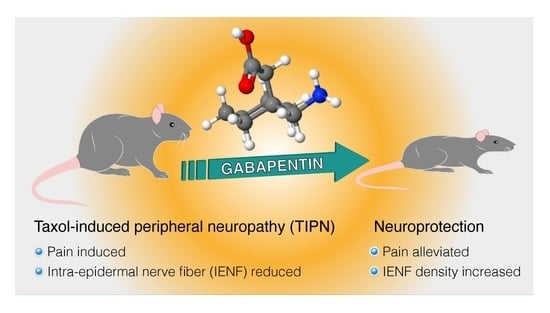
Gabapentin Increases Intra-Epidermal and Peptidergic Nerve Fibers Density and Alleviates Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in a Mouse Model of Acute Taxol-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Chemicals, Drugs, and Administration
2.3. Taxol-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (TIPN)
2.4. Evaluation of Mechanical Allodynia (Von Frey Touch Test)
2.5. Evaluation of Thermal Allodynia
2.5.1. Tail-Flick Test
2.5.2. Hot Plate Test
2.6. Immunohistochemically (IHC) Staining and Intra-Epidermal Nerve Fiber Counting
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Gabapentin Inhibited Mechanical Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Taxol-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
3.2. Gabapentin Inhibited Taxol-Induced IENF Loss
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, T.; Mizrahi, D.; Goldstein, D.; Kiernan, M.C.; Park, S.B. Chemotherapy and peripheral neuropathy. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 4109–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Lu, X.; Feng, B. A review of research progress of antitumor drugs based on tubulin targets. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 4020–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.-L.; Lou, Z.-P.; Ma, F.-Y.; Najafi, M. The interactions of paclitaxel with tumour microenvironment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 105, 108555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, L.R.; Spencer, C.M. Paclitaxel. An update of its use in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer and ovarian and other gynaecological cancers. Drugs Aging 1998, 12, 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquhar-Smith, P. Chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2011, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gadgil, S.; Ergün, M.; Heuvel, S.A.V.D.; Van Der Wal, S.E.; Scheffer, G.J.; Hooijmans, C.R. A systematic summary and comparison of animal models for chemotherapy induced (peripheral) neuropathy (CIPN). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuttle, A.H.; Philip, V.; Chesler, E.J.; Mogil, J.S. Comparing phenotypic variation between inbred and outbred mice. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 994–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennypacker, S.D.; Fonseca, M.M.; Morgan, J.W.; Dougherty, P.M.; Cubillos-Ruiz, J.R.; Strowd, R.E.; Romero-Sandoval, E.A. Methods and protocols for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) mouse models using paclitaxel. Methods Cell Biol. 2022, 168, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, W.; Kyte, S.L.; Bagdas, D.; Alkhlaif, Y.; Alsharari, S.D.; Lichtman, A.H.; Chen, Z.-J.; Del Fabbro, E.; Bigbee, J.W.; Gewirtz, D.A.; et al. Effects of paclitaxel on the development of neuropathy and affective behaviors in the mouse. Neuropharmacology 2017, 117, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molassiotis, A.; Cheng, H.L.; Lopez, V.; Au, J.S.K.; Chan, A.; Bandla, A.; Leung, K.T.; Li, Y.C.; Wong, K.H.; Suen, L.K.P.; et al. Are we mis-estimating chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy? Analysis of assessment methodologies from a prospective, multinational, longitudinal cohort study of patients receiving neurotoxic chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loprinzi, C.L.; Lacchetti, C.; Bleeker, J.; Cavaletti, G.; Chauhan, C.; Hertz, D.L.; Kelley, M.R.; Lavino, A.; Lustberg, M.B.; Paice, J.A.; et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: ASCO guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3325–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.; Gaines, C. Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2019, 24, 608–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, C.W.; Brett, A.S. A clinical overview of Off-label use of gabapentinoid drugs. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, A. Examination of the evidence for Off-label use of gabapentin. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2003, 9, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrone, B.; Di Matteo, A.; Amato, A.; Pistillo, L.; Durando, L.; Milanese, C.; Di Giorgio, F.P.; Tongiani, S. Synergistic interaction between trazodone and gabapentin in rodent models of neuropathic pain. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Boroujerdi, A.; Bennett, G.; Luo, Z. Chemotherapy-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy: Analgesic effects of gabapentin and effects on expression of the alpha-2-delta type-1 calcium channel subunit. Neuroscience 2007, 144, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woller, S.; Corr, M.; Yaksh, T. Differences in cisplatin-induced mechanical allodynia in male and female mice. Eur. J. Pain 2015, 19, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, N.; Tateishi, K.; Tsubaki, M.; Takeda, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Tsurushima, K.; Ishizaka, T.; Nishida, S. Gabapentin and duloxetine prevent oxaliplatin- and paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy by inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation in spinal cords of mice. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbârcea, C.E.; Ciotu, I.C.; Bild, V.; Chiriţă, C.; Tănase, A.M.; Şeremet, O.C.; Ştefănescu, E.; Arsene, A.L.; Bastian, A.E.; Ionică, F.E.; et al. Therapeutic potential of certain drug combinations on paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2017, 58, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Donvito, G.; Wilkerson, J.L.; Damaj, M.I.; Lichtman, A.H. Palmitoylethanolamide reverses paclitaxel-induced allodynia in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 359, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huehnchen, P.; Boehmerle, W.; Endres, M. Assessment of paclitaxel induced sensory polyneuropathy with “Catwalk” automated gait analysis in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, M.P.; Mühl, S.; Pogatzki-Zahn, E.M.; Agelopoulos, K.; Ständer, S. Intraepidermal nerve fiber density: Diagnostic and therapeutic relevance in the management of chronic pruritus: A review. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 6, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mangus, L.M.; Rao, D.B.; Ebenezer, G.J. Intraepidermal nerve fiber analysis in human patients and animal models of peripheral neuropathy: A comparative review. Toxicol. Pathol. 2019, 48, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, M.-H.; Hu, M.-E.; Hsieh, Y.-L.; Lan, C.-T.; Tseng, T.-J. Peptidergic intraepidermal nerve fibers in the skin contribute to the neuropathic pain in paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. Neuropeptides 2014, 48, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, G.; Nallasamy, N.; Downs, H.; Dana, R.; Oaklander, A.L. Corneal innervation as a window to peripheral neuropathies. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 113, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauria, G.; Lombardi, R.; Borgna, M.; Penza, P.; Bianchi, R.; Savino, C.; Canta, A.R.; Nicolini, G.; Marmiroli, P.; Cavaletti, G. Intraepidermal nerve fiber density in rat foot pad: Neuropathologic-neurophysiologic correlation. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2005, 10, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, K.M.; Vornov, J.J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Carozzi, V.A.; Rodriguez-Menendez, V.; Ballarini, E.; Alberti, P.; Pozzi, E.; Semperboni, S.; et al. Peripheral neuropathy induced by microtubule-targeted chemotherapies: Insights into acute injury and long-term recovery. Cancer Res 2018, 78, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Höke, A.; Ray, M. Rodent models of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. ILAR J. 2014, 54, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouchenaki, H.; Danigo, A.; Sturtz, F.; Hajj, R.; Magy, L.; Demiot, C. An overview of ongoing clinical trials assessing pharmacological therapeutic strategies to manage chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, based on preclinical studies in rodent models. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 35, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HHopkins, H.L.; Duggett, N.A.; Flatters, S.J.L. Chemotherapy-induced painful neuropathy: Pain-like behaviours in rodent models and their response to commonly used analgesics. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2016, 10, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Egashira, N. Drug repositioning for the prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A mechanism- and screening-based strategy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 607780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodarski, R.; Clark, A.; Grist, J.; Marchand, F.; Malcangio, M. Gabapentin reverses microglial activation in the spinal cord of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, D.R.M.; Santos, D.S.; Santo, R.F.D.E.; dos Santos, F.E.; Filho, G.B.D.O.; Leite, A.C.L.; Soares, M.B.P.; Villarreal, C.F. Structural improvement of new thiazolidinones compounds with antinociceptive activity in experimental chemotherapy-induced painful neuropathy. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 90, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghili, M.; Zare, M.; Mousavi, N.; Ghalehtaki, R.; Sotoudeh, S.; Kalaghchi, B.; Akrami, S.; Esmati, E. Efficacy of gabapentin for the prevention of paclitaxel induced peripheral neuropathy: A randomized placebo controlled clinical trial. Breast J. 2019, 25, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilley, E.; Stanford, S.; Kendall, D.E.; Alexander, S.P.; Cirino, G.; Docherty, J.R.; George, C.H.; Insel, P.A.; Izzo, A.A.; Ji, Y.; et al. ARRIVE 2.0 and the British Journal of Pharmacology: Updated guidance for 2020. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staff, N.P.; Fehrenbacher, J.C.; Caillaud, M.; Damaj, M.I.; Segal, R.A.; Rieger, S. Pathogenesis of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: A current review of in vitro and in vivo findings using rodent and human model systems. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 324, 113121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuis, J.R.; Dvorakova, L.S.; Vetter, I. Methods used to evaluate pain behaviors in rodents. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castel, D.; Sabbag, I.; Brenner, O.; Meilin, S. Peripheral neuritis trauma in pigs: A neuropathic pain model. J. Pain 2015, 17, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taliyan, R.; Sharma, P.L. Possible mechanism of protective effect of thalidomide in STZ-induced-neuropathic pain behavior in rats. Inflammopharmacology 2011, 20, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baos, S.; Rogers, C.A.; Abbadi, R.; Alzetani, A.; Casali, G.; Chauhan, N.; Collett, L.; Culliford, L.; de Jesus, S.E.; Edwards, M.; et al. Effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and safety of gabapentin versus placebo as an adjunct to multimodal pain regimens in surgical patients: Protocol of a placebo controlled randomised controlled trial with blinding (GAP study). BMJ Open 2020, 10, e041176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rullán, M.; PHN group; Bulilete, O.; Leiva, A.; Soler, A.; Roca, A.; González-Bals, M.J.; Lorente, P.; Llobera, J. Efficacy of gabapentin for prevention of postherpetic neuralgia: Study protocol for a randomized controlled clinical trial. Trials 2017, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tassone, D.M.; Boyce, E.; Guyer, J.; Nuzum, D. Pregabalin: A novel γ-aminobutyric acid analogue in the treatment of neuropathic pain, partial-onset seizures, and anxiety disorders. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/4636/smpc#PRECLINICAL_SAFETY (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Nieto, F.R.; Entrena, J.M.; Cendán, C.M.; Del Pozo, E.; Vela, J.M.; Baeyens, J.M. Tetrodotoxin inhibits the development and expression of neuropathic pain induced by paclitaxel in mice. Pain 2008, 137, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolivalt, C.G.; Frizzi, K.E.; Marquez, A.; Ochoa, J.; Calcutt, N.A. Phenotyping peripheral neuropathy in mouse models. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2017, 6, 223–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.M.; Frizzi, K.E.; Ellis, R.J.; Calcutt, N.A.; Fields, J.A. Prevention of HIV-1 TAT protein-induced peripheral neuropathy and mitochondrial disruption by the antimuscarinic pirenzepine. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 663373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakas, M.C. Peripheral neuropathy and antiretroviral drugs. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2001, 6, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manji, H. Drug-induced neuropathies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 115, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauchan, P.; Andoh, T.; Ikeda, K.; Fujita, M.; Sasaki, A.; Kato, A.; Kuraishi, Y. Mechanical allodynia induced by paclitaxel, oxaliplatin and vincristine: Different effectiveness of gabapentin and different expression of voltagedependent calcium channel.alpha.2.delta.-1 subunit. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thangamani, D.; Edafiogho, I.O.; Masocha, W. The anticonvulsant enaminone E139 attenuates paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain in rodents. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 240508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flatters, S.J.; Bennett, G.J. Ethosuximide reverses paclitaxel- and vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Pain 2004, 109, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, K.R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Rauniar, G.; Das, B. Comparison of antinociceptive effect of the antiepileptic drug gabapentin to that of various dosage combinations of gabapentin with lamotrigine and topiramate in mice and rats. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2011, 2, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sałat, K.; Cios, A.; Wyska, E.; Salat, R.; Mogilski, S.; Filipek, B.; Więckowski, K.; Malawska, B. Antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic activity of 3-[4-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-dihydrofuran-2-one compared to pregabalin in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 122, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Joo, H.S.; Chang, H.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Moon, D.E. Attenuation of neuropathy-induced allodynia following intraplantar injection of pregabalin. Can. J. Anaesth. 2010, 57, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyette-Davis, J.; Xin, W.; Zhang, H.; Dougherty, P.M. Intraepidermal nerve fiber loss corresponds to the development of Taxol-induced hyperalgesia and can be prevented by treatment with minocycline. Pain 2011, 152, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siau, C.; Xiao, W.; Bennett, G.J. Paclitaxel- and vincristine-evoked painful peripheral neuropathies: Loss of epidermal innervation and activation of Langerhans cells. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 201, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.W.; Flatters, S.J.L.; Xiao, W.H.; Mulhern, H.L.; Bennett, G.J. Prevention of paclitaxel-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy by acetyl-l-carnitine: Effects on axonal mitochondria, sensory nerve fiber terminal arbors, and cutaneous Langerhans cells. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calandre, E.P.; Rico-Villademoros, F.; Slim, M. Alpha2delta ligands, gabapentin, pregabalin and mirogabalin: A review of their clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.P.; Harris, E.W. Analgesia with gabapentin and pregabalin may involve N-Methyl-d-Aspartate receptors, neurexins, and thrombospondins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 374, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamaoka, J.; Di, Z.H.; Sun, W.; Kawana, S. Changes in cutaneous sensory nerve fibers induced by skin-scratching in mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 46, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Massri, K.F.; Ahmed, L.A.; El-Abhar, H.S. Pregabalin and lacosamide ameliorate paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy via inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and Notch-1 receptor. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 120, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, L.; Andrew, D.; Robinson, P.; Boissonade, F.; Loescher, A. Increased cutaneous NGF and CGRP-labelled trkA-positive intra-epidermal nerve fibres in rat diabetic skin. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 506, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Larson, M.J.; Kiyoshi, C.M.; Annett, A.J.; Stalker, W.A.; Peng, J.; Tedeschi, A. Gabapentinoid treatment promotes corticospinal plasticity and regeneration following murine spinal cord injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 130, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klazas, M.; Naamneh, M.S.; Zheng, W.; Lazarovici, P. Gabapentin Increases Intra-Epidermal and Peptidergic Nerve Fibers Density and Alleviates Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in a Mouse Model of Acute Taxol-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123190
Klazas M, Naamneh MS, Zheng W, Lazarovici P. Gabapentin Increases Intra-Epidermal and Peptidergic Nerve Fibers Density and Alleviates Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in a Mouse Model of Acute Taxol-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123190
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlazas, Michal, Majdi Saleem Naamneh, Wenhua Zheng, and Philip Lazarovici. 2022. "Gabapentin Increases Intra-Epidermal and Peptidergic Nerve Fibers Density and Alleviates Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in a Mouse Model of Acute Taxol-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123190
APA StyleKlazas, M., Naamneh, M. S., Zheng, W., & Lazarovici, P. (2022). Gabapentin Increases Intra-Epidermal and Peptidergic Nerve Fibers Density and Alleviates Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in a Mouse Model of Acute Taxol-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123190