and Halsan (Gossa) | Møre and Romsdal, Aukra | 62.81113 | 6.91111 | 450 | 2690 | Extremely sheltered | C |
| K2 | 62.81136 | 6.91224 | 640 | 3177 | Extremely sheltered | C | ||
| K3 | 62.81137 | 6.91039 | 280 | 2788 | Extremely sheltered | P | ||
| K4 | 62.81167 | 6.91193 | 740 | 3257 | Extremely sheltered | P | ||
| L | Kalsvika, Bud | Møre and Romsdal, Sandøy | 62.90180 | 6.92823 | 320 | 51,652 | Sheltered | n.r. |
| M | Munkefjorden | Finnmark, South-Varanger, | 69.66068 | 29.51747 | 120–150 | 7449 | Very sheltered | P |
| N | Rafsbotn | Finnmark, Alta | 70.01454 | 23.48984 | 50 | 25,053 | Sheltered | P |
| Standard | Calibration Curve a | Test Range b | R2 | LOD b | LOQ b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luteolin 1 | Y = 27353x + 57.68 | 0.0048–0.367 | 0.9993 | 0.013 | 0.038 |
| Luteolin 2 | Y = 29977x + 63.33 | 0.0061–0.4891 | 0.9995 | 0.013 | 0.041 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sævdal Dybsland, C.; Bekkby, T.; Hasle Enerstvedt, K.; Kvalheim, O.M.; Rinde, E.; Jordheim, M. Variation in Phenolic Chemistry in Zostera marina Seagrass along Environmental Gradients. Plants 2021, 10, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020334
Sævdal Dybsland C, Bekkby T, Hasle Enerstvedt K, Kvalheim OM, Rinde E, Jordheim M. Variation in Phenolic Chemistry in Zostera marina Seagrass along Environmental Gradients. Plants. 2021; 10(2):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020334
Chicago/Turabian StyleSævdal Dybsland, Cecilie, Trine Bekkby, Kjersti Hasle Enerstvedt, Olav M. Kvalheim, Eli Rinde, and Monica Jordheim. 2021. "Variation in Phenolic Chemistry in Zostera marina Seagrass along Environmental Gradients" Plants 10, no. 2: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020334
APA StyleSævdal Dybsland, C., Bekkby, T., Hasle Enerstvedt, K., Kvalheim, O. M., Rinde, E., & Jordheim, M. (2021). Variation in Phenolic Chemistry in Zostera marina Seagrass along Environmental Gradients. Plants, 10(2), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020334