Pharmacological Exploration of Phenolic Compound: Raspberry Ketone—Update 2020
Abstract
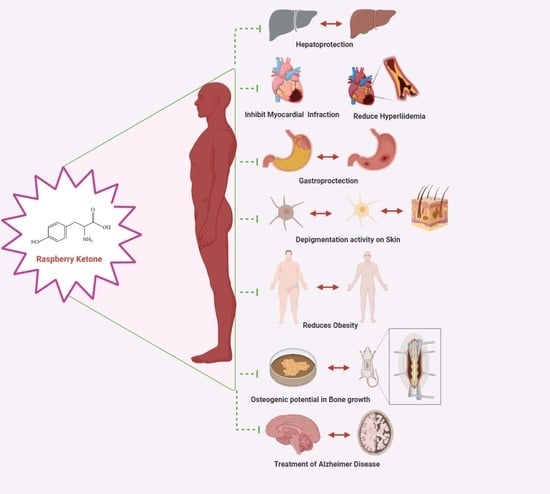
:1. Introduction to Raspberry Ketone
2. Potential Role of RK as a Hepatoprotection
3. Potential Role of RK as a Cardioprotectant
4. Potential Role of RK in the Treatment of Gastric Ulcers
5. Studies Exploring the Depigmenting Activity of RK
6. Potential Role of RK as an Anti-Obesity Agent
7. Potential Role of RK in Early Sexual Maturation
8. Potential Role of RK in Bone Regeneration
9. Pharmacokinetic (ADME) and Safety Profile of RK
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beekwilder, J.; van der Meer, I.M.; Sibbesen, O.; Broekgaarden, M.; Qvist, I.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Hall, R.D. Microbial production of natural raspberry ketone. Biotechnol. J. 2007, 2, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, H.E.; Abo-ELmatty, D.M.; Mesbah, N.M.; Saleh, S.M.; Ali, A.M.A.; Sakr, A.T. Raspberry ketone preserved cholinergic activity and antioxidant defense in obesity induced Alzheimer disease in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, Y.; Nagano, M.; Tsukamoto, K.; Futatsuka, M. In vitro studies on the depigmenting activity of 4-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone. J. Occup. Health 1998, 40, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milke, L.; Mutz, M.; Marienhagen, J. Synthesis of the character impact compound raspberry ketone and additional flavoring phenylbutanoids of biotechnological interest with Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, K.S. Raspberry ketone increases both lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1654–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosjek, B.; Stampfer, W.; Van Deursen, R.; Faber, K.; Kroutil, W. Efficient production of raspberry ketone via “green” biocatalytic oxidation. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 9517–9521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lloyd, N.D.R.; Pretorius, I.S.; Borneman, A.R. Heterologous production of raspberry ketone in the wine yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae via pathway engineering and synthetic enzyme fusion. Microb. Cell Factories 2016, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J. Further research on the biological activities and the safety of raspberry ketone is needed. NFS J. 2016, 2, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sporstøl, S.; Scheline, R.R. The metabolism of 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butan-2-one (raspberry ketone) in rats, Guinea-pigs and rabbits. Xenobiotica 1982, 12, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, C.; Satoh, Y.; Hara, M.; Inoue, S.; Tsujita, T.; Okuda, H. Anti-obese action of raspberry ketone. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, E.T.; Barakat, B.M.; ElSayed, M.H.; Tawfik, M.K. An optimized dose of raspberry ketones controls hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance in male obese rats: Effect on adipose tissue expression of adipocytokines and Aquaporin 7. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 832, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Yuan, B.; Kshatriya, D.; Polyak, A.; Simon, J.E.; Bello, N.T.; Wu, Q. Influence of Diet-Induced Obesity on the Bioavailability and Metabolism of Raspberry Ketone (4-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-Butanone) in Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1900907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, Y.; Akamatsu, M.; Hotta, Y.; Hosoda, A.; Tamura, H. Effect of essential oils, such as raspberry ketone and its derivatives, on antiandrogenic activity based on in vitro reporter gene assay. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2111–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Nagano, M.; Arimatsu, Y.; Futatsuka, M. An experimental study on depigmenting activity of 4-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone in C57 black mice. J. Occup. Health 1998, 40, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.B.; Jeong, H.J. Rheosmin, a naturally occurring phenolic compound inhibits LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression in RAW264.7 cells by blocking NF-κB activation pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2148–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.H.; Choi, C.-I. Potentials of Raspberry Ketone as a Natural Antioxidant. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of Liver Diseases in the World Introduction and Global Burden. Available online: http://www.ncdrisc.org/index.html (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Marcellin, P.; Kutala, B.K. Liver diseases: A major, neglected global public health problem requiring urgent actions and large-scale screening. In Liver International; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 38, pp. 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pulzi, F.B.U.; Cisternas, R.; Melo, M.R.; Ribeiro, C.M.F.; Malheiros, C.A.; Salles, J.E. New clinical score to diagnose nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in obese patients. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2011, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rector, R.S.; Thyfault, J.P.; Wei, Y.; Ibdah, J.A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the metabolic syndrome: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Zhang, F. Raspberry ketone protects rats fed high-fat diets against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouad, D.; Badr, A.; Attia, H.A. Hepatoprotective activity of raspberry ketone is mediated: Via inhibition of the NF-κB/TNF-α/caspase axis and mitochondrial apoptosis in chemically induced acute liver injury. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, S.M.; El-Khayat, Z.; Farrag, A.R.; Sayed, O.N.; El-Sayed, M.M.; Massoud, D. Hepatoprotective effect of Raspberry ketone and white tea against acrylamide-induced toxicity in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, Y. Chinese herbal medicine on cardiovascular diseases and the mechanisms of action. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ventura-Clapier, R.; Garnier, A.; Veksler, V.; Joubert, F. Bioenergetics of the failing heart. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orogo, A.M.; Gustafsson, Å.B. Cell death in the myocardium: My heart won’t go on. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gofman, J.W.; Young, W.; Tandy, R. Ischemic heart disease, atherosclerosis, and longevity. Circulation 1966, 34, 679–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ansari, M.A.; Iqubal, A.; Ekbbal, R.; Haque, S.E. Effects of nimodipine, vinpocetine and their combination on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, V.; Sharma, S.; Bhandari, U.; Ali, S.M.; Haque, S.E. Raspberry ketone protects against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Life Sci. 2018, 194, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleshin, S.; Reiser, G. Role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR)-α, β/δ and γ triad in regulation of reactive oxygen species signaling in brain. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 1553–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, V.; Sharma, S.; Bhandari, U.; Sharma, N.; Rishi, V.; Haque, S.E. Suppression of isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity in rats by raspberry ketone via activation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-α. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 842, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenen, M.J.M.; Kuipers, E.J.; Hansen, B.E.; Ouwendijk, R.J.T. Incidence of duodenal ulcers and gastric ulcers in a Western population: Back to where it started. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 23, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, M.; Mahata, T.; Chakraborti, S.; Kumar, P.; Bhattacharya, B.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K.; Das, M.; Stewart, A.; Saha, S.; Maity, B. Malabaricone C attenuates nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastric ulceration by decreasing oxidative/nitrative stress and inflammation and promoting angiogenic autohealing. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 766–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, Á.; Carrera-Lasfuentes, P.; Arguedas, Y.; García, S.; Bujanda, L.; Calvet, X.; Ponce, J.; Perez-Aísa, Á.; Castro, M.; Muñoz, M.; et al. Risk of upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiplatelet agents, or anticoagulants. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 906–912.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigthorsson, G.; Tibble, J.; Hayllar, J.; Menzies, I.; MacPherson, A.; Moots, R.; Scott, D.; Gumpel, M.J.; Bjarnason, I. Intestinal permeability and inflammation in patients on NSAIDs. Gut 1998, 43, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silverstein, F.E.; Graham, D.Y.; Senior, J.R.; Davies, H.W.; Struthers, B.J.; Bittman, R.M.; Geis, G.S. Misoprostol reduces serious gastrointestinal complications in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1995, 123, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Triadafilopoulos, G. Epidemiology of NSAID induced gastrointestinal complications. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1999, 56, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Malmi, H.; Kautiainen, H.; Virta, L.J.; Färkkilä, N.; Koskenpato, J.; Färkkilä, M.A. Incidence and complications of peptic ulcer disease requiring hospitalisation have markedly decreased in Finland. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmood, B. Profiling of major fatty acids in different raw and roasted sesame seeds cultivars. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 6619–6623. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, A.M.; EL-Orabi, N.F.; Ali, R.A. The implication of the crosstalk of Nrf2 with NOXs, and HMGB1 in ethanol-induced gastric ulcer: Potential protective effect is afforded by Raspberry Ketone. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, N.G.W. Omeprazole; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020.
- Lin, V.C.-H.; Ding, H.-Y.; Kuo, S.-Y.; Chin, L.-W.; Wu, J.-Y.; Chang, T.-S. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo depigmenting activity of raspberry ketone from Rheum officinale. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 4819–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, T.S.; Lin, M.Y.; Lin, H.J. Identifying 8-hydroxynaringenin as a suicide substrate of mushroom tyrosinase. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2010, 61, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.Y.; Chang, T.S.; Shen, H.C.; Tai, S.S.K. Murine tyrosinase Inhibitors from Cynanchum bungei and evaluation of in vitro and in vivo depigmenting activity. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Hinoshita, M.; Suzuki, E.; Ojika, M.; Wakamatsu, K. Tyrosinase-catalyzed oxidation of the leukoderma-inducing agent raspberry ketone produces (E)-4-(3-Oxo-1-butenyl)-1, 2-benzoquinone: Implications for melanocyte toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.B. The effect of obesity on health outcomes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 316, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yao, J.; Ji, G.; Qian, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Tian, J.; Nie, Y.; Gold, M.S.; et al. Obesity: Pathophysiology and intervention. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5153–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarpellini, E.; Tack, J. Obesity and metabolic syndrome: An inflammatory condition. Dig. Dis. 2012, 30, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Chen, L.; Mo, H.; Shastri, A.; Su, R.; Bapat, P.; Kwun, I.; Shen, C.-L. Novel insights of dietary polyphenols and obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, C.; Meireles, M.; Norberto, S.; Leite, J.; Freitas, J.; Pestana, D.; Faria, A.; Calhau, C. High-fat diet-induced obesity Rat model: A comparison between Wistar and Sprague-Dawley Rat. Adipocyte 2016, 5, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fotbolcu, H.; Zorlu, E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a multi-systemic disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 4079–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S. Raspberry ketone, a naturally occurring phenolic compound, inhibits adipogenic and lipogenic gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mill, J.G.; Stefanon, I.; dos Santos, L.; Baldo, M.P. Remodeling in the ischemic heart: The stepwise progression for heart failure. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2011, 44, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mir, T.M.; Ma, G.; Ali, Z.; Khan, I.A.; Ashfaq, M.K. Effect of Raspberry Ketone on Normal, Obese and Health-Compromised Obese Mice: A Preliminary Study. J. Diet. Suppl. 2021, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhao, D.; Kshatriya, D.; Bello, N.T.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q. UHPLC-QqQ-MS/MS method development and validation with statistical analysis: Determination of raspberry ketone metabolites in mice plasma and brain. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1149, 122146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, H.L.; Ziegenfuss, T.N.; E Hofheins, J.; Habowski, S.M.; Arent, S.M.; Weir, J.P.; Ferrando, A.A. Eight weeks of supplementation with a multi-ingredient weight loss product enhances body composition, reduces hip and waist girth, and increases energy levels in overweight men and women. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2013, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schell, L.M.; Gallo, M.V.; Ravenscroft, J. Environmental influences on human growth and development: Historical review and case study of contemporary influences. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2009, 36, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsuaki, M.N.; Klimes-Dougan, B.; Ge, X.; Shirtcliff, E.A.; Hastings, P.D.; Zahn-Waxler, C. Early pubertal maturation and internalizing problems in adolescence: Sex differences in the role of cortisol reactivity to interpersonal stress. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2009, 38, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, Z. Obesity, a serious etiologic factor for male subfertility in modern society. Reproduction 2017, 154, R123–R131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sizonenko, P.C. Sexual Maturation, Female; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sizonenko, P.C. Sexual Maturation, Male; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shelly, T. Effects of methyl eugenol and raspberry ketone/cue lure on the sexual behavior of Bactrocera species (Diptera: Tephritidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2010, 45, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akter, H.; Mendez, V.; Morelli, R.; Pérez, J.; Taylor, P.W. Raspberry ketone supplement promotes early sexual maturation in male Queensland fruit fly, Bactrocera tryoni (Diptera: Tephritidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1764–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M. Bone tissue regeneration: Biology, strategies and interface studies. Prog. Biomater. 2019, 8, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Jiang, W.; Phillips, F.M.; Haydon, R.C.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Luu, H.H.; An, N.; Breyer, B.; Vanichakarn, P.; et al. Osteogenic activity of the fourteen types of human bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. A 2003, 85, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, H.; Vakili-Ghartavol, R. Bone Regeneration: Current Status and Future Prospects. Adv. Tech. Bone Regen. 2016, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urist, M.R.; Huo, Y.K.; Brownell, A.G.; Hohl, W.M.; Buyske, J.; Lietze, A.; Tempst, P.; Hunkapiller, M.; DeLange, R.J. Purification of bovine bone morphogenetic protein by hydroxyapatite chromatography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, T.; Miranda-Garcia, O.; Adamson, A.; Sasaki, G.; Shay, N.F. Development of obesity is reduced in high-fat fed mice fed whole raspberries, raspberry juice concentrate, and a combination of the raspberry phytochemicals ellagic acid and raspberry ketone. J. Berry Res. 2016, 6, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Katagiri, T.; Ikeda, T.; Wozney, J.M.; Rosen, V.; Wang, E.A.; Kahn, A.J.; Suda, T.; Yoshiki, S. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates osteoblastic maturation and inhibits myogenic differentiation in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.M.; Pang, K.; Sundin, O.; Wedden, S.E.; Thaller, C.; Eichele, G. Molecular approaches to vertebrate limb morphogenesis. Development 1989, 107, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canalis, E.; Economides, A.N.; Gazzerro, E. Bone morphogenetic proteins, their antagonists, and the skeleton. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takata, T.; Morimoto, C. Raspberry ketone promotes the differentiation of C3H10T1/2 stem cells into osteoblasts. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bredsdorff, L.; Wedebye, E.B.; Nikolov, N.G.; Hallas-Møller, T.; Pilegaard, K. Raspberry ketone in food supplements—High intake, few toxicity data—A cause for safety concern? Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, C.; Catapang, M.; Conquer, J.; Costa, D.; Culwell, S.; D’Auria, D.; Isaac, R.; Le, C.; Marini, E.; Miller, A.; et al. Raspberry Ketone: An Evidence-Based Systematic Review by the Natural Standard Research Collaboration. Altern. Complementart Ther. 2013, 19, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Chemical Structure |  |
| Chemical Formula | C10 H12 O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 164.204 g·mol−1 |
| Solubility | ethanol, 1-propanol, 2-propanol, 1-butanol, 2-butanol, acetic acid, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, acetone, and binary mixtures of ethanol + acetone [8] |
| Melting Point | 81–85 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling Point | 292.2 ± 15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Lambda Max | 280 nm |
| LogP | 1.48 |
| Therapeutic Effect | Study Model | Mechanism of Action | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hepatoprotection | a. High-fat diet-fed Wistar rats b. Hepatotoxicity in male Wistar rats by CCL4 c. Acrylamide-induced hepatotoxicity in rats | ↑TAC, PPAR-α, LDLR ↑TAC, GSH, SOD ↓AST, ALT, ALP, NF-κB, Caspase-3 | [22,23,24] |
| 2 | Cardioprotection | a. Cardiotoxicity in Wistar albino rats by ISO b. Cardiotoxicity in Wistar albino rats by ISO | ↑TAC, GSH, SOD, CAT ↓MDA ↑PPAR-α | [16,30] |
| 3 | Gastric Ulcers | Gastric lesions in male Wistar rats by EtOH | ↑GSH px, GSH, CAT ↑Nrf2, ↓HMGB1 | [41] |
| 4 | Depigmentation | a. Murine B16 Melanoma cells in vitro, zebrafish in vivo b. Biomimetic study | ↓Cellular tyrosine, melanogenesis ↑Melanotoxicity | [3,46] |
| 5 | Anti-Obesity | a. High-fat diet-fed mice b. 3T3L1 murine adipose cells c. High-fat diet-fed Wistar rats d. Obese rats fed low-dose RK e. A clinical study in obese patients | ↓Hepatic triglycerides ↑Lipolysis ↑Triglyceride catabolism, lipolysis ↑AQP7 ↓leptin ↓Reduced weight gain ↓Weight, metabolic, and lipid parameters | [5,10,11,56,58] |
| 6 | Bone Regeneration | C3H103T1/2 cells | ↑Osteoblast, adipocyte differentiation | [70] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, S.; Kurakula, M.; Mamidipalli, N.; Tiyyagura, P.; Patel, B.; Manne, R. Pharmacological Exploration of Phenolic Compound: Raspberry Ketone—Update 2020. Plants 2021, 10, 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10071323
Rao S, Kurakula M, Mamidipalli N, Tiyyagura P, Patel B, Manne R. Pharmacological Exploration of Phenolic Compound: Raspberry Ketone—Update 2020. Plants. 2021; 10(7):1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10071323
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Shailaja, Mallesh Kurakula, Nagarjuna Mamidipalli, Papireddy Tiyyagura, Bhaumik Patel, and Ravi Manne. 2021. "Pharmacological Exploration of Phenolic Compound: Raspberry Ketone—Update 2020" Plants 10, no. 7: 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10071323
APA StyleRao, S., Kurakula, M., Mamidipalli, N., Tiyyagura, P., Patel, B., & Manne, R. (2021). Pharmacological Exploration of Phenolic Compound: Raspberry Ketone—Update 2020. Plants, 10(7), 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10071323