Selective Determination of Hydrogen Sulfide Using SnO2–Ag Sensor Working in Non-Stationary Temperature Regime
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sensor Fabrication
2.2. Sensor Measurements
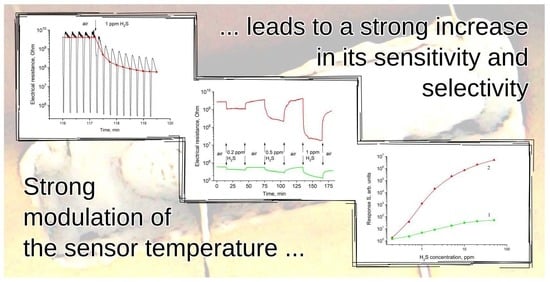
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guidotti, T.L. Hydrogen sulfide: Advances in understanding human toxicity. Int. J. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N. New approaches for improving semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1991, 5, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, T.; Tamaki, J.; Miura, N.; Yamazoe, N. Sensing behavior of CuO-loaded SnO2 element for H2S detection. Chem. Lett. 1991, 20, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, J.; Maekawa, T.; Miura, N.; Yamazoe, N. CuO‒SnO2 element for highly sensitive and selective detection of H2S. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1992, 9, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Zhang, J.; Akash, K.; Kim, S.S. H2S sensing performance of electrospun CuO-loaded SnO2 nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 169, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Jia, J. Porous CuO/SnO2 composite nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning and their H2S sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 165, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Hoffmann, M.W.G.; Prades, J.D.; Zamani, R.; Arbiol, J.; Morante, J.R.; Varechkina, E.; Rumyantseva, M.; Gaskov, A.; Giebelhaus, I.; et al. Heterostructured p-CuO (nanoparticle)/n-SnO2 (nanowire) devices for selective H2S detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.S.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, S.J.; Dong, K.Y.; Kwon, J.H.; Ju, B.K.; Lee, J.H. Enhanced H2S sensing characteristics of SnO2 nanowires functionalized with CuO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 142, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, V.R.; Debnath, A.K.; Muthe, K.P.; Kaur, M.; Dua, A.K.; Gadkari, S.C.; Gupta, S.K.; Sahni, V.C. Mechanism of drifts in H2S sensing properties of SnO2:CuO composite thin film sensors prepared by thermal evaporation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 96, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.I.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, Y.C.; Lee, J.H. Ultraselective and ultrasensitive detection of H2S in highly humid atmosphere using CuO-loaded SnO2 hollow spheres for real-time diagnosis of halitosis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.K.; Gupta, V. A highly sensitive SnO2-CuO multilayered sensor structure for detection of H2S gas. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, R.B.; Rumyantseva, M.N.; Podguzova, S.E.; Ryzhikov, A.S.; Ryabova, L.I.; Gaskov, A.M. Effect of interdiffusion on electrical and gas sensor properties of CuO/SnO2 heterostructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 1999, 57, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, R.B.; Rumyantseva, M.N.; Yakovlev, N.V.; Gaskov, A.M. CuO/SnO2 thin film heterostructures as chemical sensors to H2S. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 50, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyshev, V.V.; Pislyakov, A.V. SnO2-based thick-film-resistive sensor for H2S detection in the concentration range of 1–10 mg∙m−3. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 47, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantto, V.; Mizsei, J. H2S monitoring as an air pollutant with silver-doped SnO2 thin-film sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1991, 5, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkoma-Mattila, A.; Rantala, T.S.; Lantto, V.; Leppävuori, S. Sensitivity and selectivity of doped SnO2 thick-film sensors to H2S in the constant- and pulsed-temperature modes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1992, 6, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Chen, Q.; Lian, M.R.; Liu, N.C.; Stevenson, R.G.; Adami, F. Micromachined nanocrystalline silver doped SnO2 H2S sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, T.M.; Van Duy, N.; Hung, C.M.; Hoa, N.D.; Nguyen, H.; Tonezzer, M.; Van Hieu, N. Self-heated Ag-decorated SnO2 nanowires with low power consumption used as a predictive virtual multisensor for H2S-selective sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1069, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolhe, P.S.; Koinkar, P.M.; Maiti, N.; Sonawane, K.M. Synthesis of Ag doped SnO2 thin films for the evaluation of H2S gas sensing properties. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2017, 524, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumakova, V.; Marikutsa, A.; Rumyantseva, M.; Fasquelle, D.; Gaskov, A. Nanocrystalline LaCoO3 modified by Ag nanoparticles with improved sensitivity to H2S. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovsianytskyi, O.; Nam, Y.S.; Tsymbalenko, O.; Lan, P.T.; Moon, M.W.; Lee, K.B. Highly sensitive chemiresistive H2S gas sensor based on graphene decorated with Ag nanoparticles and charged impurities. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natkaeo, A.; Phokharatkul, D.; Hodak, J.H.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Hodak, S.K. Highly selective sub–10 ppm H2S gas sensors based on Ag-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.Y.; Zhang, M.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Deng, Z.P.; Huo, L.H.; Gao, S. Highly selective ppb-level H2S sensor for spendable detection of exhaled biomarker and pork freshness at low temperature: Mesoporous SnO2 hierarchical architectures derived from waste scallion root. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sberveglieri, G.; Groppelli, S.; Nelli, P.; Perego, C.; Valdré, G.; Camanzi, A. Detection of sub-ppm H2S concentrations by means of SnO2(Pt) thin films, grown by the RGTO technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1993, 15, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtkar, S.; Rashidi, A.; Kooti, M.; Askarieh, M.; Pourhashem, S.; Ghasemy, E.; Izadi, N. A novel highly sensitive and selective H2S gas sensor at low temperatures based on SnO2 quantum dots-C60 nanohybrid: Experimental and theory study. Talanta 2018, 188, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, C.; Wen, T.; Zhao, X.; Xie, L. Highly sensitive H2S gas sensors based on Pd-doped CuO nanoflowers with low operating temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Huang, B.; Li, Y.; Hua, X.; Liu, G.; Li, B.; Zhou, J.; et al. Binder-free CuO nanoneedle arrays based tube-type sensor for H2S gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, L.; Yu, T.; Zhao, D.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. In situ deposited hierarchical CuO/NiO nanowall arrays film sensor with enhanced gas sensing performance to H2S. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, K.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, S.; Cui, X. High response to H2S gas with facile synthesized hierarchical ZnO microstructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 219, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, Z.S.; Zad, A.I.; Mortezaali, A. Room temperature H2S gas sensor based on rather aligned ZnO nanorods with flower-like structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Na, C.W.; Hwang, I.S.; Lee, J.H. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of CuO-ZnO composite hollow spheres for selective H2S detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 168, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, M.; Deng, Z.P.; Cheng, X.L.; Huo, L.H.; Gao, S. A fast response/recovery ppb-level H2S gas sensor based on porous CuO/ZnO heterostructural tubule via confined effect of absorbent cotton. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, S. CuO nanoparticle decorated ZnO nanorod sensor for low-temperature H2S detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shewale, P.S.; Yun, K.S. Synthesis and characterization of Cu-doped ZnO/RGO nanocomposites for room-temperature H2S gas sensor. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 837, 155527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Xie, L.; Li, X.; Lin, D.; Zhu, Z. Low-temperature and highly sensitivity H2S gas sensor based on ZnO/CuO composite derived from bimetal metal-organic frameworks. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 15858–15866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuoc, P.H.; Viet, N.N.; Thong, L.V.; Hung, C.M.; Hoa, N.D.; Van Duy, N.; Hong, H.S.; Van Hieu, N. Comparative study on the gas-sensing performance of ZnO/SnO2 external and ZnO–SnO2 internal heterojunctions for ppb H2S and NO2 gases detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.M.; Phuong, H.V.; Van Thinh, V.; Hong, L.T.; Thang, N.T.; Hanh, N.H.; Dich, N.Q.; Van Duy, N.; Van Hieu, N.; Hoa, N.D. Au doped ZnO/SnO2 composite nanofibers for enhanced H2S gas sensing performance. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 317, 112454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Deng, Z.; Fang, X.; Hu, C.; Shi, L.; Dai, T.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Meng, G. Heterostructural (Sr0.6Bi0.305)2Bi2O7/ZnO for novel high-performance H2S sensor operating at low temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xie, L.; He, M.; Hu, X.; Luo, G.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Z. Metal-organic frameworks-derived bamboo-like CuO/In2O3 heterostructure for high-performance H2S gas sensor with low operating temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 310, 127828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Kim, T.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Kwak, C.H.; Lee, J.H. Ultrasensitive and ultraselective detection of H2S using electrospun CuO-loaded In2O3 nanofiber sensors assisted by pulse heating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouria, V.; Kumar, A.; Samanta, S.; Singh, A.; Debnath, A.K.; Mahajan, A.; Bedi, R.K.; Aswal, D.K.; Gupta, S.K. Nano-crystalline Fe2O3 thin films for ppm level detection of H2S. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D. Hydrogen sulfide gas sensing properties of metal organic framework-derived α-Fe2O3 hollow nanospheres decorated with MoSe2 nanoflowers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, C.S.; Hegde, M.; Rao, C.N.R. H2S sensors based on tungsten oxide nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 128, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.I.M.; Awwad, F.; Greish, Y.E.; Abu-Hani, A.F.S.; Mahmoud, S.T. Fabrication of low temperature and fast response H2S gas sensor based on organic-metal oxide hybrid nanocomposite membrane. Org. Electron. 2020, 76, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sun, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Dong, B.; Lu, G.; Song, H. Au/ZnO functionalized three–dimensional macroporous WO3: A application of selective H2S gas sensor for exhaled breath biomarker detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 324, 128725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, T.T.N.; Le, D.T.T.; Van Toan, N.; Van Duy, N.; Hung, C.M.; Van Hieu, N.; Hoa, N.D. Highly selective H2S gas sensor based on WO3-coated SnO2 nanowires. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 102094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaposhnik, A.; Moskalev, P.; Sizask, E.; Ryabtsev, S.; Vasiliev, A. Selective detection of hydrogen sulfide and methane by a single MOX-sensor. Sensors 2019, 19, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaposhnik, A.V.; Shaposhnik, D.A.; Turishchev, S.Y.; Chuvenkova, O.A.; Ryabtsev, S.V.; Vasiliev, A.A.; Vilanova, X.; Hernandez-Ramirez, F.; Morante, J.R. Gas sensing properties of individual SnO2 nanowires and SnO2 sol-gel nanocomposites. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasiliev, A.A.; Pavelko, R.G.; Gogish-Klushin, S.Y.; Kharitonov, D.Y.; Gogish-Klushina, O.S.; Sokolov, A.V.; Pisliakov, A.V.; Samotaev, N.N. Alumina MEMS platform for impulse semiconductor and IR optic gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 132, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, D. Surface processes in the detection of reducing gases with SnO2-based devices. Sens. Actuators 1989, 18, 71–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Resistance-based H2S gas sensors using metal oxide nanostructures: A review of recent advances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Pirolli, L.; Teplyakov, A.V. Investigation of the H2S poisoning process for sensing composite material based on carbon nanotubes and metal oxides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Sensing Material | Technique Used | Gas Conc. (ppm) | Response | Operating Temp (°C) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SnO2 | mesoporous hierarchical architectures derived from waste scallion root | 1 | ~5 | 92 | [23] |
| SnO2/CuO nanofibers | electrospinning | 1 | 23 | 200 | [6] |
| SnO2/CuO | ultrasonic spray pyrolysis | 1 | 78 | 300 | [10] |
| CuO/Pd | precipitation from solution (sol-gel) | 1 | 63.8 | 80/300 (pulse) | [26] |
| SnO2/Ag | precipitation from solution (sol-gel) | 1 | 1.23 × 103 | 100/450 (pulse) | this work |
| Fe2O3 | thermal oxidation of Fe films | 10 | ~5 | 250 | [41] |
| CaCu3Ti4O12/Ag | precipitation from solution (sol-gel) | 10 | ~100 | 250 | [22] |
| SnO2/CuO nanofibers | electrospinning | 10 | 1.98 × 104 | 300 | [5] |
| SnO2/Ag | precipitation from solution (sol-gel) | 10 | 7.3 × 105 | 100/450 (pulse) | this work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaposhnik, A.V.; Moskalev, P.V.; Zviagin, A.A.; Duykova, M.V.; Ryabtsev, S.V.; Ghareeb, D.A.A.; Vasiliev, A.A. Selective Determination of Hydrogen Sulfide Using SnO2–Ag Sensor Working in Non-Stationary Temperature Regime. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080203
Shaposhnik AV, Moskalev PV, Zviagin AA, Duykova MV, Ryabtsev SV, Ghareeb DAA, Vasiliev AA. Selective Determination of Hydrogen Sulfide Using SnO2–Ag Sensor Working in Non-Stationary Temperature Regime. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(8):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080203
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaposhnik, Alexey V., Pavel V. Moskalev, Alexey A. Zviagin, Margarita V. Duykova, Stanislav V. Ryabtsev, Dina A. A. Ghareeb, and Alexey A. Vasiliev. 2021. "Selective Determination of Hydrogen Sulfide Using SnO2–Ag Sensor Working in Non-Stationary Temperature Regime" Chemosensors 9, no. 8: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080203
APA StyleShaposhnik, A. V., Moskalev, P. V., Zviagin, A. A., Duykova, M. V., Ryabtsev, S. V., Ghareeb, D. A. A., & Vasiliev, A. A. (2021). Selective Determination of Hydrogen Sulfide Using SnO2–Ag Sensor Working in Non-Stationary Temperature Regime. Chemosensors, 9(8), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080203