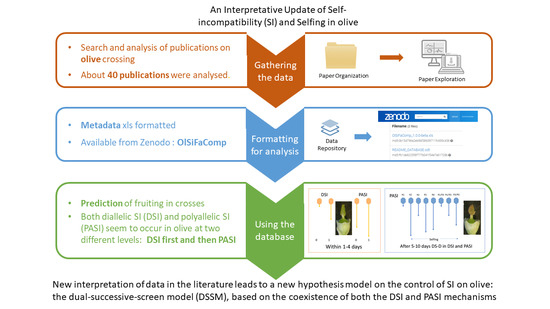
A Dual-Successive-Screen Model at Pollen/Stigma and Pollen Tube/Ovary Explaining Paradoxical Self-Incompatibility Diagnosis in the Olive Tree—An Interpretative Update of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Case of Olive Is Puzzling
2.1. Four Factors Might Explain the Difficulties
2.1.1. Difficulties Due to Methods
2.1.2. Difficulties Due to Dominance Relationships between S-alleles
2.1.3. Difficulties Due to the Number of Varieties Studied Is Insufficient
2.1.4. Difficulties Due to Confusion between Selfing and Crosses
2.2. DSI First and then PASI Follow One Another
2.3. An Approach with Olive Varieties
2.4. Limitation of the Dual-Successive-Screen Model
3. Recent Findings Argue for Duplication in the Olive Genome
4. Analyses of Methods and Results from Literature
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibbs, P.E. Late-acting self-incompatibility—The pariah breeding system in flowering plants. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscock, S.J.; Allen, A.M. Diverse cell signalling pathways regulate pollen-stigma interactions: The search for consensus. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 286–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedgley, M. Self-Incompatibility in Woody Horticultural Species. In Genetic Control of Self-Incompatibility and Reproductive Development in Flowering Plants; Williams, E.G., Clarke, A.E., Knox, R.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 141–163. [Google Scholar]
- Sassa, H.; Kakui, H.; Miyamoto, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Hanada, T.; Ushijima, K.; Kusaba, M.; Hirano, H.; Koba, T. S Locus F-Box Brothers: Multiple and Pollen-Specific F-Box Genes with S Haplotype-Specific Polymorphisms in Apple and Japanese Pear. Genetics 2007, 175, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ushijima, K.; Yamane, H.; Watari, A.; Kakehi, E.; Ikeda, K.; Hauck, N.R.; Iezzoni, A.F.; Tao, R. The S haplotype-specific F-box protein gene, SFB, is defective in self-compatible haplotypes of Prunus avium and P. mume. Plant J. 2004, 39, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodad, O.; Alonso, J.M.; Sánchez, A.; Oliveira, M.M.; I Company, R.S. Evaluation of genetic diversity of S- alleles in an almond germplasm collection. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlenbacher, S.A. Testing compatibility of hazelnut crosses using fluorescence microscopy. Acta Hortic. 1997, 445, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.V.; Griggs, W.H. Morphological evidence of incompatibility in Olea europaea L. Phytomorphology 1963, 13, 141–156. [Google Scholar]
- Breton, C.M.; Bervillé, A. New hypothesis elucidates self-incompatibility in the olive tree regarding S-alleles dominance relationships as in the sporophytic model. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2012, 335, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, C.M.; Farinelli, D.; Shafiq, S.; Heslop-Harrison, J.; Sedgley, M.; Bervillé, A.J. The self-incompatibility mating system of the olive (Olea europaea L.) functions with dominance between S-alleles. Tree Genet. Genomes 2014, 10, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinelli, D.; Breton, C.M.; Famiani, F.; Bervillé, A. Specific features for the olive sporophytic self-incompatibility system: Method to decipher S-allele pairs for worldwide spread varieties. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 181, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saumitou-Laprade, P.; Vernet, P.; Vekemans, X.; Billiard, S.; Gallina, S.; Essalouh, L.; Mhaïs, A.; Moukhli, A.; El Bakkali, A.; Barcaccia, G.; et al. Elucidation of the genetic architecture of self-incompatibility in olive: Evolutionary consequences and perspectives for orchard management. Evol. Appl. 2017, 10, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, E.; Guerin, J.; Kaiser, B.; Sedgley, M. Flowering and fruit set in olive: A review. Iran. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 5, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Saumitou-Laprade, P.; Vernet, P.; Vekemans, X.; Castric, V.; Barcaccia, G.; Khadari, B.; Baldoni, L. Controlling for genetic identity of varieties, pollen contamination and stigma receptivity is essential to characterize the self-incompatibility system of Olea europaea L. Evol. Appl. 2017, 10, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Franklin-Tong, V.E. Self-incompatibility inPapaver: Signalling to trigger PCD in incompatible pollen. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 59, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selak, G.V.; Cuevas, J.; Ban, S.G.; Perica, S. Pollen tube performance in assessment of compatibility in olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 165, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascallares, M.; Setzes, N.; Marchetti, F.; López, G.A.; Distéfano, A.M.; Cainzos, M.; Zabaleta, E.; Pagnussat, G.C. A Complex Journey: Cell Wall Remodeling, Interactions, and Integrity During Pollen Tube Growth. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 599247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouksili, A. Contribution à l’Etude de la Biologie Florale de l’olivier Europaea L de la Formation des Fleurs à la Pollinisation effective. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 1983; 143p. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, H.T. Studies on self- and cross- pollination of olives. Calif. Agric. 1961, 15, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Musho, U.-B. Contribution à l’Etude de la Biologie Florale de L’olivier Olea europaea L.: Mise en Evidence de Cas de Stérilité Mâle et Recherche de Pollinisateurs; Universidad de Montpellier 2: Montpellier, France, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Iannotta, N.; Briccoli Bati, C.; Perri, L.; Tocci, C. Interfertility tests using different pollinizers for the Carolea cultivar (Olea europaea L.). Acta Hortic. 1999, 1, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutier, N. Self-fertility and inter-compatibilities of sixteen olive varieties. Acta Hortic. 2000, 586, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-B.; Collins, G.; Sedgley, M. Sexual compatibility within and between olive varieties. J. Hort. Sci. Biotech. 2002, 77, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kasasbeh, M.F.; Atteyeh, A.F.; Qrunfleh, M.M. A study of cross pollination of three olive cultivars in Jordan. Dirasat Agric. Sci. 2005, 32, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Mookerjee, S.; Guerin, J.; Collins, G.; Ford, C.; Sedgley, M. Paternity analysis using microsatellite markers to identify pollen donors in an olive grove. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hady, E.S.; Haggag, L.F.; Abdel-Migeed, M.M.M.; Desouky, I.M. Studies on Sex Compatiblity of Some Olive varieties. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2007, 3, 504–509. [Google Scholar]
- Arbeiter, A.B.; Jakše, J.; Bandelj, D. Paternity Analysis of the Olive Variety “Istrska Belica” and Identification of Pollen Donors by Microsatellite Markers. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 208590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koubouris, G.C.; Breton, C.M.; Metzidakis, I.T.; Vasilakakis, M.D. Self-incompatibility and pollination relationships for four Greek olive cultivars. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 176, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.; Marra, F.P.; Costa, F.; Quartararo, A.; Fretto, S.; Caruso, T. An investigation of the self- and inter-incompatibility of the olive cultivars ‘Arbequina’ and ‘Koroneiki’ in the Mediterranean climate of Sicily. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2016, 10, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Guerin, J.; Sedgley, M. Cross-Pollination in Olive Cultivars Barton, Australia: Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation; Publication 2007, 07/169. Available online: https://rune.une.edu.au/web/handle/1959.11/7720 (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Farinelli, D.; Hassani, D.; Tombesi, A. Pollenizer and Cultivar Influence Seed Number and Fruit Characteristics in Olea europaea L. Acta Hort. 2008, 791, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camposeo, S.; Ferrara, G.; Palasciano, M.; Godini, A. About The Biological Behaviour of Cultivar ‘Coratina. Acta Hortic. 2012, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eassa, K.B.; El-Tweel, A.A.; Gorda, A.M. Studies and cross-pollination for Kalamata olive cultivar grown on a sandy soil. J. Agric. Kafer El-Sheik Univ. 2011, 37, 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Seifi, E.; Guerin, J.; Kaiser, B.; Sedgley, M. Sexual compatibility of the olive cultivar ‘Kalamata’ assessed by paternity analysis. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taslimpour, M.R.; Aslmoshtaghi, E. Study of self-incompatibility in some Iranian olive cultivars. Crop Breed. J. 2013, 3, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, J.; Díaz-Hermoso, A.J.; Galián, D. Response to cross pollination and choice of pollinisers for the olive cultivars. Olea Eur. 2001, 85, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, J.; Pinillos, V.; Polito, V.S. Effective pollination period for ‘‘Manzanillo’’ and ‘‘Picual’’ olive trees. J. Hort. Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz, A.; Martín, A.; Rallo, P.; Barranco, D.; De La Rosa, R. Self-incompatibility of ‘Arbequina’ and ‘Picual’ Olive Assessed by SSR Markers. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2006, 131, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vuletin Selak, G.; Perica, S.; Goreta Ban, S.; Bućan, L.; Poljak, M. Flower sterility and the germination ability of pollen as genetic traits of seven olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars grown in Croatia. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstel, D.U. Self-incompatibility in guayule. II. Inheritance. Genetics 1950, 35, 482–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, C.M.; Farinelli, D.; Koubouris, G.; Bervillé, A. A model based on S-allele dominance relationships to explain pseudo self-fertility of varieties in the olive tree. Euphytica 2016, 210, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, T.; Franklin-Tong, N. Male–female crosstalk during pollen germination, tube growth and guidance, and double Fertilization. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1018–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alagna, F.; Caceres, M.E.; Pandolfi, S.; Collani, S.; Mousavi, S.; Mariotti, R.; Cultrera, N.; Baldoni, L.; Barcaccia, G. The Paradox of Self-Fertile Varieties in the Context of Self-Incompatible Genotypes in Olive. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa, R.; Angiolillo, A.; Guerrero, C.; Pellegrini, M.; Rallo, L.; Besnard, G.; Bervillé, A.; Martín, A.; Baldoni, L. A first linkage map of olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars using RAPD, AFLP, RFLP and SSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Sexual Compatibility and Construction of Molecular Linkage Maps in Olive (Olea europaea L.). Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Adelaïde, Adelaide, Australia, 2002; 162p. [Google Scholar]
- El Aabidine, A.Z.; Charafi, J.; Grout, C.; Doligez, A.; Santoni, S.; Moukhli, A.; Jay-Allemand, C.; El Modafar, C.; Khadari, B. Construction of a Genetic Linkage Map for the Olive Based on AFLP and SSR Markers. Crop. Sci. 2010, 50, 2291–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.; Marra, F.P.; Caruso, T.; Mhelembe, K.; Costa, F.; Fretto, S.; Sargent, D.J.; Infruitec-Nietvoorbij, P.B.X.A. The first high-density sequence characterized SNP-based linkage map of olive (Olea europaea L. subsp. europaea) developed using genotyping by sequencing. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2016, 10, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saumitou-Laprade, P.; Vernet, P.; Vassiliadis, C.; Hoareau, Y.; de Magny, G.; Dommée, B.; Lepart, J. A Self-Incompatibility System Explains High Male Frequencies in an Androdioecious Plant. Science 2010, 327, 1648–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, S.; Miyatakea, K.; Endob, M.; Urashimob, S.; Kawanishib, T.; Negoroa, S.; Shimakoshib, S.; Fukuoka, H. Loss of function of the Pad-1aminotransferase gene, which is involved in auxin homeostasis, induces parthenocarpy in Solanaceae plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 117, 12784–12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koubouris, G.C.; Metzidakis, I.T.; Vasilakakis, M.D. Influence of Cross-Pollination on the Development of Parthenocarpic Olive (Olea Europaea) Fruits (Shotberries). Exp. Agric. 2009, 46, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, R.; Pandolfi, S.; De Cauwer, I.; Saumitou-Laprade, P.; Vernet, P.; Rossi, M.; Baglivo, F.; Baldoni, L.; Mousavi, S. Diallelic self-incompatibility is the main determinant of fertilization patterns in olive orchards. Evol. Appl. 2020, 14, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, C.; Koubouris, G.; Villemur, P.; Bervillé, A.J. Elucidation of the genetic architecture of self-incompatibility in olive: Evolutionary consequences and perspectives for orchard management. Evol. Appl. 2017, 10, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinardi, A.; Bassi, D. Olive fertility as affected by cross-pollination and boron. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 375631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levin, D.A. The evolutionary significance of pseudo-self-fertility. Am. Nat. 1996, 148, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Peer, Y.; Mizrachi, E.; Marchal, K. The evolutionary significance of poly-ploidy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, T.; Wu, Z.; Sterck, L.; Turktas, M.; Lohaus, R.; Li, Z.; Yang, M.; He, L.; Deng, T.; Escalante, F.J.; et al. Genome of wild olive and the evolution of oil biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9413–E9422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacombe, S.; Souyris, I.; Bervillé, A.J. An insertion of oleate desaturase homologous sequence silences via siRNA the functional gene leading to high oleic acid content in sunflower seed oil. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 281, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Rosa, R.; James, C.M.; Tobutt, K.R. Using Microsatellites for Paternity Testing in Olive Progenies. HortScience 2004, 39, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breton, C.M.; Bervillé, A.J. Identification of olive pollen donor trees and pollinizers under controlled pollination environment using STR markers. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2018, 12, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, E.; Guerin, J.; Kaiser, B.; Sedgley, M. Inflorescence architecture of olive. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 116, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, R.; Fornasiero, A.; Mousavi, S.; Cultrera, N.; Brizioli, F.; Pandolfi, S.; Passeri, V.; Rossi, M.; Magris, G.; Scalabrin, S.; et al. Genetic Mapping of the Incompatibility Locus in Olive and Development of a Linked Sequence-Tagged Site Marker. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Schnable, J.C. Functional Divergence between Subgenomes and Gene Pairs after Whole Genome Duplications. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breton, C.; Bervillé, A. OlSiFaComp: A database for Olea: Olive Self-Incompatibility Flower Allelic Composition. Available online: https://zenodo.org/deposit/5417582. [CrossRef]






| Host Variety | Pollen Source | References |
|---|---|---|
| Arbequina | Cayon, Salonenque, Giarraffa, Nocellara Messinese | [22,38] |
| Ascolana-Semi Tenara | Picholine, Moresca | [11] |
| Ascolana-Tenera | Picholine, Giarraffa, Gordal Sevillano, Itrana, Leccino, Moresca, Picholine, Santa Caterina | [11] |
| Belgentier | Cayon | [22] |
| Brun | Cayon | [11] |
| Cailletier | Selfing | [11] |
| Cayon | Cornicabra, Brun | [11] |
| Cornicabra | Cornicabra | [22] |
| Frantoio | Selfing | [31,32] |
| Frantoio | Moraiolo | [10,25] |
| Giarraffa | Selfing, Gordales, Nocellara Messina, Picholine, Leccino, Grossa di Spagna, Santa Caterina | [11] |
| Grossane | Giarraffa, Grossa di Spagna, Cayanne | [11] |
| LeccinoOit27 | Moraiolo, Moraesca, Santa Caterina, Giarraffa, Gordales, Frantoio | [32,39] |
| Moresca | Selfing, Leccino, Sorani | [11] |
| Picholine | Selfing, Sorani, Moresca, GiarraffaOit4, Leccino, SantaCaterina | [11] |
| Santa Caterina | Selfing, Grossa di Spagna, Picholine | [11] |
| Taggiasca | Selfing, Leccino, Picholine | [11,31] |
| Host Variety | Pollen Source | References |
|---|---|---|
| Aglandau | VerdaleH | [22] |
| Amellau | VerdaleH | [22] |
| Amygdalolia | Koroneiki | [28] |
| Bella di Spagna | Selfing, Carolea, Kalamon, Manzanilla, Nocellara Etnea, Tanche | [10] |
| Carolea | Nostrale Rigali, Maurino, Nocellara Etnea, Bella di Spagna, DolceAgogia, Itrana, Kalamon, Manzanilla | [11,19,21] |
| Cayet roux | Bouteillan | [10] |
| Chemlal x | Sigoise, Coratina, Blanquette | [11,18] |
| Coratina | Nabali Baladi, Carolea | [24,32] |
| DolceAgogia | Istrska Belica | [27] |
| DolceAgogia | Selfing, Ascolana Tenera | [11] |
| Itrana | Ascolana Tenera, Carolea, Itrana, Carolea, Manzanilla-Per 1, Bella di Spagna, Carolea | [11] |
| Konservolia KoroneikiOit55 Konservolia x | Amygdalolia | [35] |
| Koroneiki | Amygdalolia, Kalamata | [28] |
| Koroneiki | Aitana, Arbosana, Erbano, Indemoniata, Arbosana, Biancolilla, Indemoniata, Minuta, Nerba, Piricuddara | [29] |
| Koroneiki | Bouteillan | [26] |
| Lucques | VerdaleH, Bouteillan | [21] |
| Manzanilla-Per | Nocellara Etnea, Maurino, Manzanilla, Sevillano, Maurino | [11] |
| Manzanilla Mtp | Aglandau | [22] |
| Mastoidis | x Amygdalolia, Kalamata, Koroneiki | [28] |
| Nocellara Etnea | Bella di Spagna, ManzanillaFarinelli | [11] |
| Nocellara Messina | Bella di Spagna, Nocellara Etnea, Bella di Spagna, Bella di Spagna, Manzanilla-Ita | [11] |
| Nostrale Rigali | Selfing, Carolea | [11] |
| Olivière | Bouteillan, VerdaleH1, ManzanillaMpt1, Amygalolia, Amellau | [20,22] |
| Pendolino | Ascolana Tenera, Carolea, Manzanilla1Per Selfing | [11] |
| Picual | Selfing, Manzanillo, Pendolino, Maurino, Asolana Tenera, Rosciola, PicholineMarocaine, Kalamata | [11,23,33,36,37] |
| VerdaleH | Amellau | [22] |
| Type of Inheritance | S-Allele | Dominance Level | Encountered S-Allele Pairs | Expression Level | Expression of Pollen Tube | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSI | S1 | Recessive versus S2 | S1S1 = G2 | Stigma | S1 | Di-allelic SI |
| S2 | Dominant versus S1 | S1S2 = G1 | data | S2 | S2S2 cannot exist | |
| In stigma S2 > S1 | ||||||
| PASI | R6 | More dominant | R1R6, R2R6, R3R6, R4R6, R5R6 | Ovary [R1R6], [R2R6], [R3R6], [R4R6], [R5R6] | R6 | R6R6 cannot exist unless R7 > R6 exist |
| R2 | R1R2, R2R3, R2R4, R2R5, | Ovary [R1R2], [R2R3], [R2R4], [R2R5] | R2 | R2R2 | ||
| R1 = R3 = R5 | R1R4, R3R4, R4R5, R1R3, R1R5, R3R5 | Ovary [R1R3], [R1R5], [R3R5] | R1, R3, R5, R1R3, R1R5, R3R5 | R1, R3, R5, R1R3, R1R5, R3R5 | ||
| R4 | More recessive | Ovary | R4 | R4R4, not encountered yet |
| Compatibility Group 1 | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 (S1S2) | 8 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 3 | 2 |
| G2 (S1S1) | 1 | 15 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 3 |
| Genotype | Number of G1 (S1S2) | Number of G2 (S2S2) | Number of Deciphered Varieties | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1R2 | 0 | 3 | Manzanilla-Per | 3 | |
| R1R3 | 3 | Picholine, Arbequina | 0 | 3 | |
| R1R4 | 7 | Cayon | 0 | 8 | |
| R1R5 | 2 | Grossane, Leccino | 0 | 2 | |
| R1R6 | 1 | Barnea | 0 | 2 | |
| R2R3 | 2 | Santa Caterina | 7 | Tanche | 11 |
| R2R4 | 3 | 10 | Bouteillan | 22 | |
| R2R5 | 0 | 1 | Aglandau | 2 | |
| R2R6 | 2 | 4 | Koroneiki | 6 | |
| R3R4 | 1 | 3 | Amellau | 8 | |
| R3R5 | 1 | Salonenque | 1 | Rosciola | 3 |
| R3R6 | 0 | 1 | 3 | ||
| R4R5 | 3 | Cailletier, Frantoio | 8 | Erbano | 15 |
| R4R6 | 1 | Moraiolo | 1 | Istrska belica | 4 |
| R5R6 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| Total | 26 | 39 | 92 |
| Host Variety G2 | Father from Host Variety | Father in DSI | Diagnosis 1 in Literature [11,12] | Diagnosis 1 with DSI [12,59] | Diagnosis 1 with PASI [11] | DS-D Functions | Pollinizer after DSSM and DS-D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aglandau | Frantoio, Petit Ribier | G1 | Compatible | Accept | Reject | Yes | Reject |
| Aglandau | Cayet Roux | G2 | Compatible | Reject | Reject | No | Reject |
| Bouteillan Olivière, VerdaleH Verdale de Millas | Aglandau, Bouteillan, VerdaleH, Manzanilla | G2 | Compatible | Reject | Reject | No | Reject |
| Lucques, Tanche | Aglandau, Bouteillan | G2 | Compatible | Reject | Reject | No | Reject |
| Lucques, Tanche | Picholine, Arbequina | G1 | Compatible | Accept | Reject | Yes | Reject |
| Cayet Roux | Aglandau | G2 | Compatible | Reject | Accept | Yes | Reject |
| Host Variety G1 | Father from host variety | Father in DSI | |||||
| Grossane | Frantoio, Petit Ribier | G1 | Compatible | Accept | Reject | No | Reject |
| Cayanne Cayon Clermontaise | Picholine, Arbequina | G1 | Compatible | Rejected | Accept | Yes | Reject |
| Picholine, Arbequina | Amellau, Picual | G2 | Compatible | Accept | Reject | Yes | Reject |
| Frantoio, Petit Ribier | Cayet Roux | G2 | Compatible | Accept | Reject | Yes | Reject |
| Redouneil, Salonenque | Amellau, Frantoio, Petit Ribier | G1 | Compatible | Rejected | Reject | No | Reject |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Breton, C.M.; Farinelli, D.; Koubouris, G.; Famiani, F.; Raymond, M.; Bervillé, A. A Dual-Successive-Screen Model at Pollen/Stigma and Pollen Tube/Ovary Explaining Paradoxical Self-Incompatibility Diagnosis in the Olive Tree—An Interpretative Update of the Literature. Plants 2021, 10, 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091938
Breton CM, Farinelli D, Koubouris G, Famiani F, Raymond M, Bervillé A. A Dual-Successive-Screen Model at Pollen/Stigma and Pollen Tube/Ovary Explaining Paradoxical Self-Incompatibility Diagnosis in the Olive Tree—An Interpretative Update of the Literature. Plants. 2021; 10(9):1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091938
Chicago/Turabian StyleBreton, Catherine Marie, Daniela Farinelli, Georgios Koubouris, Franco Famiani, Michel Raymond, and André Bervillé. 2021. "A Dual-Successive-Screen Model at Pollen/Stigma and Pollen Tube/Ovary Explaining Paradoxical Self-Incompatibility Diagnosis in the Olive Tree—An Interpretative Update of the Literature" Plants 10, no. 9: 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091938
APA StyleBreton, C. M., Farinelli, D., Koubouris, G., Famiani, F., Raymond, M., & Bervillé, A. (2021). A Dual-Successive-Screen Model at Pollen/Stigma and Pollen Tube/Ovary Explaining Paradoxical Self-Incompatibility Diagnosis in the Olive Tree—An Interpretative Update of the Literature. Plants, 10(9), 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091938