The lncRNAs/miR-30e/CHI3L1 Axis Is Dysregulated in Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Plasma, Serum and White Blood Cells (WBCs) Isolation
2.3. RNA Isolation from Plasma/WBC and DNase Treatment
2.4. ELISA
2.5. miRNA:mRNA and lncRNA:miRNA Target Prediction
2.6. Reverse Transcription and qPCR
2.7. TagMan Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
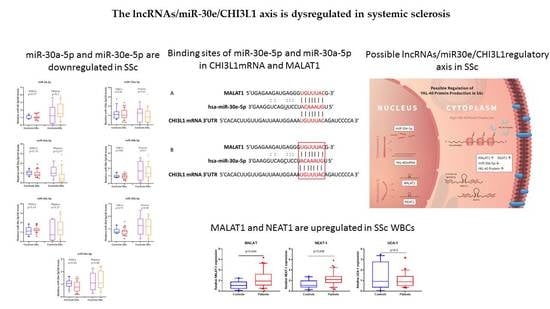
3.1. miR-30a-5p and miR-30e-5p Are Downregulated in SSc
3.2. MALAT1 and NEAT1 Are Upregulated in SSc WBCs
3.3. miR-30a-5p Plasma Levels as a Discriminatory Marker in SSc
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asano, Y. The Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis: An Understanding Based on a Common Pathologic Cascade across Multiple Organs and Additional Organ-Specific Pathologies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, M.; Barsotti, S.; Lepri, G.; Codullo, V.; Di Battista, M.; Guiducci, S.; Della Rossa, A. One year in review 2018: Systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 113), 3–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dolcino, M.; Tinazzi, E.; Puccetti, A.; Lunardi, C. In Systemic Sclerosis, a Unique Long Non Coding RNA Regulates Genes and Pathways Involved in the Three Main Features of the Disease (Vasculopathy, Fibrosis and Autoimmunity) and in Carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazzone, R.; Zwergel, C.; Artico, M.; Taurone, S.; Ralli, M.; Greco, A.; Mai, A. The emerging role of epigenetics in human autoimmune disorders. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Surace, A.E.A.; Hedrich, C.M. The Role of Epigenetics in Autoimmune/Inflammatory Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, L.L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulalio, A.; Huntzinger, E.; Izaurralde, E. Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell 2008, 132, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohel, M.H. Extracellular/Circulating MicroRNAs: Release Mechanisms, Functions and Challenges. Achiev. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, T.; Su, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; You, Q. Chitinase-3 like-protein-1 function and its role in diseases. Signal. Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, I.J.; Lee, C.K.; Han, S.B.; Yun, J.; Hong, J.T. Roles of chitinase 3-like 1 in the development of cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 203, 107394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakova, M.; Sarafian, V. YKL-40 in health and disease: A challenge for joint inflammation. Biomed. Rev. 2013, 24, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichev, V.; Mehterov, N.H.; Kazakova, M.H.; Karalilova, R.V.; Batalov, A.Z.; Sarafian, V.S. Serum protein levels of YKL-40 and plasma miR-214 expression in patients with systemic sclerosis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LeRoy, E.C.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Criteria for the classification of early systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 1573–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Betel, D.; Wilson, M.; Gabow, A.; Marks, D.S.; Sander, C. The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D149–D153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGeary, S.E.; Lin, K.S.; Shi, C.Y.; Pham, T.M.; Bisaria, N.; Kelley, G.M.; Bartel, D.P. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science 2019, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejnar, C.E.; Zdobnov, E.M. MiRmap: Comprehensive prediction of microRNA target repression strength. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 11673–11683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagkouni, D.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Tastsoglou, S.; Skoufos, G.; Karavangeli, A.; Pierros, V.; Zacharopoulou, E.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-LncBase v3: Indexing experimentally supported miRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D101–D110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Karagkouni, D.; Vlachos, I.S.; Tastsoglou, S.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. microCLIP super learning framework uncovers functional transcriptome-wide miRNA interactions. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, S.; Thomas, A.A.; Chen, S.; Aref-Eshghi, E.; Feng, B.; Gonder, J.; Sadikovic, B.; Chakrabarti, S. MALAT1: An Epigenetic Regulator of Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cao, L.; Zhou, R.; Yang, X.; Wu, M. The lncRNA Neat1 promotes activation of inflammasomes in macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, Y.; Song, Y.F.; Li, N. Increased Expression of lncRNA UCA1 and HULC Is Required for Pro-inflammatory Response During LPS Induced Sepsis in Endothelial Cells. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Xiao, R. Epigenetic mechanisms: An emerging role in pathogenesis and its therapeutic potential in systemic sclerosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 67, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, M.; Ramassone, A.; Pagotto, S.; Anastasiadou, E.; Veronese, A.; Visone, R. MicroRNAs in Autoimmunity and Hematological Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, H. Involvement of long noncoding RNAs in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2020, 3, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karalilova, R.; Kazakova, M.; Sapundzhieva, T.; Dichev, V.; Batalov, Z.; Sarafian, V.; Batalov, A. Serum YKL-40 and IL-6 levels correlate with ultrasound findings of articular and periarticular involvement in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Zhu, L.; Lv, H.; Pei, C. Quercetin promotes the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by upregulating lncRNA MALAT1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Liang, N.; Wang, M.; Fei, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Guo, C.; Cao, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is a novel inflammatory regulator in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77400–77406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Kim, D.; Han, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.; Jin, E.J. PBMC and exosome-derived Hotair is a critical regulator and potent marker for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, G.; Vasilev, V.; Kosturkova, M.B.; Stoyanov, G.S.; Radanova, M. Long Non-Coding RNAs as New Biomarkers in Lupus Nephritis: A Connection Between Present and Future. Cureus 2020, 12, e9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. LncRNA MALAT1: A Potential Fibrosis Biomarker and Therapeutic Target. Crystals 2021, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Banerjee, S.; Guo, S.; Xie, N.; Ge, J.; Jiang, D.; Zornig, M.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, G. Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates differential activation of macrophages and response to lung injury. JCI Insight. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruni, C.G.; Guignabert, C.; Manetti, M.; Cerinic, M.; Humbert, H. The multifaceted problem of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klec, C.; Prinz, F.; Pichler, M. Involvement of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in carcinogenesis. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santoro, M.; Nociti, V.; Lucchini, M.; De Fino, C.; Losavio, F.A.; Mirabella, M. Expression Profile of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Serum of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 59, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, L.; Qian, J.; Qu, B.; Xia, S.; La, T.; Wu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zeng, J.; Guo, Q.; et al. Identification of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 as a novel inflammatory regulator acting through MAPK pathway in human lupus. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 75, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.; Jia, L.; Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L. miR-30 Family: A Promising Regulator in Development and Disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9623412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dieter, C.; Assmann, T.S.; Costa, A.R.; Canani, L.H.; de Souza, B.M.; Bauer, A.C.; Crispim, D. MiR-30e-5p and MiR-15a-5p Expressions in Plasma and Urine of Type 1 Diabetic Patients With Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Sun, D.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liu, W.; Pu, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, A.; Liu, M.; Xiang, Z.; et al. MiR-30a Positively Regulates the Inflammatory Response of Microglia in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Neurosci. Bull. 2017, 33, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Jung, J.Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, H.A.; Suh, C.H. Circulating hsa-miR-30e-5p, hsa-miR-92a-3p, and hsa-miR-223-3p may be novel biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. HLA 2016, 88, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Mu, R.; Gao, Y.; Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, G. MicroRNA-30a promotes B cell hyperactivity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus by direct interaction with Lyn. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabre, L.; Maddison, P.; Sadalage, G.; Ambrose, P.A.; Punga, A.R. Circulating microRNA miR-21-5p, miR-150-5p and miR-30e-5p correlate with clinical status in late onset myasthenia gravis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 321, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yang, H.; Ma, J.; Luo, S.; Chen, S.; Gu, Q. MicroRNA-30e regulates neuroinflammation in MPTP model of Parkinson's disease by targeting Nlrp3. Hum. Cell 2018, 31, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Rawat, B.S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Niraj, K.; Chande, A.; Gandhi, P.; Khetan, D.; Aggarwal, A.; et al. MicroRNA-30e-5p has an Integrated Role in the Regulation of the Innate Immune Response during Virus Infection and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. iScience 2020, 23, 101322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Ma, J.; Yan, L.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Shui, S. Down-Regulation of Lncrna MALAT1 Attenuates Neuronal Cell Death Through Suppressing Beclin1-Dependent Autophagy by Regulating Mir-30a in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Cai, Z.; Ji, Z.; Zou, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liang, Y.; Lin, H.; Tan, M. The lncRNA MALAT1/miR-30/Spastin Axis Regulates Hippocampal Neurite Outgrowth. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020, 14, 555747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Liu, D.; Xiao, J. LncRNA MALAT1 sponges miR-30 to promote osteoblast differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by promotion of Runx2 expression. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 376, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, W.; Li, G.; Yao, L.; Zhang, R.; Xu, B. Overexpression of MALAT1 Relates to Lung Injury through Sponging miR-425 and Promoting Cell Apoptosis during ARDS. Can. Respir. J. 2019, 2019, 1871394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaleh, G.; Francois, A.; Philippe, L.; Gong, Y.Z.; Bahram, S.; Cetin, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Wachsmann, D.; Georgel, P.; et al. MiR-30a-3p negatively regulates BAFF synthesis in systemic sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Yao, H.; Lie, Z.; Chen, G.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA30a5p promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of human pulmonary artery endothelial cells under hypoxia by targeting YKL40. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Suto, A.; Ikeda, K.; Sanayama, Y.; Nakagomi, D.; Iwamoto, T.; Suzuki, K.; Kambe, N.; Matsue, H.; Matsumura, R.; et al. Alteration of circulating miRNAs in SSc: miR-30b regulates the expression of PDGF receptor beta. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koberle, V.; Pleli, T.; Schmithals, C.; Augusto Alonso, E.; Haupenthal, J.; Bonig, H.; Peveling-Oberhag, J.; Biondi, R.M.; Zeuzem, S.; Kronenberger, B.; et al. Differential stability of cell-free circulating microRNAs: Implications for their utilization as biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dichev, V.; Mehterov, N.; Kazakova, M.; Karalilova, R.; Batalov, A.; Sarafian, V. The lncRNAs/miR-30e/CHI3L1 Axis Is Dysregulated in Systemic Sclerosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020496
Dichev V, Mehterov N, Kazakova M, Karalilova R, Batalov A, Sarafian V. The lncRNAs/miR-30e/CHI3L1 Axis Is Dysregulated in Systemic Sclerosis. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020496
Chicago/Turabian StyleDichev, Valentin, Nikolay Mehterov, Maria Kazakova, Rositsa Karalilova, Anastas Batalov, and Victoria Sarafian. 2022. "The lncRNAs/miR-30e/CHI3L1 Axis Is Dysregulated in Systemic Sclerosis" Biomedicines 10, no. 2: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020496
APA StyleDichev, V., Mehterov, N., Kazakova, M., Karalilova, R., Batalov, A., & Sarafian, V. (2022). The lncRNAs/miR-30e/CHI3L1 Axis Is Dysregulated in Systemic Sclerosis. Biomedicines, 10(2), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020496