Expression of CD40 and CD192 in Classical Monocytes in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Assessed with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Abstract
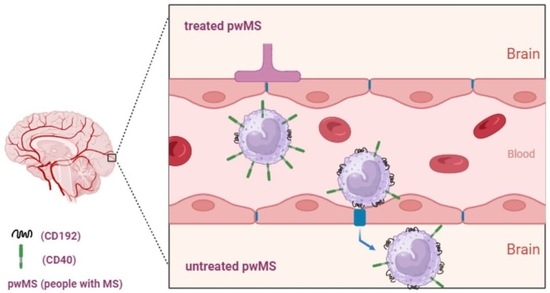
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. The Data Collection Procedures: PB Collection, Flow Cytometry, Clinical Assessment (Neurologic and Radiologic), and TMS Examination
2.3. Flow Cytometry
Flow Cytometry Data Analysis
2.4. Clinical Examination and Corticospinal Excitability Investigation with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and TMS Results of pwMS
3.2. Flow Cytometry Results of pwMS and HC Group
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodin, D.S.; Khankhanian, P.; Gourraud, P.A.; Vince, N. The nature of genetic and environmental susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, M.P.; Goldschmidt, C.H.; Rae-Grant, A.D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, H.; Brück, W.; Lucchinetti, C. Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis pathogenesis: Implications for diagnosis and therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitteri, M.; Romualdi, C.; Magliozzi, R.; Monaco, S.; Calabrese, M. Cognitive impairment predicts disability progression and cortical thinning in MS: An 8-year study. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattjes, M.P.; Ciccarelli, O.; Reich, D.S.; Banwell, B.; de Stefano, N.; Enzinger, C.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Frederiksen, J.; Gasperini, C.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis study group; Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centres; North American Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Cooperative MRI guidelines working group. MAGNIMS-CMSC-NAIMS consensus recommendations on the use of MRI in patients with multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, T.; Wang, P.; You, X.; Mann, M.; Sperling, B. Relationship between sustained disability progression and functional system scores in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: Analysis of placebo data from four randomized clinical trials. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 44, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, H.; Barkhof, F.; Antel, J.; Miller, D.H. The role of MRI as a surrogate outcome measure in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2002, 8, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli Boneschi, F.; Rovaris, M.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. The use of magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis: Lessons learned from clinical trials. Mult. Scler. 2004, 10, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, A.; Moassefi, M.; Barati, E.; Ali Sahraian, M.; Aghajani, F.; Fattahi, M.R. Correlation between the clinical disability and T1 hypointense lesions’ volume in cerebral magnetic resonance imaging of multiple sclerosis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 1268–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Or, A.; Pachner, A.; Menguy-Vacheron, F.; Kaplan, J.; Wiendl, H. Teriflunomide and its mechanism of action in multiple sclerosis. Drugs 2014, 74, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Langelaar, J.; Rijvers, L.; Smolders, J.; van Luijn, M.M. B and T Cells Driving Multiple Sclerosis: Identity, Mechanisms and Potential Triggers. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Or, A. The immunology of multiple sclerosis. Semin. Neurol. 2008, 28, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjelstrup, M.C.; Stilund, M.; Petersen, T.; Møller, H.J.; Petersen, E.L.; Christensen, T. Subsets of activated monocytes and markers of inflammation in incipient and progressed multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stampanoni Bassi, M.; Buttari, F.; Gilio, L.; De Paolis, N.; Fresegna, D.; Centonze, D.; Iezzi, E. Inflammation and Corticospinal Functioning in Multiple Sclerosis: A TMS Perspective. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardmeier, M.; Schindler, C.; Kuhle, J.; Fuhr, P. Validation of Quantitative Scores Derived from Motor Evoked Potentials in the Assessment of Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: A Longitudinal Study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardmeier, M.; Leocani, L.; Fuhr, P. A new role for evoked potentials in MS? Repurposing evoked potentials as biomarkers for clinical trials in MS. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalah, M.A.; Palm, U.; Ayache, S.S. Editorial: Corticospinal Excitability in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 11, 635612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoei, S.; Hvid, L.G.; Boye Jensen, H.; Zijdewind, I.; Stenager, E.; Dalgas, U. Neurophysiological impairments in multiple sclerosis—Central and peripheral motor pathways. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2020, 142, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neva, J.L.; Lakhani, B.; Brown, K.E.; Wadden, K.P.; Mang, C.S.; Ledwell, N.H.M.; Borich, M.R.; Vavasour, I.M.; Laule, C.; Traboulsee, A.L.; et al. Multiple measures of corticospinal excitability are associated with clinical features of multiple sclerosis. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 297, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogić Vidaković, M.; Ćurković Katić, A.; Jerković, A.; Šoda, J.; Košta, V.; Režić Mužinić, N.; Mastelić, A.; Benzon, B.; Poljičanin, A.; Buljan, I.; et al. Neurophysiological impairment in multiple sclerosis patient confirmed by transcranial magnetic stimulation of the central nervous system but not with electrical stimulation of peripheral nervous system. Artif. Organs 2022, 46, E182–E186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triggs, W.J.; Calvanio, R.; Macdonell, R.A.; Cros, D.; Chiappa, K.H. Physiological motor asymmetry in human handedness: Evidence from transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Res. 1994, 636, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, A.A.; Shtybel, W. Clinical experience with transcranial magnetic stimulation. Muscle Nerve 1990, 13, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonell, R.A.; Donnan, G.A. Magnetic cortical stimulation in acute spinal cord injury. Neurology 1995, 45, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claus, D. Central motor conduction: Method and normal results. Muscle Nerve 1990, 13, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantone, M.; Lanza, G.; Vinciguerra, L.; Puglisi, V.; Ricceri, R.; Fisicaro, F.; Vagli, C.; Bella, R.; Ferri, R.; Pennisi, G.; et al. Age, Height, and Sex on Motor Evoked Potentials: Translational Data from a Large Italian Cohort in a Clinical Environment. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Lah, A.D.; Mills, K.R. Optimising the detection of upper motor neuron function dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. J. Neurol. 2004, 251, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Hallett, M.; Rossini, P.M.; Pascual-Leone, A. Screening questionnaire before TMS: An update. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šoda, J.; Rogić Vidaković, M.; Lorincz, J.; Jerković, A.; Vujović, I. Novel Latency Estimation Algorithm of Motor Evoked Potential Signals. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193356–193374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonda, M.; Amoruso, A.; Grasso, R.; Di Francescantonio, V.; Avolio, C. Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Affect Monocyte-Derived Microvesicle Production. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Delohery, T.; Zhang, D.; Arendt, C.; Jones, C. The effects of teriflunomide on lymphocyte subpopulations in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 265, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivan, D.C.; Walthert, S.; Locatelli, G. Central Nervous System Barriers Impact Distribution and Expression of iNOS and Arginase-1 in Infiltrating Macrophages during Neuroinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 666961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarts, S.A.B.M.; Seijkens, T.T.P.; van Dorst, K.J.F.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Kooij, G.; Lutgens, E. The CD40-CD40L Dyad in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaitaitis, G.M.; Yussman, M.G.; Waid, D.M. Th40 cells (CD4+CD40+ Tcells) drive a more severe form of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis than conventional CD4 T cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aversa, T.G.; Weidenheim, K.M.; Berman, J.W. CD40-CD40L interactions induce chemokine expression by human microglia: Implications for human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis and multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Goër de Herve, M.G.; Delfraissy, J.F.; Taoufik, Y. Following direct CD40 activation, human primary microglial cells produce IL-12 p40 but not bioactive IL-12 p70. Cytokine 2001, 14, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girvin, A.M.; Dal Canto, M.C.; Miller, S.D. CD40/CD40L interaction is essential for the induction of EAE in the absence of CD28-mediated co-stimulation. J. Autoimmun. 2002, 18, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, B.; Steinman, L. Nonclassical monocytes: Are they the next therapeutic targets in multiple sclerosis? Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, R.; Francis, H.; Dervish, S.; Li, S.C.H.; Medbury, H.; Williams, H. Characterization of Human Monocyte Subsets by Whole Blood Flow Cytometry Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 140, e57941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ożańska, A.; Szymczak, D.; Rybka, J. Pattern of human monocyte subpopulations in health and disease. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92, e12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.L.; Tai, J.J.; Wong, W.C.; Han, H.; Sem, X.; Yeap, W.H.; Kourilsky, P.; Wong, S.C. Gene expression profiling reveals the defining features of the classical, intermediate, and nonclassical human monocyte subsets. Blood 2011, 118, e16–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimen, M.; Yates, C.M.; McGettrick, H.M.; Ward, L.S.; Harrison, M.J.; Apta, B.; Dib, L.H.; Imhof, B.A.; Harrison, P.; Nash, G.B.; et al. Monocyte Subsets Coregulate Inflammatory Responses by Integrated Signaling through TNF and IL-6 at the Endothelial Cell Interface. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 2834–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paré, A.; Mailhot, B.; Lévesque, S.A.; Juzwik, C.; Ignatius Arokia Doss, P.M.; Lécuyer, M.A.; Prat, A.; Rangachari, M.; Fournier, A.; Lacroix, S. IL-1β enables CNS access to CCR2hi monocytes and the generation of pathogenic cells through GM-CSF released by CNS endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1194–E1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitnis, T.; Khoury, S.J. Role of costimulatory pathways in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Cui, K.; Fu, X.; Man, J.; Lu, H.; Yu, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liao, L.; et al. Neuroprotective Action of Teriflunomide in a Mouse Model of Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Neuroscience 2020, 428, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherwinski, H.M.; Cohn, R.G.; Cheung, P.; Webster, D.J.; Xu, Y.Z.; Caulfield, J.P.; Young, J.M.; Nakano, G.; Ransom, J.T. The immunosuppressant leflunomide inhibits lymphocyte proliferation by inhibiting pyrimidine biosynthesis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 275, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahad, D.J.; Ransohoff, R.M. The role of MCP-1 (CCL2) and CCR2 in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Semin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fife, B.T.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Kuziel, W.A.; Karpus, W.J. CC chemokine receptor 2 is critical for induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.R.; Wang, J.; Kivisakk, P.; Rollins, B.J.; Ransohoff, R.M. Absence of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in mice leads to decreased local macrophage recruitment and antigen-specific T helper cell type 1 immune response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahad, D.; Callahan, M.K.; Williams, K.A.; Ubogu, E.E.; Kivisäkk, P.; Tucky, B.; Kidd, G.; Kingsbury, G.A.; Chang, A.; Fox, R.J.; et al. Modulating CCR2 and CCL2 at the blood-brain barrier: Relevance for multiple sclerosis pathogenesis. Brain 2006, 129, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuluundorj, D.; Harding, S.A.; Abernethy, D.; La Flamme, A.C. Expansion and preferential activation of the CD14+CD16+ monocyte subset during multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.W.; Kawano, Y.; Shi, N.; Masaki, K.; Isobe, N.; Yonekawa, T.; Matsushita, T.; Tateishi, T.; Yamasaki, R.; Murai, H.; et al. Alterations in chemokine receptor expressions on peripheral blood monocytes in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Clin. Exp. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 4, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.; Sainz de la Maza, S.; Villarrubia, N.; Álvarez-Lafuente, R.; Costa-Frossard, L.; Arroyo, R.; Monreal, E.; Tejeda-Velarde, A.; Rodríguez-Martín, E.; Roldán, E.; et al. Teriflunomide induces a tolerogenic bias in blood immune cells of MS patients. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogić Vidaković, M.; Ćurković Katić, A.; Pavelin, S.; Bralić, A.; Mikac, U.; Šoda, J.; Jerković, A.; Mastelić, A.; Dolić, K.; Markotić, A.; et al. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Measures, Pyramidal Score on Expanded Disability Status Scale and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Corticospinal Tract in Multiple Sclerosis. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, N.J.; Wadden, K.P.; Chaves, A.R.; Ploughman, M. Transcranisal Magnetic Stimulation as a Potential Biomarker in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review with Recommendations for Future Research. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, 6430596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherwinski, H.M.; McCarley, D.; Schatzman, R.; Devens, B.; Ransom, J.T. The immunosuppressant leflunomide inhibits lymphocyte progression through cell cycle by a novel mechanism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 272, 460–468. [Google Scholar]






| Parameter Mean ± SD | pwMS (n = 23) | HC (n = 10) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 41.65 ± 8.89 | 37 ± 13.90 | 0.25 |
| Height (cm) | 175 ± 10.27 | 179 ± 10.34 | 0.30 |
| Weight (kg) | 77.96 ± 19.08 | 74.2 ± 11.72 | 0.57 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.14 ± 3.78 | 23 ± 1.84 | 0.10 |
| Female/Male (n) | 14/9 | 6/4 |
| % of CD40+ of Total Monocytes | % of CD40+ CD14+CD16++ | MFI of CD40 in CD14+CD16++ | % CD40+ CD14++CD16− | MFI of CD40 in CD14++CD16− | MFI of CD192 in CD14++CD16− | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All pwMS (N = 23) | M | 71.85 | 91.55 | 3976.09 | 74.00 | 1904.00 | 68,443.67 |
| SD | 10.62 | 9.42 | 1776.75 | 11.58 | 719.04 | 11,411.64 | |
| HC (N = 10) | M | 59.50 | 87.59 | 3336.56 | 53.26 | 1180.03 | 82,983.35 |
| SD | 13.72 | 9.51 | 700.70 | 16.83 | 701.25 | 8768.82 | |
| pwMS MEP Altered (N = 15) | M | 71.59 | 92.03 | 3957.61 | 72.96 | 1954.22 | 67,545.47 |
| SD | 11.19 | 7.25 | 1757.29 | 13.39 | 859.98 | 9819.92 | |
| pwMS MEP Normal (N = 8) | M | 72.35 | 90.71 | 4008.45 | 75.96 | 1809.71 | 70,127.81 |
| SD | 10.18 | 12.94 | 1932.27 | 7.49 | 360.83 | 14,541.25 | |
| All pwMS vs. HC | t | −2.8 | 1.09 | −1.90 | −4.11 | −2.46 | 3.58 |
| df | 31 | 31 | 29 | 32 | 30 | 32 | |
| p | 0.008 ** | 0.280 | 0.283 | 0.0002 *** | 0.019 * | 0.001 ** | |
| pwMS MEP Altered vs. HC | t | −2.41 | −1.32 | −1.105 | −3.25 | −2.18 | 4.01 |
| df | 16 | 16 | 23 | 24 | 22 | 20 | |
| p | 0.023 * | 0.203 | 0.303 | 0.003 ** | 0.04 * | 0.0005 *** | |
| pwMS MEP Normal vs. HC | t | −2.2 | −0.59 | −1.25 | −3.52 | −2.25 | 2.32 |
| df | 16 | 12 | 17 | 17 | 15 | 11 | |
| p | 0.042 * | 0.563 | 0.32 | 0.002 ** | 0.040 * | 0.033 * | |
| pwMS MEP Altered vs. pwMS MEP Normal | t | 0.16 | −0.31 | 0.063 | 0.58 | −0.45 | 0.50 |
| df | 22 | 21 | 21 | 22 | 22 | 22 | |
| p | 0.876 | 0.759 | 0.95 | 0.565 | 0.656 | 0.616 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Režić Mužinić, N.; Markotić, A.; Pavelin, S.; Polančec, D.; Buljubašić Šoda, M.; Bralić, A.; Šoda, J.; Mastelić, A.; Mikac, U.; Jerković, A.; et al. Expression of CD40 and CD192 in Classical Monocytes in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Assessed with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102870
Režić Mužinić N, Markotić A, Pavelin S, Polančec D, Buljubašić Šoda M, Bralić A, Šoda J, Mastelić A, Mikac U, Jerković A, et al. Expression of CD40 and CD192 in Classical Monocytes in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Assessed with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102870
Chicago/Turabian StyleRežić Mužinić, Nikolina, Anita Markotić, Sanda Pavelin, Denis Polančec, Maja Buljubašić Šoda, Antonia Bralić, Joško Šoda, Angela Mastelić, Una Mikac, Ana Jerković, and et al. 2023. "Expression of CD40 and CD192 in Classical Monocytes in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Assessed with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102870
APA StyleRežić Mužinić, N., Markotić, A., Pavelin, S., Polančec, D., Buljubašić Šoda, M., Bralić, A., Šoda, J., Mastelić, A., Mikac, U., Jerković, A., & Rogić Vidaković, M. (2023). Expression of CD40 and CD192 in Classical Monocytes in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Assessed with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102870