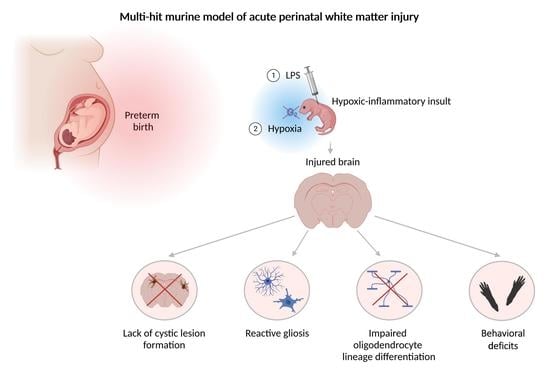
A Novel Murine Multi-Hit Model of Perinatal Acute Diffuse White Matter Injury Recapitulates Major Features of Human Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Animal Model
2.3. Tissue Preparation
2.4. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H and E) Staining
2.5. Histologic Analysis
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Image Analysis
2.8. Hindlimb Foot Angle
2.9. Rotarod
2.10. Novel Object Recognition
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Perinatal Inflammation–Hypoxia Does Not Lead to the Formation of Macroscopic or Microscopic Cystic Lesions
3.2. Perinatal Inflammation–Hypoxia Insult Induces White Matter Hypomyelination
3.3. Perinatal Inflammation–Hypoxia Leads to Impaired Oligodendrocyte Lineage Differentiation
3.4. Perinatal Inflammation–Hypoxia Induces Reactive Changes in Microglia and Astrocytes
3.5. Perinatal Inflammation–Hypoxia Results in Sensorimotor and Cognitive Deficits
4. Discussion
4.1. Perinatal Inflammation and Hypoxia Produce Diffuse Perinatal White Matter Injury
4.2. Impaired Oligodendrocyte Differentiation Appears to Underlie Perinatal Hypoxia–Inflammation-Induced Myelination Defects
4.3. Observed Reactive Changes in Microglia and Astrocytes after Perinatal Inflammation–Hypoxia Appear to Be Transient
4.4. Glial Reactivity in Developing Versus Mature Brains
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Volpe, J.J. Dysmaturation of Premature Brain: Importance, Cellular Mechanisms, and Potential Interventions. Pediatr. Neurol. 2019, 95, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, S.A. White matter injury in the preterm infant: Pathology and mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaindl, A.M.; Favrais, G.; Gressens, P. Molecular mechanisms involved in injury to the preterm brain. J. Child Neurol. 2009, 24, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, J.R.; Maire, J.; Riddle, A.; Gong, X.; Nguyen, T.; Nelson, K.; Luo, N.L.; Ren, J.; Struve, J.; Sherman, L.S.; et al. Arrested preoligodendrocyte maturation contributes to myelination failure in premature infants. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, J.J.; Kinney, H.C.; Jensen, F.E.; Rosenberg, P.A. The developing oligodendrocyte: Key cellular target in brain injury in the premature infant. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Back, S.A.; Han, B.H.; Luo, N.L.; Chricton, C.A.; Xanthoudakis, S.; Tam, J.; Arvin, K.L.; Holtzman, D.M. Selective vulnerability of late oligodendrocyte progenitors to hypoxia-ischemia. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penn, A.A.; Gressens, P.; Fleiss, B.; Back, S.A.; Gallo, V. Controversies in preterm brain injury. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 92, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rumajogee, P.; Bregman, T.; Miller, S.P.; Yager, J.Y.; Fehlings, M.G. Rodent Hypoxia-Ischemia Models for Cerebral Palsy Research: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silbereis, J.C.; Huang, E.J.; Back, S.A.; Rowitch, D.H. Towards improved animal models of neonatal white matter injury associated with cerebral palsy. Dis. Model. Mech. 2010, 3, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomi, G.; Joerger-Messerli, M.; Haesler, V.; Muri, L.; Surbek, D.; Schoeberlein, A. Intranasally Administered Exosomes from Umbilical Cord Stem Cells Have Preventive Neuroprotective Effects and Contribute to Functional Recovery after Perinatal Brain Injury. Cells 2019, 8, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerger-Messerli, M.S.; Thomi, G.; Haesler, V.; Keller, I.; Renz, P.; Surbek, D.V.; Schoeberlein, A. Human Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Drive Oligodendroglial Maturation by Restraining MAPK/ERK and Notch Signaling Pathways. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 622539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomi, G.; Surbek, D.; Haesler, V.; Joerger-Messerli, M.; Schoeberlein, A. Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in perinatal brain injury. Stem. Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yawno, T.; Sutherland, A.; Loose, J.; Nitsos, I.; Bischof, R.; Castillo-Melendez, M.; McDonald, C.A.; Wong, F.Y.; Jenkin, G.; et al. Preterm white matter brain injury is prevented by early administration of umbilical cord blood cells. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 283, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mike, J.K.; Wu, K.Y.; White, Y.; Pathipati, P.; Ndjamen, B.; Hutchings, R.S.; Losser, C.; Vento, C.; Arellano, K.; Vanhatalo, O.; et al. Defining Longer-Term Outcomes in an Ovine Model of Moderate Perinatal Hypoxia-Ischemia. Dev. Neurosci. 2022, 44, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, B.D.; Blomgren, K.; Gimlin, K.; Ferriero, D.M.; Noble-Haeusslein, L.J. Brain development in rodents and humans: Identifying benchmarks of maturation and vulnerability to injury across species. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 106-107, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billiards, S.S.; Haynes, R.L.; Folkerth, R.D.; Borenstein, N.S.; Trachtenberg, F.L.; Rowitch, D.H.; Ligon, K.L.; Volpe, J.J.; Kinney, H.C. Myelin abnormalities without oligodendrocyte loss in periventricular leukomalacia. Brain Pathol. 2008, 18, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, C.R.; Folkerth, R.D.; Billiards, S.S.; Trachtenberg, F.L.; Drinkwater, M.E.; Volpe, J.J.; Kinney, H.C. Gray matter injury associated with periventricular leukomalacia in the premature infant. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovens, I.B.; Nyakas, C.; Schoemaker, R.G. A novel method for evaluating microglial activation using ionized calcium-binding adaptor protein-1 staining: Cell body to cell size ratio. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2014, 1, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feather-Schussler, D.N.; Ferguson, T.S. A Battery of Motor Tests in a Neonatal Mouse Model of Cerebral Palsy. J. Vis. Exp. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bevins, R.A.; Besheer, J. Object recognition in rats and mice: A one-trial non-matching-to-sample learning task to study ‘recognition memory’. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, B.Q.; Larroche, J.C. Periventricular leukomalacia of infancy. A form of neonatal anoxic encephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1962, 7, 386–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellantuono, I.; de Cabo, R.; Ehninger, D.; Di Germanio, C.; Lawrie, A.; Miller, J.; Mitchell, S.J.; Navas-Enamorado, I.; Potter, P.K.; Tchkonia, T.; et al. A toolbox for the longitudinal assessment of healthspan in aging mice. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 540–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favrais, G.; van de Looij, Y.; Fleiss, B.; Ramanantsoa, N.; Bonnin, P.; Stoltenburg-Didinger, G.; Lacaud, A.; Saliba, E.; Dammann, O.; Gallego, J.; et al. Systemic inflammation disrupts the developmental program of white matter. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Steenwinckel, J.; Schang, A.L.; Sigaut, S.; Chhor, V.; Degos, V.; Hagberg, H.; Baud, O.; Fleiss, B.; Gressens, P. Brain damage of the preterm infant: New insights into the role of inflammation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagberg, H.; Peebles, D.; Mallard, C. Models of white matter injury: Comparison of infectious, hypoxic-ischemic, and excitotoxic insults. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2002, 8, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.E., 3rd; Vannucci, R.C.; Brierley, J.B. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann. Neurol. 1981, 9, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, S.J.; Back, S.A. The Vannucci Model of Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury in the Neonatal Rodent: 40 years later. Dev. Neurosci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Sedik, C.; Ferriero, D.M. Strain-related brain injury in neonatal mice subjected to hypoxia-ischemia. Brain Res. 1998, 810, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzeniewski, S.J.; Romero, R.; Cortez, J.; Pappas, A.; Schwartz, A.G.; Kim, C.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Yoon, B.H.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; et al. A “multi-hit” model of neonatal white matter injury: Cumulative contributions of chronic placental inflammation, acute fetal inflammation and postnatal inflammatory events. J. Perinat. Med. 2014, 42, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leviton, A.; Fichorova, R.N.; O’Shea, T.M.; Kuban, K.; Paneth, N.; Dammann, O.; Allred, E.N. Two-hit model of brain damage in the very preterm newborn: Small for gestational age and postnatal systemic inflammation. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 73, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tilborg, E.; Achterberg, E.J.M.; van Kammen, C.M.; van der Toorn, A.; Groenendaal, F.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Heijnen, C.J.; Vanderschuren, L.; Benders, M.; Nijboer, C.H.A. Combined fetal inflammation and postnatal hypoxia causes myelin deficits and autism-like behavior in a rat model of diffuse white matter injury. Glia 2018, 66, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adén, U.; Favrais, G.; Plaisant, F.; Winerdal, M.; Felderhoff-Mueser, U.; Lampa, J.; Lelièvre, V.; Gressens, P. Systemic inflammation sensitizes the neonatal brain to excitotoxicity through a pro-/anti-inflammatory imbalance: Key role of TNFalpha pathway and protection by etanercept. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, S.A.; Riddle, A.; McClure, M.M. Maturation-dependent vulnerability of perinatal white matter in premature birth. Stroke 2007, 38, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Folkerth, R.D.; Trachtenberg, F.L.; Haynes, R.L. Oxidative injury in the cerebral cortex and subplate neurons in periventricular leukomalacia. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haynes, R.L.; Folkerth, R.D.; Keefe, R.J.; Sung, I.; Swzeda, L.I.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Volpe, J.J.; Kinney, H.C. Nitrosative and oxidative injury to premyelinating oligodendrocytes in periventricular leukomalacia. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 62, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, J.K.; Romanko, M.J.; Rothstein, R.P.; Wood, T.L.; Levison, S.W. Perinatal hypoxia-ischemia induces apoptotic and excitotoxic death of periventricular white matter oligodendrocyte progenitors. Dev. Neurosci. 2001, 23, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaye-Duriez, A.; Dufour, A.; Bokobza, C.; Gressens, P.; Van Steenwinckel, J. Targeting Microglial Disturbances to Protect the Brain From Neurodevelopmental Disorders Associated With Prematurity. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 80, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobuta, H.; Ghiani, C.A.; Paez, P.M.; Spreuer, V.; Dong, H.; Korsak, R.A.; Manukyan, A.; Li, J.; Vinters, H.V.; Huang, E.J.; et al. STAT3-mediated astrogliosis protects myelin development in neonatal brain injury. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 750–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiow, L.R.; Favrais, G.; Schirmer, L.; Schang, A.L.; Cipriani, S.; Andres, C.; Wright, J.N.; Nobuta, H.; Fleiss, B.; Gressens, P.; et al. Reactive astrocyte COX2-PGE2 production inhibits oligodendrocyte maturation in neonatal white matter injury. Glia 2017, 65, 2024–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, L.; Pembroke, W.G.; Rexach, J.E.; Godoy, M.I.; Condro, M.C.; Alvarado, A.G.; Harteni, M.; Chen, Y.W.; Stiles, L.; et al. Conservation and divergence of vulnerability and responses to stressors between human and mouse astrocytes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T.R.; Dufort, C.; Dissing-Olesen, L.; Giera, S.; Young, A.; Wysoker, A.; Walker, A.J.; Gergits, F.; Segel, M.; Nemesh, J.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Microglia throughout the Mouse Lifespan and in the Injured Brain Reveals Complex Cell-State Changes. Immunity 2019, 50, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, L.; Darmanis, S.; Neff, N.F.; Okamoto, J.; Gulati, G.; Bennett, M.L.; Sun, L.O.; Clarke, L.E.; et al. Developmental Heterogeneity of Microglia and Brain Myeloid Cells Revealed by Deep Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Neuron 2019, 101, 207–223.e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volpe, J.J. Microglia: Newly discovered complexity could lead to targeted therapy for neonatal white matter injury and dysmaturation. J. Neonatal. Perinatal. Med. 2019, 12, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pașca, A.M.; Park, J.Y.; Shin, H.W.; Qi, Q.; Revah, O.; Krasnoff, R.; O’Hara, R.; Willsey, A.J.; Palmer, T.D.; Pașca, S.P. Human 3D cellular model of hypoxic brain injury of prematurity. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renz, P.; Schoeberlein, A.; Haesler, V.; Maragkou, T.; Surbek, D.; Brosius Lutz, A. A Novel Murine Multi-Hit Model of Perinatal Acute Diffuse White Matter Injury Recapitulates Major Features of Human Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112810
Renz P, Schoeberlein A, Haesler V, Maragkou T, Surbek D, Brosius Lutz A. A Novel Murine Multi-Hit Model of Perinatal Acute Diffuse White Matter Injury Recapitulates Major Features of Human Disease. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(11):2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112810
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenz, Patricia, Andreina Schoeberlein, Valérie Haesler, Theoni Maragkou, Daniel Surbek, and Amanda Brosius Lutz. 2022. "A Novel Murine Multi-Hit Model of Perinatal Acute Diffuse White Matter Injury Recapitulates Major Features of Human Disease" Biomedicines 10, no. 11: 2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112810
APA StyleRenz, P., Schoeberlein, A., Haesler, V., Maragkou, T., Surbek, D., & Brosius Lutz, A. (2022). A Novel Murine Multi-Hit Model of Perinatal Acute Diffuse White Matter Injury Recapitulates Major Features of Human Disease. Biomedicines, 10(11), 2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112810