Impact of Seed Dressing and Soil Application of Potassium Humate on Cotton Plants Productivity and Fiber Quality
Abstract
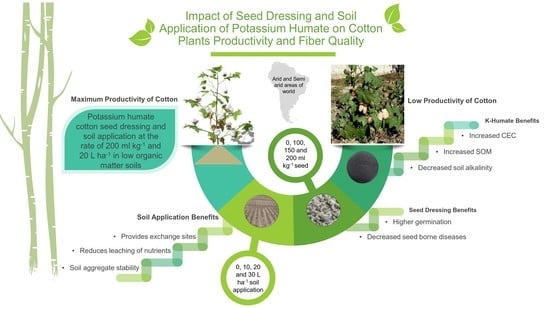
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Weather Conditions
2.2. Soil Properties
2.3. Plant Height, Number of Nodes and Number of Sympodial Branches
2.4. No. of Bolls Per Plant, Boll Weight and Seed Cotton Yield
2.5. Ginning out Turn and Fiber Length
2.6. Fiber Strength and Fitness
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Site Description
4.2. Treatments
4.3. Field Experiment
4.4. Data Collection
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, E.A. The nature and dynamics of soil organic matter: Plant inputs, microbial transformations, and organic matter stabilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Z.; Lin, H.; Hao, J.; Kong, X.; Tian, K.; Bei, Z.; Tian, X. Impact of vermiculite on ammonia emissions and organic matter decomposition of food waste during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, A.; Raha, P.; Rakshit, A.; Singh, C.; Kishor, P. Potassium Humate: A potential soil conditioner and plant growth promoter. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.S.; Kumar, S.; Datta, R.; Lal, R.; Vijayakumar, V.; Brtnicky, M.; Sharma, M.P.; Yadav, G.S.; Jhariya, M.K.; Jangir, C.K. Impact of agrochemicals on soil microbiota and management: A review. Land 2020, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brtnicky, M.; Dokulilova, T.; Holatko, J.; Pecina, V.; Kintl, A.; Latal, O.; Vyhnanek, T.; Prichystalova, J.; Datta, R. Long-Term Effects of Biochar-Based Organic Amendments on Soil Microbial Parameters. Agronomy 2019, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molaei, A.; Lakzian, A.; Datta, R.; Haghnia, G.; Astaraei, A.; Rasouli-Sadaghiani, M.; Ceccherini, M.T. Impact of chlortetracycline and sulfapyridine antibiotics on soil enzyme activities. Int. Agrophys. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molaei, A.; Lakzian, A.; Haghnia, G.; Astaraei, A.; Rasouli-Sadaghiani, M.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Datta, R. Assessment of some cultural experimental methods to study the effects of antibiotics on microbial activities in a soil: An incubation study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suddarth, S.R.P.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Cavalcante, L.F.; Fraga, V.S.; Anderson, R.G.; Halvorson, J.J.; Bezerra, F.T.C.; Medeiros, S.A.S.; Costa, C.R.G.; Dias, N.S. Can humic substances improve soil fertility under salt stress and drought conditions? J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, S.; Younis, U.; Akhtar, N.; Ameer, A.; Ijaz, M.; Nasreen, S.; Huma, F.; Sharif, S.; Ehsanullah, M. Phosphorus solubilizing bacteria and rice straw biochar consequence on maize pigments synthesis. Int. J. Biosci. 2015, 5, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, S.; Younis, U.; Nasreen, S.; Akhtar, N.; Iqbal, M.T. Biochar consequences on cations and anions of sandy soil. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Danish, S.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M. Co-application of ACC-deaminase producing PGPR and timber-waste biochar improves pigments formation, growth and yield of wheat under drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danish, S.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M. Combined role of ACC deaminase producing bacteria and biochar on cereals productivity under drought. Phyton 2020, 89, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, U.; Danish, S.; Malik, S.A.; Ahmed, N.; Munir, T.M.; Rasheed, M.K. Role of cotton sticks biochar in immobilization of nickel under induced toxicity condition and growth indices of Trigonella corniculata L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; Tahzeeb-ul-Hassan, M.; Abid, M.; Fahad, S.; Brtnicky, M.; Dokulilova, T.; Datta, R.; Danish, S. Potential role of compost mixed biochar with rhizobacteria in mitigating lead toxicity in spinach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, H.; Ahmed, N.; Mubashir, M.; Danish, S. Chemical production of acidified activated carbon and its influences on soil fertility comparative to thermo-pyrolyzed biochar. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izhar Shafi, M.; Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Wahid, F.; Khan, A.; Yue, Z.; Danish, S.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; Brtnicky, M.; Datta, R. Application of Single Superphosphate with Humic Acid Improves the Growth, Yield and Phosphorus Uptake of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in Calcareous Soil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latal, R.D.O.; Hammerschmiedt, T.; Elbl, J.; Pecina, V.; Kintl, A.; Balakova, L.; Radziemska, M.; Baltazar, T.; Skarpa, P.; Danish, S.; et al. Bentonite-Based Organic Amendment Enriches Microbial Activity in Agricultural Soils. Land 2020, 9, 258. [Google Scholar]
- Marfo, T.D.; Datta, R.; Pathan, S.I.; Vranová, V. Ecotone Dynamics and Stability from Soil Scientific Point of View. Diversity 2019, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marfo, T.D.; Vranová, V.; Ekielski, A. Ecotone Dynamics and Stability from Soil Perspective: Forest-Agriculture Land Transition. Agriculture 2019, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, G.S.; Datta, R.; Imran Pathan, S.; Lal, R.; Meena, R.S.; Babu, S.; Das, A.; Bhowmik, S.; Datta, M.; Saha, P. Effects of conservation tillage and nutrient management practices on soil fertility and productivity of rice (Oryza sativa L.)–rice system in North Eastern region of India. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.Y.A.; Ibrahim, M.E.H.; Zhou, G.; Nimir, N.E.A.; Jiao, X.; Zhu, G.; Elsiddig, A.M.I.; Zhi, W.; Chen, X.; Lu, H. Ameliorative effects of jasmonic acid and humic acid on antioxidant enzymes and salt tolerance of forage sorghum under salinity conditions. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleda, L.; Park, H.J.; Yun, D.J.; Jeon, J.R.; Kim, M.G.; Cha, J.Y.; Kim, W.Y. Humic acid confers high-affinity K+ transporter 1-mediated salinity stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, R.; Anand, S.; Moulick, A.; Baraniya, D.; Pathan, S.I.; Rejsek, K.; Vranova, V.; Sharma, M.; Sharma, D.; Kelkar, A.; et al. How enzymes are adsorbed on soil solid phase and factors limiting its activity: A Review. Int. Agrophys. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, R.; Baraniya, D.; Wang, Y.-F.; Kelkar, A.; Meena, R.S.; Yadav, G.S.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Formanek, P. Amino acid: Its dual role as nutrient and scavenger of free radicals in soil. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imran, M.A.; Ali, A.; Ashfaq, M.; Hassan, S.; Culas, R.; Ma, C. Impact of climate smart agriculture (CSA) practices on cotton production and livelihood of farmers in Punjab, Pakistan. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, K.R.; Brand, D.; Wijewardana, C. Temperature effects on cotton seedling emergence, growth, and development. Agron. J 2017, 109, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Martinez, V.; Cotton, J. Lasting effects of soil health improvements with management changes in cotton-based cropping systems in a sandy soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.A.; Butt, M.B. Soil fertility status of cultivated lands in different agro-ecological zones of Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan. J. Appl. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jamal, A.; Hifsa, J. Assessment and Distribution of Macro and Micro Nutrients in Different Soil Series of District Swabi, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Hortic. Plant Res. 2018, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-ashmouny, A.A.A.; El-naqma, K.A. Role of application method in responses of cotton plants to micronutrients and potassium humate. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2018, 9, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drwish, A.S.; Abd Rabou, R.S.; Zaky, A.; Hamoda, S.A. Effect of some nutrients on growth, yield and fiber quality of egyptian cotton under saline condition. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 26, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, R.B.; Kadam, A.S.; Wadje, S.S. Role of potassium humate on growth and yield of soybean and black gram. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2011, 2, 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, A.P.; Raha, P.; Singh, C.M. Effect of potassium humate and chemical fertilizers on growth, yield and quality of rice (Oryza sative L.). Bangladesh J. Bot. 2014, 43, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basbag, S. Effects of humic acid application on yield and quality of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Asian J. Chem. 2008, 3, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar]
- Imbufe, A.U.; Patti, A.F.; Burrow, D.; Surapaneni, A.; Jackson, W.R.; Milner, A.D. Effects of potassium humate on aggregate stability of two soils from Victoria, Australia. Geoderma 2005, 125, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shujrah, A.A.; Mohd, K.Y.; Hussin, A.; Othman, R.; Haruna, O. Impact of potassium humate on selected chemical properties of an Acidic soil. In Proceedings of the 19th World Congress of Soil Science, Brisbane, Australia, 1–6 August 2010; pp. 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanpanah, D.; Khodadadi, M. Evaluation of potassium humate effects on germination, yield and yield components of HPS-II/67 hybrid true poato seed under in vitro and vivo conditions. Am. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 4, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, S.Z.; Islam, A.; Yoilmaz, M. Effect of potassium humate on hazelnut seed germination. Acta Hortic. 2001, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, S.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; Mohsin, F.; Hussain, M. ACC-deaminase producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and biochar mitigate adverse effects of drought stress on maize growth. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; Danish, S.; Abbas, M.; Ahmad, M.; Munir, T.M. ACC deaminase producing PGPR Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and agrobacterium fabrum along with biochar improve wheat productivity under drought stress. Agronomy 2019, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pervez, H.; Ashraf, M.; Makhdum, M.I. Influence of potassium nutrition on gas exchange characteristics and water relations in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Photosynthetica 2004, 42, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Yang, J.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Oosterhuis, D.M.; Zhou, Z. Potassium application affects carbohydrate metabolism in the leaf subtending the cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) boll and its relationship with boll biomass. Filed Crop. Res. 2015, 179, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Lv, F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Abudurezike, A.; Oosterhuis, D.M. Changes of sucrose metabolism in leaf subtending to cotton boll under cool temperature due to late planting. Filed Crop. Res. 2013, 144, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formánek, L.L.P.; Drápelová, I.; Brtnicky, M.; Datta, R.V.V. Enantiomers of Carbohydrates and Their Role in Ecosystem Interactions: A Review. Symmetry 2020, 12, 470. [Google Scholar]
- Hemida, K.A.; Eloufey, A.Z.A.; Seif El-Yazal, M.A.; Rady, M.M. Integrated effect of potassium humate and α-tocopherol applications on soil characteristics and performance of Phaseolus vulgaris plants grown on a saline soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, R.; Malavasi, F.F.F.; Predieri, S.; Castagneto, M. Effect of potassium humate on apple cv. “Golden Delicious” cultured in vitro. Plant Cell. Tissue Organ Cult. 1991, 24, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report, F. Use of Biochar from the Pyrolysis of Waste Organic Material as a Soil Amendment Ecology Publication Number 09-07-062; Washington State University: Pullman, WA, USA, 2009; ISBN 3604076900. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.L.; Miller, R.H.; Keeny, D.R. Soil pH and lime requirement. In Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A. An Examination of Methods for Determining Organic Carbon and Nitrogen in Soils. J. Agric. Sci. 1935, 25, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Method of Soil Analysis, Agronomy No. 9, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Page, A.L., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, H.D. Cation-Exchange Capacity. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 9.2; Norman, A.G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1965; pp. 891–901. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, P.F. Potassium. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 9.2; Norman, A.G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1965; pp. 1022–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.F.; Bilal, M.F.; Awais, M.; Shahid, M.; Anjum, S.A. Effect of nitrogen on seed cotton yield and fiber qualities of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2010, 20, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- R_Core_Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]






| Soil Applied Potassium Humate | Electrical Conductivity | pH | Organic Matter | Nitrogen | Available Phosphorus | Exchangeable Potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L ha−1 | µS cm−1 | 5 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |
| 0 | 3020 | 8.40 | 0.62 | 0.31 | 7.06 | 195.00 |
| 10 | 3010 | 8.45 | 0.64 | 0.32 | 7.25 | 207.00 |
| 20 | 2890 | 8.45 | 0.66 | 0.33 | 7.52 | 212.5 |
| 30 | 2710 | 8.37 | 0.67 | 0.34 | 7.95 | 222.5 |
| Effect | Plant Height | Nodes Plant−1 | Sympodial Branches | Bolls Plant−1 | Boll Weight | Seed Cotton Yield | GOT | Fiber Length | Fiber Strength | Fiber Fitness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH soil application (S) | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| PH seed dressing (D) | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| S × D | 0.001 | 0.220 | 0.001 | 0.020 | 0.210 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Soil Application (L ha−1) | GOT (%) | Fiber Length (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seed Dressing (mL kg−1) | Seed Dressing (mL kg−1) | |||||||
| 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |
| 0 | 38.1 ± 1.87 a | 40.1 ± 1.47 a | 40.2 ± 2.13 ab | 42.1 ± 1.81 a | 27.53 ± 0.15 a | 28.30 ± 0.4 ab | 28.8 ± 0.35 a | 29.13 ± 0.35 a |
| 10 | 39.73 ± 1.72 a | 40.2 ± 0.87 a | 40.4 ± 1.11 ab | 42.3 ± 1.35 a | 27.8 ± 0.10 a | 28.50 ± 0.4 a | 28.97 ± 0.31 a | 29.33 ± 0.55 a |
| 20 | 39.97 ± 1.65 a | 40.7 ± 1.22 a | 42.73 ± 10 a | 44.4 ± 0.46 a | 28.17 ± 0.31 a | 28.7 ± 0.36 a | 29.07 ± 0.40 a | 29.5 ± 0.79 a |
| 30 | 36.67 ± 1.55 a | 36.9 ± 1.51 a | 37.23 ± 1.47 b | 37.43 ± 1.72 b | 27.23 ± 0.15 a | 27.27 ± 0.45 b | 27.3 ± 0.36 b | 27.33 ± 0.38 b |
| Soil Application (L ha−1) | Fiber Strength (g/tex) | Fiber Fineness (mic) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seed Dressing (mL kg−1) | Seed Dressing (mL kg−1) | |||||||
| 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |
| 0 | 25.73 ± 0.15 b | 26.30 ± 0.10 b | 27.10 ± 0.10 c | 28.20 ± 0.10 b | 4.73 ± 0.06 a | 4.63 ± 0.04 b | 4.53 ± 0.04 b | 4.38 ± 0.05 b |
| 10 | 25.83 ± 0.15 ab | 26.57 ± 0.06 b | 27.50 ± 0.10 b | 28.53 ± 0.06 a | 4.70 ± 0.10 a | 4.59 ± 0.04 b | 4.48 ± 0.04 b | 4.33 ± 0.04 b |
| 20 | 26.10 ± 0.10 a | 26.90 ± 0.10 a | 27.90 ± 0.10 a | 28.73 ± 0.15 a | 4.65 ± 0.05 a | 4.57 ± 0.04 b | 4.43 ± 0.04 b | 4.25 ± 0.04 b |
| 30 | 25.30 ± 0.10 c | 25.40 ± 0.10 c | 25.50 ± 0.10 d | 25.60 ± 0.10 c | 4.77 ± 0.06 a | 4.86 ± 0.04 a | 4.73 ± 0.06 a | 4.70 ± 0.10 a |
| Soil Depth | pH | Electric Conductivity | Organic Matter | Available Phosphorus | Nitrogen | Exchangeable Potassium | CEC | Texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | - | µS cm−1 | % | mg kg−1 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mmol (+) kg−1 | - |
| 0–15 | 8.50 | 3500 | 0.56 | 6.70 | 0.28 | 210.00 | 250 | Loam |
| 15–30 | 8.40 | 2930 | 0.58 | 5.70 | 0.29 | 180.00 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, A.; Ali, M.; Shahzad, K.; Ahmad, F.; Iqbal, S.; Rahman, M.H.U.; Ahmad, S.; Iqbal, M.M.; Danish, S.; Fahad, S.; et al. Impact of Seed Dressing and Soil Application of Potassium Humate on Cotton Plants Productivity and Fiber Quality. Plants 2020, 9, 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111444
Ullah A, Ali M, Shahzad K, Ahmad F, Iqbal S, Rahman MHU, Ahmad S, Iqbal MM, Danish S, Fahad S, et al. Impact of Seed Dressing and Soil Application of Potassium Humate on Cotton Plants Productivity and Fiber Quality. Plants. 2020; 9(11):1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111444
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Asmat, Muqarrab Ali, Khurram Shahzad, Fiaz Ahmad, Shahid Iqbal, Muhammad Habib Ur Rahman, Shakeel Ahmad, Muhammad Mazhar Iqbal, Subhan Danish, Shah Fahad, and et al. 2020. "Impact of Seed Dressing and Soil Application of Potassium Humate on Cotton Plants Productivity and Fiber Quality" Plants 9, no. 11: 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111444
APA StyleUllah, A., Ali, M., Shahzad, K., Ahmad, F., Iqbal, S., Rahman, M. H. U., Ahmad, S., Iqbal, M. M., Danish, S., Fahad, S., Alkahtani, J., Soliman Elshikh, M., & Datta, R. (2020). Impact of Seed Dressing and Soil Application of Potassium Humate on Cotton Plants Productivity and Fiber Quality. Plants, 9(11), 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111444