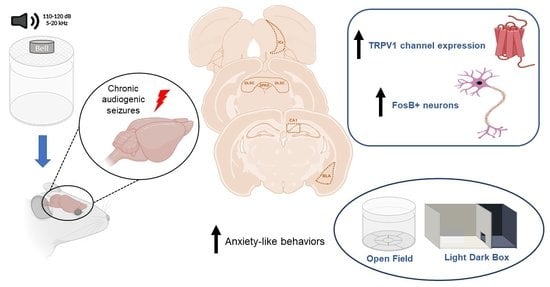
Increased TRPV1 Channels and FosB Protein Expression Are Associated with Chronic Epileptic Seizures and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in a Preclinical Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Chronic Audiogenic Seizure (AGS) Protocol: Audiogenic Kindling (AK)
2.3. Behavioral Tests for Anxiety
2.4. Tissue Processing and Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Image Processing and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Audiogenic Kindling (AK) Progression
3.2. Open-Field (OF) Test
3.3. Light Dark Box (LDB) Test
3.4. Immunohistochemistry for FosB+ Neurons
3.5. Immunofluorescence for TRPV1 Channels
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, J.H.; Elger, C.E.; Engel, J., Jr.; Forsgren, L.; French, J.A.; Glynn, M.; et al. ILAE Official Report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanner, A.M. Psychiatric comorbidities in new onset epilepsy: Should they be always investigated? Seizure 2017, 49, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beyenburg, S.; Mitchell, A.J.; Schmidt, D.; Elger, C.E.; Reuber, M. Anxiety in patients with epilepsy: Systematic review and suggestions for clinical management. Epilepsy Behav. 2005, 7, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrotti, A.; Carrozzino, D.; Milioni, M.; Minna, M.; Fulcheri, M. Epilepsy and its main psychiatric comorbidities in adults and children. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 343, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, A.M. Anxiety Disorders in Epilepsy: The Forgotten Psychiatric Comorbidity. Epilepsy Curr. 2011, 11, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salpekar, J.A.; Salpekar, J.A.; Basu, T.; Basu, T.; Thangaraj, S.; Thangaraj, S.; Maguire, J.; Maguire, J. The intersections of stress, anxiety and epilepsy. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2020, 152, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.; Sharpe, L.; Loomes, M.; Gandy, M. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Anxiety and Depression in Youth with Epilepsy. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2020, 45, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.; Sharpe, L.; Hunt, C.; Gandy, M. Anxiety and depressive disorders in people with epilepsy: A meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, O.S. Antiepileptic Drugs Beyond Epilepsy (Use of Anticonvulsants in the Treatment of Pain Syndromes). Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2014, 44, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesdorffer, D.C.; Ishihara, L.; Mynepalli, L.; Webb, D.J.; Weil, J.; Hauser, W.A. Epilepsy, suicidality, and psychiatric disorders: A bidirectional association. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mula, M. Bidirectional link between epilepsy and psychiatric disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.K.; Jones, J.E.; Seidenberg, M.; Hermann, B.P. The Relative Impact of Anxiety, Depression, and Clinical Seizure Features on Health-related Quality of Life in Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanner, A.M. Management of psychiatric and neurological comorbidities in epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarini-Lopes, W.; Silva, R.A.D.V.-D.; da Silva-Júnior, R.M.P.; Cunha, A.O.S.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Cannabinoids in Audiogenic Seizures: From Neuronal Networks to Future Perspectives for Epilepsy Treatment. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faingold, C.L.; Raisinghani, M.; N’Gouemo, P. Chapter 26-Neuronal Networks in Epilepsy: Comparative Audiogenic Seizure Networks. In Neuronal Networks in Brain Function, CNS Disorders, and Therapeutics; Faingold, C.L., Blumenfeld, H., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Gouemo, P.; Faingold, C. Periaqueductal gray neurons exhibit increased responsiveness associated with audiogenic seizures in the genetically epilepsy-prone rat. Neuroscience 1998, 84, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soper, C.; Wicker, E.; Kulick, C.V.; N’Gouemo, P.; Forcelli, P.A. Optogenetic activation of superior colliculus neurons suppresses seizures originating in diverse brain networks. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 87, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baas, J.M.; Milstein, J.; Donlevy, M.; Grillon, C. Brainstem Correlates of Defensive States in Humans. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, M.L.; Troncoso, A.C.; de Souza Silva, M.A.; Huston, J.P. The relevance of neuronal substrates of defense in the midbrain tectum to anxiety and stress: Empirical and conceptual considerations. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 463, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Piper, W.; Branigan, L.A.; Vazey, E.M.; Aston-Jones, G.; Lin, L.; LeDoux, J.E.; Sears, R.M. A brainstem-central amygdala circuit underlies defensive responses to learned threats. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 25, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tye, K.M.; Prakash, R.; Kim, S.-Y.; Fenno, L.E.; Grosenick, L.; Zarabi, H.; Thompson, K.R.; Gradinaru, V.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Deisseroth, K. Amygdala circuitry mediating reversible and bidirectional control of anxiety. Nature 2011, 471, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, D.; Moreira, F.; Terzian, A.; Fogaça, M.; Lisboa, S.; Wotjak, C.; Guimaraes, F. Modulation of defensive behavior by Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type-1 (TRPV1) Channels. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 46, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Angeles, M.; Morales-Lázaro, S.L.; Juárez-González, E.; Rosenbaum, T. TRPV1: Structure, Endogenous Agonists, and Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Liao, Q.; Chen, C.; Yang, X.; Xie, R.; Xu, J. The Role of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 in Common Diseases of the Digestive Tract and the Cardiovascular and Respiratory System. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.G. TRPV1 in the Central Nervous System: Synaptic Plasticity, Function, and Pharmacological Implications. In Capsaicin as a Therapeutic Molecule, Progress in Drug Research; Abdel-Salam, O.M.E., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ruwe, D.; Saffari, R.; Kravchenko, M.; Zhang, W. Effects of TRPV1 Activation by Capsaicin and Endogenous N-Arachidonoyl Taurine on Synaptic Transmission in the Prefrontal Cortex. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, A.; Boczán, J.; Kedei, N.; Lizanecz, E.; Bagi, Z.; Papp, Z.; Édes, I.; Csiba, L.; Blumberg, P.M. Expression and distribution of vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) in the adult rat brain. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 135, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschenderlein, C.; Gebhardt, C.; Halbach, O.V.B.U.; Kulisch, C.; Albrecht, D. Capsaicin-Induced Changes in LTP in the Lateral Amygdala Are Mediated by TRPV1. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakimizadeh, E.; Oryan, S.; Hajizadeh moghaddam, A.; Shamsizadeh, A.; Roohbakhsh, A. Endocannabinoid System and TRPV1 Receptors in the Dorsal Hippocampus of the Rats Modulate Anxiety-like Behaviors. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2012, 15, 795–802. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-H.; Ledri, M.; Tóth, B.; Marchionni, I.; Henstridge, C.M.; Dudok, B.; Kenesei, K.; Barna, L.; Szabo, S.I.; Renkecz, T.; et al. Multiple Forms of Endocannabinoid and Endovanilloid Signaling Regulate the Tonic Control of GABA Release. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 10039–10057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Stelt, M.; Trevisani, M.; Vellani, V.; De Petrocellis, L.; Moriello, A.S.; Campi, B.; McNaughton, P.; Geppetti, P.; Di Marzo, V. Anandamide acts as an intracellular messenger amplifying Ca2+ influx via TRPV1 channels. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3026–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Xie, Z.; Zuo, H. TRPV1: A potential target for antiepileptogenesis. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 73, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazıroglu, M. TRPV1 Channel: A Potential Drug Target for Treating Epilepsy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saffarzadeh, F.; Eslamizade, M.; Mousavi, S.; Abraki, S.; Hadjighassem, M.; Gorji, A. TRPV1 receptors augment basal synaptic transmission in CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons in epilepsy. Neuroscience 2016, 314, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.-J.; Guo, W.; Zheng, D.-H.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Li, S.; Liu, S.-Y.; Yin, Q.; Yang, H.; Shu, H.-F. Increased Expression of TRPV1 in the Cortex and Hippocampus from Patients with Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 49, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, M.D.; Smith, B.N. Cannabinoid-Mediated Inhibition of Recurrent Excitatory Circuitry in the Dentate Gyrus in a Mouse Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirazi, M.; Izadi, M.; Amin, M.; Rezvani, M.E.; Roohbakhsh, A.; Shamsizadeh, A. Involvement of central TRPV1 receptors in pentylenetetrazole and amygdala-induced kindling in male rats. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.C.; Guimarães, F.S. Evidence for a potential role for TRPV1 receptors in the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray in the attenuation of the anxiolytic effects of cannabinoids. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.J.; Stern, C.A.; Bertoglio, L.J. Attenuation of anxiety-related behaviour after the antagonism of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 channels in the rat ventral hippocampus. Behav. Pharmacol. 2008, 19, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Umeoka, E.; de Oliveira, J.A.C. The Wistar Audiogenic Rat (WAR) strain and its contributions to epileptology and related comorbidities: History and perspectives. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 71, 250–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Terra, V.; Doretto, M. Midbrain substrates of audiogenic seizures in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1993, 58, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marescaux, C.; Vergnes, M.; Kiesmann, M.; Depaulis, A.; Micheletti, G.; Warter, J. Kindling of audiogenic seizures in Wistar rats: An EEG study. Exp. Neurol. 1987, 97, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.F.D.; Galvis-Alonso, O.Y.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Audiogenic kindling in the Wistar rat: A potential model for recruitment of limbic structures. Epilepsy Res. 2000, 39, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Wakamatsu, H.; Oliveira, J.; Gomes, E.; Del Bel, E.; Mello, L. Neuroethological and morphological (Neo-Timm staining) correlates of limbic recruitment during the development of audiogenic kindling in seizure susceptible Wistar rats. Epilepsy Res. 1996, 26, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naritoku, D.K.; Mecozzi, L.B.; Aiello, M.T.; Faingold, C.L. Repetition of audiogenic seizures in genetically epilepsy-prone rats induces cortical epileptiform activity and additional seizure behaviors. Exp. Neurol. 1992, 115, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romcy-Pereira, R.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Hippocampal cell proliferation and epileptogenesis after audiogenic kindling are not accompanied by mossy fiber sprouting or fluoro-jade staining. Neuroscience 2003, 119, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.; Chavali, M.; Mishra, P.; Jobe, P.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. A comprehensive electrographic and behavioral analysis of generalized tonic-clonic seizures of GEPR-9s. Brain Res. 2005, 1033, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, L.V. Audiogenic kindling and secondary subcortico-cortical epileptogenesis: Behavioral correlates and electrographic features. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 71, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation: II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Oliveira, J.; Wakamatsu, H.; Bueno, S.; Guimarães, F. Reduced exploratory activity of audiogenic seizures suceptible Wistar rats. Physiol. Behav. 1998, 64, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.; de Oliveira, J.; Almeida, S.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Leão, R. Inhibition of long-term potentiation in the schaffer-CA1 pathway by repetitive high-intensity sound stimulation. Neuroscience 2015, 310, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitaí, D.L.G.; Martinelli, H.N.; Valente, V.; Pereira, M.G.A.G.; Oliveira, J.A.C.; Elias, C.F.; Bittencourt, J.C.; Leite, J.P.; Costa-Neto, C.M.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; et al. Increased expression of GluR2-flip in the hippocampus of the Wistar audiogenic rat strain after acute and kindled seizures. Hippocampus 2009, 20, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarini-Lopes, W.; Da Silva-Júnior, R.M.P.; Servilha-Menezes, G.; Silva, R.A.D.V.-D.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 (CB1R) Expression in Limbic Brain Structures After Acute and Chronic Seizures in a Genetic Model of Epilepsy. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 602258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, F.; Rodrigues, M.C.A.; de Oliveira, J.A.C.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. EEG wavelet analyses of the striatum–substantia nigra pars reticulata–superior colliculus circuitry: Audiogenic seizures and anticonvulsant drug administration in Wistar audiogenic rats (War strain). Epilepsy Res. 2006, 72, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Cardoso, G.K.; Lazarini-Lopes, W.; Hallak, J.E.; Crippa, J.A.; Zuardi, A.W.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Leite-Panissi, C.R. Cannabidiol effectively reverses mechanical and thermal allodynia, hyperalgesia, and anxious behaviors in a neuropathic pain model: Possible role of CB1 and TRPV1 receptors. Neuropharmacology 2021, 197, 108712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarini-Lopes, W.; Do Val-Da Silva, R.A.; da Silva-Júnior, R.M.P.; Silva-Cardoso, G.K.; Leite-Panissi, C.R.A.; Leite, J.P.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Chronic cannabidiol (CBD) administration induces anticonvulsant and antiepileptogenic effects in a genetic model of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 119, 107962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvis-Alonso, O.Y.; De Oliveira, J.C.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Limbic epileptogenicity, cell loss and axonal reorganization induced by audiogenic and amygdala kindling in wistar audiogenic rats (WAR strain). Neuroscience 2004, 125, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-B.; Mao, R.-R.; Zhang, J.-C.; Yang, Y.; Cao, J.; Xu, L. Antistress Effect of TRPV1 Channel on Synaptic Plasticity and Spatial Memory. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-X.; Yu, F.; Sanchez, R.M.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Min, J.-W.; Hu, J.-J.; Bsoul, N.B.; Han, S.; Yin, J.; Liu, W.-H.; et al. TRPV1 promotes repetitive febrile seizures by pro-inflammatory cytokines in immature brain. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, B.; Malkova, L.; N’Gouemo, P.; Forcelli, P. Genetically Epilepsy-Prone Rats Display Anxiety-Like Behaviors and Neuropsychiatric Comorbidities of Epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkisova, K.Y.; Fedotova, I.B.; Surina, N.M.; Nikolaev, G.M.; Perepelkina, O.V.; Kostina, Z.A.; Poletaeva, I.I. Genetic background contributes to the co-morbidity of anxiety and depression with audiogenic seizure propensity and responses to fluoxetine treatment. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 68, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Vaca, M.A.; Miranda, C.J.; N’Gouemo, P. Inhibition of transient potential receptor vanilloid type 1 suppresses seizure susceptibility in the genetically epilepsy-prone rat. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 24, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.C.; Salzberg, M.R.; Kumar, G.; Couper, A.; Morris, M.; O’Brien, T. Elevated anxiety and depressive-like behavior in a rat model of genetic generalized epilepsy suggesting common causation. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 209, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkisova, K.; van Luijtelaar, G. The WAG/Rij strain: A genetic animal model of absence epilepsy with comorbidity of depressiony. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 35, 854–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricobaraza, A.; Mora-Jimenez, L.; Puerta, E.; Sanchez-Carpintero, R.; Mingorance, A.; Artieda, J.; Nicolas, M.J.; Besne, G.; Bunuales, M.; Gonzalez-Aparicio, M.; et al. Epilepsy and neuropsychiatric comorbidities in mice carrying a recurrent Dravet syndrome SCN1A missense mutation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anesti, M.; Stavropoulou, N.; Atsopardi, K.; Lamari, F.N.; Panagopoulos, N.T.; Margarity, M. Effect of rutin on anxiety-like behavior and activity of acetylcholinesterase isoforms in specific brain regions of pentylenetetrazol-treated mice. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 102, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mao, S.; Yao, B.; Xiang, D.; Fang, C. Effects of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in epileptic rats. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2019, 18, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröticke, I.; Hoffmann, K.; Löscher, W. Behavioral alterations in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 207, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.W.; Lopes, S.C.; Santos, D.B.; Costa, A.P.; Gonçalves, F.M.; de Mello, N.; Prediger, R.D.; Farina, M.; Walz, R.; Leal, R.B. Time course evaluation of behavioral impairments in the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 55, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, S.; Ohkido, T.; Itakura, M.; Watanabe, S.; Yamamori, S.; Iida, Y.; Saito, M.; Miyaoka, H.; Takahashi, M. Dual mechanisms of rapid expression of anxiety-related behavior in pilocarpine-treated epileptic mice. Epilepsy Res. 2016, 123, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, G.P.; Medeiros, D.; Guarnieri, L.D.O.; Mourão, F.; Pinto, H.P.P.; Pereira, G.; Moraes, M.F.D. Wistar audiogenic rats display abnormal behavioral traits associated with artificial selection for seizure susceptibility. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 71, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powell, K.; Tang, H.; Ng, C.; Guillemain, I.; Dieuset, G.; Dezsi, G.; Çarçak, N.; Onat, F.; Martin, B.; O’Brien, T.; et al. Seizure expression, behavior, and brain morphology differences in colonies of Genetic Absence Epilepsy Rats from Strasbourg. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cairasco, N. A critical review on the participation of inferior colliculus in acoustic-motor and acoustic-limbic networks involved in the expression of acute and kindled audiogenic seizures. Hear. Res. 2002, 168, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.R.; Clerici, W.J. Sources of projections to subdivisions of the inferior colliculus in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1987, 262, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simler, S.; Vergnes, M.; Marescaux, C. Spatial and Temporal Relationships between C-Fos Expression and Kindling of Audiogenic Seizures in Wistar Rats. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 157, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder-Keller, A.M.; Pierson, M.G. Audiogenic seizures induce c-fos in a model of developmental epilepsy. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 135, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, K.; Coleman, J. Developmental and genetic audiogenic seizure models: Behavior and biological substrates. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheiro, E.A.; Leite, J.P.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Turski, W.A.; Ikonomidou, C.; Turski, L. Long-Term Effects of Pilocarpine in Rats: Structural Damage of the Brain Triggers Kindling and Spontaneous I Recurrent Seizures. Epilepsia 1991, 32, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.O.S.; Ceballos, C.; De Deus, J.L.; Pena, R.F.D.O.; De Oliveira, J.A.C.; Roque, A.C.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Leão, R.M. Intrinsic and synaptic properties of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons of the Wistar Audiogenic Rat (WAR) strain, a genetic model of epilepsy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, F.; Aguiar, J.F.; Oliveira, J.A.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Varanda, W.A. Electrophysiological properties of cultured hippocampal neurons from Wistar Audiogenic Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2005, 65, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Rodriguez, O.C.; Albanese, C.; Santos, V.R.; de Oliveira, J.A.C.; Donatti, A.L.F.; Fernandes, A.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; N’Gouemo, P.; Forcelli, P.A. Divergent brain changes in two audiogenic rat strains: A voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging comparison of the genetically epilepsy prone rat (GEPR-3) and the Wistar Audiogenic Rat (WAR). Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 111, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.R.; Bernardino, T.C.; da Silva, M.C.M.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Drumond, L.E.; Rosa, D.V.; Massensini, A.R.; Moraes, M.F.; Doretto, M.C.; Romano-Silva, M.A.; et al. Neurochemical abnormalities in the hippocampus of male rats displaying audiogenic seizures, a genetic model of epilepsy. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 761, 136123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupal, S.; Faingold, C. Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in amygdala blocks the effect of audiogenic seizure kindling in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Neuropharmacology 2010, 59, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raisinghani, M.; Faingold, C.L. Neurons in the amygdala play an important role in the neuronal network mediating a clonic form of audiogenic seizures both before and after audiogenic kindling. Brain Res. 2005, 1032, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doretto, M.C.; Cortes-De-Oliveira, J.A.; Rossetti, F.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Cortes-De-Oliveira, J.A. Role of the superior colliculus in the expression of acute and kindled audiogenic seizures in Wistar audiogenic rats. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almada, R.; Genewsky, A.J.; Heinz, D.E.; Kaplick, P.M.; Coimbra, N.C.; Wotjak, C.T. Stimulation of the Nigrotectal Pathway at the Level of the Superior Colliculus Reduces Threat Recognition and Causes a Shift From Avoidance to Approach Behavior. Front. Neural Circuits 2018, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, M.L.; Zanoveli, J.; Ruiz-Martinez, R.C.; Oliveira, L.C.; Landeira-Fernandez, J. Different patterns of freezing behavior organized in the periaqueductal gray of rats: Association with different types of anxiety. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 188, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, L.C.; Marques, T.D.A.; Schenberg, L.C. Micturition and defensive behaviors are controlled by distinct neural networks within the dorsal periaqueductal gray and deep gray layer of the superior colliculus of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 280, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, D.C.; Gomes, K.S.; Nunes-De-Souza, R.L. Anxiogenic-like effect induced by TRPV1 receptor activation within the dorsal periaqueductal gray matter in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 250, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzian, A.L.B.; De Aguiar, D.C.; Guimarães, F.S.; Moreira, F.A. Modulation of anxiety-like behaviour by Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type 1 (TRPV1) channels located in the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 19, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maione, S.; Cristino, L.; Migliozzi, A.L.; Georgiou, A.L.; Starowicz, K.; Salt, T.E.; Di Marzo, V. TRPV1 channels control synaptic plasticity in the developing superior colliculus. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 2521–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, C.S.; Currie, P.J. N-Arachidonoyl-serotonin in the basolateral amygdala increases anxiolytic behavior in the elevated plus maze. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 233, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, C.W.; Connor, M.; Bagley, E.; Christie, M. Actions of cannabinoids on membrane properties and synaptic transmission in rat periaqueductal gray neurons in vitro. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Starowicz, K.; Maione, S.; Cristino, L.; Palazzo, E.; Marabese, I.; Rossi, F.; De Novellis, V.; Di Marzo, V. Tonic Endovanilloid Facilitation of Glutamate Release in Brainstem Descending Antinociceptive Pathways. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 13739–13749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.; Li, J. TRPV1 Receptor Mediates Glutamatergic Synaptic Input to Dorsolateral Periaqueductal Gray (dl-PAG) Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casarotto, P.; Terzian, A.L.B.; De Aguiar, D.C.; Zangrossi, H.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Wotjak, C.T.; Moreira, F.A. Opposing Roles for Cannabinoid Receptor Type-1 (CB1) and Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type-1 Channel (TRPV1) on the Modulation of Panic-Like Responses in Rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 37, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeff, F.G.; Silveira, M.C.L.; Nogueira, R.L.; Audi, E.A.; Oliveira, R.M.W. Role of the amygdala and periaqueductal gray in anxiety and panic. Behav. Brain Res. 1993, 58, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotova, I.B.; Surina, N.M.; Nikolaev, G.M.; Revishchin, A.V.; Poletaeva, I.I. Rodent Brain Pathology, Audiogenic Epilepsy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazarini-Lopes, W.; Silva-Cardoso, G.K.; Leite-Panissi, C.R.A.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Increased TRPV1 Channels and FosB Protein Expression Are Associated with Chronic Epileptic Seizures and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in a Preclinical Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020416
Lazarini-Lopes W, Silva-Cardoso GK, Leite-Panissi CRA, Garcia-Cairasco N. Increased TRPV1 Channels and FosB Protein Expression Are Associated with Chronic Epileptic Seizures and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in a Preclinical Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020416
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazarini-Lopes, Willian, Gleice Kelli Silva-Cardoso, Christie Ramos Andrade Leite-Panissi, and Norberto Garcia-Cairasco. 2022. "Increased TRPV1 Channels and FosB Protein Expression Are Associated with Chronic Epileptic Seizures and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in a Preclinical Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy" Biomedicines 10, no. 2: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020416
APA StyleLazarini-Lopes, W., Silva-Cardoso, G. K., Leite-Panissi, C. R. A., & Garcia-Cairasco, N. (2022). Increased TRPV1 Channels and FosB Protein Expression Are Associated with Chronic Epileptic Seizures and Anxiogenic-like Behaviors in a Preclinical Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Biomedicines, 10(2), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020416