New Phenolic Compounds in Posidonia oceanica Seagrass: A Comprehensive Array Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
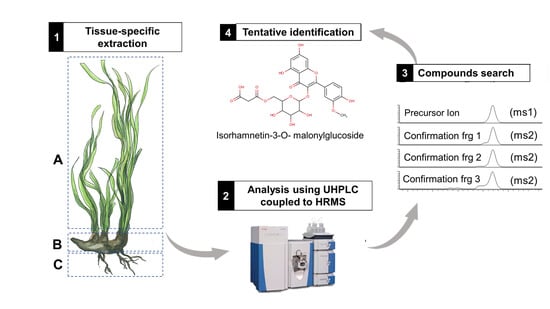
2.1. Extraction Procedure
2.2. Chromatographic Conditions
2.3. Phenolic Identification
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Sampling
3.2. Sample Pre-Treatment
3.3. Chemical and Reagents
3.4. Extraction Procedure
3.5. Chromatographic Conditions
3.6. Orbitrap-MS Analysis
3.7. Phenolic Identification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EEC, 1992. Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. Off. J. Eur. 1992, 206, 7–50. [Google Scholar]
- Campagne, C.S.; Salles, J.M.; Boissery, P.; Deter, J. The seagrass Posidonia oceanica: Ecosystem services identification and economic evaluation of goods and benefits. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 97, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pergent, G.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Boudouresque, C.F. Utilisation de l’herbier à Posidonia oceanica comme indicateur biologique de la qualité du milieu littoral en Méditerranée: État des connaissances. Mésogée 1995, 54, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Bernard, G.; Pergent, G.; Shili, A.; Verlaque, M. Regression of Mediterranean seagrasses caused by natural processes and anthropogenic disturbances and stress: A critical review. Bot. Mar. 2009, 52, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.M.; Romero, J. Effects of disturbances caused by coastal constructions on spatial structure, growth dynamics and photosynthesis of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, I.; Focaracci, F.; Cerfolli, F.; Papetti, P. Relationships between trace elements in Posidonia oceanica shoots and in sediment fractions along Latium coasts (northwestern Mediterranean Sea). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannac, M.; Ferrat, L.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Pergent, G.; Pasqualini, V. Effects of fish farming on flavonoids in Posidonia oceanica. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergent, G.; Boudouresque, C.-F.; Dumay, O.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Wyllie-Echeverria, S. Competition between the invasive macrophyte Caulerpa taxifolia and the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: Contrasting strategies. BMC Ecol. 2008, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccherelli, G.; Oliva, S.; Pinna, S.; Piazzi, L.; Procaccini, G.; Marin-Guirao, L.; Dattolo, E.; Gallia, R.; La Manna, G.; Gennaro, P.; et al. Seagrass collapse due to synergistic stressors is not anticipated by phenological changes. Oecologia 2018, 186, 1137–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, A.; Förster, N.; Zander, M.; Ulrichs, C. Compound-specific responses of phenolic metabolites in the bark of drought-stressed Salix daphnoides and Salix purpurea. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.I.; Zhang, W.; Son, J.E. Optimal Duration of Drought Stress Near Harvest for Promoting Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity in Kale with or without UV-B Radiation in Plant Factories. Plants 2020, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, I.; Domínguez, I.; Morales-Diaz, N.; Escribano, M.I.; Merodio, C.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T. Regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis pathway by a single or dual short-term CO2 treatment in black table grapes stored at low temperature. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Ghimire, B.K.; Kim, S.-H.; Yu, C.Y.; Oh, D.-H.; Chelliah, R.; Kwon, C.; Kim, Y.-J.; Chung, I.M. Assessment of Mineral and Phenolic Profiles and Their Association with the Antioxidant, Cytotoxic Effect, and Antimicrobial Potential of Lycium chinense Miller. Plants 2020, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornara, L.; Pastorino, G.; Borghesi, B.; Salis, A.; Clericuzio, M.; Marchetti, C.; Damonte, G.; Burlando, B. Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile Ethanolic Extract Modulates Cell Activities with Skin Health Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haznedaroglu, M.Z.; Zeybek, U. HPLC Determination of Chicoric Acid in Leaves of Posidonia oceanica. Pharm. Biol. 2007, 45, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, S.; Desjobert, J.-M.; Pergent, G. Distribution of phenolic compounds in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grignon-Dubois, M.; Rezzonico, B. Phenolic fingerprint of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica from four locations in the Mediterranean Sea: First evidence for the large predominance of chicoric acid. Bot. Mar. 2015, 58, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumay, O.; Costa, J.; Desjobert, J.; Pergent, G. Variations in the concentration of phenolic compounds in the seagrass under conditions of competition. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariello, L.; Zanetti, L.; De Stefano, S. Posidonia ecosystem—V. Phenolic compounds from marine phanerogames, Cymodocea nodosa and Posidonia oceanica. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1979, 62, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Rotini, A.; Randazzo, D.; Albanese, N.N.; Giallongo, A. Phenols content and 2-D electrophoresis protein pattern: A promising tool to monitor Posidonia meadows health state. BMC Ecol. 2007, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rotini, A.; Belmonte, A.; Barrote, I.; Micheli, C.; Peirano, A.; Santos, R.O.; Silva, J.; Migliore, L. Effectiveness and consistency of a suite of descriptors for assessing the ecological status of seagrass meadows (Posidonia oceanica L. Delile). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaal, J.; Serrano, O.; del Río, J.C.; Rencoret, J. Radically different lignin composition in Posidonia species may link to differences in organic carbon sequestration capacity. Org. Geochem. 2018, 124, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.; Yu, N.; Toyama, T.; Inoue, D.; Sei, K.; Ike, M. Accelerated degradation of a variety of aromatic compounds by Spirodela polyrrhiza-bacterial associations and contribution of root exudates released from S. polyrrhiza. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, H.; Wen, B. Effects of maize root exudates and organic acids on the desorption of phenanthrene from soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechri, B.; Tekaya, M.; Hammami, M.; Chehab, H. Root verbascoside and oleuropein are potential indicators of drought resistance in olive trees (Olea europaea L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaal, J.; Serrano, O.; Nierop, K.G.J.; Schellekens, J.; Martínez Cortizas, A.; Mateo, M.-Á. Molecular composition of plant parts and sediment organic matter in a Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) mat. Aquat. Bot. 2016, 133, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giambanelli, E.; Filippo D’Antuono, L.; Romero-González, R.; Garrido Frenich, A. Identification and quantification of phenolic compounds in edible wild leafy vegetables by UHPLC/Orbitrap-MS. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gutiérrez, N.; Romero-González, R.; Garrido Frenich, A.; Martínez Vidal, J.L. Identification and quantification of the main isoflavones and other phytochemicals in soy based nutraceutical products by liquid chromatography–orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1348, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gutiérrez, N.; Romero-González, R.; Plaza-Bolaños, P.; Martínez Vidal, J.L.; Garrido Frenich, A. Identification and quantification of phytochemicals in nutraceutical products from green tea by UHPLC-Orbitrap-MS. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuny, P.; Serve, L.; Jupin, H.; Boudouresque, C.F. Water soluble phenolic compounds of the marine phanerogam Posidonia oceanica in a Mediterranean area colonised by the introduced chlorophyte Caulerpa taxifolia. Aquat. Bot. 1995, 52, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, E.; Ramazzotti, M.; Fratianni, F.; Pessani, D.; Degl’Innocenti, D. Hydrophilic extract from Posidonia oceanica inhibits activity and expression of gelatinases and prevents HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cell line invasion. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, C.; Parrot, D.; Wiese, J.; Sönnichsen, F.D.; Saha, M.; Tasdemir, D.; Weinberger, F. Identification of rosmarinic acid and sulfated flavonoids as inhibitors of microfouling on the surface of eelgrass Zostera marina. Biofouling 2017, 33, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harborne, J.B.; Williams, C.A. Occurrence of sulphated flavones and caffeic acid esters in members of the fluviales. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1976, 4, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhashini, P.; Dilipan, E.; Thangaradjou, T.; Papenbrock, J. Bioactive natural products from marine angiosperms: Abundance and functions. Nat. Prod. Bioprospecting 2013, 3, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grignon-Dubois, M.; Rezzonico, B. Phenolic chemistry of the seagrass Zostera noltei Hornem. Part 1: First evidence of three infraspecific flavonoid chemotypes in three distinctive geographical regions. Phytochemistry 2018, 146, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, I.; Arrebola, F.J.; Martínez Vidal, J.L.; Garrido Frenich, A. Assessment of wastewater pollution by gas chromatography and high resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1619, 460964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klejdus, B.; Lojková, L.; Plaza, M.; Šnóblová, M.; Štěrbová, D. Hyphenated technique for the extraction and determination of isoflavones in algae: Ultrasound-assisted supercritical fluid extraction followed by fast chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7956–7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviranta, N.M.; Anttonen, M.J.; von Wright, A.; Karjalainen, R.O. Red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) isoflavones: Determination of concentrations by plant stage, flower colour, plant part and cultivar. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.M.; Barrote, I.; Silva, J.; Olivé, I.; Alexandre, A.; Albano, S.; Santos, R. Epiphytes Modulate Posidonia oceanica Photosynthetic Production, Energetic Balance, Antioxidant Mechanisms, and Oxidative Damage. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| RT (min) | Compound Name | Elemental Composition | Polarity | Theoretical Mass (m/z) | Mass Error (ppm) | Fragment 1 (m/z) | Fragment 2 (m/z) | Fragment 3 (m/z) | Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.3 | Catechin (+) [31] | C15H14O6 | ESI+ | 291.08631 | 0.080 | 139.03895 | 123.04502 | ● ■ ◊ | |
| 14.9 | Caffeic acid [17,19] | C9H8O4 | ESI− | 179.03498 | −0.127 | 135.04429 | 134.03628 | 89.03847 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 16.1 | Epicatechin (−) [31] | C15H14O6 | ESI+ | 291.08631 | 0.122 | 139.03895 | 123.04502 | ● ■ ◊ | |
| 16.3 | Genistein * | C15H10O5 | ESI+ | 271.06010 | 0.189 | 153.01779 | 215.06962 | 243.06434 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 16.3 | Baicalein * | C15H10O5 | ESI+ | 271.06010 | 0.056 | 253.04950 | 243.06520 | ● ■ ◊ | |
| 16.9 | Eriodictyol * | C15H12O6 | ESI− | 287.05611 | 1.633 | 151.00235 | 107.01253 | ● ■ ◊ | |
| 17.6 | p-Coumaric acid [8,15] | C9H8O3 | ESI− | 163.04007 | −0.362 | 119.04881 | 93.03316 | 163.03950 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 18.1 | Ferulic Acid [16,31] | C10H10O4 | ESI− | 193.05063 | −1.482 | 134.03643 | 149.06100 | 178.02640 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 19.6 | Quercetin-3-O-glucoside [14] | C21H20O12 | ESI− | 463.08710 | 0.821 | 300.02700 | 302.03696 | 301.03455 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 20.7 | Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside * + Luteolin-4’-O-glucoside * | C21H20O11 | ESI− | 447.09328 | 1.939 | 284.03200 | 255.02924 | 285.03995 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 20.8 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside [14] | C22H22O12 | ESI+ | 479.11840 | 0.646 | 317.06550 | ● ■ ◊ | ||
| 22.4 | Quercetin [7] | C15H10O7 | ESI+ | 303.04993 | 0.001 | 201.05453 | 153.01834 | 165.01837 | ● ■ |
| 23.2 | Naringenin * | C15H12O5 | ESI− | 271.06012 | 0.271 | 119.04879 | 151.00226 | 107.01350 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 23.4 | Luteolin * | C15H10O6 | ESI− | 285.04046 | 0.269 | 133.02834 | 151.00260 | 175.03898 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 26.3 | Isorhamnetin [7] | C16H12O7 | ESI− | 315.05103 | 2.013 | 300.02685 | 151.00245 | ● ■ ◊ | |
| 26.5 | Apigenin * | C15H10O5 | ESI+ | 271.06010 | −0.037 | 153.01779 | 119.04943 | ◊ | |
| 27.4 | Naringenin Chalcone * | C15H12O5 | ESI− | 271.06012 | 0.281 | 119.04879 | 151.00226 | 107.01350 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 30.6 | Pinocembrin * | C15H12O4 | ESI− | 255.06628 | 0.241 | 151.00241 | 213.05467 | ● ■ ◊ | |
| 30.7 | Biochanin A * | C16H12O5 | ESI− | 283.06120 | 1.142 | 268.03634 | ● ■ | ||
| 30.7 | Glycitein * | C16H12O5 | ESI+ | 285.07575 | −0.667 | 270.05097 | 242.05613 | ● ■ | |
| 33.3 | Galangin * | C15H10O5 | ESI− | 269.04555 | 0.068 | 213.05450 | ● ◊ | ||
| 34.4 | Sakuranetin * + Isosakuranetin * | C16H14O5 | ESI− | 285.07685 | 1.844 | 119.04883 | 221.15330 | 165.01802 | ● ■ ◊ |
| RT (min) | Compound Name | Elemental Composition | Polarity | Theoretical Mass (m/z) | Mass Error (ppm) | Fragment 1 (m/z) | Fragment 2 (m/z) | Fragment 3 (m/z) | Tissue | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.6 | Protocatechualdehyde | C7H6O3 | ESI− | 137.02442 | −4.850 | 136.01660 | 108.02050 | 109.03050 | ● ■ ◊ | [16] |
| 13.1 | Zosteric acid@ | C9H8O6S | ESI− | 242.99688 | 0.371 | 163.04010 | 145.02950 | 117.03460 | ● ■ ◊ | [19,35] |
| 16.1 | p-Anisic acid | C8H8O3 | ESI− | 151.04007 | −1.210 | 133.02861 | 123.04398 | ● ■ ◊ | [16] | |
| 16.3 | Caftaric Acid | C13H12O9 | ESI− | 311.04086 | 1.437 | 130.99800 | 161.02390 | 267.05050 | ● ■ ◊ | [17] |
| 16.3 | Chicoric acid | C22H18O12 | ESI− | 473.07255 | 1.672 | 311.04071 | 293.02844 | 149.00810 | ● ■ ◊ | [14,19] |
| 17.7 | Fertaric acid | C14H14O9 | ESI− | 325.05651 | 1.658 | 193.05010 | 130.99800 | 87.00820 | ■ ◊ | [17] |
| 18.3 | Cinnamic Acid | C9H8O2 | ESI− | 147.04515 | −0.713 | 119.04916 | 117.03351 | 101.03851 | ● ■ | [15] |
| 19.9 | Quercetin-3-O-malonylglucoside | C24H22O15 | ESI− | 549.08859 | 1.007 | 505.10006 | 300.02737 | 301.03183 | ● ■ ◊ | [14] |
| 21.3 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-malonylglucoside | C25H24O15 | ESI− | 563.10424 | 2.148 | 459.09270 | 315.05050 | 299.01920 | ● ■ ◊ | [14] |
| RT (min) | Compound Name | Elemental Composition | Polarity | Theoretical Mass (m/z) | Mass Error (ppm) | Fragment 1 (m/z) | Fragment 2 (m/z) | Fragment 3 (m/z) | Fragment 4 (m/z) | Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.3 | Gambiriin A1 | C30H28O12 | ESI− | 579.15080 | 2.881 | 125.02390 | 289.07120 | 151.03950 | 139.03950 | ● ■ |
| 18.1 | Mascaroside | C26 H36 O11 | ESI− | 523.21849 | 1.447 | 361.16510 | 331.15450 | ● ■ ◊ | ||
| 18.3 | Astilbin | C21H22O11 | ESI− | 449.10893 | 1.575 | 151.00322 | 150.03022 | 303.05050 | 285.03990 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 18.9 | Tracheloside | C27 H34 O12 | ESI− | 549.19775 | 1.640 | 387.14440 | 357.13380 | ● ■ | ||
| 21.0 | Quercetin 3-O-sulfate | C15H10O10S | ESI− | 380.99219 | 0.372 | 301.03480 | 80.96460 | ● ■ ◊ | ||
| 33.7 | Glabridin | C20H20O4 | ESI− | 323.12888 | 1.317 | 187.07590 | 267.06570 | ◊ | ||
| 34.5 | Piceatannol | C14H12O4 | ESI+ | 245.08084 | 0.002 | 135.04460 | 215.07080 | 227.07080 | ● ■ ◊ | |
| 39.1 | Sophoraflavanone B | C20H20O5 | ESI− | 339.12380 | 1.093 | 219.06418 | 119.04871 | ● ■ ◊ | ||
| 40.7 | Tetrahydrocurcumin | C21H24O6 | ESI− | 372.15790 | 0.637 | 177.05520 | 193.08650 | 219.06570 | ● ■ ◊ | |
| 41.8 | Demethoxycurcumin | C20 H18 O5 | ESI− | 337.10815 | 1.836 | 119.04970 | 161.06030 | 175.03950 | 217.05010 | ● ■ ◊ |
| 45.3 | Xanthohumol | C21H22O5 | ESI− | 353.13945 | 1.155 | 207.10210 | 119.04900 | 145.02900 | ● ■ ◊ |
| Flavonoids | Phenolic Acids | Other Polyphenols | Total Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE3 | Leaf | 20 | 9 | 3 | 32 |
| Rhizome | 22 | 5 | 3 | 30 | |
| Root | 22 | 5 | 3 | 30 | |
| FAN7 | Leaf | 19 | 9 | 3 | 31 |
| Rhizome | 24 | 5 | 3 | 32 | |
| Root | 20 | 4 | 3 | 27 | |
| AL2x | Leaf | 21 | 9 | 3 | 33 |
| Rhizome | 21 | 5 | 3 | 29 | |
| Root | 21 | 5 | 3 | 29 | |
| AL3 | Leaf | 22 | 9 | 2 | 33 |
| Rhizome | 21 | 5 | 2 | 28 | |
| Root | 19 | 5 | 2 | 26 | |
| CG4 | Leaf | 23 | 8 | 3 | 34 |
| Rhizome | 23 | 5 | 3 | 31 | |
| Root | 24 | 5 | 3 | 32 | |
| Maximum | 24 | 9 | 3 | 34 |
| Site | Water Depth (m) | Location (WGS84_UTM) | Distance from Coast (m) | Area Description | Sampling Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE3 | 10.3 | 36.682721, −2.781700 | 670 | Limit between a harbor and a nature spot. Influenced by watershed with intensive agriculture (greenhouses) | 31 Oct 2019 |
| AL2x | 7.8 | 36.824655, −2.452103 | 80 | Touristic city, harbor | 18 Dec 2019 |
| AL3 | 7.8 | 36.828547, −2.385920 | 540 | Sewage, airport, and watercourse (seasonal) | 11 Nov 2019 |
| FAN7 | - | 36.835713, −2.352617 | - | Submarine natural gas pipeline (MEDGAZ) and watercourse (seasonal) | 2 Jul 2019 |
| CG4 | 1.5 | 36.862794, −2.003661 | 5 | Marine Protected Area | 5 Jan 2020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Astudillo-Pascual, M.; Domínguez, I.; Aguilera, P.A.; Garrido Frenich, A. New Phenolic Compounds in Posidonia oceanica Seagrass: A Comprehensive Array Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Plants 2021, 10, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050864
Astudillo-Pascual M, Domínguez I, Aguilera PA, Garrido Frenich A. New Phenolic Compounds in Posidonia oceanica Seagrass: A Comprehensive Array Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Plants. 2021; 10(5):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050864
Chicago/Turabian StyleAstudillo-Pascual, Marina, Irene Domínguez, Pedro A. Aguilera, and Antonia Garrido Frenich. 2021. "New Phenolic Compounds in Posidonia oceanica Seagrass: A Comprehensive Array Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry" Plants 10, no. 5: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050864
APA StyleAstudillo-Pascual, M., Domínguez, I., Aguilera, P. A., & Garrido Frenich, A. (2021). New Phenolic Compounds in Posidonia oceanica Seagrass: A Comprehensive Array Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Plants, 10(5), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050864