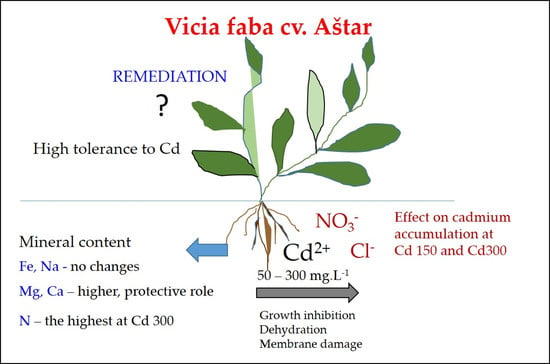
Effect of Cadmium Chloride and Cadmium Nitrate on Growth and Mineral Nutrient Content in the Root of Fava Bean (Vicia faba L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Cd on Germination of Seeds and Root Growth
2.2. Effect of Cd on the Mineral Content in Roots
2.3. Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
4.2. Determination of Seed Germination
4.3. Measurement of Growth Parameters
4.4. Determination of Cell Viability
4.5. Visualization of H2O2 with the Diaminobenzidine (DAB) Method
4.6. Detection of Mineral Elements in Roots
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, S.; Xiaoe Yang, X.; He, Z.; Baligar, V.C. Morphological and physiological responses of plants to cadmium toxicity: A review. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, T.A.; Popova, L.P. Functions and toxicity of cadmium in plants: Recent advances and future prospects. Turk. J. Bot. 2013, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohanová, J.; Martinka, M.; Vaculík, M.; White, P.J.; Hauser, M.T.; Lux, A. Root hair abundance impacts cadmium accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana shoots. Ann. Bot. 2018, 122, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazar, R.; Iqbal, N.; Mashood, A.; Khan, M.I.R.; Syeed, S.; Khan, N.A. Cadmium toxicity in plants and role of mineral nutrients in its alleviation. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 1476–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rucińska-Sobkowiak, R. Water relations in plants subjected to heavy metal stresses. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abedi, T.; Mojiri, A. Cadmium uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): An overview. Plants 2020, 9, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Heavy metal tolerance in plants: Role of transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and ionomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, S.; Liu, H.; Nie, Z.; Rengel, Z.; Gao, W.; Li, C.H.; Zhao, P. Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: A review. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzardo, C.; Tomasi, N.; Monte, R.; Varanini, Z.; Nocito, F.F.; Cesco, S.; Pinton, R. Cadmium inhibits the induction of high-affinity nitrate uptake in maize (Zea mays L.) roots. Planta 2012, 236, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Hamid, Y.; Zehrab, A.; Sahito, Z.A.; He, Z.; Hussaina, B.; Gurajala, H.K.; Yang, X. Characterization of fava bean (Vicia faba L.) genotypes for phytoremediation of cadmium and lead co-contaminated soils coupled with agro-production. Exotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronski, T.; Szubinska, S.; Jakubowski, M.; Pawlik, B. Cadmium availability to the cyanobacterium Synechocystis aquatilis in solutions containing chloride. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 76, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tůma, J.; Skalický, M.; Tůmova, L.; Flidr, J. Influence of cadmium dose and form on the yield of oat (Avena sativa L.) and the metal distribution in the plant. J. Elem. 2014, 19, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimek, J.; Tůma, J. Response of Phaseolus vulgaris plants to cadmium with different accompanying anions exposure. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2016, 25, 3781–3788. [Google Scholar]
- Hofslagare, O.; Samuelsson, G.; Sjoberg, S. Cadmium effects on photosynthesis and nitrate assimilation in Scendesmus obliquus. A potentiometric study in an open CO2 system. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1985, 25, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wege, S.; Gilliham, M.; Henderson, S.W. Chloride: Not simply a ‘cheap osmoticum’, but a beneficial plant macronutrient. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 3057–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenero-Flores, J.M.; Franco-Navarro, J.D.; Cubero-Font, P.; Peinado-Torrubia, P.; Rosales, M.A. Chloride as a beneficial macronutrient in higher plants: New roles and regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; 889p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidal, E.A.; Moyano, T.C.; Canales, J.; Gutierrez, R.A. Nitrogen control of developmental phase transitions in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5611–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souri, M.K.; Hatamian, M. Aminochelates in plant nutrition; a review. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Chen, R.; Fu, G.; Chen, T.; Tao, L. Excessive nitrate enhances cadmium (Cd) uptake by up-regulating the expression of OsIRT1 in rice (Oryza sativa). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 122, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; López-Lefebre, L.R.; García, P.C.; Rivero, R.M.; Ruiz, J.M.; Romero, L. Proline metabolism in response to highest nitrogen dosages in green bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Strike). J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 158, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Q.Y.; Sun, P.; Zhang, W.H. Ethylene is involved in nitrate-dependent root growth and branching in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, L.; Morère-Le Paven, M.-C.; Clochard, T.; Porcher, A.; Satour, P.; Mojović, M.; Vidović, M.; Limami, A.M.; Montrichard, F. Nitrate inhibits primary root growth by reducing accumulation of reactive oxygen species in the root tip in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 146, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.Z.; Wang, T.; Han, G.J.; Li, J.X.; Chen, N.L. Effects of intercropping and accompanying anion fertilizer on Cd uptake by Brassica campestris L. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2013, 21, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.; McLaughlin, M.; Tiller, K. Influence of chloride on Cd availability to Swiss chard: A resin buffered solution culture system. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1443–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.; McLaughlin, M.J. Effect of Cl on Cd uptake by Swiss chard in nutrient solutions. Plant Soil 1996, 179, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, Š.; Arčon, I.; Kump, P.; Nečemer, M.; Vogel-Mikuš, K. Influence of CdCl2 and CdSO4 supplementation on Cd distribution and ligand environment in leaves of the Cd hyperaccumulator Noccaea (Thlaspi) praecox. Plant Soil 2013, 370, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasafi, T.E.; Nouri, M.; Bouda, S.; Haddioui, A. The Effect of Cd, Zn and Fe on seed germination and early seedling growth of wheat and bean. Ekológia 2016, 35, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahoui, S.; Chaoui, A.; El Ferjani, E. Differential sensitivity to cadmium in germinating seeds of three cultivars of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2008, 30, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapustka, L.A.; Lipton, J.; Galbraith, H.; Cacela, D.; Lejeune, K. Metal and arsenic impacts to soil, vegetation communities and wildlife habitat in southwest Montana uplands contaminated by smelter emissions: II. Laboratory phytotoxicity studies. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 1995, 14, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Gao, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, R.; Zhao, J.; You, J. Changes in element accumulation, phenolic metabolism, and antioxidative enzyme activities in the red-skin roots of Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 41, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, A.J.; Zhang, X.H.; Chen, M.M.; Cao, Q. Oxidative stress and DNA damages induced by cadmium accumulation. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piršelová, B.; Kuna, R.; Lukáč, P.; Havrlentová, M. Effect of cadmium on growth, photosynthesis pigments, iron and cadmium accumulation of faba bean (Vicia faba cv. Aštar), Agriculture 2016, 62, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, H.M.; Huang, X. Inhibition of root meristem growth by cadmium involves nitric oxide-mediated repression of auxin accumulation and signalling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holubek, R.; Deckert, J.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Vergel, K.; Frontasyeva, M.; Sirotkin, A.; Bajia, D.S.; Chmielowska-Bak, J. The recovery of soybean plants after short-term cadmium stress. Plants 2020, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Khan, J.; Hayat, K.; Elateeq, A.A.; Salam, U.; Yu, B.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, Z.H. Comparative study of growth, cadmium accumulation and tolerance of three chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars. Plants 2020, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lux, A.; Martinka, M.; Vaculík, M.; Philip, J.W. Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: A review. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merkl, N.; Schultze-Kraft, R.; Infante, C. Phytoremediation in the tropics influence of heavy crude oil on root morphological characteristics of graminoids. Environ.Pollut. 2005, 138, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, N.D.; Cholewa, E.; Ryser, P. Effects of combined drought and heavy metal stresses on xylem structure and hydraulic conductivity in red maple (Acer rubrum L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5957–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kováčik, J.; Klejdus, B.; Štork, F.; Hedbavny, J. Nitrate deficiency reduces cadmium and nickel accumulation in chamomile plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5139–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsova, E.; Dobrikova, A.; Stefanov, M.; Misheva, S.; Bardáčová, M.; Matušíková, I.; Žideková, L.; Blehová, A.; Apostolova, E. Effects of cadmium on two wheat cultivars depending on different nitrogen supply. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.; Marques, T.; Soares, A. Cadmium effects on mineral nutrition of the Cd hyperaccumulator Pfaffia glomerata. Biologia 2013, 68, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, Q.Q.; Guan, M.Y.; Lu, K.X.; Du, S.T.; Fan, S.K.; Ye, Y.Q.; Lin, X.Y.; Jin, C.W. Inhibition of nitrate transporter 1.1-controlled nitrate uptake reduces cadmium uptake in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.Y.; Fan, S.K.; Fang, X.Z.; Jin, C.W. Modification of nitrate uptake pathway in plants affects the cadmium uptake by roots. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e990794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jian, S.; Luo, J.; Liao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Guan, C.; Zhang, Z. NRT1.1 Regulates nitrate allocation and cadmium tolerance in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Wang, A.; Liu, Z.; Gendall, A.R.; Rochfort, S.; Tang, C. Sodium chloride decreases cadmium accumulation and changes the response of metabolites to cadmium stress in the halophyte Carpobrotus rossii. Ann. Bot. 2018, 122, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Souguir, D.; Hörmann, G.; Hachicha, M. Salinity decreases cadmium accumulation in Vicia faba. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18893–18901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muradoglu, F.; Gundogdu, M.; Ercisli, S.; Encu, T.; Balta, F.; Jaafar, H.Z.E.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M. Cadmium toxicity affects chlorophyll a and b content, antioxidant enzyme activities and mineral nutrient accumulation in strawberry. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thor, K. Calcium-Nutrient and Messenger. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.A.A.; Vega, A.; Bouguyon, E.; Krouk, G.; Gojon, A.; Coruzzi, G.; Gutiérrez, R.A.A. Nitrate transport, sensing, and responses in plants. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 837–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudo, H.; Kudo, K.; Uemura, M.; Kawai, S. Magnesium inhibits cadmium translocation from roots to shoots rather than the uptake from roots, in barley. Botany 2015, 93, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Gong, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Bashir, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Xu, P.; Cheng, M.; et al. Effects of calcium at toxic concentrations of cadmium in plants. Planta 2017, 245, 863–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milone, M.T.; Sgherri, C.; Clijsters, H.; Navari-Izzo, F. Antioxidative responses of wheat treated with realistic concentration of cadmium. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2003, 50, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.; He, Q.; Khan, M.D.; Zhu, S. Characterization of physiological traits, yield and fiber quality in three upland cotton cultivars grown under cadmium stress. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2012, 6, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Hédiji, H.; Djebali, W.; Belkadhi, A.; Cabasson, C.; Moing, A.; Rolin, D.; Brouquisse, R.; Gallusci, P.; Chaïbi, W. Impact of long-term cadmium exposure on mineral content of Solanum lycopersicum plants: Consequences on fruit production. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 97, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Bai, X.Y.; Dong, Y.J.; Chen, W.F.; Song, Y.L.; Tian, X.Y. Effects of application of exogenous NO on the physiological characteristics of perennial ryegrass grown in Cd-contaminated soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 16, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibril, S.A.; Hassan, S.A.; Ishak, C.F.; Megat Wahab, P.E. Cadmium toxicity affects phytochemicals and nutrient elements composition of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Adv. Agric. 2017, 1236830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Ballesta, M.C.; Egea-Gilabert, C.; Conesa, E.; Ochoa, J.; Vicente, M.J.; Franco, J.A.; Bañon, S.; Martínez, J.J.; Fernández, J.A. The importance of ion homeostasis and nutrient status in seed development and germination. Agronomy 2020, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkins, D.A. The measurement of tolerance to edaphic factors by means of root length. New Phytol. 1978, 80, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.J.; Mock, N.M. An improved method for monitoring cell death in cell suspension and leaf disc assays using Evans blue. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 1994, 39, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thordal-Christensen, H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Wei, Y.D.; Collinge, D.B. Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants. H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley-powdery mildew interaction. Plant J. 1997, 11, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Applied Form of Cd2+ | Concentration of Cd2+ (mg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 300 | |
| Nitrate | 100 | 97 | 98 | 100 | 98 |
| Chloride | 99 | 100 | 99 | 98 | 99 |
| Cd Doses | RL | FW | DW | EB | RD | Cd | Fe | N | Ca | Mg | Na | H2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd doses | 1 | ||||||||||||
| RL | −1.00 | 1 | |||||||||||
| FW | −0.99 | 0.98 | 1 | ||||||||||
| DW | −0.97 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 1 | |||||||||
| EU | 0.97 | −0.98 | −0.94 | −0.88 | 1 | ||||||||
| RD | 0.99 | −0.98 | −0.99 | −0.99 | 0.92 | 1 | |||||||
| Cd | 0.99 | −0.98 | −1.00 | −0.99 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 1 | ||||||
| Fe | 0.52 | −0.56 | −0.44 | −0.31 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 1 | |||||
| N | 0.98 | −0.97 | −1.0 | −0.98 | 0.91 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.34 | 1 | ||||
| Ca | 0.98 | −0.98 | −0.99 | −0.98 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.47 | 0.96 | 1 | |||
| Mg | 0.981 | −0.98 | −0.97 | −0.93 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.65 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 1 | ||
| Na | 0.46 | −0.48 | −0.42 | −0.33 | 0.59 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.90 | 0.26 | 0.49 | 0.62 | 1 | |
| H2O | −0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.99 | −0.93 | −0.99 | −0.99 | −0.43 | −0.98 | −0.99 | −0.97 | −0.42 | 1 |
| Cd Doses | RL | FW | DW | EB | RD | Cd | Fe | N | Ca | Mg | Na | H2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd doses | – | ||||||||||||
| RL | −1.00 | – | |||||||||||
| FW | −0.99 | 0.99 | – | ||||||||||
| DW | −0.97 | 0.98 | 1.00 | – | |||||||||
| EU | 1.00 | −1.00 | −0.99 | −0.97 | – | ||||||||
| RD | 0.95 | −0.94 | −0.89 | −0.85 | 0.95 | – | |||||||
| Cd | 0.97 | −0.98 | −1.00 | −1.00 | 0.98 | 0.86 | – | ||||||
| Fe | 0.45 | −0.48 | −0.55 | −0.61 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.59 | – | |||||
| N | 0.58 | −0.62 | −0.69 | −0.75 | 0.59 | 0.33 | 0.74 | 0.65 | – | ||||
| Ca | 0.95 | −0.96 | −0.98 | −0.99 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.99 | 0.59 | 0.81 | – | |||
| Mg | 0.99 | −0.99 | −1.00 | −0.99 | 0.99 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 0.97 | – | ||
| Na | 0.52 | −0.56 | −0.64 | −0.71 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 0.75 | 0.63 | – | |
| H2O | −0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | −0.99 | −0.90 | −1.00 | −0.54 | −0.68 | −0.98 | −1.00 | −0.63 | – |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piršelová, B.; Ondrušková, E. Effect of Cadmium Chloride and Cadmium Nitrate on Growth and Mineral Nutrient Content in the Root of Fava Bean (Vicia faba L.). Plants 2021, 10, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10051007
Piršelová B, Ondrušková E. Effect of Cadmium Chloride and Cadmium Nitrate on Growth and Mineral Nutrient Content in the Root of Fava Bean (Vicia faba L.). Plants. 2021; 10(5):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10051007
Chicago/Turabian StylePiršelová, Beáta, and Emília Ondrušková. 2021. "Effect of Cadmium Chloride and Cadmium Nitrate on Growth and Mineral Nutrient Content in the Root of Fava Bean (Vicia faba L.)" Plants 10, no. 5: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10051007
APA StylePiršelová, B., & Ondrušková, E. (2021). Effect of Cadmium Chloride and Cadmium Nitrate on Growth and Mineral Nutrient Content in the Root of Fava Bean (Vicia faba L.). Plants, 10(5), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10051007