Analyzing the Electrochemical Interaction of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Batimastat by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Analysis
2.2. Raman and SERS Measurements
2.3. Electrode Preparation for SERS Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Vibrational Characterization of Batimastat (BB-94)
3.2. SERS Detection of BB-94 on Silver Electrode
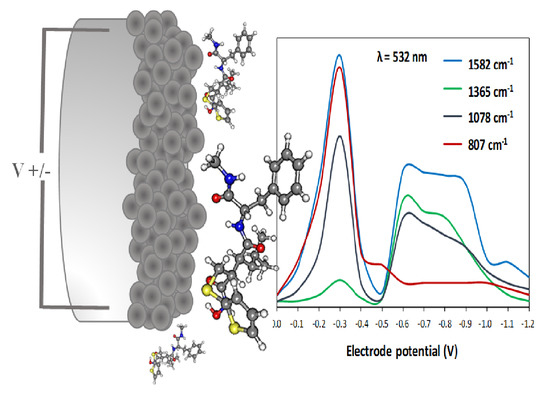
3.3. Analyzing Electrode-Potential Profiles of SERS Spectra of BB-94
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panneerselvam, R.; Liu, G.K.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Ding, S.Y.; Li, J.F.; Wu, D.Y.; Tian, Z.Q. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Bottlenecks and future direction. Chem. Comm. 2018, 54, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Chang, S.; Tsukruk, V.V. Porous substrates for label-free molecular level detection of nonresonant organic molecules. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, C.; Xu, M.; Xu, L.-J.; Wei, T.; Ma, X.; Zheng, X.-S.; Hu, R.; Ren, B. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bioanalysis: Reliability and challenges. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4946–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneipp, K.; Kneipp, H.; Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering and biophysics. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, R597–R624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroca, R. Surface-Enhanced Vibrational Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, England, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Masango, S.S.; Hackler, R.A.; Large, N.; Henry, A.I.; McAnally, M.O.; Schatz, G.C.; Stair, P.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. High-resolution distance dependence study of surface-enhanced Raman scattering enabled by atomic layer deposition. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 4251–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieringer, J.A.; McFarland, A.D.; Shah, N.C.; Stuart, D.A.; Whitney, A.V.; Yonzon, C.R.; Young, M.A.; Zhang, X.Y.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy: New materials, concepts, characterization tools, and applications. Faraday Discuss 2006, 132, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willets, K.A. Super-resolution imaging of SERS hot spots. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3854–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z. Surface enhanced Raman scattering revealed by interfacial charge-transfer transitions. Innovation 2020, 1, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, J.R.; Birke, R.L. A unified approach to surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 5605–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pięta, E.; Proniewicz, E.; Boduszek, B.; Olszewski, T.K.; Nattich-Rak, M.; Kim, Y. Probing the Ag, Au, and Cu electrode/pyridine-α-hydroxymethyl biphenyl phosphine oxide isomer interface with SERS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 335, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pięta, E.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Oćwieja, M.; Kwiatek, W.M. Potential drug—Nanosensor conjugates: Raman, infrared absorption, surface—Enhanced Raman, and density functional theory investigations of indolic molecules. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 404, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pięta, E.; Piergies, N.; Oćwieja, M.; Domin, H.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Bielańska, E.; Kwiatek, W.M. Monitoring the interfacial behavior of selective Y5 receptor antagonist on colloidal gold nanoparticle surfaces: Surface-enhanced vibrational spectroscopy studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 17276–17288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pięta, E.; López-Ramirez, M.R.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Kwiatek, W.M. Insights into the binding interactions at the nano-bio interface: Electrode potential and wavelength dependence study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 562, 150228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pięta, E.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Kwiatek, W.M. Multianalytical approach for surface- and tip-enhanced infrared spectroscopy study of a molecule–metal conjugate: Deducing its adsorption geometry. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 27992–28000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, M.; Hendra, P.J.; McQuillan, A.J. Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 26, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, T.M. Advances in Spectroscopy. In Spectroscopy of Surfaces; Clark, R.J.H., Hester, R.E., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 16, pp. 91–146. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.; Peng, X.H.; Ansari, D.O.; Yin-Goen, Q.; Chen, G.Z.; Shin, D.M.; Yang, L.; Young, A.N.; Wang, M.D.; Nie, S. In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.Y.; Li, J.F.; Ren, B.; Tian, Z.Q. Electrochemical surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1025–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.Q.; Ren, B.; Wu, D.Y. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering: From noble to transition metals and from rough surfaces to ordered nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 9463–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birke, R.L.; Lombardi, J.R. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering. In Spectroelectrochemistry—Theory and Practice; Gale, R.J., Ed.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 263–344. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, A.; Soeltl, R.; Sopov, I.; Kopitz, C.; Arlt, M.; Magdolen, V.; Harbeck, N.; Gänsbacher, B.; Schmitt, M. Hydroxamate-type matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat promotes liver metastasis. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Deryugina, E.I.; Ratnikov, B.I.; Strongin, A.Y. Prinomastat, a hydroxamate inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases, has a complex effect on migration of breast carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 104, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, J.A.; Johnson, M.D.; Bone, E.A.; Dickson, R.B. The matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat (BB-94) retards human breast cancer solid tumor growth but not ascites formation in nude mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 1996, 2, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sledge, G.W., Jr.; Qulali, M.; Goulet, R.; Bone, E.A.; Fife, R. Effect of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat on breast cancer Rregrowth and metastasis in athymic mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, H.S.; McCann, P.P. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition as a novel anticancer strategy: A review with special focus on batimastat and marimastat. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 75, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenberg, M.L.; Nelson, A.R.; Hande, K.R. New drugs on the horizon: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Stem Cells 1999, 17, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Burcl, R.; Handy, N.C.; Carter, S. Vibrational spectra of furan, pyrrole, and thiophene from a density functional theory anharmonic force field. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2003, 59, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Phillips, D.L. Resonance Raman study of the A-band short-time photodissociation dynamics of 2-iodothiophene. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 054510-1–054510-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdaline, J.D.; Chithambarathanu, T. Vibrational spectra (FT-IR, FT-Raman), NBO and HOMO, LUMO studies of 2-thiophene carboxylic acid based on density functional method. IOSR J. Appl. Chem 2015, 8, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran, V.; Janaki, A.; Nataraj, A. Theoretical investigations on molecular structure, vibrational spectra, HOMO, LUMO, NBO analysis and hyperpolarizability calculations of thiophene-2-carbohydrazide. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Hutchison, J.A.; Uji-i, H.; Hofkens, J.; Lagae, L.; Maes, G.; Borghsa, G.; Van Dorpe, P. Excitation wavelength dependent surface enhanced Raman scattering of 4-aminothiophenol on gold nanorings. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.B., Jr. The normal modes and frequencies of vibration of the regular plane hexagon model of the benzene molecule. Phys. Rev. 1934, 45, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ramirez, M.R.; Aranda Ruiz, D.; Avila Ferrer, F.J.; Centeno, S.P.; Arenas, J.F.; Otero, J.C.; Soto, J. Analysis of the potential dependent surface-enhanced Raman scattering of p-aminothiophenol on the basis of MS-CASPT2 calculations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 19322–19328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, J.F.; Fernandez, D.J.; Soto, J.; Lopez-Tocon, I.; Otero, J.C. Role of the electrode potential in the charge-transfer mechanism of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 13143–13149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, J.F.; Soto, J.; Pelaez, D.; Fernandez, D.J.; Otero, J.C. Understanding complex surface-enhanced Raman scattering, using quantum chemical calculations. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2005, 104, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurouski, D.; Postiglione, T.; Deckert-Gaudig, T.; Deckert, V.; Lednev, I.K. Amide I vibrational mode suppression in surface (SERS) and tip (TERS) enhanced Raman spectra of protein specimens. Analyst 2013, 138, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Ramirez, M.R.; Ruano, C.; Castro, J.L.; Arenas, J.F.; Soto, J.; Otero, J.C. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of benzoate anion adsorbed on silver nanoclusters: Evidence of the transient formation of the radical dianion. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7666–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, J.F.; López-Tocón, I.; Castro, J.L.; Centeno, S.P.; López-Ramírez, M.R.; Otero, J.C. Resonant charge transfer on the nanoscale: Studying doublet states of adsorbates by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Raman Spect. 2005, 36, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskovits, M. Surface-Enhanced Spectroscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1985, 57, 783–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felidj, M.; Aubard, J.; Levi, G.; Krenn, J.R.; Salerno, M.; Schider, G.; Lamprecht, B.; Leitner, A.; Aussenegg, F.R. Controlling the optical response of regular arrays of gold particles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 075419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.A. Effects of the excitation wavelength on the SERS spectrum. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safar, W.; Lequeux, M.; Solard, J.; Fischer, A.P.A.; Felidj, N.; Gucciardi, P.G.; Edely, M.; de la Chapelle, M.L. Gold nanocylinders on gold film as a multi-spectral SERS substrate. Nanomater 2020, 10, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| νexp λ = 785 nm | νcalc B3LYP/6-31G | Assignment 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1660 vw | 1702 | ν(C=O)Ab, Amide I |
| 1643 vw | 1681 | ν(C=O)Aa, Amide I |
| 1606 w | 1596 | 8a; ν(CC)ring |
| 1585 vw | 1575 | 8b; ν(CC)ring |
| 1445 vw | 1468 | δ(CH3) |
| 1401 vs | 1407 | ν(CC)Thp |
| 1338 m | 1328 | ν(CC)Thp, δ(CH)Thp |
| 1298 w | 1277 | δ(NH), δ(CH2) |
| 1238 w | 1219 | ν(N-CO), δ(NH) |
| 1218 w | 1180 | ν(CX)ring, δ(NH) |
| 1158 w | 1146 | δ(CH2), δ(CH)ring |
| 1083 w | 1078 | δ(CH)Thp |
| 1032 w | 1017 | δ(CH)ring |
| 1002 m | 1001 | δ(CC)ring |
| 946 w | 942 | ν(CS)Thp |
| 845 w | 820 | δ(CSC)Thp |
| 825 vw | 807 | δ(CC)ring |
| 739 w | 738 | γ(CH)ring |
| 643 w | 689 | ν(S-CH2), γ(CH)Thp |
| 620 w | 610 | δ(CC)ring |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pięta, E.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Kwiatek, W.M.; López-Ramírez, M.R. Analyzing the Electrochemical Interaction of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Batimastat by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11020128
Pięta E, Paluszkiewicz C, Kwiatek WM, López-Ramírez MR. Analyzing the Electrochemical Interaction of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Batimastat by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(2):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11020128
Chicago/Turabian StylePięta, Ewa, Czesława Paluszkiewicz, Wojciech M. Kwiatek, and María Rosa López-Ramírez. 2023. "Analyzing the Electrochemical Interaction of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Batimastat by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy" Chemosensors 11, no. 2: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11020128
APA StylePięta, E., Paluszkiewicz, C., Kwiatek, W. M., & López-Ramírez, M. R. (2023). Analyzing the Electrochemical Interaction of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Batimastat by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Chemosensors, 11(2), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11020128