Simulation Model to Calculate Bird-Aircraft Collisions and Near Misses in the Airport Vicinity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Simulation Environment
2.1.1. Simulation Platform
2.1.2. Bird Movement
2.1.3. Flock Composition
2.2. Monte Carlo Simulations
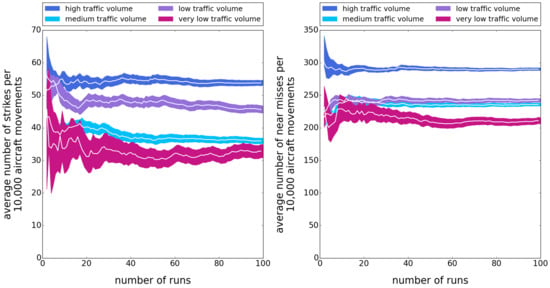
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernhardt, G.E.; Blackwell, B.F.; DeVault, T.L.; Kutschbach-Brohl, L. Fatal injuries to birds from collisions with aircraft reveal anti-predator behaviours. Ibis 2010, 152, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolbeer, R.A.; Weller, J.R.; Anderson, A.L.; Begier, M.J. Wildlife Strikes to Civil Aircraft in the United States 1990–2015; Serial Report Number 22; Federal Aviation Administration National Wildlife Strike Database: Washington, DC, USA, November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, J. Update to ‘100 Years of Fatalities and Destroyed Civil Aircraft due to Bird Strikes’. In Proceedings of the 31th Meeting of the World Bird Strike Association, Stavanger, Norway, 25–29 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dolbeer, R.A. Increasing Trend of damaging bird strikes with aircraft outside the airport boundary: Implications for mitigation measures. Hum.-Wildl. Interact. 2011, 5, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, J.; Shaw, P.; Dekker, A.; Patrick, K. Approaches to Wildlife Management in Aviation. In Problematic Wildlife. A Cross-Disciplinary Approach; Angelici, F.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Chapter 22; pp. 465–488. [Google Scholar]
- Dolbeer, R.A. Height Distribution of Birds Recorded by Collisions with Civil Aircraft. J. Wildl. Manag. 2006, 70, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamoun-Baranes, J.; van Gasteren, H.; Ross-Smith, V. Sharing the aerosphere: Conflicts and potential solutions. In Aeroecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 465–497. [Google Scholar]
- ICAO. Wildlife Control and Reduction. In Airport Services Manual, 4th ed.; International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO): Montreal, QC, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- DeVault, T.L.; Blackwell, B.F.; Seamans, T.W.; Belant, J.L. Identification of off airport interspecific avian hazards to aircraft. J. Wildl. Manag. 2016, 80, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hale, M.R.; Stanley, R. Evaluating the Design and Suitability of the Wildlife Surveillance Concept. In Proceedings of the Integrated Communications Navigation and Surveillance Conference, Herndon, VA, USA, 18–20 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dolbeer, R.A. Feathers in the fan. AeroSafety World 2008, 3, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- National Transportation Safety Board NTSB. Loss of Thrust in Both Engines After Encountering a Flock of Birds and Subsequent Ditching on the Hudson River, US Airways Flight 1549, Airbus A320-214, N106US. In Proceedings of the Animation for Aircraft Accident, Weehawken, NJ, USA, 15 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- European Organization for the Safety of Air Navigation. Bird Strike on Final Approach: Guidance for Flight Crews. 2017. Available online: https://www.skybrary.aero/index.php/Bird_Strike_on_Final_Approach:_Guidance_for_Flight_Crews (accessed on 2 February 2018).
- Metz, I.; Ellerbroek, J.; Mühlhausen, T.; Kügler, D.; Hoekstra, J.M. Simulating the Risk of Bird Strikes. In Proceedings of the 7th SESAR Innovation Days, Serbia, Balkans, 28–30 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, J.M.; Ellerbroek, J. BlueSky ATC Simulator Project: An Open Data and Open Source Approach. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Research in Air Transportation, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 20–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Metz, I.; Hoekstra, J.M.; Ellerbroek, J.; Kügler, D. Aircraft Performance for Open Air Traffic Simulations. In Proceedings of the AIAA Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, T.; O’Callaghan, M.; Bolger, R. The Avoidance Behaviour Shown by the Rook (Corvus frugilegus) to Commercial Aircraft. In Advances in Vertebrate Pest Management; Pelz, H.J., Crowan, D., Feare, C., Eds.; Filander Verlag: Furth, Germany, 2001; pp. 291–299. [Google Scholar]
- Frid, A.; Dill, L. Human-caused disturbance stimuli as a form of predation risk. Conserv. Ecol. 2002, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, B.F.; Bernhardt, G.E. Efficacy of aircraft landing lights in stimulating avoidance behavior in birds. J. Wildl. Manag. 2004, 68, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beason, R.C.; Nohara, T.J.; Weber, P. Beware the Boojum: Caveats and strengths of avian radar. Hum.-Wildl. Interact. 2013, 7, 16–46. [Google Scholar]
- Dokter, A.M.; Baptist, M.J.; Ens, B.J.; Krijgsveld, K.L.; van Loon, E.E. Bird radar validation in the field by time-referencing line-transect surveys. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerringer, M.B.; Lima, S.L.; DeVault, T.L. Evaluation of an avian radar system in a midwestern landscape. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2016, 40, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, E. Radar Ornithology; Methuen: London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Gauthreaux, S.A., Jr. Weather Radar Quantification of Bird Migration. BioScience 2014, 20, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamoun-Baranes, J.; Alves, J.A.; Bauer, S.; Dokter, A.M.; Húppop, O.; Koistinen, J.; Leijnse, H.; Liechti, F.; van Gasteren, H.; Chapman, J.W. Continental-scale radar monitoring of the aerial movements of animals. Mov. Ecol. 2014, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, C.; Dokter, A.M.; Verlinden, L.; Shamoun-Baranes, J.; Schmid, B.; Desmet, P.; Bauer, S.; Chapman, J.; Alves, J.A.; Stepanian, P.M.; et al. Revealing patterns of nocturnal migration using the European weather radar network. Ecography 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gasteren, H.; Holleman, I.; Bouten, W.; van Loon, E.; Shamoun-Baranes, J. Extracting bird migration information from C-band Doppler weather radars. Ibis 2008, 150, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokter, A.M.; Liechti, F.; Stark, H.; Delobbe, L.; Tabary, P.; Holleman, I. Bird migration flight altitudes studied by a network of operational weather radars. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, R.P.; Szafoni, R.E. Evidence for widely dispersed birds migrating together at night. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2008, 48, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newton, I. The Migration Ecology of Birds; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dolbeer, R.A. The History of Wildlife Strikes and Management at Airports. In Wildlife in Airport Environments. Preventing Animal-Aircraft Collisions through Science-Based Management, 1st ed.; DeVault, T.L., Blackwell, B.F., Belant, J.L., Eds.; The John Jopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2013; Chapter 1; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lensink, R.; Kwak, R. Vogeltrek over Arnhem in 1983 met een samenvatting over de periode 1981–1983 en methodieken voor het bewerken van telmateriaal. deel I en II. LIMOSA 1985, 59, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Dunning, J.B., Jr. CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, B. Nearest neighbour distances in day and night migrating birds. A study using stereophotography. Vogelwarte 1984, 32, 206–218. [Google Scholar]
- Hüppop, O.; Dierschke, J.; Exo, K.M.; Fredrich, E.; Hill, R. Bird migration studies and potential collision risk with offshore wind turbines. Ibis 2006, 148, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Australian Transport Safety Bureau. Australian Aviation Wildlife Strike Statistics 2006 to 2015; Australian Transport Safety Bureau: Canberra, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon, B. Sharing the Skies. An Aviation Industry Guide to the Management of Wildlife Hazards; Transport Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Juricic, E.; Gaffney, J.; Blackwelll, B.F.; Baumhardt, P. Bird strikes and aircraft fuselage color: A correlational study. Hum.-Wildl. Interact. 2011, 5, 224–234. [Google Scholar]
- Air Traffic Control The Netherlands. AD 2.24 EHEH Charts Related to an Aerodrome. AIP The Netherlands. Effective 10 November 2016. Available online: http://www.ais-netherlands.nl/aim/2017-05-11-AIRAC/eAIP/html/index-en-GB.html (accessed on 7 April 2017).
- Dekker, A.; van Gasteren, H. EURBASE: Military bird strike frequency in Europe. In Proceedings of the International Bird Strike Committee Conference, Athens, Greece, 23–27 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, J. Bird Strikes in the German Civil Aviation 2011 to 2015. Vogel und Luftverkehr Online. 2016. Available online: http://www.davvl.de/sites/default/files/2018-06/2016_ebert_vogelschlaege_deutschen_zivilluftfahrt_11bis15.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2018).
- Van Gasteren, H.; Both, I.; Shamoun-Baranes, J.; Laloë, J.O.; Bouten, W. GPS logger onderzoek aan Buizerds helpt vogelaanvaringen op militaire vliegvelden te voorkomen. Limosa 2014, 87, 107–116. [Google Scholar]






| Range Avian Radar (0 m–200 m) | Range Weather Radar (200 m–400 m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Ratio a | Cumulated Ratio | Bird Size | Species | Ratio b | Cumulated Ratio | Bird Size |
| common chaffinch | 25.94 | 25.94 | small | redwing | 25.40 | 25.40 | small |
| common starling | 11.49 | 37.43 | small | lapwing | 23.58 | 48.98 | medium |
| meadow pipit | 8.40 | 45.83 | small | black-headed gull | 16.41 | 65.39 | medium |
| redwing | 7.42 | 53.25 | small | rook | 12.67 | 78.06 | medium |
| barn swallow | 4.68 | 57.93 | small | eurasian skylark | 4.02 | 82.08 | small |
| common house martin | 4.56 | 62.49 | small | western jackdaw | 3.31 | 85.39 | medium |
| black-headed gull | 4.19 | 66.68 | medium | common wood pigeon | 3.18 | 88.57 | medium |
| common wood pigeon | 4.07 | 70.75 | medium | common chaffinch | 3.05 | 91.62 | small |
| eurasian skylark | 3.98 | 74.73 | small | common swift | 2.68 | 94.30 | small |
| lapwing | 3.91 | 78.64 | medium | fieldfare | 1.78 | 96.08 | medium |
| red crossbill | 2.81 | 81.45 | medium | european herring gull | 1.19 | 97.27 | large |
| common linnet | 2.52 | 83.97 | small | buzzard | 0.93 | 98.20 | large |
| fieldfare | 2.47 | 86.44 | medium | eurasian sparrowhawk | 0.92 | 99.12 | medium |
| common swift | 1.71 | 88.15 | small | common house martin | 0.88 | 100.00 | small |
| eurasian siskin | 1.33 | 89.48 | small | ||||
| Group Identifier | Represented Birds (%) | Average Flock Size (-) | Small Birds (%) | Medium Birds (%) | Large Birds (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 48 | 3.61 | 10 | 90 | 0 |
| II | 25 | 6.55 | 57 | 43 | 0 |
| III | 27 | 10.86 | 83 | 17 | 0 |
| Group Identifier | Represented Birds a (%) | Average Flock Size b (-) | Small Birds c (%) | Medium Birds c (%) | Large Birds c (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 51 | 15.00 | 80 | 20 | 0 |
| II | 26 | 7.50 | 80 | 20 | 0 |
| III | 23 | 3.50 | 80 | 20 | 0 |
| Group Identifier | Represented Birds (%) | Average Flock Size (-) | Small Birds (%) | Medium Birds (%) | Large Birds (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 21 | 1.87 | 24 | 34 | 42 |
| II | 22 | 6.49 | 48 | 52 | 0 |
| III | 51 | 13.51 | 34 | 66 | 0 |
| IV | 6 | 1.00 | 36 | 62 | 2 |
| Group Identifier | Represented Birds a (%) | Average Flock Size b (-) | Small Birds c (%) | Medium Birds c (%) | Large Birds c (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 10 | 3.50 | 27 | 37 | 36 |
| II | 5 | 7.50 | 27 | 37 | 36 |
| III | 5 | 15.00 | 27 | 37 | 36 |
| IV | 80 | 1.00 | 27 | 37 | 36 |
| Parameter | Radar Source | Range |
|---|---|---|
| altitude | AR, WR | respective altitude band |
| latitude | WR | entire area |
| longitude | WR | entire area |
| speed | WR | |
| heading | WR |
| n | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | p | p | ||||||||
| collisions, entire year | ||||||||||
| very low | −0.14 | 0.091 | 0.13 | 0.108 | 0.31 | 0.001 | 93 | |||
| low | 0.07 | 0.251 | 0.21 | 0.017 | 0.38 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| medium | 0.23 | 0.011 | 0.36 | <0.001 | 0.51 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| high | 0.06 | 0.226 | 0.28 | 0.002 | 0.42 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| collisions, w/o June | ||||||||||
| very low | 0.00 | 0.5 | 0.19 | 0.036 | 0.40 | <0.001 | 87 | |||
| low | 0.12 | 0.127 | 0.31 | 0.001 | 0.48 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| medium | 0.23 | 0.010 | 0.39 | <0.001 | 0.51 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| high | 0.23 | 0.01 | 0.43 | <0.001 | 0.59 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| near misses, entire year | ||||||||||
| very low | 0.16 | 0.055 | 0.30 | 0.001 | 0.49 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| low | 0.48 | <0.001 | 0.53 | <0.001 | 0.61 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| medium | 0.63 | <0.001 | 0.70 | <0.001 | 0.77 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| high | 0.43 | <0.001 | 0.52 | <0.001 | 0.58 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| near misses, w/o June | ||||||||||
| very low | 0.25 | 0.006 | 0.42 | <0.001 | 0.61 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| low | 0.59 | <0.001 | 0.66 | <0.001 | 0.75 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| medium | 0.71 | <0.001 | 0.78 | <0.001 | 0.85 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
| high | 0.61 | <0.001 | 0.72 | <0.001 | 0.81 | <0.001 | 100 | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Metz, I.C.; Mühlhausen, T.; Ellerbroek, J.; Kügler, D.; Van Gasteren, H.; Kraemer, J.; Hoekstra, J.M. Simulation Model to Calculate Bird-Aircraft Collisions and Near Misses in the Airport Vicinity. Aerospace 2018, 5, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace5040112
Metz IC, Mühlhausen T, Ellerbroek J, Kügler D, Van Gasteren H, Kraemer J, Hoekstra JM. Simulation Model to Calculate Bird-Aircraft Collisions and Near Misses in the Airport Vicinity. Aerospace. 2018; 5(4):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace5040112
Chicago/Turabian StyleMetz, Isabel C., Thorsten Mühlhausen, Joost Ellerbroek, Dirk Kügler, Hans Van Gasteren, Jan Kraemer, and Jacco M. Hoekstra. 2018. "Simulation Model to Calculate Bird-Aircraft Collisions and Near Misses in the Airport Vicinity" Aerospace 5, no. 4: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace5040112
APA StyleMetz, I. C., Mühlhausen, T., Ellerbroek, J., Kügler, D., Van Gasteren, H., Kraemer, J., & Hoekstra, J. M. (2018). Simulation Model to Calculate Bird-Aircraft Collisions and Near Misses in the Airport Vicinity. Aerospace, 5(4), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace5040112