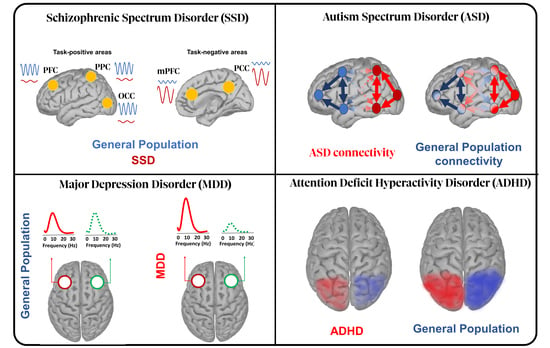
The Role of Alpha Oscillations among the Main Neuropsychiatric Disorders in the Adult and Developing Human Brain: Evidence from the Last 10 Years of Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
The Use of Alpha Rhythm for the Study of the Cognitive Functioning
2. Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder (SSD)
2.1. Resting State Data
2.2. Perceptual Impairments
2.3. Cognitive Deficits
3. Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
3.1. Resting State Data
3.2. Cognition, MDD and Alpha Rhythms
4. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
4.1. The Role of Alpha Oscillations in ASD’s Symtomatology
4.2. EEG Indices for an Early ASD Diagnosis
5. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
5.1. The Role of Alpha Oscillations in ADHD’s Symtomatology
5.2. Normalizing Alpha Power Using the Neurofeedback Technique
6. General Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | Anterior cingulate cortex |
| ADHD | attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |
| ASD | autism spectrum disorders |
| dlPFC | dorsolateral prefrontal cortex |
| DMN | default mode network |
| DSM-5 | diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders |
| EEG | electroencephalogram |
| ERD | event-related desynchronization |
| ERP | event related potential |
| ERS | event-related synchronization |
| FAA | frontal alpha asymmetry |
| IAF | individual alpha frequency |
| ITC | intertrial coherence |
| MDD | major depressive disorders |
| MEG | magnetoencephalography |
| mPFC | medial prefrontal cortex |
| OCC | occipital cortex |
| PAA | posterior/parietal alpha asymmetry |
| PAC | phase amplitude coupling |
| PCC | posterior cingulate cortex |
| PFC | prefrontal cortex |
| PPC | posterior parietal cortex |
| PSD | power spectral density |
| SSD | schizophrenia spectrum disorder |
| tACS | transcranial alternating current stimulation |
| tDCS | transcranial direct-current stimulation |
| TMS | transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| WM | working memory |
References
- Trautmann, S.; Rehm, J.; Wittchen, H.-U. The Economic Costs of Mental Disorders. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigo, D.; Thornicroft, G.; Atun, R. Estimating the True Global Burden of Mental Illness. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baranne, M.L.; Falissard, B. Global Burden of Mental Disorders among Children Aged 5–14 Years. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health Health 2018, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pies, R. How “Objective” Are Psychiatric Diagnoses? Psychiatry 2007, 4, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadock, B.J.; Sadock, V.A.; Ruiz, P.; Kaplan, H.I. Kaplan & Sadock’s Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry, 9th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-7817-6899-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kohrt, B.A.; Rasmussen, A.; Kaiser, B.N.; Haroz, E.E.; Maharjan, S.M.; Mutamba, B.B.; de Jong, J.T.; Hinton, D.E. Cultural Concepts of Distress and Psychiatric Disorders: Literature Review and Research Recommendations for Global Mental Health Epidemiology. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 365–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayano, G.; Demelash, S.; Yohannes, Z.; Haile, K.; Tulu, M.; Assefa, D.; Tesfaye, A.; Haile, K.; Solomon, M.; Chaka, A.; et al. Misdiagnosis, Detection Rate, and Associated Factors of Severe Psychiatric Disorders in Specialized Psychiatry Centers in Ethiopia. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2021, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahnke, B. A Systematic Review of Misdiagnosis in Those with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 2021, 6, 100231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermani, M.; Marcus, M.; Katzman, M.A. Rates of Detection of Mood and Anxiety Disorders in Primary Care: A Descriptive, Cross-Sectional Study. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2011, 13, PCC.10m01013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, M.L.; Kupfer, D.J. Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis: Challenges and Future Directions. Lancet 2013, 381, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivera, M.J.; Teruel, M.A.; Maté, A.; Trujillo, J. Diagnosis and Prognosis of Mental Disorders by Means of EEG and Deep Learning: A Systematic Mapping Study. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 1209–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahata, N.; Kasai, K.; Kawato, M. Computational Neuroscience Approach to Biomarkers and Treatments for Mental Disorders. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 71, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, S.D.; Périn, B.; Michel, V.; Debs, R.; Navarro, V.; Convers, P. EEG in Adults in the Laboratory or at the Patient’s Bedside. Neurophysiol. Clin. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 45, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathelt, J.; O’Reilly, H.; de Haan, M. Cortical Source Analysis of High-Density EEG Recordings in Children. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 88, e51705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Gregorio, F.; La Porta, F.; Petrone, V.; Battaglia, S.; Orlandi, S.; Ippolito, G.; Romei, V.; Piperno, R.; Lullini, G. Accuracy of EEG Biomarkers in the Detection of Clinical Outcome in Disorders of Consciousness after Severe Acquired Brain Injury: Preliminary Results of a Pilot Study Using a Machine Learning Approach. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, N.; de la Salle, S.; Ibrahim, M.-H.; Blier, P.; Knott, V. Leveraging Machine Learning Approaches for Predicting Antidepressant Treatment Response Using Electroencephalography (EEG) and Clinical Data. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norton, E.S.; MacNeill, L.A.; Harriott, E.M.; Allen, N.; Krogh-Jespersen, S.; Smyser, C.D.; Rogers, C.E.; Smyser, T.A.; Luby, J.; Wakschlag, L. EEG/ERP as a Pragmatic Method to Expand the Reach of Infant-Toddler Neuroimaging in HBCD: Promises and Challenges. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2021, 51, 100988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, A.; Szucs, A.; Csukly, G.; Sakovics, A.; Stefanics, G.; Kamondi, A. EEG and ERP biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: A critical review. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 183–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, H. Über das Elektrenkephalogramm des Menschen. Arch. Psychiatr. 1929, 87, 527–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, E. Brain Oscillations in Neuropsychiatric Disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoory, K.; Schoffelen, J.-M.; Keitel, A.; Gross, J. The Frequency Gradient of Human Resting-State Brain Oscillations Follows Cortical Hierarchies. eLife 2020, 9, e53715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, P.; Tang, C.; Wiesenfeld, K. Self-Organized Criticality: An Explanation of the 1/f Noise. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakaş, S.; Barry, R.J. A Brief Historical Perspective on the Advent of Brain Oscillations in the Biological and Psychological Disciplines. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 75, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, D.S.; Chen, L. Brain Oscillations in Perception, Timing and Action. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 8, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.M. Synchronous Neural Oscillations and Cognitive Processes. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2003, 7, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, E.; Güntekin, B. Chapter 19—Review of Delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Response Oscillations in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. In Supplements to Clinical Neurophysiology. Application of Brain Oscillations in Neuropsychiatric Diseases; Başar, E., Başar-Eroĝlu, C., Özerdem, A., Rossini, P.M., Yener, G.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 62, pp. 303–341. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, W. EEG Alpha and Cognitive Processes. In Time and the Brain; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-429-17831-3. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, W. EEG Alpha and Theta Oscillations Reflect Cognitive and Memory Performance: A Review and Analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.; Mazaheri, A. Shaping Functional Architecture by Oscillatory Alpha Activity: Gating by Inhibition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klimesch, W. Alpha-Band Oscillations, Attention, and Controlled Access to Stored Information. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sigala, R.; Haufe, S.; Roy, D.; Dinse, H.; Ritter, P. The Role of Alpha-Rhythm States in Perceptual Learning: Insights from Experiments and Computational Models. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Stancák, A.; Neuper, C. Event-Related Synchronization (ERS) in the Alpha Band—An Electrophysiological Correlate of Cortical Idling: A Review. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1996, 24, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.; Schwiedrzik, C.M.; Wibral, M.; Singer, W.; Melloni, L. Expecting to See a Letter: Alpha Oscillations as Carriers of Top-Down Sensory Predictions. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasi, L.; di Pellegrino, G.; Romei, V. Are You an Empiricist or a Believer? Neural Signatures of Predictive Strategies in Humans. Prog. Neurobiol. 2022, 219, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romei, V.; Gross, J.; Thut, G. On the Role of Prestimulus Alpha Rhythms over Occipito-Parietal Areas in Visual Input Regulation: Correlation or Causation? J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8692–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samaha, J.; Iemi, L.; Postle, B.R. Prestimulus Alpha-Band Power Biases Visual Discrimination Confidence, but Not Accuracy. Conscious. Cogn. 2017, 54, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iemi, L.; Chaumon, M.; Crouzet, S.M.; Busch, N.A. Spontaneous Neural Oscillations Bias Perception by Modulating Baseline Excitability. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Gregorio, F.; Trajkovic, J.; Roperti, C.; Marcantoni, E.; Di Luzio, P.; Avenanti, A.; Thut, G.; Romei, V. Tuning Alpha Rhythms to Shape Conscious Visual Perception. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 988–998.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecere, R.; Rees, G.; Romei, V. Individual Differences in Alpha Frequency Drive Crossmodal Illusory Perception. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minami, S.; Amano, K. Illusory Jitter Perceived at the Frequency of Alpha Oscillations. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2344–2351.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, J.; Poch, C.; Gillmeister, H.; Costantini, M.; Romei, V. Oscillatory Properties of Functional Connections Between Sensory Areas Mediate Cross-Modal Illusory Perception. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 5711–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friston, K.J. Functional and Effective Connectivity: A Review. Brain Connect. 2011, 1, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejko, N.; Larabi, D.I.; Herrmann, C.S.; Aleman, A.; Ćurčić-Blake, B. Alpha Power and Functional Connectivity in Cognitive Decline: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 78, 1047–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douw, L.; de Groot, M.; van Dellen, E.; Heimans, J.J.; Ronner, H.E.; Stam, C.J.; Reijneveld, J.C. ‘Functional Connectivity’ Is a Sensitive Predictor of Epilepsy Diagnosis after the First Seizure. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morand-Beaulieu, S.; Wu, J.; Mayes, L.C.; Grantz, H.; Leckman, J.F.; Crowley, M.J.; Sukhodolsky, D.G. Increased Alpha-Band Connectivity During Tic Suppression in Children with Tourette Syndrome Revealed by Source Electroencephalography Analyses. Biol. Psychiatry: Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinkley, L.B.N.; Vinogradov, S.; Guggisberg, A.G.; Fisher, M.; Findlay, A.M.; Nagarajan, S.S. Clinical Symptoms and Alpha Band Resting-State Functional Connectivity Imaging in Patients with Schizophrenia: Implications for Novel Approaches to Treatment. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fingelkurts, A.A.; Fingelkurts, A.A.; Rytsälä, H.; Suominen, K.; Isometsä, E.; Kähkönen, S. Impaired Functional Connectivity at EEG Alpha and Theta Frequency Bands in Major Depression. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2007, 28, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozhilova, N.; Kuntsi, J.; Rubia, K.; Asherson, P.; Michelini, G. Event-Related Brain Dynamics during Mind Wandering in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: An Experience-Sampling Approach. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 35, 103068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenartowicz, A.; Mazaheri, A.; Jensen, O.; Loo, S.K. Aberrant Modulation of Brain Oscillatory Activity and Attentional Impairment in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, A.; Delorme, R.; Delanoë, C.; Amsellem, F.; Beggiato, A.; Germanaud, D.; Bourgeron, T.; Toro, R.; Dumas, G. Alpha Waves as a Neuromarker of Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Challenge of Reproducibility and Heterogeneity. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, S.K.; McGough, J.J.; McCracken, J.T.; Smalley, S.L. Parsing Heterogeneity in Attention-deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Using EEG-based Subgroups. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2018, 59, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edition, F. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Am. Psychiatric Assoc. 2013, 21, 591–643. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlhaas, P.J.; Singer, W. Oscillations and Neuronal Dynamics in Schizophrenia: The Search for Basic Symptoms and Translational Opportunities. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlhaas, P.J. Dysconnectivity, Large-Scale Networks and Neuronal Dynamics in Schizophrenia. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, K.E.; Friston, K.J.; Frith, C.D. Dysconnection in Schizophrenia: From Abnormal Synaptic Plasticity to Failures of Self-Monitoring. Schizophr. Bull. 2009, 35, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pittman-Polletta, B.R.; Kocsis, B.; Vijayan, S.; Whittington, M.A.; Kopell, N.J. Brain Rhythms Connect Impaired Inhibition to Altered Cognition in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lozano-Soldevilla, D.; ter Huurne, N.; Cools, R.; Jensen, O. GABAergic Modulation of Visual Gamma and Alpha Oscillations and Its Consequences for Working Memory Performance. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2878–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puig, M.V.; Antzoulatos, E.G.; Miller, E.K. Prefrontal Dopamine in Associative Learning and Memory. Neuroscience 2014, 282, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemercier, C.E.; Holman, C.; Gerevich, Z. Aberrant Alpha and Gamma Oscillations Ex Vivo after Single Application of the NMDA Receptor Antagonist MK-801. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 188, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, E.; Schmiedt-Fehr, C.; Mathes, B.; Femir, B.; Emek-Savaş, D.D.; Tülay, E.; Tan, D.; Düzgün, A.; Güntekin, B.; Özerdem, A.; et al. What Does the Broken Brain Say to the Neuroscientist? Oscillations and Connectivity in Schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Bipolar Disorder. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2016, 103, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garakh, Z.; Zaytseva, Y.; Kapranova, A.; Fiala, O.; Horacek, J.; Shmukler, A.; Ya Gurovich, I.; Strelets, V.B. EEG Correlates of a Mental Arithmetic Task in Patients with First Episode Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 2090–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, M.R.; Peterson, M.J.; Sanguinetti, J.L.; Tononi, G.; Ferrarelli, F. Topographic Deficits in Alpha-Range Resting EEG Activity and Steady State Visual Evoked Responses in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 168, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, D.H.; Min, K.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, K. Diagnostic Utility of Quantitative EEG in Un-Medicated Schizophrenia. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 589, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canali, P.; Sarasso, S.; Rosanova, M.; Casarotto, S.; Sferrazza-Papa, G.; Gosseries, O.; Fecchio, M.; Massimini, M.; Mariotti, M.; Cavallaro, R.; et al. Shared Reduction of Oscillatory Natural Frequencies in Bipolar Disorder, Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 184, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelaria-Cook, F.T.; Schendel, M.E.; Ojeda, C.J.; Bustillo, J.R.; Stephen, J.M. Reduced Parietal Alpha Power and Psychotic Symptoms: Test-Retest Reliability of Resting-State Magnetoencephalography in Schizophrenia and Healthy Controls. Schizophr. Res. 2020, 215, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Nizamie, S.H.; Goyal, N.; Tikka, S.K. Electroencephalogram Alpha-to-Theta Ratio over Left Fronto-Temporal Region Correlates with Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia. Asian J. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Mellin, J.M.; Alagapan, S.; Alexander, M.L.; Gilmore, J.H.; Jarskog, L.F.; Fröhlich, F. Targeting Reduced Neural Oscillations in Patients with Schizophrenia by Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation. NeuroImage 2019, 186, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeum, T.-S.; Kang, U.G. Reduction in Alpha Peak Frequency and Coherence on Quantitative Electroencephalography in Patients with Schizophrenia. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018, 33, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.; Öngür, D. Decreased Peak Alpha Frequency and Impaired Visual Evoked Potentials in First Episode Psychosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 22, 101693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freche, D.; Naim-Feil, J.; Hess, S.; Peled, A.; Grinshpoon, A.; Moses, E.; Levit-Binnun, N. Phase-Amplitude Markers of Synchrony and Noise: A Resting-State and TMS-EEG Study of Schizophrenia. Cereb. Cortex Commun. 2020, 1, tgaa013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.E.; Summerfelt, A.; Mitchell, B.D.; O’Donnell, P.; Thaker, G.K. A Shared Low-Frequency Oscillatory Rhythm Abnormality in Resting and Sensory Gating in Schizophrenia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, M.D.; Snyder, A.Z.; Vincent, J.L.; Corbetta, M.; Van Essen, D.C.; Raichle, M.E. The Human Brain Is Intrinsically Organized into Dynamic, Anticorrelated Functional Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9673–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakhnikian, A.; Oribe, N.; Hirano, S.; Hirano, Y.; Levin, M.; Spencer, K. Lower Peak Alpha Frequency Accounts for Elevated Theta-Alpha Power in Resting State EEG in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, S411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, B.; O’Neil, K.; Berwise, C.; Stevens, M.C.; Calhoun, V.D.; Clementz, B.A.; Tamminga, C.A.; Sweeney, J.A.; Keshavan, M.S.; Pearlson, G.D. Resting State Electroencephalogram Oscillatory Abnormalities in Schizophrenia and Psychotic Bipolar Patients and Their Relatives from the Bipolar and Schizophrenia Network on Intermediate Phenotypes Study. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhnikian, A.; Oribe, N.; Hirano, S.; Hirano, Y.; Levin, M.; Spencer, K. Increased Theta/Alpha Source Activity and Default Mode Network Connectivity in Schizophrenia During Eyes-Closed Rest. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, S150–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Shin, K.S.; Jung, W.H.; Kim, S.N.; Kwon, J.S.; Chung, C.K. Power Spectral Aspects of the Default Mode Network in Schizophrenia: An MEG Study. BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koshiyama, D.; Miyakoshi, M.; Tanaka-Koshiyama, K.; Joshi, Y.B.; Sprock, J.; Braff, D.L.; Light, G.A. Abnormal Phase Discontinuity of Alpha- and Theta-Frequency Oscillations in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2021, 231, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertaccini, R.; Ellena, G.; Macedo-Pascual, J.; Carusi, F.; Trajkovic, J.; Poch, C.; Romei, V. Parietal Alpha Oscillatory Peak Frequency Mediates the Effect of Practice on Visuospatial Working Memory Performance. Vision 2022, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovic, J.; Di Gregorio, F.; Ferri, F.; Marzi, C.; Diciotti, S.; Romei, V. Resting State Alpha Oscillatory Activity Is a Valid and Reliable Marker of Schizotypy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, I.S.; Lynn, P.A.; Schermitzler, B.; Sponheim, S.R. Individual Alpha Peak Frequency Is Slower in Schizophrenia and Related to Deficits in Visual Perception and Cognition. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garakh, Z.V.; Novototsky-Vlasov, V.Y.; Zaitseva, Y.S.; Rebreikina, A.B.; Strelets, V.B. Frequency of the Alpha Activity Spectral Peak and Psychopathological Symptoms in Schizophrenia. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2012, 42, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Dong, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, X.; Tong, Y.; Yang, R.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Yan, T. Occipital Alpha Connectivity During Resting-State Electroencephalography in Patients with Ultra-High Risk for Psychosis and Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kam, J.W.Y.; Bolbecker, A.R.; O’Donnell, B.F.; Hetrick, W.P.; Brenner, C.A. Resting State EEG Power and Coherence Abnormalities in Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baenninger, A.; Palzes, V.A.; Roach, B.J.; Mathalon, D.H.; Ford, J.M.; Koenig, T. Abnormal Coupling Between Default Mode Network and Delta and Beta Band Brain Electric Activity in Psychotic Patients. Brain Connect. 2017, 7, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olejarczyk, E.; Jernajczyk, W. Graph-Based Analysis of Brain Connectivity in Schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phalen, H.; Coffman, B.A.; Ghuman, A.; Sejdić, E.; Salisbury, D.F. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization Reveals Resting-State Cortical Alpha Network Abnormalities in the First-Episode Schizophrenia Spectrum. Biol. Psychiatry: Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2020, 5, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, G.; Daverio, A.; Ferrentino, F.; Santarnecchi, E.; Ciabattini, F.; Monaco, L.; Lisi, G.; Barone, Y.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Niolu, C.; et al. Altered Resting-State EEG Source Functional Connectivity in Schizophrenia: The Effect of Illness Duration. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, D.; Faber, P.L.; Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Milz, P.; Herrmann, W.M.; Koukkou, M.; Saito, N.; Winterer, G.; Kochi, K. Functionally Aberrant Electrophysiological Cortical Connectivities in First Episode Medication-Naive Schizophrenics from Three Psychiatry Centers. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Postmes, L.; Sno, H.N.; Goedhart, S.; van der Stel, J.; Heering, H.D.; de Haan, L. Schizophrenia as a Self-Disorder Due to Perceptual Incoherence. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 152, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, D.A.; Hamm, J.P.; McDowell, J.E.; Keedy, S.K.; Gershon, E.S.; Ivleva, E.I.; Pearlson, G.D.; Keshavan, M.S.; Tamminga, C.A.; Sweeney, J.A.; et al. Auditory Steady-State EEG Response across the Schizo-Bipolar Spectrum. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 209, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Nakhnikian, A.; Hirano, Y.; Oribe, N.; Kanba, S.; Onitsuka, T.; Levin, M.; Spencer, K.M. Phase-Amplitude Coupling of the Electroencephalogram in the Auditory Cortex in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry: Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, J.C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lanza, M.; Howell, B.; Chow, V.Y.; Heiken, K.; Liu, S.; Wootton, C.; Hunter, M.A.; Huang, M.; et al. Cortical Thickness as a Contributor to Abnormal Oscillations in Schizophrenia? NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 4, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carolus, A.M.; Schubring, D.; Popov, T.G.; Popova, P.; Miller, G.A.; Rockstroh, B.S. Functional Cognitive and Cortical Abnormalities in Chronic and First-Admission Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 157, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, J.P.; Ethridge, L.E.; Shapiro, J.R.; Stevens, M.C.; Boutros, N.N.; Summerfelt, A.T.; Keshavan, M.S.; Sweeney, J.A.; Pearlson, G.; Tamminga, C.A.; et al. Spatiotemporal and Frequency Domain Analysis of Auditory Paired Stimuli Processing in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder with Psychosis. Psychophysiology 2012, 49, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, L.M.; Edden, R.A.E.; Kontson, K.; Zhu, H.; Barker, P.B.; Hong, L.E. GABA Predicts Inhibition of Frequency-Specific Oscillations in Schizophrenia. J. Nucl. Phys. 2013, 25, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar-Eroğlu, C.; Schmiedt-Fehr, C.; Mathes, B. Auditory-Evoked Alpha Oscillations Imply Reduced Anterior and Increased Posterior Amplitudes in Schizophrenia. In Supplements to Clinical Neurophysiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 62, pp. 121–129. ISBN 978-0-7020-5307-8. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, T.G.; Carolus, A.; Schubring, D.; Popova, P.; Miller, G.A.; Rockstroh, B.S. Targeted Training Modifies Oscillatory Brain Activity in Schizophrenia Patients. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 7, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keil, J.; Roa Romero, Y.; Balz, J.; Henjes, M.; Senkowski, D. Positive and Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia Relate to Distinct Oscillatory Signatures of Sensory Gating. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Sehatpour, P.; Dias, E.C.; Silipo, G.S.; Kantrowitz, J.T.; Martinez, A.M.; Javitt, D.C. A Tale of Two Sites: Differential Impairment of Frequency and Duration Mismatch Negativity across a Primarily Inpatient versus a Primarily Outpatient Site in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 191, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Sehatpour, P.; Hoptman, M.J.; Lakatos, P.; Dias, E.C.; Kantrowitz, J.T.; Martinez, A.M.; Javitt, D.C. Neural Mechanisms of Mismatch Negativity Dysfunction in Schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, L.E.; Moran, L.V.; Du, X.; O’Donnell, P.; Summerfelt, A. Mismatch Negativity and Low Frequency Oscillations in Schizophrenia Families. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 1980–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kayser, J.; Tenke, C.E.; Kroppmann, C.J.; Alschuler, D.M.; Fekri, S.; Ben-David, S.; Corcoran, C.M.; Bruder, G.E. Auditory Event-Related Potentials and Alpha Oscillations in the Psychosis Prodrome: Neuronal Generator Patterns during a Novelty Oddball Task. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 91, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Núñez, P.; Poza, J.; Bachiller, A.; Gomez-Pilar, J.; Lubeiro, A.; Molina, V.; Hornero, R. Exploring Non-Stationarity Patterns in Schizophrenia: Neural Reorganization Abnormalities in the Alpha Band. J. Neural. Eng. 2017, 14, 046001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujimoto, T.; Okumura, E.; Takeuchi, K.; Kodabashi, A.; Tanaka, H.; Otsubo, T.; Nakamura, K.; Sekine, M.; Kamiya, S.; Higashi, Y.; et al. Changes in Event-Related Desynchronization and Synchronization during the Auditory Oddball Task in Schizophrenia Patients. Open Neuroimag. J. 2012, 6, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubonnet, R.; Banea, O.C.; Sirica, R.; Wassermann, E.M.; Yassine, S.; Jacob, D.; Magnúsdóttir, B.B.; Haraldsson, M.; Stefansson, S.B.; Jónasson, V.D.; et al. P300 Analysis Using High-Density EEG to Decipher Neural Response to RTMS in Patients With Schizophrenia and Auditory Verbal Hallucinations. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 575538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffman, B.A.; Haas, G.; Olson, C.; Cho, R.; Ghuman, A.S.; Salisbury, D.F. Reduced Dorsal Visual Oscillatory Activity During Working Memory Maintenance in the First-Episode Schizophrenia Spectrum. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.A.; Albrecht, M.A.; Robinson, B.; Luck, S.J.; Gold, J.M. Impaired Suppression of Delay-Period Alpha and Beta Is Associated with Impaired Working Memory in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2017, 2, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kustermann, T.; Rockstroh, B.; Kienle, J.; Miller, G.A.; Popov, T. Deficient Attention Modulation of Lateralized Alpha Power in Schizophrenia. Psychophysiology 2016, 53, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, A.L.; Coffman, B.A.; Longenecker, J.M.; Curtis, M.; Salisbury, D.F. Load-Dependent Functional Connectivity Deficits during Visual Working Memory in First-Episode Psychosis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 153, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, P.S.; Hughes, M.E. Impaired Theta and Alpha Oscillations Underlying Stopsignal Response Inhibition Deficits in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 193, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, T.; Kustermann, T.; Popova, P.; Miller, G.A.; Rockstroh, B. Oscillatory Brain Dynamics Supporting Impaired Stroop Task Performance in Schizophrenia-Spectrum Disorder. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 204, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.F.; Horan, W.P.; Lee, J. Social Cognition in Schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, T.G.; Rockstroh, B.S.; Popova, P.; Carolus, A.M.; Miller, G.A. Dynamics of Alpha Oscillations Elucidate Facial Affect Recognition in Schizophrenia. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 14, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.Y.; Schiffman, J.; Hu, D.K.; Lopour, B.A.; Martin, E.A. An Effortful Approach to Social Affiliation in Schizophrenia: Preliminary Evidence of Increased Theta and Alpha Connectivity during a Live Social Interaction. Brain. Sci. 2021, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.S.; Radua, J.; Kempton, M.J.; Mehta, M.A. The Ultimatum Game and the Brain: A Meta-Analysis of Neuroimaging Studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 47, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billeke, P.; Armijo, A.; Castillo, D.; López, T.; Zamorano, F.; Cosmelli, D.; Aboitiz, F. Paradoxical Expectation: Oscillatory Brain Activity Reveals Social Interaction Impairment in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Liu, M.; Huang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, S.; Go, R.; Yan, T.; Wu, J. Abnormal Alpha Rhythm During Self-Referential Processing in Schizophrenia Patients. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fingelkurts, A.A.; Fingelkurts, A.A. Altered Structure of Dynamic Electroencephalogram Oscillatory Pattern in Major Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuchter, A.; Cook, I.; Jin, Y.; Phillips, B. The Relationship between Brain Oscillatory Activity and Therapeutic Effectiveness of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eidelman-Rothman, M.; Levy, J.; Feldman, R. Alpha Oscillations and Their Impairment in Affective and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 794–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.J.; Saron, C.D.; Senulis, J.A.; Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Approach-Withdrawal and Cerebral Asymmetry: Emotional Expression and Brain Physiology. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1990, 58, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horato, N.; Quagliato, L.A.; Nardi, A.E. The Relationship between Emotional Regulation and Hemispheric Lateralization in Depression: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodziej, A.; Magnuski, M.; Ruban, A.; Brzezicka, A. No Relationship between Frontal Alpha Asymmetry and Depressive Disorders in a Multiverse Analysis of Five Studies. eLife 2021, 10, e60595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Vinne, N.; Vollebregt, M.A.; van Putten, M.J.A.M.; Arns, M. Frontal Alpha Asymmetry as a Diagnostic Marker in Depression: Fact or Fiction? A Meta-Analysis. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 16, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Aguiar Neto, F.S.; Rosa, J.L.G. Depression Biomarkers Using Non-Invasive EEG: A Review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 105, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamian, G.; Hincapié, A.-S.; Combrisson, E.; Thiery, T.; Martel, V.; Althukov, D.; Jerbi, K. Alterations of Intrinsic Brain Connectivity Patterns in Depression and Bipolar Disorders: A Critical Assessment of Magnetoencephalography-Based Evidence. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Northoff, G. Spatiotemporal Psychopathology I_ No Rest for the Brain’s Resting State Activity in Depression? Spatiotemporal Psychopathology of Depressive Symptoms. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 13, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.; Pereira, A.R.; Sampaio, A.; Buján, A.; Pinal, D. Frontal Alpha Asymmetry and Negative Mood: A Cross-Sectional Study in Older and Younger Adults. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantisani, A.; Koenig, T.; Stegmayer, K.; Federspiel, A.; Horn, H.; Müller, T.J.; Wiest, R.; Strik, W.; Walther, S. EEG Marker of Inhibitory Brain Activity Correlates with Resting-State Cerebral Blood Flow in the Reward System in Major Depression. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 266, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesulola, E.; Sharpley, C.F.; Agnew, L.L. The Effects of Gender and Depression Severity on the Association between Alpha Asymmetry and Depression across Four Brain Regions. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 321, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworska, N.; Blier, P.; Fusee, W.; Knott, V. Alpha Power, Alpha Asymmetry and Anterior Cingulate Cortex Activity in Depressed Males and Females. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 46, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quinn, C.R.; Rennie, C.J.; Harris, A.W.F.; Kemp, A.H. The Impact of Melancholia versus Non-Melancholia on Resting-State, EEG Alpha Asymmetry: Electrophysiological Evidence for Depression Heterogeneity. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 215, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, P.C.; Berger, C.; Kronenberg, G.; Bartz, J.; Wybitul, P.; Reis, O.; Hoeppner, J. Combined Cognitive, Psychomotor and Electrophysiological Biomarkers in Major Depressive Disorder. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 269, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustubayeva, A.; Kamzanova, A.; Kudaibergenova, S.; Pivkina, V.; Matthews, G. Major Depression and Brain Asymmetry in a Decision-Making Task with Negative and Positive Feedback. Symmetry 2020, 12, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, R.P.; Stewart, J.G.; Stanton, C.H.; Mueller, E.M.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Emotion-Processing Biases and Resting Eeg Activity in Depressed Adolescents. Depress. Anxiety 2015, 32, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Jung, W.; Kim, S.; Jeon, H.; Lee, S.-H. Frontal Alpha Asymmetry Correlates with Suicidal Behavior in Major Depressive Disorder. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2019, 17, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, E.E.; Cavanagh, J.F.; Allen, J.J.B. Intracranial Source Activity (ELORETA) Related to Scalp-Level Asymmetry Scores and Depression Status. Psychophysiology 2018, 55, e13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gollan, J.K.; Hoxha, D.; Chihade, D.; Pflieger, M.E.; Rosebrock, L.; Cacioppo, J. Frontal Alpha EEG Asymmetry before and after Behavioral Activation Treatment for Depression. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 99, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riddle, J.; Alexander, M.L.; Schiller, C.E.; Rubinow, D.R.; Frohlich, F. Reduction in Left Frontal Alpha Oscillations by Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation in Major Depressive Disorder Is Context Dependent in a Randomized Clinical Trial. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2022, 7, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.L.; Alagapan, S.; Lugo, C.E.; Mellin, J.M.; Lustenberger, C.; Rubinow, D.R.; Fröhlich, F. Double-Blind, Randomized Pilot Clinical Trial Targeting Alpha Oscillations with Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (TACS) for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Umemoto, A.; Panier, L.Y.X.; Cole, S.L.; Kayser, J.; Pizzagalli, D.A.; Auerbach, R.P. Resting Posterior Alpha Power and Adolescent Major Depressive Disorder. J. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 141, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quraan, M.A.; Protzner, A.B.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Giacobbe, P.; Tang, C.W.; Kennedy, S.H.; Lozano, A.M.; McAndrews, M.P. EEG Power Asymmetry and Functional Connectivity as a Marker of Treatment Effectiveness in DBS Surgery for Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishida, K.; Koshikawa, Y.; Morishima, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Katsura, K.; Ueda, S.; Ikeda, S.; Ishii, R.; Pascual-Marqui, R.; Kinoshita, T. Pre-Stimulus Brain Activity Is Associated with State-Anxiety Changes During Single-Session Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benschop, L.; Baeken, C.; Vanderhasselt, M.-A.; de Steen, F.V.; Heeringen, K.V.; Arns, M. Electroencephalogram Resting State Frequency Power Characteristics of Suicidal Behavior in Female Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2019, 80, 5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhong, X.; Lin, G.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, B.; Ning, Y. Resting-State Electroencephalography of Neural Oscillation and Functional Connectivity Patterns in Late-Life Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 316, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.F.; Kan, D.P.X.; Croarkin, P.; Phang, C.K.; Doruk, D. Neurophysiological Correlates of Depressive Symptoms in Young Adults: A Quantitative EEG Study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woźniak-Kwaśniewska, A.; Szekely, D.; Harquel, S.; Bougerol, T.; David, O. Resting Electroencephalographic Correlates of the Clinical Response to Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: A Preliminary Comparison between Unipolar and Bipolar Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 183, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.T.; Hadas, I.; Zomorrodi, R.; Voineskos, D.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; Blumberger, D.M.; Daskalakis, Z.J. Characterizing Cortical Oscillatory Responses in Major Depressive Disorder Before and After Convulsive Therapy: A TMS-EEG Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 287, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, D.P.X.; Lee, P.F. Decrease Alpha Waves in Depression: An Electroencephalogram (EEG) Study. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on BioSignal Analysis, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26-28 May 2015; Processing and Systems (ICBAPS). pp. 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, A.; de la Salle, S.; Sorgini, A.; Lynn, E.; Blier, P.; Knott, V.; Northoff, G. Atypical Temporal Dynamics of Resting State Shapes Stimulus-Evoked Activity in Depression-An EEG Study on Rest-Stimulus Interaction. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Popov, T.; Jylänki, P.; Bi, K.; Yao, Z.; Lu, Q.; Jensen, O.; van Gerven, M.A.J. Predictability of Depression Severity Based on Posterior Alpha Oscillations. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2108–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.S.; Ball, T.M.; Williams, L.M. Deep Phenotyping of Attention Impairments and the ‘Inattention Biotype’ in Major Depressive Disorder. Psychol. Med. 2020, 50, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, I.A.; Wilson, A.C.; Corlier, J.; Leuchter, A.F. Brain Activity and Clinical Outcomes in Adults with Depression Treated with Synchronized Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: An Exploratory Study. Neuromodulation: Technol. Neural Interface 2019, 22, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Saeki, T.; Inoue, M.; Iwanari, H.; Kasai, K. Potentiation of Quantitative Electroencephalograms Following Prefrontal Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Patients with Major Depression. Neurosci. Res. 2013, 77, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Tian, F.; Zhou, S.; Parra, M.A.; Wang, H.; Yu, X. Disrupted Spatiotemporal Complexity of Resting-State Electroencephalogram Dynamics Is Associated with Adaptive and Maladaptive Rumination in Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 829755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Y.; Moradi, M.H. Prediction of Depression Severity Scores Based on Functional Connectivity and Complexity of the EEG Signal. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2021, 52, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, M.; Im, C.-H.; Kim, Y.-W.; Lee, S.-H. Altered Cortical Functional Network in Major Depressive Disorder: A Resting-State Electroencephalogram Study. NeuroImage: Clin. 2018, 19, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugent, A.C.; Ballard, E.D.; Gilbert, J.R.; Tewarie, P.K.; Brookes, M.J.; Zarate, C.A. Multilayer MEG Functional Connectivity as a Potential Marker for Suicidal Thoughts in Major Depressive Disorder. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 28, 102378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corlier, J.; Wilson, A.; Hunter, A.M.; Vince-Cruz, N.; Krantz, D.; Levitt, J.; Minzenberg, M.J.; Ginder, N.; Cook, I.A.; Leuchter, A.F. Changes in Functional Connectivity Predict Outcome of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 4958–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tas, C.; Cebi, M.; Tan, O.; Hızlı-Sayar, G.; Tarhan, N.; Brown, E.C. EEG Power, Cordance and Coherence Differences between Unipolar and Bipolar Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 172, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuchter, A.F.; Cook, I.A.; Hunter, A.M.; Cai, C.; Horvath, S. Resting-State Quantitative Electroencephalography Reveals Increased Neurophysiologic Connectivity in Depression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olbrich, S.; Tränkner, A.; Chittka, T.; Hegerl, U.; Schönknecht, P. Functional Connectivity in Major Depression: Increased Phase Synchronization between Frontal Cortical EEG-Source Estimates. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2014, 222, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, S.; Tang, H.; Liu, X.; Yan, R.; Hua, L.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, R.; Lu, Q.; et al. Identification of Major Depressive Disorder and Prediction of Treatment Response Using Functional Connectivity between the Prefrontal Cortices and Subgenual Anterior Cingulate: A Real-World Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 252, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, S.; Kato, M.; Ikeda, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Ueda, S.; Koshikawa, Y.; Takekita, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Nishida, K. Association between the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex and Anterior Insula in the Salience Network on Response to Antidepressants in Major Depressive Disorder as Revealed by Isolated Effective Coherence. Neuropsychobiology 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuchter, A.F.; Wilson, A.C.; Vince-Cruz, N.; Corlier, J. Novel Method for Identification of Individualized Resonant Frequencies for Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Using Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (RTMS): A Proof-of-Concept Study. Brain Stimul. 2021, 14, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kang, C.; Qu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, Y. Depression-Related Brain Connectivity Analyzed by EEG Event-Related Phase Synchrony Measure. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, N.W. Impaired Upper Alpha Synchronisation during Working Memory Retention in Depression and Depression Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 10, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, O.W.; Hoy, K.E.; Wong, D.; Bailey, N.W.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; Segrave, R.A. Individuals with Depression Display Abnormal Modulation of Neural Oscillatory Activity during Working Memory Encoding and Maintenance. Biol. Psychol. 2019, 148, 107766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kang, C.; Wei, Z.; Qu, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y. Beta Oscillations in Major Depression—Signalling a New Cortical Circuit for Central Executive Function. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W.; Tang, H.; Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Yao, Z.; Lu, Q. Alpha-Beta Decoupling Relevant to Inhibition Deficits Leads to Suicide Attempt in Major Depressive Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 314, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenberg, P.L.A.; Speckens, A.E.M. Multi-Dimensional Modulations of α and γ Cortical Dynamics Following Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy in Major Depressive Disorder. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2015, 9, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messerotti Benvenuti, S.; Buodo, G.; Mennella, R.; Dal Bò, E.; Palomba, D. Appetitive and Aversive Motivation in Depression: The Temporal Dynamics of Task-Elicited Asymmetries in Alpha Oscillations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zotev, V.; Yuan, H.; Misaki, M.; Phillips, R.; Young, K.D.; Feldner, M.T.; Bodurka, J. Correlation between Amygdala BOLD Activity and Frontal EEG Asymmetry during Real-Time FMRI Neurofeedback Training in Patients with Depression. NeuroImage: Clin. 2016, 11, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Segrave, R.A.; Thomson, R.H.; Cooper, N.R.; Croft, R.J.; Sheppard, D.M.; Fitzgerald, P.B. Emotive Interference during Cognitive Processing in Major Depression: An Investigation of Lower Alpha 1 Activity. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 141, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller-Schlaud, K.; Ströhle, A.; Bärwolf, E.; Behr, J.; Rentzsch, J. EEG Frontal Asymmetry and Theta Power in Unipolar and Bipolar Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 276, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheza, D.; Bakic, J.; Baeken, C.; De Raedt, R.; Pourtois, G. Abnormal Approach-Related Motivation but Spared Reinforcement Learning in MDD: Evidence from Fronto-Midline Theta Oscillations and Frontal Alpha Asymmetry. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 19, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escolano, C.; Navarro-Gil, M.; Garcia-Campayo, J.; Congedo, M.; De Ridder, D.; Minguez, J. A Controlled Study on the Cognitive Effect of Alpha Neurofeedback Training in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kessler, K.; Seymour, R.A.; Rippon, G. Brain Oscillations and Connectivity in Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD): New Approaches to Methodology, Measurement and Modelling. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Association, A.P. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: Dsm-5, 5th ed.; Amer Psychiatric Pub Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-89042-555-8. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Zeng, K.; Kang, J.; Tong, Z.; Cai, E.; Chen, H.; Ding, M.; Gu, Y.; Ouyang, G.; Li, X. Development of Brain Network in Children with Autism from Early Childhood to Late Childhood. Neuroscience 2017, 367, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, A.; DiStefano, C.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Scheffler, A.W.; Senturk, D.; Jeste, S.S. Interhemispheric Alpha-Band Hypoconnectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 348, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarasi, L.; Trajkovic, J.; Diciotti, S.; di Pellegrino, G.; Ferri, F.; Ursino, M.; Romei, V. Predictive Waves in the Autism-Schizophrenia Continuum: A Novel Biobehavioral Model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, R.; Ey, E.; Toro, R.; Leboyer, M.; Gillberg, C.; Bourgeron, T. Progress toward Treatments for Synaptic Defects in Autism. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, J.J.; Swanson, M.R.; Elison, J.T.; Gerig, G.; Pruett, J.R.; Styner, M.A.; Vachet, C.; Botteron, K.N.; Dager, S.R.; Estes, A.M.; et al. Neural Circuitry at Age 6 Months Associated with Later Repetitive Behavior and Sensory Responsiveness in Autism. Mol. Autism 2017, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Gramfort, A.; Shetty, N.R.; Kitzbichler, M.G.; Ganesan, S.; Moran, J.M.; Lee, S.M.; Gabrieli, J.D.E.; Tager-Flusberg, H.B.; Joseph, R.M.; et al. Local and Long-Range Functional Connectivity Is Reduced in Concert in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3107–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riva, V.; Marino, C.; Piazza, C.; Riboldi, E.M.; Mornati, G.; Molteni, M.; Cantiani, C. Paternal—But Not Maternal—Autistic Traits Predict Frontal EEG Alpha Asymmetry in Infants with Later Symptoms of Autism. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, T.; Kang, J.; Cong, F.; Li, D.X. Early Childhood Developmental Functional Connectivity of Autistic Brains with Non-Negative Matrix Factorization. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 26, 102251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, A.; Daniel, M.; Marin, A.; Gaonkar, B.; Dapretto, M.; McDonald, N.M.; Jeste, S. Multivariate Neural Connectivity Patterns in Early Infancy Predict Later Autism Symptoms. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, Y.; Bloy, L.; Christopher Edgar, J.; Blaskey, L.; Verma, R.; Roberts, T.P.L. Joint Analysis of Band-Specific Functional Connectivity and Signal Complexity in Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarasi, L.; Magosso, E.; Ricci, G.; Ursino, M.; Romei, V. The Directionality of Fronto-Posterior Brain Connectivity Is Associated with the Degree of Individual Autistic Traits. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursino, M.; Serra, M.; Tarasi, L.; Ricci, G.; Magosso, E.; Romei, V. Bottom-up vs. Top-down Connectivity Imbalance in Individuals with High-Autistic Traits: An Electroencephalographic Study. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 932128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courchesne, E.; Pierce, K.; Schumann, C.M.; Redcay, E.; Buckwalter, J.A.; Kennedy, D.P.; Morgan, J. Mapping Early Brain Development in Autism. Neuron 2007, 56, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wass, S. Distortions and Disconnections: Disrupted Brain Connectivity in Autism. Brain Cogn. 2011, 75, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Courchesne, E.; Pierce, K. Why the Frontal Cortex in Autism Might Be Talking Only to Itself: Local over-Connectivity but Long-Distance Disconnection. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2005, 15, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.; Estévez, M.; Leisman, G.; Melillo, R.; Rodríguez, R.; DeFina, P.; Hernández, A.; Pérez-Nellar, J.; Naranjo, R.; Chinchilla, M.; et al. QEEG Spectral and Coherence Assessment of Autistic Children in Three Different Experimental Conditions. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palva, S.; Palva, J.M. Functional Roles of Alpha-Band Phase Synchronization in Local and Large-Scale Cortical Networks. Front. Psychol. 2011, 2, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, J.W.; Foxe, J.J.; Peters, J.B.; Molholm, S. Susceptibility to Distraction in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Probing the Integrity of Oscillatory Alpha-Band Suppression Mechanisms. Autism Res. 2014, 7, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keehn, B.; Westerfield, M.; Müller, R.-A.; Townsend, J. Autism, Attention, and Alpha Oscillations: An Electrophysiological Study of Attentional Capture. Biol. Psychiatry: Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2017, 2, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeyer, E.; Da Silva, L. Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, A.; Rychlowska, M.; Korb, S.; Niedenthal, P. Fashioning the Face: Sensorimotor Simulation Contributes to Facial Expression Recognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2016, 20, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Harris, A.M.; Atkinson, A.P.; Reed, C.L. Dissociable Processing of Emotional and Neutral Body Movements Revealed by μ-Alpha and Beta Rhythms. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewen, J.B.; Lakshmanan, B.M.; Pillai, A.S.; McAuliffe, D.; Nettles, C.; Hallett, M.; Crone, N.E.; Mostofsky, S.H. Decreased Modulation of EEG Oscillations in High-Functioning Autism during a Motor Control Task. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matlis, S.; Boric, K.; Chu, C.J.; Kramer, M.A. Robust Disruptions in Electroencephalogram Cortical Oscillations and Large-Scale Functional Networks in Autism. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornew, L.; Roberts, T.P.L.; Blaskey, L.; Edgar, J.C. Resting-State Oscillatory Activity in Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2012, 42, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takesaki, N.; Kikuchi, M.; Yoshimura, Y.; Hiraishi, H.; Hasegawa, C.; Kaneda, R.; Nakatani, H.; Takahashi, T.; Mottron, L.; Minabe, Y. The Contribution of Increased Gamma Band Connectivity to Visual Non-Verbal Reasoning in Autistic Children: A MEG Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronconi, L.; Vitale, A.; Federici, A.; Pini, E.; Molteni, M.; Casartelli, L. Altered Neural Oscillations and Connectivity in the Beta Band Underlie Detail-Oriented Visual Processing in Autism. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 28, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.R.; Naples, A.J.; Scheffler, A.W.; Webb, S.J.; Shic, F.; Sugar, C.A.; Murias, M.; Bernier, R.A.; Chawarska, K.; Dawson, G.; et al. Day-to-Day Test-Retest Reliability of EEG Profiles in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Typical Development. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzan, N.; Amran, N.H. Brain Waves and Connectivity of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 171, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregory, M.D.; Mandelbaum, D.E. Evidence of a Faster Posterior Dominant EEG Rhythm in Children with Autism. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2012, 6, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.S.; Kadhim, Z.M. Use of Quantitative Electroencephalography as a Marker of Severity of Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 6(S2), 4418–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter Leno, V.; Pickles, A.; van Noordt, S.; Huberty, S.; Desjardins, J.; Webb, S.J.; Elsabbagh, M. 12-Month Peak Alpha Frequency Is a Correlate but Not a Longitudinal Predictor of Non-Verbal Cognitive Abilities in Infants at Low and High Risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2021, 48, 100938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, J.C.; Dipiero, M.; McBride, E.; Green, H.L.; Berman, J.; Ku, M.; Liu, S.; Blaskey, L.; Kuschner, E.; Airey, M.; et al. Abnormal Maturation of the Resting-state Peak Alpha Frequency in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 3288–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammad-Rezazadeh, I.; Frohlich, J.; Loo, S.K.; Jeste, S.S. Brain Connectivity in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Barstein, J.; Ethridge, L.E.; Mosconi, M.W.; Takarae, Y.; Sweeney, J.A. Resting State EEG Abnormalities in Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2013, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knyazev, G.G.; Bocharov, A.V.; Pylkova, L.V. Extraversion and Fronto-Posterior EEG Spectral Power Gradient: An Independent Component Analysis. Biol. Psychol. 2012, 89, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, G.G. Antero-Posterior EEG Spectral Power Gradient as a Correlate of Extraversion and Behavioral Inhibition. Open Neuroimag. J. 2010, 4, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Just, M.A.; Keller, T.A.; Malave, V.L.; Kana, R.K.; Varma, S. Autism as a Neural Systems Disorder: A Theory of Frontal-Posterior Underconnectivity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 1292–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardo, M.V.; Chakrabarti, B.; Bullmore, E.T.; MRC AIMS Consortium; Baron-Cohen, S. Specialization of Right Temporo-Parietal Junction for Mentalizing and Its Relation to Social Impairments in Autism. Neuroimage 2011, 56, 1832–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orekhova, E.V.; Elsabbagh, M.; Jones, E.J.; Dawson, G.; Charman, T.; Johnson, M.H. EEG Hyper-Connectivity in High-Risk Infants Is Associated with Later Autism. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2014, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fair, D.A.; Cohen, A.L.; Power, J.D.; Dosenbach, N.U.F.; Church, J.A.; Miezin, F.M.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Functional Brain Networks Develop from a “Local to Distributed” Organization. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Supekar, K.; Musen, M.; Menon, V. Development of Large-Scale Functional Brain Networks in Children. PLOS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, J.L.R.; Merzenich, M.M. Model of Autism: Increased Ratio of Excitation/Inhibition in Key Neural Systems. Genes Brain Behav. 2003, 2, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, D.M.; Wallace, M.T. Dysfunction of Sensory Oscillations in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singer, W.; Gray, C.M. Visual Feature Integration and the Temporal Correlation Hypothesis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1995, 18, 555–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canolty, R.T.; Knight, R.T. The Functional Role of Cross-Frequency Coupling. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2010, 14, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnal, L.H.; Giraud, A.-L. Cortical Oscillations and Sensory Predictions. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Driel, J.; Knapen, T.; van Es, D.M.; Cohen, M.X. Interregional Alpha-Band Synchrony Supports Temporal Cross-Modal Integration. NeuroImage 2014, 101, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, O.; Bonnefond, M.; Marshall, T.R.; Tiesinga, P. Oscillatory Mechanisms of Feedforward and Feedback Visual Processing. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, A.K.; Fries, P.; Singer, W. Dynamic Predictions: Oscillations and Synchrony in Top-down Processing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, R.A.; Rippon, G.; Gooding-Williams, G.; Schoffelen, J.M.; Kessler, K. Dysregulated Oscillatory Connectivity in the Visual System in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain 2019, 142, 3294–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berman, J.I.; Liu, S.; Bloy, L.; Blaskey, L.; Roberts, T.P.L.; Edgar, J.C. Alpha-to-Gamma Phase-Amplitude Coupling Methods and Application to Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Connect. 2015, 5, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortese, S.; Kelly, C.; Chabernaud, C.; Proal, E.; Di Martino, A.; Milham, M.P.; Castellanos, F.X. Toward Systems Neuroscience of ADHD: A Meta-Analysis of 55 FMRI Studies. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 1038–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willcutt, E.G.; Doyle, A.E.; Nigg, J.T.; Faraone, S.V.; Pennington, B.F. Validity of the Executive Function Theory of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Meta-Analytic Review. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S.; Wilton, L.; Murray, M.L.; Hodgkins, P.; Asherson, P.; Wong, I.C.K. The Epidemiology of Pharmacologically Treated Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Children, Adolescents and Adults in UK Primary Care. BMC Pediatr. 2012, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franke, B.; Michelini, G.; Asherson, P.; Banaschewski, T.; Bilbow, A.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Cormand, B.; Faraone, S.V.; Ginsberg, Y.; Haavik, J.; et al. Live Fast, Die Young? A Review on the Developmental Trajectories of ADHD across the Lifespan. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 28, 1059–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelini, G.; Salmastyan, G.; Vera, J.D.; Lenartowicz, A. Event-Related Brain Oscillations in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2022, 174, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, S.; Dias, E.C.; Epstein, M.L.; Javitt, D.C. Expectancy-Related Modulations of Neural Oscillations in Continuous Performance Tasks. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spitzer, B.; Haegens, S. Beyond the Status Quo: A Role for Beta Oscillations in Endogenous Content (Re)Activation. eNeuro 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neuper, C.; Pfurtscheller, G. Event-Related Dynamics of Cortical Rhythms: Frequency-Specific Features and Functional Correlates. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2001, 43, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenartowicz, A.; Truong, H.; Salgari, G.C.; Bilder, R.M.; McGough, J.; McCracken, J.T.; Loo, S.K. Alpha Modulation during Working Memory Encoding Predicts Neurocognitive Impairment in ADHD. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2019, 60, 13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, R.; Perroud, N.; Meziane, H.B.; Herrmann, F.; Prada, P.; Giannakopoulos, P.; Deiber, M.-P. Attention-Related EEG Markers in Adult ADHD. Neuropsychologia 2016, 87, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhilova, N.; Cooper, R.; Kuntsi, J.; Asherson, P.; Michelini, G. Electrophysiological Correlates of Spontaneous Mind Wandering in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 391, 112632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooneyham, B.W.; Schooler, J.W. The Costs and Benefits of Mind-Wandering: A Review. Can. J. Exp. Psychol. Rev. Can. Psychol. Exp. 2013, 67, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollebregt, M.A.; Zumer, J.M.; Ter Huurne, N.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Jensen, O. Posterior Alpha Oscillations Reflect Attentional Problems in Boys with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2182–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yordanova, J.; Kolev, V.; Rothenberger, A. Event-Related Oscillations Reflect Functional Asymmetry in Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Suppl. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 62, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Luo, X.; Li, B.; Chang, Q.; Sun, L.; Song, Y. Abnormal Modulation of Theta Oscillations in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 27, 102314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Luo, X.; Wang, E.; Li, B.; Chang, Q.; Sun, L.; Song, Y. Abnormal Alpha Modulation in Response to Human Eye Gaze Predicts Inattention Severity in Children with ADHD. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 38, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Huurne, N.; Lozano-Soldevilla, D.; Onnink, M.; Kan, C.; Buitelaar, J.; Jensen, O. Diminished Modulation of Preparatory Sensorimotor Mu Rhythm Predicts Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Severity. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longarzo, M.; Cavaliere, C.; Alfano, V.; Mele, G.; Salvatore, M.; Aiello, M. Electroencephalographic and Neuroimaging Asymmetry Correlation in Patients with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri, A.; Fassbender, C.; Coffey-Corina, S.; Hartanto, T.A.; Schweitzer, J.B.; Mangun, G.R. Differential Oscillatory Electroencephalogram Between Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Subtypes and Typically Developing Adolescents. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loo, S.K.; Makeig, S. Clinical Utility of EEG in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Research Update. Neurotherapeutics 2012, 9, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arns, M.; Heinrich, H.; Strehl, U. Evaluation of Neurofeedback in ADHD: The Long and Winding Road. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 95, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolano, C.; Navarro-Gil, M.; Garcia-Campayo, J.; Congedo, M.; Minguez, J. The Effects of Individual Upper Alpha Neurofeedback in ADHD: An Open-Label Pilot Study. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2014, 39, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deiber, M.-P.; Hasler, R.; Colin, J.; Dayer, A.; Aubry, J.-M.; Baggio, S.; Perroud, N.; Ros, T. Linking Alpha Oscillations, Attention and Inhibitory Control in Adult ADHD with EEG Neurofeedback. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 25, 102145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Lowenstein, M.; Campusano, R.; Hu, Y.; Diaz-Delgado, J.; Ayyoub, J.; Jain, R.; Gazzaley, A. Closed-Loop Neurofeedback of α Synchrony during Goal-Directed Attention. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 5699–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Table of EEG Indices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Index | Full Name | Description |
| ERD/ERS | event-related synchronization/desynchronization | Amplitude up/down-modulation in response to a specific event, due to a synchronized activity of a large number of neurons |
| FAA (PAA) | frontal (or posterior) alpha asymmetry | Relatively higher alpha power recorded from the left (as compared to the right) hemisphere over frontal (or posterior) regions |
| IAF | individual alpha frequency | The frequency bin displaying the highest power value within the alpha band (8–13 Hz) |
| ITC | intertrial coherence | The degree of oscillatory phase-synchronization across different trials |
| PAC | phase amplitude coupling | Coupling between the phase of slower oscillations with the amplitude of faster oscillations (i.e., reflecting integrative mechanisms of neural activity within the brain) |
| PSD | power spectral density | Measure of signal’s power content versus frequency |
| Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder (SSD) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Studies | Analytic Method | Main Findings |
| [68,69,70,73,77,80] | Resting state IAF | Slower IAF over posterior regions |
| [60,61,62,63,64,65,66] | Resting state PSD | Posterior and frontal Alpha power reduction |
| [75,76,77] | Resting state PSD | Alpha power increase in the DMN |
| [68,75,76,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,97,109,114,117] | Functional connectivity | Aberrant long-range functional connectivity |
| [71,93,94,96,99,100,101,102,103,104,105] | Auditory evoked response | Aberrant Alpha ERD/ERS over posterior and frontocentral areas |
| [106,107,108,110,111] | Evoked response during WM and attentive tasks | Aberrant Alpha ERD modulation |
| Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Studies | Analytic Method | Main Findings |
| [118,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137] | Resting state PSD | Frontal Alpha asymmetry |
| [118,131,141,142] | Resting state PSD | Posterior Alpha asymmetry |
| [144,145,146,149,150,151,152] | Resting state PSD | Aberrant posterior Alpha power |
| [126,127,156,157,158,160,161,162,163,164,169] | Functional connectivity | Aberrant short and long-range functional connectivity |
| [134,167,168,170] | Evoked response during WM and attentive tasks | Aberrant Alpha power over posterior (reduced) and midfrontal (increased) areas |
| Autistic Spectrum Disorder (ASD) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Studies | Analytic Method | Main Findings |
| [195,197,198] | Task-induced PSD | Impaired modulation of Alpha power |
| [186,203,215] | Topographical distribution of Alpha power | Aberrant Alpha power in frontal regions |
| [185,230,231] | PAC | Aberrant Alpha–Gamma PAC |
| [180,181,184,185,187,189] | Functional connectivity | Aberrant short- (enhanced) and long-range (reduced) functional connectivity |
| [201,202] | Evoked response during motor tasks | Less suppressed Mu–Alpha ERD/ERS over sensorimotor areas |
| Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Studies | Analytic Method | Main Findings |
| [49,240,241,244,246,247,250] | Topographical distribution of Alpha power during attentional tasks | Aberrant Alpha ERD/ERS lateralization |
| [240,245] | Topographical distribution of Alpha power during motor tasks | Reduced Mu–Alpha ERD/ERS lateralization |
| [48,242] | Evoked response during spontaneous mind wandering and tasks | Reduced Alpha ERD/ERS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ippolito, G.; Bertaccini, R.; Tarasi, L.; Di Gregorio, F.; Trajkovic, J.; Battaglia, S.; Romei, V. The Role of Alpha Oscillations among the Main Neuropsychiatric Disorders in the Adult and Developing Human Brain: Evidence from the Last 10 Years of Research. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123189
Ippolito G, Bertaccini R, Tarasi L, Di Gregorio F, Trajkovic J, Battaglia S, Romei V. The Role of Alpha Oscillations among the Main Neuropsychiatric Disorders in the Adult and Developing Human Brain: Evidence from the Last 10 Years of Research. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123189
Chicago/Turabian StyleIppolito, Giuseppe, Riccardo Bertaccini, Luca Tarasi, Francesco Di Gregorio, Jelena Trajkovic, Simone Battaglia, and Vincenzo Romei. 2022. "The Role of Alpha Oscillations among the Main Neuropsychiatric Disorders in the Adult and Developing Human Brain: Evidence from the Last 10 Years of Research" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123189
APA StyleIppolito, G., Bertaccini, R., Tarasi, L., Di Gregorio, F., Trajkovic, J., Battaglia, S., & Romei, V. (2022). The Role of Alpha Oscillations among the Main Neuropsychiatric Disorders in the Adult and Developing Human Brain: Evidence from the Last 10 Years of Research. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123189