Co-Players in Chronic Pain: Neuroinflammation and the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway
Abstract
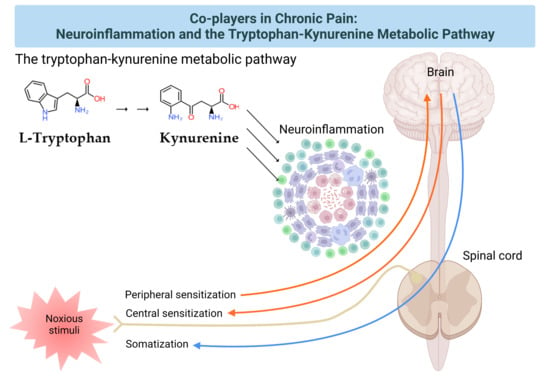
:1. Introduction
2. The Pain Pathway, Mechanisms, Neuroinflammation, and Tryptophan Metabolism
3. Transduction and Nociceptive Pain
4. Conduction, Transmission, and Neuropathic Pain
5. Modulation and Nociplastic Pain
6. Cortical Perception and Psychogenic Pain
7. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | anthranilic acid |
| Aß fiber | A-beta fiber |
| Aδ fiber | A-delta fiber |
| AMPA | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid |
| AS | ankle sprain |
| AT | Achilles tendinopathy |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BDNF | brain-derived growth factor |
| CCL | (C-C motif) chemokine ligand |
| CGRP | calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CPS | chronic pain syndrome |
| CRP | c-reactive protein |
| CX3CL1 | fractalkine |
| Cx43 | connexin-43 |
| CXCL | (C-X-C motif) chemokine ligand |
| DRG | dorsal root ganglion |
| DSM-5 | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition |
| FM | fibromyalgia |
| fMRI | functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| GAD | generalized anxiety disorder |
| 3-HAA | 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid |
| 3-HK | 3-hydroxykynurenine |
| HAOO | 3-hydroxyanthranilate dioxygenase |
| ICD-11 | 11th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems |
| IDO | indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| IFN | interferon |
| IL | interleukin |
| KAT | kynurenine aminotransferase |
| KMO | kynurenine 3-monooxygenase |
| KYN | kynurenine |
| KYNA | kynurenic acid |
| KYNU | kynureninase |
| LBP | low back pain |
| MAP | mitogen-activated |
| MDD | major depressive disorder |
| MMP | matrix metalloprotease |
| NAD+ | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| OA | osteoarthritis |
| QA | quinolinic acid |
| SGCs | satellite glial cells |
| SSD | somatic symptom disorder |
| T-cells | T lymphocytes |
| TDO | tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase |
| TMD | temporomandibular joint disorder |
| TNF-γ | tumor necrosis factor gamma |
| TRP | tryptophan |
| TRPA1 | transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A member 1 |
| TRPV1 | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 |
| TRPV4 | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4 |
| XA | xanthurenic acid |
References
- IASP. Definitions of Chronic Pain Syndromes. Available online: https://www.iasp-pain.org/Advocacy/icd.aspx?ItemNumber=5354#chronicpain (accessed on 18 December 2020).
- Di Lernia, D.; Lacerenza, M.; Ainley, V.; Riva, G. Altered Interoceptive Perception and the Effects of Interoceptive Analgesia in Musculoskeletal, Primary, and Neuropathic Chronic Pain Conditions. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medicina. Special Issue “Chronic Pain Management”. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/medicina/special_issues/chronic_pain_management (accessed on 18 December 2020).
- Mäntyselkä, P.; Kumpusalo, E.; Ahonen, R.; Kumpusalo, A.; Kauhanen, J.; Viinamäki, H.; Halonen, P.; Takala, J. Pain as a reason to visit the doctor: A study in Finnish primary health care. Pain 2001, 89, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.; Nicolson, K.P.; Smith, B.H. Chronic pain: A review of its epidemiology and associated factors in population-based studies. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, e273–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.I. The Landscape of Chronic Pain: Broader Perspectives. Medicina 2019, 55, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Pain 2019, 160, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 (accessed on 27 December 2020).
- Ciaramella, A.; Silvestri, S.; Pozzolini, V.; Federici, M.; Carli, G. A retrospective observational study comparing somatosensory amplification in fibromyalgia, chronic pain, psychiatric disorders and healthy subjects. Scand. J. Pain 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivat, C.; Ballantyne, J. The dark side of opioids in pain management: Basic science explains clinical observation. Pain Rep. 2016, 1, e570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Kim, P.Y. Allodynia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537129/ (accessed on 27 December 2020).
- Yasaei, R.; Peterson, E.; Saadabadi, A. Chronic Pain Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470523/ (accessed on 18 December 2020).
- Chimenti, R.L.; Frey-Law, L.A.; Sluka, K.A. A Mechanism-Based Approach to Physical Therapist Management of Pain. Phys. Ther. 2018, 98, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, F.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. The Role of the Kynurenine Signaling Pathway in Different Chronic Pain Conditions and Potential Use of Therapeutic Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lovelace, M.D.; Varney, B.; Sundaram, G.; Franco, N.F.; Ng, M.L.; Pai, S.; Lim, C.K.; Guillemin, G.J.; Brew, B.J. Current Evidence for a Role of the Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunolog. 2016, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ong, W.Y.; Stohler, C.S.; Herr, D.R. Role of the Prefrontal Cortex in Pain Processing. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1137–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trouvin, A.P.; Perrot, S. New concepts of pain. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 33, 101415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Verri, W.A.; Chiu, I.M. Nociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves dos Santos, G.; Delay, L.; Yaksh, T.L.; Corr, M. Neuraxial Cytokines in Pain States. Front Immunol. 2020, 10, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, R.R.; Chamessian, A.; Zhang, Y.Q. Pain regulation by non-neuronal cells and inflammation. Science 2016, 354, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuda, M.; Huh, Y.; Ji, R.-R. Roles of Inflammation, Neurogenic inflammation, and Neuroinflammation in Pain. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, B.; Frydecka, D.; Stanczykiewicz, B.; Samochowiec, J. Editorial: Peripheral Markers of Immune Response in Major Psychiatric Disorders: Where Are We Now and Where Do We Want to Be? Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlaet, A.A.J.; Maasakkers, C.M.; Hermans, N.; Savelkoul, H.F.J. Rationale for Dietary Antioxidant Treatment of ADHD. Nutrients 2018, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fung, T.C.; Olson, C.A.; Hsiao, E.Y. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encyclopedia. The Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/8633 (accessed on 13 April 2021).
- Tanaka, M.; Tóth, F.; Polyák, H.; Szabó, Á.; Mándi, Y.; Vécsei, L. Immune Influencers in Action: Metabolites and Enzymes of the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Bohár, Z.; Vécsei, L. Are Kynurenines Accomplices or Principal Villains in Dementia? Maintenance of Kynurenine Metabolism. Molecules 2020, 25, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dezsi, L.; Tuka, B.; Martos, D.; Vecsei, L. Alzheimer’s disease, astrocytes and kynurenines. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2015, 12, 462–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Török, N.; Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Searching for Peripheral Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Diseases: The Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erabi, H.; Okada, G.; Shibasaki, C.; Setoyama, D.; Kang, D.; Takamura, M.; Yoshino, A.; Fuchikami, M.; Kurata, A.; Kato, T.A.; et al. Kynurenic acid is a potential overlapped biomarker between diagnosis and treatment response for depression from metabolome analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Mora, P.; Pérez-De la Cruz, V.; Estrada-Cortés, B.; Toussaint-González, P.; Martínez-Cortéz, J.A.; Rodríguez-Barragán, M.; Quinzaños-Fresnedo, J.; Rangel-Caballero, F.; Gamboa-Coria, G.; Sánchez-Vázquez, I.; et al. Serum Kynurenines Correlate with Depressive Symptoms and Disability in Poststroke Patients: A Cross-sectional Study. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2020, 34, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Vécsei, L. Novel Pharmaceutical Approaches in Dementia. In NeuroPsychopharmacotherapy; Riederer, P., Laux, G., Nagatsu, T., Le, W., Riederer, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56015-1_444-1 (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Ulivieri, M.; Wierońska, J.M.; Lionetto, L.; Martinello, K.; Cieslik, P.; Chocyk, A.; Curto, M.; Di Menna, L.; Iacovelli, L.; Traficante, A.; et al. The Trace Kynurenine, Cinnabarinic Acid, Displays Potent Antipsychotic-Like Activity in Mice and Its Levels Are Reduced in the Prefrontal Cortex of Individuals Affected by Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2020, 46, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Monitoring the Redox Status in Multiple Sclerosis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Exploring the Etiological Links behind Neurodegenerative Diseases: Inflammatory Cytokines and Bioactive Kynurenines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Török, N.; Maszlag-Török, R.; Molnár, K.; Szolnoki, Z.; Somogyvári, F.; Boda, K.; Tanaka, M.; Klivényi, P.; Vécsei, L. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 Influenced the Age Onset of Parkinson’s Disease. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Monitoring the Kynurenine System in Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Illnesses: Concentrations, Ratios, or What Else? Adv. Clin. Exp. Med 2021, 30. in press. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, S.A.; Herr, M.J. Physiology, Nociception. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551562/ (accessed on 27 December 2020).
- Tompkins, D.A.; Hobelmann, J.G.; Compton, P. Providing chronic pain management in the “Fifth Vital Sign” Era: Historical and treatment perspectives on a modern-day medical dilemma. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 173 (Suppl. 1), S11–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Robbins, S.R.; McDougall, J.J. Osteoarthritis: The genesis of pain. Rheumatology 2018, 57 (Suppl. 4), iv43–iv50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talagas, M.; Lebonvallet, N.; Berthod, F.; Misery, L. Lifting the veil on the keratinocyte contribution to cutaneous nociception. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, C.; Cevikbas, F.; Pasolli, H.A.; Chen, Y.; Kong, W.; Kempkes, C.; Parekh, P.; Lee, S.H.; Kontchou, N.A.; Yeh, I.; et al. UVB radiation generates sunburn pain and affects skin by activating epidermal TRPV4 ion channels and triggering endothelin-1 signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3225–E3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, S.-M.; Chung, G.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, C.-K. The Role of Maresins in Inflammatory Pain: Function of Macrophages in Wound Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvo, M.; Dawes, J.M.; Bennett, D.L. The role of the immune system in the generation of neuropathic pain. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, A.E.; Patapoutian, A. Nociceptors: The sensors of the pain pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3760–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yam, M.F.; Loh, Y.C.; Tan, C.S.; Khadijah Adam, S.; Abdul Manan, N.; Basir, R. General Pathways of Pain Sensation and the Major Neurotransmitters Involved in Pain Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raney, E.B.; Thankam, F.G.; Dilisio, M.F.; Agrawal, D.K. Pain and the pathogenesis of biceps tendinopathy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2668–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Barohn, R.J.; Amato, A.A. Pattern-recognition approach to neuropathy and neuronopathy. Neurol. Clin. 2013, 31, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourne, S.; Machado, A.G.; Nagel, S.J. Basic anatomy and physiology of pain pathways. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakin, E.; Abrams, R.; Simpson, D.M. Diabetic Neuropathy. Semin. Neurol. 2019, 39, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macone, A.; Otis, J.A.D. Neuropathic Pain. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 644–653. [Google Scholar]
- Meacham, K.; Shepherd, A.; Mohapatra, D.P.; Haroutounian, S. Neuropathic Pain: Central vs. Peripheral Mechanisms. Curr. Pain. Headache Rep. 2017, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, J.C.; Sandroni, P. Central Neuropathic Pain Syndromes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.Y.; Oh, J. Neuropathic cancer pain: Prevalence, pathophysiology, and management. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radat, F.; Margot-Duclot, A.; Attal, N. Psychiatric co-morbidities in patients with chronic peripheral neuropathic pain: A multicentre cohort study. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, H. Analgesic Mechanisms of Antidepressants for Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooten, W.M. Chronic Pain and Mental Health Disorders: Shared Neural Mechanisms, Epidemiology, and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 955–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.A.; Yu, J.; Cheung, C.W. Immune Actions on the Peripheral Nervous System in Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Tsuda, M. Nociceptive signaling mediated by P2X3, P2X4 and P2X7 receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 114309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempe, R.G.; Hartz, A.; Bauer, B. Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood-brain barrier: Versatile breakers and makers. J. Cereb. Blood. Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1481–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, Y.; Ji, R.R.; Chen, G. Neuroinflammation, Bone Marrow Stem Cells, and Chronic Pain. Front. Immunol. 2017, 21, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, R.R.; Nackley, A.; Huh, Y.; Terrando, N.; Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and Central Sensitization in Chronic and Widespread Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qadri, Y.J.; Serhan, C.N.; Ji, R.R. Microglia in Pain: Detrimental and Protective Roles in Pathogenesis and Resolution of Pain. Neuron 2018, 100, 1292–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, R.R.; Donnelly, C.R.; Nedergaard, M. Astrocytes in chronic pain and itch. Nat. Rev. Neurosc. 2019, 20, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.C.; Cao, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.J.; He, L.N.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, W.W.; Wu, X.B.; Berta, T.; Ji, R.R.; et al. CXCL13 drives spinal astrocyte activation and neuropathic pain via CXCR5. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.K.; Hayashi, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Shibata, K.; Shigetomi, E.; Shinozaki, Y.; Inada, H.; Roh, S.E.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, G.; et al. Cortical astrocytes rewire somatosensory cortical circuits for peripheral neuropathic pain. J. Clinvinvest. 2016, 126, 1983–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malta, I.; Moraes, T.; Rodrigues, G.; Franco, P.; Galdino, G. The role of oligodendrocytes in chronic pain: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Mika, J. Targeting the Microglial Signaling Pathways: New Insights in the Modulation of Neuropathic Pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2908–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starobova, H.; Vetter, I. Pathophysiology of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineda-Farias, J.B.; Perez-Severiano, F.; Gonzalez-Esquivel, D.F.; Barragan-Iglesias, P.; Bravo-Hernandez, M.; Cervantes-Duran, C.; Aguilera, P.; Ríos, C.; Granados-Soto, V. The L-kynurenine-probenecid combination reduces neuropathic pain in rats. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laumet, G.; Zhou, W.; Dantzer, R.; Edralin, J.D.; Huo, X.; Budac, D.P.; O’Connor, J.C.; Lee, A.W.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. Upregulation of neuronal kynurenine 3-monooxygenase mediates depression-like behavior in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojewska, E.; Ciapała, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Makuch, W.; Mika, J. Pharmacological Inhibition of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-2 and Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase, Enzymes of the Kynurenine Pathway, Significantly Diminishes Neuropathic Pain in a Rat Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojewska, E.; Piotrowska, A.; Makuch, W.; Przewlocka, B.; Mika, J. Pharmacological kynurenine 3-monooxygenase enzyme inhibition significantly reduces neuropathic pain in a rat model. Neuropharmacology 2016, 102, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyer, R.; Mehta, N.; Gungor, S.; Gulati, A. A Systematic Review of NMDA Receptor Antagonists for Treatment of Neuropathic Pain in Clinical Practice. Clin. J. Pain 2018, 34, 450–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Lim, J.Y.; Seong, J.Y.; Hwang, S.W. The Role of Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone at Peripheral Nociceptors: Implications for Pain Modulation. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IASP. IASP Terminology. Available online: https://www.iasp-pain.org/Education/Content.aspx?ItemNumber=1698#Nociplasticpain (accessed on 27 December 2020).
- Aydede, M.; Shriver, A. Recently introduced definition of “nociplastic pain” by the International Association for the Study of Pain needs better formulation. Pain 2018, 159, 1176–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeus, M.; Nijs, J. Central sensitization: A biopsychosocial explanation for chronic widespread pain in patients with fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meeus, M.; Nijs, J.; Van de Wauwer, N.; Toeback, L.; Truijen, S. Diffuse noxious inhibitory control is delayed in chronic fatigue syndrome: An experimental study. Pain 2008, 139, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.-J.; Na, H.-S.; Do, S.-H. Magnesium and Pain. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, F.; Maihöfner, C. Central mechanisms of experimental and chronic neuropathic pain: Findings from functional imaging studies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrepf, A.; Williams, D.A.; Gallop, R.; Naliboff, B.D.; Basu, N.; Kaplan, C.; Harper, D.E.; Landis, J.R.; Clemens, J.Q.; Strachan, E.; et al. Sensory sensitivity and symptom severity represent unique dimensions of chronic pain: A MAPP Research Network study. Pain 2018, 159, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Journal of Clinical Medicine. Special Issue “New Frontiers in the Diagnosis, Prediction, Prevention, and Management of Fibromyalgia”. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/jcm/special_issues/NF_Fibromyalgia (accessed on 27 December 2020).
- Rodriguez-Pintó, I.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Howard, A.; Shoenfeld, Y. Fibromyalgia and cytokines. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 161, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.I.; Park, I.Y.; Kim, H.A. Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Pathogenesis of Arthritis Pain Using Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barjandi, G.; Louca Jounger, S.; Löfgren, M.; Bileviciute-Ljungar, I.; Kosek, E.; Ernberg, M. Plasma tryptophan and kynurenine in females with temporomandibular disorders and fibromyalgia-An exploratory pilot study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2020, 47, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, M.C.; Ceko, M.; Low, L.A. Cognitive and emotional control of pain and its disruption in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Z.F.; Hsieh, S. Neurocognitive Mechanism of Human Resilience: A Conceptual Framework and Empirical Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Editorial of Special Issue “Crosstalk between Depression, Anxiety, and Dementia: Comorbidity in Behavioral Neurology and Neuropsychiatry”. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bransfield, R.C.; Friedman, K.J. Differentiating Psychosomatic, Somatopsychic, Multisystem Illnesses, and Medical Uncertainty. Healthcare 2019, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Defrin, R.; Amanzio, M.; de Tommaso, M.; Dimova, V.; Filipovic, S.; Finn, D.P.; Gimenez-Llort, L.; Invitto, S.; Jensen-Dahm, C.; Lautenbacher, S.; et al. Experimental pain processing in individuals with cognitive impairment: Current state of the science. Pain 2015, 156, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, F.; Yan, C.; Guo, W. Editorial: Brain and Somatization Symptoms in Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, H.B.; Stiles, T.C.; Stubhaug, A.; Landrø, N.I.; Hansson, P. Comparing objective cognitive impairments in patients with peripheral neuropathic pain or fibromyalgia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Llort, L.; Serrano, A.; Roquer, A.; Moriana, I.; Pajuelos, L.; Monllau, A.; Sanchez, M. Loose Verbal Communication of Pain in the Elderly People with Dementia. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2019, 31, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Howren, M.B.; Lamkin, D.M.; Suls, J. Associations of depression with C-reactive protein, IL-1, and IL-6: A meta-analysis. Psychosom. Med. 2009, 71, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dowlati, Y.; Herrmann, N.; Swardfager, W.; Liu, H.; Sham, L.; Reim, E.K.; Lanctôt, K.L. A meta-analysis of cytokines in major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ho, R.C.; Mak, A. Interleukin (IL)-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and soluble interleukin-2 receptors (sIL-2R) are elevated in patients with major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. J. Affec. Disord. 2012, 139, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkanova, V.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Allan, C.L. CRP, IL-6 and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 150, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haapakoski, R.; Mathieu, J.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Alenius, H.; Kivimäki, M. Cumulative meta-analysis of interleukins 6 and 1β, tumour necrosis factor α and C-reactive protein in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 49, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costello, H.; Gould, R.L.; Abrol, E.; Howard, R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between peripheral inflammatory cytokines and generalized anxiety disorder. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, R.; Garne, M.; Holmes, C.; Osmond, C.; Teeling, J.; Lau, L.; Baldwin, D.S. Peripheral inflammatory cytokines and immune balance in Generalised Anxiety Disorder: Case-controlled study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 62, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, S.; Fujii, T.; Koga, N.; Hori, H.; Teraishi, T.; Hattori, K.; Noda, T.; Higuchi, T.; Motohashi, N.; Kunugi, H. Plasma L-tryptophan concentration in major depressive disorder: New data and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, e906-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogyu, K.; Kubo, K.; Noda, Y.; Iwata, Y.; Tsugawa, S.; Omura, Y.; Wada, M.; Tarumi, R.; Plitman, E.; Moriguchi, S.; et al. Kynurenine pathway in depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 90, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réus, G.; Jansen, K.; Titus, S.; Carvalho, A.F.; Gabbay, V.; Quevedo, J. Kynurenine pathway dysfunction in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression: Evidences from animal and human studies. J. Psychiatric Res. 2015, 68, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orlikov, A.B.; Prakhye, I.B.; Ryzov, I.V. Kynurenine in blood plasma and DST in patients with endogenous anxiety and endogenous depression. Biol. Psychiatry 1994, 36, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Vécsei, L. Editorial: Are 5-HT1 receptor agonists effective anti-migraine drugs? Opin. Pharmacother. 2021, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- González-Sanmiguel, J.; Schuh, C.M.A.P.; Muñoz-Montesino, C.; Contreras-Kallens, P.; Aguayo, L.G.; Aguayo, S. Complex Interaction between Resident Microbiota and Misfolded Proteins: Role in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Cells 2020, 9, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Iriepa, D.; Chamorro, B.; Talaván, M.; Chioua, M.; Iriepa, I.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; López-Muñoz, F.; Marco-Contelles, J.; Oset-Gasque, M.J. Homo-Tris-Nitrones Derived from α-Phenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone: Synthesis, Neuroprotection and Antioxidant Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, C.; Macedo e Cordeiro, T.; Suchting, R.; de Dios, C.; Cuellar Leal, V.A.; Soares, J.C.; Dantzer, R.; Teixeira, A.L.; Selvaraj, S. Effect of immune activation on the kynurenine pathway and depression symptoms—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobeha. Rev. 2020, 118, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Vilariño-García, T.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of Leptin in Inflammation and Vice Versa. Int. J Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jiménez, F.J.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; García-Martín, E.; Agúndez, J.A.G. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Amantadine and Memantine: Possible Therapeutics for the Treatment of Covid-19? J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Aziz, N.U.; Chiroma, S.M.; Mohd Moklas, M.A.; Adenan, M.I.; Ismail, A.; Hidayat Baharuldin, M.T. Antidepressant-Like Properties of Fish Oil on Postpartum Depression-Like Rats Model: Involvement of Serotonergic System. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. Curcumin in antidepressant treatments: An overview of potential mechanisms, pre-clinical/clinical trials and ongoing challenges. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonel Javeres, M.N.; Habib, R.; Judith, N.; Iqbal, M.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Batool, S.; Nurulain, S.M. Analysis of PON1 gene polymorphisms (rs662 and rs854560) and inflammatory markers in organophosphate pesticides exposed cohorts from two distinct populations. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małgorzata, P.; Paweł, K.; Iwona, M.L.; Brzostek, T.; Andrzej, P. Glutamatergic dysregulation in mood disorders: Opportunities for the discovery of novel drug targets. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 1187–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koola, M.M. Galantamine-Memantine combination in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and beyond. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Bohár, Z.; Martos, D.; Telegdy, G.; Vécsei, L. Antidepressant-like effects of kynurenic acid in a modified forced swim test. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negro, A.; Martelletti, P. Novel synthetic treatment options for migraine. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, P.; Harat, M.; Zieliński, P.; Furtak, J.; Paczkowski, D.; Rusinek, M. Motor cortex stimulation in patients with chronic central pain. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harat, A.; Sokal, P.; Zieliński, P.; Harat, M.; Rusicka, T.; Herbowski, L. Assessment of economic effectiveness in treatment of neuropathic pain and refractory angina pectoris using spinal cord stimulation. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2012, 21, 653–663. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, Y. Endothelin ETB Receptor-Mediated Astrocytic Activation: Pathological Roles in Brain Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncheva, N.D.; Vasileva, L.; Saracheva, K.; Dimitrova, D.; Getova, D. Study of antinociceptive effect of ketamine in acute and neuropathic pain models in rats. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchacki, R.; Szkilnik, R.; Malinowska-Borowska, J.; Żelazko, A.; Lewkowicz, Ł.; Nowak, P.G. Impairment in Pain Perception in Adult Rats Lesioned as Neonates with 5.7-Dihydroxytryptamine. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañete, T.; Gimenez-Llort, L. Preserved thermal pain in 3xTg-AD mice with increased sensory-discriminative pain sensitivity in females but affective-emotional dimension in males as early sex-specific AD. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Krzywoszański, Ł.; Droś, J.; Pasińska, P.; Wilk, A.; Klimkowicz-Mrowiec, A. Early Depression Independently of Other Neuropsychiatric Conditions, Influences Disability and Mortality after Stroke (Research Study—Part of PROPOLIS Study). Biomedicines 2020, 8, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón-Habas, V.; Rich-Ruiz, M.; Romero-Saldaña, M.; Carrera-González, M.P. Depression as a Risk Factor for Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Bak, A.; Kim, S.; Nam, Y.; Kim, H.; Yoo, D.-H.; Moon, M. Animal-Assisted and Pet-Robot Interventions for Ameliorating Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.D.; Moayedi, M. Central mechanisms of pain revealed through functional and structural MRI. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 518–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh, L.; Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Vécsei, L.; Taguchi, S. Crosstalk between Existential Phenomenological Psychotherapy and Neurological Sciences in Mood and Anxiety Disorders. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.-K. Crosstalk between Depression and Dementia with Resting-State fMRI Studies and Its Relationship with Cognitive Functioning. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, H.; Watanabe, E.; Fukuchi, M. Psychiatric Neural Networks and Precision Therapeutics by Machine Learning. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannister, K.; Kucharczyk, M.; Dickenson, A.H. Hopes for the future of pain control. Pain Ther. 2017, 6, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kordestani-Moghadam, P.; Assari, S.; Nouriyengejeh, S.; Mohammadipour, F.; Pourabbasi, A. Cognitive impairments and associated structural brain changes in metabolic syndrome and implications of neurocognitive intervention. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 29, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordestani-Moghadam, P.; Nasehi, M.; Vaseghi, S.; Khodagholi, F.; Zarrindast, M.R. The role of sleep disturbances in depressive-like behavior with emphasis on α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 224, 113023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Pain Pathway Components | Pain Mechanisms | Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries |
|---|---|---|
| Transduction | Nociceptive pain | Ankle sprain and osteoarthritis |
| Conduction transmission | Neuropathic pain | Diabetic neuropathy, shingles, nutritional deficiencies, toxins, cancer, Guillain-Barre syndrome, amyloidosis, Fabry’s disease, and nerve trunk injuries |
| Modulation | Nociplastic pain | Fibromyalgia temporomandibular disorders, and nonspecific back pain |
| Perception | Psychogenic pain | Depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Tóth, F.; Szabó, Á.; Vécsei, L. Co-Players in Chronic Pain: Neuroinflammation and the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080897
Tanaka M, Török N, Tóth F, Szabó Á, Vécsei L. Co-Players in Chronic Pain: Neuroinflammation and the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(8):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080897
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Masaru, Nóra Török, Fanni Tóth, Ágnes Szabó, and László Vécsei. 2021. "Co-Players in Chronic Pain: Neuroinflammation and the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway" Biomedicines 9, no. 8: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080897
APA StyleTanaka, M., Török, N., Tóth, F., Szabó, Á., & Vécsei, L. (2021). Co-Players in Chronic Pain: Neuroinflammation and the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines, 9(8), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080897