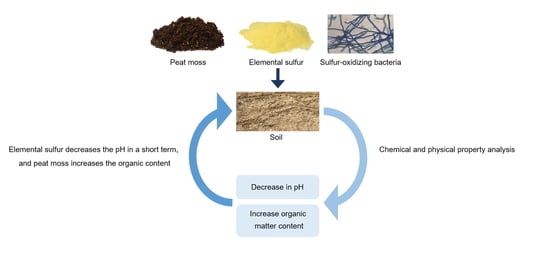
Effect on Chemical and Physical Properties of Soil Each Peat Moss, Elemental Sulfur, and Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Preparation and Peat Moss Treatments
2.2. Treatment of Elemental Sulfur and Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria
2.3. Investigation of the Physical Properties of Treated Soil
2.4. Investigation of Chemical Properties of Treated Soil
2.5. Soil Acidity Measurement
2.6. Electrical Conductivity Measurement
2.7. Analysis of Nitrogen and Phosphorus by Spectrometry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Peat Moss Treatment on Physical Properties
3.2. Effects of Peat Moss Treatment on Soil Chemical Property
3.3. Soil Acidity Changes for Peat Moss Treatment
3.4. Changes in the Content of Ammonium Nitrogen, Nitrate-Nitrogen, and Soluble Phosphorus
3.5. Changes in Soil Acidity on Elemental Sulfur and Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria Treatment
3.6. Changes in the Content of Ammonium Nitrogen, Nitrate-Nitrogen, and Soluble Phosphorus
3.7. EC Measurement Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strik, B.C.; Yarborough, D. Blueberry production trends in North America, 1992 to 2003, and predictions for growth. Horttechnology 2005, 15, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalt, W.; Cassidy, A.; Howard, L.R.; Krikorian, R.; Stull, A.J.; Tremblay, F.; Zamora-Ros, R. Recent Research on the Health Benefits of Blueberries and Their Anthocyanins. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, B.M.; Howell, A.B.; McEniry, B.; Knight, C.T.; Seigler, D.; Erdman, J.W.; Lila, M.A. Effective separation of potent antiproliferation and antiadhesion components from wild blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium Ait.) fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6433–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellappan, S.; Akoh, C.C.; Krewer, G. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of Georgia-grown blueberries and blackberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2432–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainland, C.M.; Frederick, V. Coville and the History of North American Highbush Blueberry Culture. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2012, 12, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, E.A.; Hepp, R.F.; Mariño, M.A. Effect of irrigation on fruit production in blueberry. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 67, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochmian, I.; Malinowski, R.; Kubus, M.; Malinowska, K.; Sotek, Z.; Racek, M. The feasibility of growing highbush blueberry (V. corymbosum L.) on loamy calcic soil with the use of organic substrates. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFacio, P.; Pickerel, L.; Rhyne, S.M. Greenhouse Operation and Management, 6th ed.; Apex Publishers: Delhi, India, 2002; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Margenot, A.J.; Griffin, D.E.; Alves, B.S.Q.; Rippner, D.A.; Li, C.; Parikh, S.J. Substitution of peat moss with softwood biochar for soil-free marigold growth. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 112, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kingston, P.H.; Scagel, C.F.; Bryla, D.R. Suitability of sphagnum moss, coir, and douglas fir bark as soilless substrates for container production of highbush blueberry. HortScience 2017, 52, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-L.; Kwack, Y.-B.; Kim, H.-D.; Kim, J.-G.; Choi, Y.-H. Effect of Different Soil Water Potentials on Growth Properties of Northern-Highbush Blueberry. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2011, 44, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, B.K.; Son, J.E.; Choi, J.M. Physico.chemical Properties of Peatmoss and Coir Dust Currently Used as Root Medium Components for Crop Production in Korean Plant Factories. J. Bio-Environ. Control 2012, 21, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.L.; Kim, H.D.; Kwack, Y.B.; Choi, Y.H. Effect of organic substrates mixture ratio on 2-year-old highbush blueberry growth and soil chemical properties. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2010, 43, 858–863. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.J.; Swift, R.S. Effects of soil acidifacation on the chemical extractability of Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu and the growth and micronutrient uptake of highbush blueberry plants. Plant Soil 1985, 84, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochmian, I.; Oszmiański, J.; Lachowicz, S.; Krupa-Małkiewicz, M. Rootstock effect on physico-chemical properties and content of bioactive compounds of four cultivars Cornelian cherry fruits. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J. Laboratory study of soil acidification and leaching of nutrients from a soil amended with various surface-incorporated acidifying agents. Fertil. Res. 1986, 10, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Christie, P.; Li, X.; Horlacher, D.; Liebig, H.P. Evaluation of current fertilizer practice and soil fertility in vegetable production in the Beijing region. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2004, 69, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pokorna, B.; Mandl, M.; Borilova, S.; Ceskova, P.; Markova, R.; Janiczek, O. Kinetic constant variability in bacterial oxidation of elemental sulfur. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3752–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Xin, H.; Han, P.; Li, D.; Yang, B.; Li, P.; Ullah, S.; Fan, H.; Zhu, C.; et al. Ultrahigh level nitrogen/sulfur co-doped carbon as high performance anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Carbon N. Y. 2018, 126, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, L. Effect of ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen, separately and in combination, on the growth of the highbush blueberry. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1967, 47, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merhaut, D.J.; Darnell, R.L. Ammonium and nitrate accumulation in containterized southern highbush blueberry plants. HortScience 1995, 30, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañados, M.P. Expanding blueberry production into non-traditional production areas: Northern Chile and Argentina, Mexico and Spain. Acta Hortic. 2009, 810, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Heo, J.; Kim, M.; Hong, K.; Kim, E.; Song, W.; Rho, C.; Lee, J.; Jeon, W. Monitoring of Heavy Metal Contents from Paddy Soil in Gyeongnam Province. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2010, 43, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Korcak, R.F. Nutrition of Blueberry and Other Calcifuges. HortScience 1989, 24, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.L.; Lim, J.H.; Sohn, B.K.; Kim, Y.J. -J. Chemical Properties of Cut-flower Rose-growing Soils in Plastic Film Houses. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fert. 2003, 36, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.; Kim, H.; Guak, S. Effect of Peatmoss-Based Organic Material Mixtures on Soil pH, Growth and Fruit Quality of Highbush Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) Plants. Prot. Hortic. Plant Fact. 2017, 26, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.C.; Parida, S.; Dutta, S.K.; Thatoi, H.N. Isolation and Identification of Cellulose Degrading Bacteria from Mangrove Soil of Mahanadi River Delta and Their Cellulase Production Ability. Am. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 2, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, S.J. Thiobacillus populations in some agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Moritsuka, N.; Kusaba, S.; Hiraoka, K. Concentrations of natural stable cs in organs of blueberry bushes grown in three types of soils treated with acidification or fertilization. Hortic. J. 2019, 88, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusk, M. Formula to get desired soil density. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2000, 126, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Mualem, Y. Hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils: Prediction and formulas. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; Volume 5, pp. 799–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gori, F.; Corasaniti, S. New model to evaluate the effective thermal conductivity of three-phase soils. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.J.; Pielke, R.A. Estimating the soil surface specific humidity. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1992, 31, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Nitrogen Analysis of Soil and Plant Tissues. J. AOAC Int. 1980, 63, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, T.; Karp, K.; Starast, M.; Paal, T. The effect of mulching and pruning on the vegetative growth and yield of the half-high blueberry. Agron. Res. 2010, 8, 759–768. [Google Scholar]
- Rhie, Y.H.; Kim, J. Changes in physical properties of various coir dust and perlite mixes and their capacitance sensor volumetric water content calibrations. HortScience 2017, 52, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odneal, M.B.; Kaps, M.L. Fresh and Aged Pine Bark as Soil Amendments for Establishment of Highbush Blueberry. HortScience 1990, 25, 1228–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, F.F.; Wallach, R.; Chen, Y. Hydraulic properties of sphagnum peat moss and tuff (scoria) and their potential effects on water availability. Plant Soil 1993, 154, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Chen, S.J.; Li, K.T. Symbiotic fungi in nature Finnish peat moss promote vegetative growth in rabbiteye blueberry cuttings. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2021, 62, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vano, I.; Matsushima, M.; Tang, C.; Inubushi, K. Effects of peat moss and sawdust compost applications on N2O emission and N leaching in blueberry cultivating soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 57, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarnezhad, F.; Shahinrokhsar, P.; Vahed, H.S. Influence of Elemental Sulfur and Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria on Some Nutrient Deficiency in Calcareous Soils. Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 2012, 4, 735–739. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Yemoto, K. Salinity: Electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1442–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.B.; Ro, H.M.; Lim, J.H.; Yiem, M.S. Estimating Saturation-paste Electrical Conductivities of Rose-cultivated Soils from their Diluted Soil Extracts. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2000, 33, 398–404. [Google Scholar]
- Hayne, R.J.; Williams, P.H. Changes in soil solution composition and pH in urine-affected areas of pasture. J. Soil Sci. 1992, 43, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.-S.; Kang, S.-S.; Chae, M.-J.; Jung, H.; Sonn, Y.-G.; Lee, D.-B.; Kim, Y.-H. Changes of Chemical Properties in Upland Soils in Korea. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2015, 48, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbas, F.; Ke, Y.; Yu, R.; Yue, Y.; Amanullah, S.; Jahangir, M.M.; Fan, Y. Volatile terpenoids: Multiple functions, biosynthesis, modulation and manipulation by genetic engineering. Planta 2017, 246, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.; Kim, S.-H.; Maeng, W.-Y.; Lee, I.-E.; Chang, K.-W.; Lee, J.-J. Effects of Soil Acidity and Organic Matter by Application of Organic Materials and Soil Mulching with Pine Needles for Soil Surface Management in Blueberry Eco-Friendly Farming. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2013, 46, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, J.R.; Germida, J.J. Enumeration of sulfur-oxidizing populations in Saskatchewan agricultural soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1991, 71, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Stoven, K.; Haneklaus, S.; Singh, B.R.; Schnug, E. Elemental Sulfur Oxidation by Thiobacillus spp. and Aerobic Heterotrophic Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Chung, D.; Hwang, S.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.; Choi, W.; Ha, S.; Kim, S. Patterns of Leaching and Distribution of Cations in Reclaimed Soil according to Gypsum Incorporation Rate. Korean J. Soil. Sci. Fertil. 2010, 43, 596–601. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, C.G. Physiology and genetics of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. In Advances in Microbial Physiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; Volume 39, ISBN 0120277395. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.J.; Park, S.J.; Yoon, D.N.; Schouten, S.; Damsté, J.S.S.; Rhee, S.K. Cultivation of autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing archaea from marine sediments in coculture with sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7575–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oburger, E.; Jones, D.L.; Wenzel, W.W. Phosphorus saturation and pH differentially regulate the efficiency of organic acid anion-mediated P solubilization mechanisms in soil. Plant Soil 2011, 341, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, E.-G.; Park, J.-R.; Ryu, Y.-H.; Moon, W.; Park, G.-H.; Ubaidillah, M.; Ryu, S.-N.; Kim, K.-M. Effect on Chemical and Physical Properties of Soil Each Peat Moss, Elemental Sulfur, and Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria. Plants 2021, 10, 1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091901
Lee S-Y, Kim E-G, Park J-R, Ryu Y-H, Moon W, Park G-H, Ubaidillah M, Ryu S-N, Kim K-M. Effect on Chemical and Physical Properties of Soil Each Peat Moss, Elemental Sulfur, and Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria. Plants. 2021; 10(9):1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091901
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, So-Young, Eun-Gyeong Kim, Jae-Ryoung Park, Young-Hyun Ryu, Won Moon, Gyu-Hwan Park, Mohammad Ubaidillah, Su-Noh Ryu, and Kyung-Min Kim. 2021. "Effect on Chemical and Physical Properties of Soil Each Peat Moss, Elemental Sulfur, and Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria" Plants 10, no. 9: 1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091901
APA StyleLee, S.-Y., Kim, E.-G., Park, J.-R., Ryu, Y.-H., Moon, W., Park, G.-H., Ubaidillah, M., Ryu, S.-N., & Kim, K.-M. (2021). Effect on Chemical and Physical Properties of Soil Each Peat Moss, Elemental Sulfur, and Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria. Plants, 10(9), 1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091901