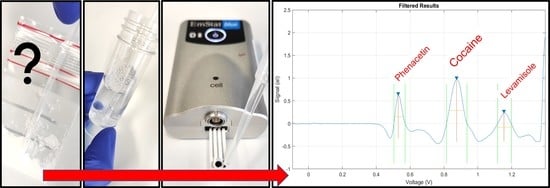
Rapid On-Site Detection of Illicit Drugs in Smuggled Samples with a Portable Electrochemical Device †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Profiling of Illicit Drugs
3.2. Generating the Library of Electrochemical Profiles
3.3. Testing the Portable Electrochemical Device with Confiscated Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). European Drug Report 2021: Trends and Developments; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2021; Division for Policy Analysis and Public Affairs: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction and Europol. EU Drug Markets: Impact of COVID-19; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020; ISBN 9789294974938. [Google Scholar]
- Philp, M.; Fu, S. A review of chemical ‘spot’ tests: A presumptive illicit drug identification technique. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.; Powell, J.; Pijl, E.M. An overview of forensic drug testing methods and their suitability for harm reduction point-of-care services. Harm Reduct. J. 2017, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katainen, E.; Elomaa, M.; Laakkonen, U.M.; Sippola, E.; Niemelä, P.; Suhonen, J.; Järvinen, K. Quantification of the amphetamine content in seized street samples by Raman spectroscopy. J. Forensic Sci. 2007, 52, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Penido, C.A.F.; Pacheco, M.T.T.; Lednev, I.K.; Silveira, L. Raman spectroscopy in forensic analysis: Identification of cocaine and other illegal drugs of abuse. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2016, 47, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg, R.F.; Verduin, J.; Ridder, R.; Weesepoel, Y.; Alewijn, M.; Heerschop, M.; Keizers, P.H.J.; Esch, A.; Asten, A.C. Performance Evaluation of Handheld Raman Spectroscopy for Cocaine Detection in Forensic Case Samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 13, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg, R.F.; Verduin, J.; Weesepoel, Y.; Alewijn, M.; Heerschop, M.; Koomen, G.; Keizers, P.; Bakker, F.; Wallace, F.; van Esch, A.; et al. Rapid and robust on-scene detection of cocaine in street samples using a handheld near-infrared spectrometer and machine learning algorithms. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deconinck, E.; Aït-Kaci, C.; Raes, A.; Canfyn, M.; Bothy, J.L.; Duchateau, C.; Mees, C.; De Braekeleer, K.; Gremaux, L.; Blanckaert, P. An infrared spectroscopic approach to characterise white powders, easily applicable in the context of drug checking, drug prevention and on-site analysis. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, A.M.; Parrilla, M.; Feier, B.; Oprean, R.; Cristea, C.; De Wael, K. Analytical techniques for the determination of Amphetamine-type substances in different matrices: A comprehensive review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, M.; Florea, A.; Eliaerts, J.; Van Durme, F.; Samyn, N.; De Wael, K. Tackling Poor Specificity of Cocaine Color Tests by Electrochemical Strategies. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6811–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, S.T.; Van Echelpoel, R.; Boeye, G. Towards Developing a Screening Strategy for Ecstasy: Revealing the Electrochemical Profile. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 4826–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerace, E.; Seganti, F.; Luciano, C.; Lombardo, T.; Di Corcia, D.; Teifel, H.; Vincenti, M.; Salomone, A. On-site identification of psychoactive drugs by portable Raman spectroscopy during drug-checking service in electronic music events. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2019, 38, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Araujo, W.R.; Cardoso, T.M.G.; da Rocha, R.G.; Santana, M.H.P.; Muñoz, R.A.A.; Richter, E.M.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Coltro, W.K.T. Portable analytical platforms for forensic chemistry: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1034, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, P.C.; Ataíde, V.N.; Silva Chagas, C.L.; Angnes, L.; Tomazelli Coltro, W.K.; Longo Cesar Paixão, T.R.; Reis de Araujo, W. Wearable electrochemical sensors for forensic and clinical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanfrognini, B.; Pigani, L.; Zanardi, C. Recent advances in the direct electrochemical detection of drugs of abuse. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2020, 24, 2603–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rycke, E.; Stove, C.; Dubruel, P.; De Saeger, S.; Beloglazova, N. Recent developments in electrochemical detection of illicit drugs in diverse matrices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.; Dennany, L. Applications of electrochemical sensors: Forensic drug analysis. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, J.R.B.; Díaz, V.C.; Garcia, A.C.; Blanco, P.T. Voltammetric assay of heroin in illicit dosage forms. Analyst 1990, 115, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedul, M.T.F.; Rodríguez, J.R.B.; García, A.C.; Blanco, P.T. Voltammetric determination of cocaine in confiscated samples. Electroanalysis 1991, 3, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squella, J.A.; Cassels, B.K.; Arata, M.; Bavestrello, M.P.; Nuñez-Vergara, L.J. Electrochemical oxidation of methylenedioxyamphetamines. Talanta 1993, 40, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Okada, K.; Katsu, T. Determination of methamphetamine in urine in-situ using a methamphetamine-sensitive membrane electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 274, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Parrilla, M.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Montiel, N.F.; Barfidokht, A.; Van Echelpoel, R.; De Wael, K.; Wang, J. Wearable Electrochemical Sensors for the Monitoring and Screening of Drugs. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2679–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfidokht, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Seenivasan, R.; Liu, S.; Hubble, L.J.; Wang, J.; Hall, D.A. Wearable electrochemical glove-based sensor for rapid and on-site detection of fentanyl. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Li, Z.; Brown, C.; Galdino, N.M.; Shah, R.; Liu, S.; Hubble, L.J.; Bagot, K.; Tapert, S.; et al. Simultaneous detection of salivary Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and alcohol using a Wearable Electrochemical Ring Sensor. Talanta 2020, 211, 120757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Joosten, F.; De Wael, K. Enhanced electrochemical detection of illicit drugs in oral fluid by the use of surfactant-mediated solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Slosse, A.; Van Echelpoel, R.; Felipe Montiel, N.; Van Durme, F.; De Wael, K. Portable Electrochemical Detection of Illicit Drugs in Smuggled Samples: Towards More Secure Borders. Chem. Proc. 2021, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asturias-Arribas, L.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J. Sensitive and selective cocaine electrochemical detection using disposable sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 834, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, J.M.; Ramos, D.L.O.; Sousa, R.M.F.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Santana, M.H.P.; Muñoz, R.A.A.; Richter, E.M. A portable electrochemical method for cocaine quantification and rapid screening of common adulterants in seized samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murilo Alves, G.; Soares Castro, A.; McCord, B.R.; de Oliveira, M.F. MDMA Electrochemical Determination and Behavior at Carbon Screen-printed Electrodes: Cheap Tools for Forensic Applications. Electroanalysis 2020, 33, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teófilo, K.R.; Arantes, L.C.; Marinho, P.A.; Macedo, A.A.; Pimentel, D.M.; Rocha, D.P.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Richter, E.M.; Munoz, R.A.A.; dos Santos, W.T.P. Electrochemical detection of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy) using a boron-doped diamond electrode with differential pulse voltammetry: Simple and fast screening method for application in forensic analysis. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, E.M.P.J.; Garrido, J.M.P.J.; Milhazes, N.; Borges, F.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Electrochemical oxidation of amphetamine-like drugs and application to electroanalysis of ecstasy in human serum. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 79, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, A.M.; Farag, M.A.; Tantawy, M.A. A novel trimodal system on a paper-based microfluidic device for on-site detection of the date rape drug “ketamine”. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1104, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, J.; Parrilla, M.; Sleegers, N.; Samyn, N.; Bijvoets, S.M.; Heerschop, M.W.J.; van Nuijs, A.L.N.; De Wael, K. Identifying Electrochemical Fingerprints of Ketamine with Voltammetry and Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry for Its Detection in Seized Samples. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13485–13492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulladofonou, G.; Freris, C.; Economou, A.; Kokkinos, C. Wearable Electronic Finger for Date Rape Drugs Screening: From “Do-It-Yourself” Fabrication to Self-Testing. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 4087–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe Montiel, N.; Parrilla, M.; Beltrán, V.; Nuyts, G.; Van Durme, F.; De Wael, K. The opportunity of 6-monoacetylmorphine to selectively detect heroin at preanodized screen printed electrodes. Talanta 2021, 226, 122005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaee, A.; Salimi, A.; Teymourian, H. Graphene nanosheets modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous detection of heroine, morphine and noscapine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, J.; Parrilla, M.; Sleegers, N.; Van Durme, F.; van den Berg, J.; van Nuijs, A.L.N.; De Wael, K. Electrochemical profiling and LC-MS characterization of synthetic cathinones: From methodology to detection in forensic samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1282–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.P.; Metters, J.P.; Khreit, O.I.G.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Banks, C.E. Forensic electrochemistry applied to the sensing of new psychoactive substances: Electroanalytical sensing of synthetic cathinones and analytical validation in the quantification of seized street samples. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9985–9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieiro, M.O.B.; Arantes, L.C.; Moreira, D.A.R.; Pimentel, D.M.; Lima, C.D.; Costa, L.M.F.; Verly, R.M.; dos Santos, W.T.P. Electrochemical detection of eutylone using screen-printed electrodes: Rapid and simple screening method for application in forensic samples. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 412, 140106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Smith, J.P.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Banks, C.E. Regal electrochemistry: Sensing of the synthetic cathinone class of new psychoactive substances (NPSs). Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6470–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Montiel, N.F.; Van Durme, F.; De Wael, K. Derivatization of amphetamine to allow its electrochemical detection in illicit drug seizures. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2021, 337, 129819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Aguayo, D.; De Wael, K.; Valle, M. del Voltammetric sensing using an array of modified SPCE coupled with machine learning strategies for the improved identification of opioids in presence of cutting agents. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 902, 115770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slosse, A.; Van Durme, F.; Samyn, N.; Mangelings, D.; Vander Heyden, Y. Evaluation of data preprocessings for the comparison of GC–MS chemical profiles of seized cannabis samples. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 310, 110228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Echelpoel, R.; de Jong, M.; Daems, D.; Van Espen, P.; De Wael, K. Unlocking the full potential of voltammetric data analysis: A novel peak recognition approach for (bio)analytical applications. Talanta 2021, 233, 122605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, G.; Barich, H.; Driesen, K.; Felipe Montiel, N.; Neven, L.; Mendonça, C.D.; Shanmugam, S.T.; Daems, E.; Wael, K. De Unlocking the full power of electrochemical fingerprinting for on-site sensing applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 5955–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milhazes, N.; Martins, P.; Uriarte, E.; Garrido, J.; Calheiros, R.; Marques, M.P.M.; Borges, F. Electrochemical and spectroscopic characterisation of amphetamine-like drugs: Application to the screening of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and its synthetic precursors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 596, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broséus, J.; Gentile, N.; Esseiva, P. The cutting of cocaine and heroin: A critical review. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 262, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentin, T.R.; Krotulski, A.J.; Martin, D.M.; Browne, T.; Triplett, J.; Conti, T.; Logan, B.K. Detection of Cutting Agents in Drug-Positive Seized Exhibits within the United States. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 64, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Target Compound/ Ep (V) | SPE pH 12 | SPE p-SPE | SPE pH 5 | SPE pH 10 + NQS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cocaine | 0.85 | 0.78 | - | 0.84 |
| Heroin | 0.16, 0.81 | 0.19, 0.77 | 0.97 | 0.20, 0.80 |
| MDMA | 0.93 | 0.71, 0.91 | 1.08 | 0.82, 0.97 |
| Amphetamine | - | - | - | 0.66 |
| Methamphetamine | 0.91 | 0.76 | - | 0.87 |
| Paracetamol | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.22 |
| Levamisole | 1.12 | 1.04 | 1.25 | - |
| Lidocaine | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.92 | - |
| Caffeine | - | - | - | - |
| Phenacetin | 0.54 | 0.52 | 0.85 | - |
| Benzocaine | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.86 | - |
| Procaine | 0.67 | 0.52 | 0.88 | - |
| Sample | GC-MS | Electrochemical Reader | Portable Raman | Compact ATR-FTIR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cocaine | Cocaine | Cocaine mixture | Cocaine HCl |
| 2 | Cocaine, caffeine, levamisole | Cocaine | Cocaine mixture | Cocaine HCl |
| 3 | Cocaine, levamisole | Cocaine | Cocaine mixture | Cocaine HCl |
| 4 | Cocaine, lidocaine, levamisole, phenacetin | Cocaine, lidocaine | Lidocaine, cocaine mixture | Cocaine HCl, lidocaine HCl |
| 5 | Cocaine, phenacetin, levamisole | Cocaine, phenacetin | Cocaine mixture | Cocaine HCl, phenacetin |
| 6 | Cocaine, levamisole | Cocaine | Cocaine mixture | Cocaine HCl |
| 7 | Cocaine base | Cocaine | Benzyl benzoate, cocaine mixture | Benzoylecgonine |
| 8 | Cocaine, levamisole | Cocaine, levamisole | Cocaine mixture | Cocaine, levamisole |
| 9 | Cocaine, caffeine | Cocaine | Cocaine mixture | Cocaine HCl |
| 10 | Cocaine, lidocaine, levamisole, caffeine, phenacetin | Cocaine, lidocaine | Lidocaine | Lidocaine base |
| 11 | Heroin, caffeine, 6-MAM, noscapine, papaverine | Heroin | Normorphine, heroin base | Heroin HCl, caffeine |
| 12 | Heroin, caffeine, 6-MAM, morphine, noscapine, papaverine | Heroin | CTMACl, tin(II) Cl dihydrate | 6-MAM, caffeine |
| 13 | Heroin, caffeine, paracetamol, 6-MAM, noscapine, papaverine | Heroin, paracetamol * | CTMACl, tin(II) Cl dihydrate | Heroin, paracetamol, caffeine |
| 14 | Heroin, caffeine, 6-MAM, noscapine, papaverine, paracetamol | Heroin | Unknown (lead tin, CTMACl) | Paracetamol, caffeine |
| 15 | Heroin, 6-MAM, noscapine, papaverine | Heroin | CTMACl | Heroin, noscapine |
| 16 | Heroin, paracetamol, 6-MAM, morphine, caffeine, codeine, noscapine, papaverine | Heroin, paracetamol | CTMACl, a-pyrrolidinohexanophenone | Heroin, noscapine |
| 17 | Heroin, paracetamol, 6-MAM, caffeine, noscapine, papaverine | Heroin, paracetamol | CTMACl, tin(II) Cl dihydrate | Heroin, paracetamol, caffeine |
| 18 | Heroin, paracetamol, 6-MAM, caffeine, noscapine, papaverine | Heroin | Unknown (heroin base) | Heroin HCl, caffeine |
| 19 | Heroin, paracetamol, 6-MAM, caffeine, noscapine, papaverine | Heroin, paracetamol | CTMACl | Heroin, caffeine, paracetamol, noscapine |
| 20 | Heroin, paracetamol, 6-MAM, caffeine, noscapine, papaverine | Heroin, paracetamol | CTMACl, tin(II) Cl dihydrate | Heroin, paracetamol, caffeine |
| 21 | MDMA | MDMA | MDMA tablet | MDMA |
| 22 | MDMA | MDMA | MDMA crystals | MDMA |
| 23 | MDMA | MDMA | MDMA tablet | MDMA |
| 24 | MDMA | Negative | MDMA crystals | MDMA |
| 25 | MDMA | MDMA | MDMA tablet | MDMA |
| 26 | MDMA | MDMA | MDMA tablet | MDMA |
| 27 | MDMA | MDMA | MDMA crystals | MDMA |
| 28 | MDMA | MDMA | MDMA crystals | MDMA |
| 29 | MDMA | MDMA | MDMA crystals | MDMA |
| 30 | MDMA | MDMA | MDMA crystals | Euthylon, safrole |
| 31 | Amphetamine | Amphetamine | Paraform, KH2PO4 | Lactose, amphetamine |
| 32 | Amphetamine | Amphetamine | Norephedrine HCl | Amphetamine, saccharose |
| 33 | Amphetamine | Amphetamine | Desoxy-D2PM, norephedrine HCl | Amphetamine |
| 34 | Amphetamine | Amphetamine | Desoxy-D2PM, norephedrine HCl | Amphetamine |
| 35 | Amphetamine, caffeine | Amphetamine | Amphetamine | Caffeine, amphetamine |
| 36 | Amphetamine, caffeine | Amphetamine | Unknown (deltamethrin, 2-phenylethylamine) | di-amphetamine, caffeine |
| 37 | Amphetamine | Amphetamine | 1-phenyl-1-propanol, 2-phenylethylamine | Amphetamine oil |
| 38 | Amphetamine | Amphetamine | 1-phenyl-1-propanol, 2-phenylethylamine | Amphetamine oil |
| 39 | Amphetamine | Amphetamine | 1-phenyl-1-propanol, B-methylphenethylamine | Amphetamine |
| 40 | Amphetamine, caffeine | Amphetamine | Amphetamine | Caffeine |
| 41 | Methamphetamine | Negative | 1,2-diphenyl-2-propanol, trytil alcohol | Methamphetamine |
| 42 | Methamphetamine | Negative | Ephedrine HCl | Methamphetamine |
| 43 | Methamphetamine | Methamphetamine | Ephedrine HCl | Methamphetamine |
| 44 | Methamphetamine base | Methamphetamine | 1-phenyl-1-propanol, 2-phenylethylamine | Methamphetamine |
| 45 | Methamphetamine | Methamphetamine | 1-phenyl-1-propanol, pentylbenzene | BMK, amphetamine oil |
| 46 | Methamphetamine | Methamphetamine | Ephedrine HCl | Methamphetamine |
| 47 | Methamphetamine | Methamphetamine | Ephedrine HCl | Methamphetamine |
| 48 | Methamphetamine | Methamphetamine | Ephedrine HCl | Methamphetamine |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parrilla, M.; Slosse, A.; Van Echelpoel, R.; Felipe Montiel, N.; Langley, A.R.; Van Durme, F.; De Wael, K. Rapid On-Site Detection of Illicit Drugs in Smuggled Samples with a Portable Electrochemical Device. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030108
Parrilla M, Slosse A, Van Echelpoel R, Felipe Montiel N, Langley AR, Van Durme F, De Wael K. Rapid On-Site Detection of Illicit Drugs in Smuggled Samples with a Portable Electrochemical Device. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(3):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030108
Chicago/Turabian StyleParrilla, Marc, Amorn Slosse, Robin Van Echelpoel, Noelia Felipe Montiel, Amelia R. Langley, Filip Van Durme, and Karolien De Wael. 2022. "Rapid On-Site Detection of Illicit Drugs in Smuggled Samples with a Portable Electrochemical Device" Chemosensors 10, no. 3: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030108
APA StyleParrilla, M., Slosse, A., Van Echelpoel, R., Felipe Montiel, N., Langley, A. R., Van Durme, F., & De Wael, K. (2022). Rapid On-Site Detection of Illicit Drugs in Smuggled Samples with a Portable Electrochemical Device. Chemosensors, 10(3), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030108