Utility of Three-Dimensional Cultures of Primary Human Hepatocytes (Spheroids) as Pharmacokinetic Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Recent 3D-Culture Studies of PHHs for Pharmacokinetic Models
3. Recent 3D-Culture Studies Using PHHs for Hepatotoxicity Detection Models
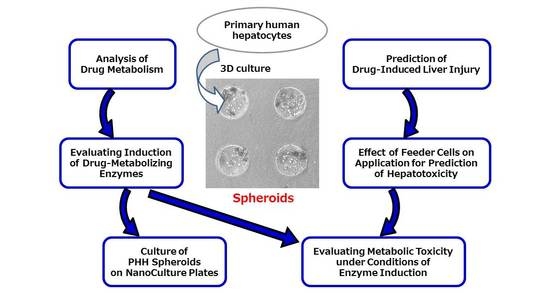
4. Application of PHH Spheroids for Analysis of Drug Metabolism
5. Application of PHH Spheroids for Prediction of Drug-Induced Liver Injury
6. Effect of Feeder Cells on Application of PHH Spheroids for Prediction of Hepatotoxicity
7. Application of PHH Spheroids for Evaluating Induction of Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes
8. Application of PHH Spheroids for Evaluating Metabolic Toxicity under Conditions of Enzyme Induction
9. Culture of PHH Spheroids on NanoCulture Plates
10. Other Hepatocyte Culture Systems as Potential Alternatives to PHHs
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waring, M.J.; Arrowsmith, J.; Leach, A.R.; Leeson, P.D.; Mandrell, S.; Owen, R.M.; Pairaudeau, G.; Pennie, W.D.; Pickett, S.D.; Wang, J.; et al. An analysis of the attrition of drug candidates from four major pharmaceutical companies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, O.J.; McKee, M.; Luyten, J. Estimated Research and Development Investment Needed to Bring a New Medicine to Market, 2009–2018. JAMA 2020, 323, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMasi, J.A.; Grabowski, H.G.; Hansen, R.W. Innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: New estimates of R&D costs. J. Health. Econ. 2016, 47, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almazroo, O.A.; Miah, M.K.; Venkataramanan, R. Drug Metabolism in the Liver. Clin. Liver Dis. 2017, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, T.; Strigun, A.; Verlohner, A.; Huener, H.A.; Peter, E.; Herold, M.; Bordag, N.; Mellert, W.; Walk, T.; Spitzer, M.; et al. Prediction of liver toxicity and mode of action using metabolomics in vitro in HepG2 cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuykx, M.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Laukens, K.; Vanhaecke, T.; Covaci, A. In vitro assessment of hepatotoxicity by metabolomics: A review. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 3007–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, V.; Hariparsad, N.; Li, F.; Desai, P.; Thummel, K.E.; Unadkat, J.D. Cytochrome P450 Enzymes and Transporters Induced by Anti-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Protease Inhibitors in Human Hepatocytes: Implications for Predicting Clinical Drug Interactions. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanebratt, K.P.; Andersson, T.B. HepaRG Cells as an in Vitro Model for Evaluation of Cytochrome P450 Induction in Humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizoi, K.; Fukai, Y.; Matsumoto, E.; Koyama, S.; Ishida, S.; Kojima, H.; Ogihara, T. Usefulness and limitations of mRNA measurement in HepaRG cells for evaluation of cytochrome P450 induction. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 7, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosokawa, M. Structure and Catalytic Properties of Carboxylesterase Isozymes Involved in Metabolic Activation of Prodrugs. Molecules 2008, 13, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukami, T.; Yokoi, T. The Emerging Role of Human Esterases. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 27, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoi, K.; Takahashi, M.; Haba, M.; Hosokawa, M. Synthesis and evaluation of atorvastatin esters as prodrugs metabolically activated by human carboxylesterases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoi, K.; Takahashi, M.; Sakai, S.; Ogihara, T.; Haba, M.; Hosokawa, M. Structure-activity relationship of atorvastatin derivatives for metabolic activation by hydrolases. Xenobiotica 2020, 50, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasser, K.E.; Allen, P.D.; Woolhandler, S.J.; Himmelstein, D.U.; Wolfe, S.M.; Bor, D.H. Timing of New Black Box Warnings and Withdrawals for Prescription Medications. JAMA 2002, 287, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downing, N.S.; Shah, N.D.; Aminawung, J.A.; Pease, A.M.; Zeitoun, J.D.; Krumholz, H.M.; Ross, J.S. Postmarket Safety Events Among Novel Therapeutics Approved by the US Food and Drug Administration Between 2001 and 2010. JAMA 2017, 317, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorrink, S.U.; Zhou, Y.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Lauschke, V.M. Prediction of Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity Using Long-Term Stable Primary Hepatic 3D Spheroid Cultures in Chemically Defined Conditions. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 163, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Saxena, R. Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2015, 139, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martignoni, M.; Groothuis, G.M.; de Kanter, R. Species differences between mouse, rat, dog, monkey and human CYP-mediated drug metabolism, inhibition and induction. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2006, 2, 875–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, H.; Betton, G.; Robinson, D.; Thomas, K.; Monro, A.; Kolaja, G.; Lilly, P.; Sanders, J.; Sipes, G.; Bracken, W.; et al. Concordance of the Toxicity of Pharmaceuticals in Humans and in Animals. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2000, 32, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.J.; Henstock, P.V.; Dunn, M.C.; Smith, A.R.; Chabot, J.R.; de Graaf, D. Cellular Imaging Predictions of Clinical Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 105, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, M.; Steger-Hartmann, T. A big data approach to the concordance of the toxicity of pharmaceuticals in animals and humans. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 96, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyffin, J.A.; Sharma, P.; Leedale, J.; Colley, H.E.; Murdoch, C.; Mistry, P.; Webb, S.D. Impact of cell types and culture methods on the functionality of in vitro liver systems-A review of cell systems for hepatotoxicity assessment. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 48, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Duan, Z. Innovation for hepatotoxicity in vitro research models: A review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerets, H.H.; Tilmant, K.; Gerin, B.; Chanteux, H.; Depelchin, B.O.; Dhalluin, S.; Atienzar, F.A. Characterization of primary human hepatocytes, HepG2 cells, and HepaRG cells at the mRNA level and CYP activity in response to inducers and their predictivity for the detection of human hepatotoxins. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2012, 28, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sison-Young, R.L.; Lauschke, V.M.; Johann, E.; Alexandre, E.; Antherieu, S.; Aerts, H.; Gerets, H.H.J.; Labbe, G.; Hoët, D.; Dorau, M.; et al. A multicenter assessment of single-cell models aligned to standard measures of cell health for prediction of acute hepatotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1385–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hewitt, N.J.; Lechón, M.J.; Houston, J.B.; Hallifax, D.; Brown, H.S.; Maurel, P.; Kenna, J.G.; Gustavsson, L.; Lohmann, C.; Skonberg, C.; et al. Primary Hepatocytes: Current Understanding of the Regulation of Metabolic Enzymes and Transporter Proteins, and Pharmaceutical Practice for the Use of Hepatocytes in Metabolism, Enzyme Induction, Transporter, Clearance, and Hepatotoxicity Studies. Drug Metab. Rev. 2007, 39, 159–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillouzo, A.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Evolving concepts in liver tissue modeling and implications for in vitro toxicology. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 1279–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapałczyńska, M.; Kolenda, T.; Przybyła, W.; Zajączkowska, M.; Teresiak, A.; Filas, V.; Ibbs, M.; Bliźniak, R.; Łuczewski, Ł.; Lamperska, K. 2D and 3D cell cultures-a comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q. Three-dimensional culture of hepatocytes for prediction of drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2010, 6, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauschke, V.M.; Hendriks, D.F.; Bell, C.C.; Andersson, T.B.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Novel 3D Culture Systems for Studies of Human Liver Function and Assessments of the Hepatotoxicity of Drugs and Drug Candidates. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 1936–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennema, E.; Rivron, N.; Rouwkema, J.; van Blitterswijk, C.; de Boer, J. Spheroid culture as a tool for creating 3D complex tissues. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunness, P.; Mueller, D.; Shevchenko, V.; Heinzle, E.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Noor, F. 3D Organotypic Cultures of Human HepaRG Cells: A Tool for in Vitro Toxicity Studies. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 133, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaiahgari, S.C.; Waidyanatha, S.; Dixon, D.; DeVito, M.J.; Paules, R.S.; Ferguson, S.S. Three-Dimensional (3D) HepaRG Spheroid Model With Physiologically Relevant Xenobiotic Metabolism Competence and Hepatocyte Functionality for Liver Toxicity Screening. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 159, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandon, M.; Huet, S.; Dubreil, E.; Fessard, V.; Le Hégarat, L. Three-dimensional HepaRG spheroids as a liver model to study human genotoxicity in vitro with the single cell gel electrophoresis assay. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Koshidaka, Y.; Noguchi, H.; Oishi, K.; Saito, H.; Yukawa, H.; Kaji, N.; Ikeya, T.; Suzuki, S.; Iwata, H.; et al. Observation of Positively Charged Magnetic Nanoparticles Inside HepG2 Spheroids Using Electron Microscopy. Cell Med. 2013, 5, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramaiahgari, S.C.; den Braver, M.W.; Herpers, B.; Terpstra, V.; Commandeur, J.N.; van de Water, B.; Price, L.S. A 3D in vitro model of differentiated HepG2 cell spheroids with improved liver-like properties for repeated dose high-throughput toxicity studies. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aritomi, K.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Tomishima, Y.; Shimizu, D.; Abe, N.; Shuto, T.; Irikura, M.; Kai, H.; Irie, T. Evaluation of Three-Dimensional Cultured HepG2 Cells in a Nano Culture Plate System: An In Vitro Human Model of Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 124, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.R.; Kang, H.M.; Ryu, J.W.; Kim, D.S.; Noh, K.H.; Kim, E.S.; Leem, H.J.; Chung, K.S.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, N.S.; et al. Cell Spheroids with Enhanced Aggressiveness to Mimic Human Liver Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerink, W.M.; Schoonen, W.G. Cytochrome P450 enzyme levels in HepG2 cells and cryopreserved primary human hepatocytes and their induction in HepG2 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2007, 21, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthérieu, S.; Chesné, C.; Li, R.; Camus, S.; Lahoz, A.; Picazo, L.; Turpeinen, M.; Tolonen, A.; Uusitalo, J.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; et al. Stable Expression, Activity, and Inducibility of Cytochromes P450 in Differentiated HepaRG Cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorrink, S.U.; Ullah, S.; Schmidt, S.; Nandania, J.; Velagapudi, V.; Beck, O.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Lauschke, V.M. Endogenous and xenobiotic metabolic stability of primary human hepatocytes in long-term 3D spheroid cultures revealed by a combination of targeted and untargeted metabolomics. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2696–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, L.; Hong, X.; Sakban, R.B.; Qu, Y.; Singh, N.H.; McMillian, M.; Dallas, S.; Silva, J.; Sensenhauser, C.; Zhao, S.; et al. Cytochrome P450 induction response in tethered spheroids as a three-dimensional human hepatocyte in vitro model. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Sakban, R.B.; Qu, Y.; Hong, X.; Zhang, W.; Nugraha, B.; Tong, W.H.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Zheng, B.; Chau, I.Y.; et al. Tethered spheroids as an in vitro hepatocyte model for drug safety screening. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.K.; Tseng, H.; Souza, G.R. Assembly of Hepatocyte Spheroids Using Magnetic 3D Cell Culture for CYP450 Inhibition/Induction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, C.C.; Dankers, A.C.A.; Lauschke, V.M.; Sison-Young, R.; Jenkins, R.; Rowe, C.; Goldring, C.E.; Park, K.; Regan, S.L.; Walker, T.; et al. Comparison of Hepatic 2D Sandwich Cultures and 3D Spheroids for Long-term Toxicity Applications: A Multicenter Study. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bell, C.C.; Hendriks, D.F.; Moro, S.M.; Ellis, E.; Walsh, J.; Renblom, A.; Fredriksson Puigvert, L.; Dankers, A.C.; Jacobs, F.; Snoeys, J.; et al. Characterization of primary human hepatocyte spheroids as a model system for drug-induced liver injury, liver function and disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, C.C.; Chouhan, B.; Andersson, L.C.; Andersson, H.; Dear, J.W.; Williams, D.P.; Söderberg, M. Functionality of primary hepatic non-parenchymal cells in a 3D spheroid model and contribution to acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, C.C.; Lauschke, V.M.; Vorrink, S.U.; Palmgren, H.; Duffin, R.; Andersson, T.B.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Transcriptional, functional, and mechanistic comparisons of stem cell-derived hepatocytes, heparg cells, and three-dimensional human hepatocyte spheroids as predictive in vitro systems for drug-induced liver injury. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2017, 45, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parmentier, C.; Hendriks, D.F.G.; Heyd, B.; Bachellier, P.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Richert, L. Inter-individual differences in the susceptibility of primary human hepatocytes towards drug-induced cholestasis are compound and time dependent. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 295, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Cao, L.; Parikh, S.; Zuo, R. Three-Dimensional Spheroids with Primary Human Liver Cells and Differential Roles of Kupffer Cells in Drug-Induced Liver Injury. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, D.F.G.; Puigvert, L.F.; Messner, S.; Mortiz, W.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Hepatic 3D spheroid models for the detection and study of compounds with cholestatic liability. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkura, T.; Ohta, K.; Nagao, T.; Kusumoto, K.; Koeda, A.; Ueda, T.; Jomura, T.; Ikeya, T.; Ozeki, E.; Wada, K.; et al. Evaluation of Human Hepatocytes Cultured by Three-dimensional Spheroid Systems for Drug Metabolism. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2014, 29, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogihara, T.; Iwai, H.; Inoue, Y.; Katagi, J.; Matsumoto, N.; Motoi-Ohtsuji, M.; Kakiki, M.; Kaneda, S.; Nagao, T.; Kusumoto, K.; et al. Utility of human hepatocyte spheroids for evaluation of hepatotoxicity. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 2, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogihara, T.; Arakawa, H.; Jomura, T.; Idota, Y.; Koyama, S.; Yano, K.; Kojima, H. Utility of human hepatocyte spheroids without feeder cells for evaluation of hepatotoxicity. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 42, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, H.; Kamioka, H.; Jomura, T.; Koyama, S.; Idota, Y.; Yano, K.; Kojima, H.; Ogihara, T. Preliminary Evaluation of Three-Dimensional Primary Human Hepatocyte Culture System for Assay of Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme-Inducing Potential. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizoi, K.; Hosono, M.; Kojima, H.; Ogihara, T. Establishment of a primary human hepatocyte spheroid system for evaluating metabolic toxicity using dacarbazine under conditions of CYP1A2 induction. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 35, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Arakawa, H.; Itoh, M.; Masuda, N.; Yano, K.; Kojima, H.; Ogihara, T. Evaluation of the metabolic capability of primary human hepatocytes in three-dimensional cultures on microstructural plates. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2018, 39, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozyra, M.; Johansson, I.; Nordling, Å.; Ullah, S.; Lauschke, V.M.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Human hepatic 3D spheroids as a model for steatosis and insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chua, A.C.Y.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Ong, J.J.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; Yip, A.; Singh, N.H.; Qu, Y.; Dembele, L.; McMillian, M.; Ubalee, R.; et al. Hepatic spheroids used as an in vitro model to study malaria relapse. Biomaterials 2019, 216, 119221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prill, S.; Caddeo, A.; Baselli, G.; Jamialahmadi, O.; Dongiovanni, P.; Rametta, R.; Kanebratt, K.P.; Pujia, A.; Pingitore, P.; Mancina, R.M.; et al. The TM6SF2 E167K genetic variant induces lipid biosynthesis and reduces apolipoprotein B secretion in human hepatic 3D spheroids. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusumoto, K.; Nagao, T.; Ogihara, T. A New High-Throughput Analysis for Drug Metabolism Profiling Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Drug Res. (Stuttg) 2013, 63, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, M.; Ulvestad, M.; Ellis, E.; Weidolf, L.; Andersson, T.B. In Vitro Evaluation of Major In Vivo Drug Metabolic Pathways Using Primary Human Hepatocytes and HepaRG Cells in Suspension and a Dynamic Three-Dimensional Bioreactor System. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Syed, M.; Skonberg, C.; Hansen, S.H. Mitochondrial toxicity of diclofenac and its metabolites via inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation (ATP synthesis) in rat liver mitochondria: Possible role in drug induced liver injury (DILI). Toxicol. In Vitro 2016, 31, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawase, A.; Hashimoto, R.; Shibata, M.; Shimada, H.; Iwaki, M. Involvement of Reactive Metabolites of Diclofenac in Cytotoxicity in Sandwich-Cultured Rat Hepatocytes. Int. J. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, S.; Shirai, Y.; Akai, S.; Nakajima, A.; Tsuneyama, K.; Yokoi, T. Toxicological role of an acyl glucuronide metabolite in diclofenac-induced acute liver injury in mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvie, D.; Obach, R.S.; Kang, P.; Prakash, C.; Loi, C.M.; Hurst, S.; Nedderman, A.; Goulet, L.; Smith, E.; Bu, H.Z.; et al. Assessment of Three Human in Vitro Systems in the Generation of Major Human Excretory and Circulating Metabolites. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwo, P.Y.; Cohen, S.M.; Lim, J.K. ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowsher, R.R.; Compton, J.A.; Kirkwood, J.A.; Place, G.D.; Jones, C.D.; Mabry, T.E.; Hyslop, D.L.; Hatcher, B.L.; DeSante, K.A. Sensitive and Specific Radioimmunoassay for Fialuridine: Initial Assessment of Pharmacokinetics after Single Oral Doses to Healthy Volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 2134–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Draft Test Guideline, Determination of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzyme Activity Induction Using Differentiated Human Hepatic Cells. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/testing/Draft_TG_CYP_induction_for_2nd_WNT_review.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2019).
- Moscovitz, J.E.; Kalgutkar, A.S.; Nulick, K.; Johnson, N.; Lin, Z.; Goosen, T.C.; Weng, Y. Establishing Transcriptional Signatures to Differentiate PXR-, CAR-, and AhR-Mediated Regulation of Drug Metabolism and Transport Genes in Cryopreserved Human Hepatocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 365, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Katoh, M.; Okumura, H.; Nakagawa, N.; Negishi, T.; Hashizume, T.; Nakajima, M.; Yokoi, T. Metabolic Activation of Benzodiazepines by CYP3A4. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Nieber, K.; Bader, A. Hepatotoxicity and hepatic metabolism of available drugs: Current problems and possible solutions in preclinical stages. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2010, 6, 895–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Lechón, M.J.; Tolosa, L.; Donato, M.T. Metabolic activation and drug-induced liver injury: In vitro approaches for the safety risk assessment of new drugs. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 752–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Terasaki, N.; Kawataki, T.; Takekawa, K.; Iwase, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Sanoh, S.; Ohta, S. Comparison of Drug Metabolism and Its Related Hepatotoxic Effects in HepaRG, Cryopreserved Human Hepatocytes, and HepG2 Cell Cultures. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourahmad, J.; Amirmostofian, M.; Kobarfard, F.; Shahraki, J. Biological reactive intermediates that mediate dacarbazine cytotoxicity. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshita, H.; Tateno, C. Propagation of Human Hepatocytes in uPA/SCID Mice: Producing Chimeric Mice with Humanized Liver. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1506, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, T.; Hirata, Y.; Naito, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Kikkawa, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Yamasaki, C.; Tateno, C.; Ochiya, T.; Kohara, M. Transmission of HBV DNA Mediated by Ceramide-Triggered Extracellular Vesicles. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 3, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishitsuji, H.; Harada, K.; Ujino, S.; Zhang, J.; Kohara, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Mizokami, M.; Shimotohno, K. Investigating the hepatitis B virus life cycle using engineered reporter hepatitis B viruses. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, R.; Kakiki, M.; Oshikata, A.; Takezawa, T.; Yamasaki, C.; Ishida, Y.; Tateno, C.; Kuroda, Y.; Ishida, S.; Kusano, K. A long-term culture system based on a collagen vitrigel membrane chamber that supports liver-specific functions of hepatocytes isolated from mice with humanized livers. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanamori, T.; Iwata, Y.T.; Segawa, H.; Yamamuro, T.; Kuwayama, K.; Tsujikawa, K.; Inoue, H. Metabolism of Butyrylfentanyl in Fresh Human Hepatocytes: Chemical Synthesis of Authentic Metabolite Standards for Definitive Identification. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsuda, T.; Kawamata, M.; Hagiwara, K.; Takahashi, R.U.; Yamamoto, Y.; Camargo, F.D.; Ochiya, T. Conversion of Terminally Committed Hepatocytes to Culturable Bipotent Progenitor Cells with Regenerative Capacity. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takayama, K.; Mizuguchi, H. Generation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells for drug toxicity screening. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 32, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Takayama, K.; Sakurai, F.; Mizuguchi, H. Billion-scale production of hepatocyte-like cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirenko, O.; Hancock, M.K.; Hesley, J.; Hong, D.; Cohen, A.; Gentry, J.; Carlson, C.B.; Mann, D.A. Phenotypic Characterization of Toxic Compound Effects on Liver Spheroids Derived from iPSC Using Confocal Imaging and Three-Dimensional Image Analysis. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2016, 14, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Long-Term Stability | High-Throughput Capability | Versatility | Required Cell Numbers | Complexity | Scaffold | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D monolayer | − | ●●● | − | ●● | ● | Collagen |
| Sandwich culture | ●● (2 weeks) | ● | − | ●● | ●● | Collagen or Matrigel |
| 3D spheroids | ●●● (>5 weeks) | ●● | ●●● | ● | ●● | Mostly scaffold-free |
| Hollow-fiber bioreactors | ●●● (>5 weeks) | − | ● | ●●● | ●●● | Synthetic polymers |
| Micro-patterned co-cultures | ●●● (>5 weeks) | ●● | ●● | ●● | ●● | Collagen-coated islands |
| Perfused multiwell plates | ●● (2 weeks) | ●● | ●● | ●● | ●● | Extracellular matrix -coated polymer wafer |
| Microfluidic liver biochips | ●● (1–4 weeks) | ●● | ●● | ●● | ●●● | Mainly scaffold-free |
| Microfluidic multiorgan devices | ●●● (>4 weeks) | − | ●● | ●● | ●●● | Mainly scaffold-free |
| Category | Purpose of Experiment | Plate/Membrane | Culture Period | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmacokinetic models | |||||
| 1 | Metabolic activity of CYPs | Examination of metabolic stability using spheroid and 2D monolayer cultures | Ultra-low attachment plate (CORNING) | Culture for 21 days after seeding | [41] |
| 2 | Induction of CYPs | Comparison of spheroid and collagen sandwich cultures | Arginine, glycine, and aspartic acid/galactose-conjugated membrane | Culture for 5 days after seeding Induction for 2 days from 3 days after seeding | [42] |
| 3 | Induction of CYPs | Evaluation of the usefulness of spheroid cultures (compared with sandwich cultures) | Arginine, glycine, and aspartic acid/galactose-conjugated membrane | Culture for 5 days after seeding Induction for 2 days from 3 days after seeding | [43] |
| 4 | Induction/inhibition of CYPs | Assembly and handling of magnetic 3D cell culture | Cell-repellent plate (CELLSTAR, Greiner Bio-One) | Drug exposure for 3 days from 3 days after seeding | [44] |
| Hepatotoxicity detection models | |||||
| 5 | Hepatotoxicity | Evaluation of hepatotoxicity of 123 drugs using spheroid cultures | Ultra-low attachment plate (CORNING) | Drug exposure for 14 days from 7 days after seeding | [16] |
| 3 | Hepatotoxicity Metabolic activity of CYPs Proteomics | Comparison of spheroid and 2D sandwich cultures at six laboratories | Ultra-low attachment plate (CORNING) | Drug exposure for 14 days from 7–10 days after seeding | [45] |
| 4 | Hepatotoxicity Metabolic activity of CYPs Proteomics | Evaluation of the usefulness of spheroid cultures | Ultra-low attachment plate (CORNING) | Culture for 35 days after seeding | [46] |
| 5 | Hepatotoxicity | Applied a 3D co-culture system of acetaminophen-induced toxicity | Ultra-low attachment plate (CORNING) | Drug exposure for 14 days from 8 days after seeding | [47] |
| 6 | Hepatotoxicity Transcriptomics | Compared three emerging cell systems at transcriptional and functional levels in a multicenter study | Ultra-low attachment plate (CORNING) | Drug exposure for 14 days from 7 days after seeding | [48] |
| 7 | Hepatotoxicity | Assess the inter-donor variability in the response of PHHs towards cholestatic compounds | Ultra-low attachment plate (CORNING) | Drug exposure for 14 days from 8 days after seeding | [49] |
| 8 | Hepatotoxicity | To evaluate the role of Kupffer cells in DILI using co-culture spheroids | Spheroid microplate (CORNING) | Culture for 15 days after seeding | [50] |
| 9 | Hepatotoxicity | Evaluation of two 3D spheroid models for the detection of compounds with cholestatic liability | Ultra-low attachment plate (CORNING) | Drug exposure for 14 days from 5–6 or 5 or 8 days after seeding | [51] |
| Our studies | |||||
| 10 | Drug metabolism | Metabolic experiments using spheroid cultures | Micro-patterned plate (Cell-able, Toyo Gosei) | Culture for 21 days after seeding Drug exposure for 2 or 7 days | [52] |
| 11 | Hepatotoxicity | Utility of spheroid for evaluation of hepatotoxicity | Micro-patterned plate (Cell-able, Toyo Gosei) | Drug exposure for 21 days from 2 days after seeding | [53] |
| 12 | Hepatotoxicity | Evaluation of hepatotoxicity using spheroid cultures (with or without feeder cells) | Micro-patterned plate (Cell-able, Toyo Gosei) | Drug exposure for 14 days from 2 days after seeding | [54] |
| 13 | Induction of CYPs | Metabolic induction experiment using spheroid cultures (compared with 2D cultures) | Micro-patterned plate (Cell-able, Toyo Gosei) | Induction for 14 days from 7 days after seeding | [55] |
| 14 | Induction of CYP1A2 Drug metabolism Metabolic toxicity | Evaluation of metabolic toxicity using spheroid cultures | Micro-patterned plate (Cell-able, Toyo Gosei) | Culture for 16 days after seeding Drug exposure for 7 days | [56] |
| 15 | Induction of CYPs Drug metabolism | Evaluation of the usefulness of spheroid cultures using NanoCulture Plate | Micro-patterned plate (NanoCulture plate, MBL) | Culture for 21 days after seeding | [57] |
| Compound. | Albumin Secretion IC50 (μM) | Reported IC50 (μM) of Conventional Assays | Clinical Cmax (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 21 | |||
| Acetaminophen | 1295.2 | 809.3 | 772.4 | 28,200 (HH) 29,755 (HepG2) | 139 |
| Benzbromarone | 48.8 | <20 | 22.2 | >40 (HepG2) | 4.3 |
| Chlorpromazine | 10.3 | 11.7 | 6.1 | 1.73–18.3 (HH) 42.9–62.6 (HepG2) | 1.41 |
| Cyclosporine A | 3.9 | 2.7 | 2.0 | 24.4–56.8 (HH) >100 (HepG2) | 0.78 |
| Diclofenac | 98.4 | 103.3 | 104.6 | 331 (HH) 763 (HepG2) | 8.1 |
| Fialuridine | 18.1 | 3.4 | 0.9 | >400 (HepG2) | 0.64 |
| Flutamide | 21.0 | 60.4 | 46.5 | 6.29–100 (HH) >100 (HepG2) | 4.16 |
| Imipramine | 37.0 | 4.1 | 16.8 | 37 (HepG2) | 0.14 |
| Isoniazid | >1000 | 254.1 | 336.2 | >10,000 (HepG2) | 76.6 |
| Ticlopidine | 55.8 | 23.9 | 28.1 | Not reported | 7.1 |
| Troglitazone | 42.0 | 46.6 | 21.5 | >50 (HH) 30 (HepG2) | 6.4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizoi, K.; Arakawa, H.; Yano, K.; Koyama, S.; Kojima, H.; Ogihara, T. Utility of Three-Dimensional Cultures of Primary Human Hepatocytes (Spheroids) as Pharmacokinetic Models. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100374
Mizoi K, Arakawa H, Yano K, Koyama S, Kojima H, Ogihara T. Utility of Three-Dimensional Cultures of Primary Human Hepatocytes (Spheroids) as Pharmacokinetic Models. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(10):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100374
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizoi, Kenta, Hiroshi Arakawa, Kentaro Yano, Satoshi Koyama, Hajime Kojima, and Takuo Ogihara. 2020. "Utility of Three-Dimensional Cultures of Primary Human Hepatocytes (Spheroids) as Pharmacokinetic Models" Biomedicines 8, no. 10: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100374
APA StyleMizoi, K., Arakawa, H., Yano, K., Koyama, S., Kojima, H., & Ogihara, T. (2020). Utility of Three-Dimensional Cultures of Primary Human Hepatocytes (Spheroids) as Pharmacokinetic Models. Biomedicines, 8(10), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100374