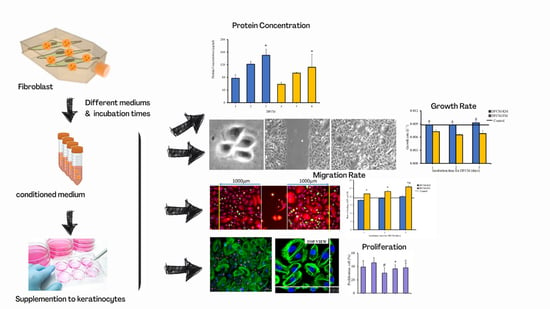
Effect of Different Collection Times of Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium (DFCM) on In Vitro Re-Epithelialisation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Cells and Primary Culture
2.2. Preparation of Dermal Fibroblast Condition Medium (DFCM)
2.3. Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) Assay
2.4. Multiplex ELISA
2.5. Keratinocyte Attachment and Growth
2.6. Single-Cell Migration
2.7. Scratch Assay
2.8. Dialysis
2.9. Concentration of Calcium
2.10. Immunocytochemical Staining
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphology of Cells and Concentration of Proteins in DFCM
3.2. Effect of DFCM on In Vitro Re-Epithelialisation
3.3. Identification of Wound-Healing Mediators in DFCM
3.4. Expression and Distribution of Actin, Vinculin, and Integrin in Keratinocytes Treated with DFCM
3.5. Concentration of Calcium in DFCM
3.6. Effect of Calcium in DFCM on Keratinocyte Morphology
3.7. Effect of Calcium in DFCM on Keratinocyte Proliferation and Differentiation
3.8. Effect of Calcium in DFCM on Keratinocyte Migration
3.9. Proliferative Potential of Keratinocytes during In Vitro Healing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Diegelmann, R.F.; Evans, M.C.J.F. Wound healing: An overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Masri, S.; Zawani, M.; Zulkiflee, I.; Salleh, A.; Fadilah, N.I.M.; Maarof, M.; Wen, A.P.Y.; Duman, F.; Tabata, Y.; Aziz, I.A.; et al. Cellular Interaction of Human Skin Cells towards Natural Bioink via 3D-Bioprinting Technologies for Chronic Wound: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastar, I.; Stojadinovic, O.; Yin, N.C.; Ramirez, H.; Nusbaum, A.G.; Sawaya, A.; Patel, S.B.; Khalid, L.; Isseroff, R.R.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelialization in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramasastry, S.S. Acute Wounds. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2005, 32, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riha, S.M.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M.B. Synergistic Effect of Biomaterial and Stem Cell for Skin Tissue Engineering in Cutaneous Wound Healing: A Concise Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.L.; Curtsinger, L.; Jurkiewicz, M.J.; Nahai, F.; Schultz, G.J.P. Stimulation of healing of chronic wounds by epidermal growth factor. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1991, 88, 189—194, discussion 195. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, S.; Smola, H. Paracrine regulation of keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, C.; Felici, A.; Visco, V.; Lucania, G.; Igarashi, M.; Picardo, M.; Frati, L.; Torrisi, M.R. Fibroblast Growth Factor 10 Induces Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Primary Cultured Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boxman, I.; Löwik, C.; Aarden, L.; Ponec, M. Modulation of IL-6 Production of IL-1 Activity by Keratinocyte-Fibroblast Interaction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 101, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, S.; Grose, R. Regulation of Wound Healing by Growth Factors and Cytokines. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 835–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, J.; Rosenbloom, J.; Jimenez, S.A. Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) causes a persistent increase in steady-state amounts of type I and type III collagen and fibronectin mRNAs in normal human dermal fibroblasts. Biochem. J. 1987, 247, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, R.; Xie, J.; Liu, X.; Qi, S. Correction: Conditioned Medium from Hypoxic Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhances Wound Healing in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Aminuddin, B.S.; Ruszymah, B.H. Effect of supplementation of dermal fibroblasts conditioned medium on expansion of keratinocytes through enhancing attachment. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 50, 332–339. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, M.N.M.; Wright, K.T.; Fuller, H.R.; MacNeil, S.; Johnson, W.E.B. Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium accelerates skin wound healing: An in vitro study of fibroblast and keratinocyte scratch assays. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Md Fadilah, N.I.; Mohd Abdul Kader Jailani, M.S.; Badrul Hisham, M.A.I.; Sunthar Raj, N.; Shamsuddin, S.A.; Ng, M.H.; Fauzi, M.B.; Maarof, M. Cell secretomes for wound healing and tissue regeneration: Next generation acellular based tissue engineered products. J. Tissue Eng. 2022, 13, 20417314221114273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Xia, Y.; Kim, W.-S.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, K.J.; Park, B.-S.; Sung, J.-H. Hypoxia-enhanced wound-healing function of adipose-derived stem cells: Increase in stem cell proliferation and up-regulation of VEGF and bFGF. Wound Repair Regen. 2009, 17, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakudo, N.; Morimoto, N.; Ogawa, T.; Taketani, S.; Kusumoto, K. Hypoxia Enhances Proliferation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells via HIF-1ɑ Activation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riis, S.; Stensballe, A.; Emmersen, J.; Pennisi, C.P.; Birkelund, S.; Zachar, V.; Fink, T. Mass spectrometry analysis of adipose-derived stem cells reveals a significant effect of hypoxia on pathways regulating extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burlacu, A.; Grigorescu, G.; Rosca, A.-M.; Preda, M.B.; Simionescu, M. Factors Secreted by Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Endothelial Progenitor Cells Have Complementary Effects on Angiogenesis In Vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 22, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maarof, M.; Lokanathan, Y.; Ruszymah, H.I.; Saim, A.; Chowdhury, S.R. Proteomic Analysis of Human Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium (DFCM). Protein J. 2018, 37, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, L.J.; Roy Chowdhury, S.; Bin Saim, A.; Bt Hj Idrus, R. Concentration-dependent effect of platelet-rich plasma on keratinocyte and fibroblast wound healing. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarof, M.; Law, J.X.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Khairoji, K.A.; Saim, A.B.; Idrus, R.B.H. Secretion of wound healing mediators by single and bi-layer skin substitutes. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spiekstra, S.W.; Breetveld, M.; Rustemeyer, T.; Scheper, R.J.; Gibbs, S. Wound-healing factors secreted by epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts in skin substitutes. Wound Repair Regen. 2007, 15, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.; McGrath, J.A.; Navsaria, H. The role of fibroblasts in tissue engineering and regeneration. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarof, M.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Saim, A.; Bt Hj Idrus, R.; Lokanathan, Y. Concentration Dependent Effect of Human Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium (DFCM) from Three Various Origins on Keratinocytes Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawitan, J.A. Prospect of Stem Cell Conditioned Medium in Regenerative Medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 965849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wojtowicz, A.M.; Oliveira, S.; Carlson, M.W.; Zawadzka, A.; Rousseau, C.F.; Baksh, D. The importance of both fibroblasts and keratinocytes in a bilayered living cellular construct used in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen 2014, 22, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, B.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Interplay Between Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts: A Systematic Review Providing a New Angle for Understanding Skin Fibrotic Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 648. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, T.J.; Martin, P. Wound repair at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3209–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, P. Wound healing–aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 1997, 276, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas-Szabowski, N.; Szabowski, A.; Stark, H.J.; Andrecht, S.; Kolbus, A.; Schorpp-Kistner, M.; Angel, P.; Fusenig, N.E. Organotypic cocultures with genetically modified mouse fibroblasts as a tool to dissect molecular mechanisms regulating keratinocyte growth and differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.-Q.; Kondo, T.; Ishida, Y.; Takayasu, T.; Mukaida, N. Essential involvement of IL-6 in the skin wound-healing process as evidenced by delayed wound healing in IL-6-deficient mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 73, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eroglu, E.; Agalar, F.; Altuntas, I.; Eroglu, F. Effects of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor on Wound Healing in a Mouse Model of Burn Trauma. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2004, 204, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrientos, S.; Stojadinovic, O.; Golinko, M.S.; Brem, H.; Tomic-Canic, M. PERSPECTIVE ARTICLE: Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008, 16, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkilde, M.M.; Schwartz, T.W. The chemokine system–A major regulator of angiogenesis in health and disease. APMIS 2004, 112, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, D.; Gherardi, E.; Fan, T.-P.; Edwards, D.; Warn, R. Diverse and potent activities of HGF/SF in skin wound repair. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Takeda, A.; Uchinuma, E.; Kuroyanagi, Y. Effect of EGF and bFGF on Fibroblast Proliferation and Angiogenic Cytokine Production from Cultured Dermal Substitutes. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, P.; Kodra, A.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Golinko, M.S.; Ehrlich, H.P.; Brem, H. The Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Wound Healing. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 153, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maarof, M.; Mohd Nadzir, M.; Sin Mun, L.; Fauzi, M.B.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Idrus, R.B.H.; Lokanathan, Y. Hybrid Collagen Hydrogel/Chondroitin-4-Sulphate Fortified with Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium for Skin Therapeutic Application. Polymers 2021, 13, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeben, A.; Landuyt, B.; Highley, M.S.; Wildiers, H.; Van Oosterom, A.T.; De Bruijn, E.A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Angiogenesis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaoka, T.; Kaburagi, Y.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Takehara, K.; Steeber, D.A.; Tedder, T.F.; Sato, S. Delayed Wound Healing in the Absence of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 or L-Selectin Expression. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.-M.; Xu, Z.-H. Serum deprivation enhances DNA synthesis of human hepatoma SMMC7721 cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 4, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghababazadeh, M.; Kerachian, M.A. Cell fasting: Cellular response and application of serum starvation. J. Fasting Health 2014, 2, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Jean, J.; Bernard, G.; Duque-Fernandez, A.; Auger, F.A.; Pouliot, R. Effects of Serum-Free Culture at the Air–Liquid Interface in a Human Tissue-Engineered Skin Substitute. Tissue Eng. Part A 2010, 17, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, B.; Kumar, A.H.S.; O’Sullivan, J.; Klein Buneker, C.; Leblond, A.-L.; Weiss, S.; Schmeckpeper, J.; Martin, K.; Caplice, N.M. Potent endothelial progenitor cell-conditioned media-related anti-apoptotic, cardiotrophic, and pro-angiogenic effects post-myocardial infarction are mediated by insulin-like growth factor-1. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-P.; Chio, C.-C.; Cheong, C.-U.; Chao, C.-M.; Cheng, B.-C.; Lin, M.-T. Hypoxic preconditioning enhances the therapeutic potential of the secretome from cultured human mesenchymal stem cells in experimental traumatic brain injury. Clin. Sci. 2012, 124, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.; Kaplan, M.H. A Brief History of IL-9. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bikle, D.D.; Ratnam, A.; Mauro, T.; Harris, J.; Pillai, S. Changes in calcium responsiveness and handling during keratinocyte differentiation. Potential role of the calcium receptor. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennings, H.; Michael, D.; Cheng, C.; Steinert, P.; Holbrook, K.; Yuspa, S.H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell 1980, 19, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, E.J.; Briggaman, R.A.; Herman, B. Calcium-induced assembly of adherens junctions in keratinocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnaswamy, V.R.; Korrapati, P.S. Role of Dermatopontin in re-epithelialization: Implications on keratinocyte migration and proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauffenburger, D.A.; Horwitz, A.F. Cell migration: A physically integrated molecular process. Cell 1996, 84, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilina, O.; Friedl, P. Mechanisms of collective cell migration at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3203–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huttenlocher, A.; Horwitz, A.R. Integrins in cell migration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, K.S.; Farboud, B.; Nuccitelli, R.; Isseroff, R.R. Migration of Human Keratinocytes in Electric Fields Requires Growth Factors and Extracellular Calcium. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 111, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, S.; Southgate, J. Calcium signalling in wound-responsive normal human urothelial cell monolayers. Cell Calcium 2008, 44, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, W. Wound Healing: Calcium Flashes Illuminate Early Events. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R14–R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geer, D.J.; Andreadis, S.T. A Novel Role of Fibrin in Epidermal Healing: Plasminogen-Mediated Migration and Selective Detachment of Differentiated Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrie, R.J.; Yamada, K.M. At the leading edge of three-dimensional cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5917–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metcalfe, A.D.; Ferguson, M.W.J. Tissue engineering of replacement skin: The crossroads of biomaterials, wound healing, embryonic development, stem cells and regeneration. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 413–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Toole, E.A. Extracellular matrix and keratinocyte migration. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 26, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koivisto, L.; Häkkinen, L.; Larjava, H. Re-epithelialization of wounds. Endod. Top. 2011, 24, 59–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peplow, P.V.; Chatterjee, M.P. A review of the influence of growth factors and cytokines in in vitro human keratinocyte migration. Cytokine 2013, 62, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Mediator | |
|---|---|
| Chemokines | |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| GRO-α | Growth-related oncogene-α |
| ENA-78 | Epithelial cell-derived neutrophil-activating factor |
| Eotaxin | Eotaxin |
| RANTES | Regulated on activation normal T-cell-expressed and secreted |
| Cytokines | |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-1α | Interleukin-1α |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| G-CSF | Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor |
| TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor-α |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion protein-1 |
| Growth factors | |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| VEGF-α | Vascular endothelial growth factor-α |
| FGF-β | Fibroblast growth factor-β |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β |
| PDGF-BB | Platelet-derived growth factor-BB |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| Conditions | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| DFCM-KM-1 | DFCM-KM acquired by incubating fibroblasts for 1 day |
| DFCM-KM-2 | DFCM-KM acquired by incubating fibroblasts for 2 days |
| DFCM-KM-3 | DFCM-KM acquired by incubating fibroblasts for 3 days |
| DFCM-FM-1 | DFCM-FM acquired by incubating fibroblasts for 1 day |
| DFCM-FM-2 | DFCM-FM acquired by incubating fibroblasts for 2 days |
| DFCM-FM-3 | DFCM-FM acquired by incubating fibroblasts for 3 days |
| Control | Epilife (keratinocyte-specific medium, KM) alone |
| Conditioned Medium | Calcium Concentration (mmol/L) |
|---|---|
| DFCM-KM-3 | 0.06 |
| DFCM-FM-3 | 1.08 |
| DFCM-FM-3 (dialysis) | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdul Ghani, N.‘I.; Razali, R.A.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Fauzi, M.B.; Bin Saim, A.; Ruszymah, B.H.I.; Maarof, M. Effect of Different Collection Times of Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium (DFCM) on In Vitro Re-Epithelialisation Process. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123203
Abdul Ghani N‘I, Razali RA, Chowdhury SR, Fauzi MB, Bin Saim A, Ruszymah BHI, Maarof M. Effect of Different Collection Times of Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium (DFCM) on In Vitro Re-Epithelialisation Process. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123203
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdul Ghani, Nurul ‘Izzah, Rabiatul Adawiyah Razali, Shiplu Roy Chowdhury, Mh Busra Fauzi, Aminuddin Bin Saim, Binti Haji Idrus Ruszymah, and Manira Maarof. 2022. "Effect of Different Collection Times of Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium (DFCM) on In Vitro Re-Epithelialisation Process" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123203
APA StyleAbdul Ghani, N. ‘I., Razali, R. A., Chowdhury, S. R., Fauzi, M. B., Bin Saim, A., Ruszymah, B. H. I., & Maarof, M. (2022). Effect of Different Collection Times of Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium (DFCM) on In Vitro Re-Epithelialisation Process. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123203