Evaluation of Intraligamentous and Intraosseous Computer-Controlled Anesthetic Delivery Systems in Pediatric Dentistry: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
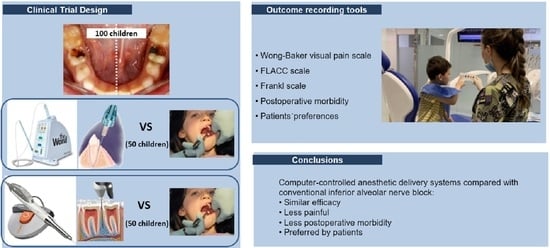
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Group
2.3. Interventions
2.4. Blinding
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Outcome Variables
2.7. Sample Size
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furgała, D.; Markowicz, K.; Koczor-Rozmus, A.; Zawilska, A. Causes and Severity of Dentophobia in Polish Adults-A Questionnaire Study. Healthcare 2021, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guideline on Behavior Guidance for the Pediatric Dental Patient. Pediatr. Dent. 2016, 38, 185–198.
- Schmoeckel, J.; Mustafa Ali, M.; Wolters, P.; Santamaría, R.M.; Usichenko, T.I.; Splieth, C.H. Pain perception during injection of local anesthesia in pedodontics. Quintessence Int. 2021, 52, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meechan, J.G.; Howlett, P.C.; Smith, B.D. Factors influencing the discomfort of intraoral needle penetration. Anesth. Prog. 2005, 52, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aghababaie, S.T.; Monteiro, J.; Stratigaki, E.; Ashley, P.F. Techniques for effective local anaesthetic administration for the paediatric patient. Br. Dent. J. 2020, 229, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libonati, A.; Nardi, R.; Gallusi, G.; Angotti, V.; Caruso, S.; Coniglione, F.; Marzo, G.; Mattei, A.; Tecco, S.; Paglia, L. Pain and anxiety associated with Computer-Controlled Local Anaesthesia: Systematic review and meta-analysis of cross-over studies. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2018, 19, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Use of local anesthesia for pediatric dental patients. In The Reference Manual of Pediatric Dentistry; American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry: Chicago, IL, USA, 2021; pp. 332–337. [Google Scholar]
- Oulis, C.J.; Vadiakas, G.P.; Vasilopoulou, A. The effectiveness of mandibular infiltration compared to mandibular block anesthesia in treating primary molars in children. Pediatr. Dent. 1996, 18, 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Tirupathi, S.P.; Rajasekhar, S.; Ganesh, M.; Vamshi, A.; Tyro, D. Can 4% Articaine Buccal Infiltration Replace Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block (IANB) with 2% Xylocaine for Pulp Therapy in Primary Mandibular Molars? A Systematic Review. Int. J. Clin.Pediatr. Dent. 2021, 14, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, N.; Aps, J. Efficacy of dental local anesthetics: A review. J. Dent. Anesth. Pain. Med. 2018, 18, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.R.; Rao, D.; Panwar, S.; Ameen, S. An in vivo, randomized, controlled comparative evaluation of efficacy, hemodynamic changes, and postoperative complications of 4% articaine using buccal infiltration and 2% lidocaine using inferior alveolar nerve block in mandibular primary molars of children aged 6 to 8 years. Quintessence Int. 2021, 52, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olley, R.C.; Renton, T.F.; Frost, P. A 15-year unique observational study of intraligamentary local anaesthesia for posterior mandibular extractions. Br. Dent. J. 2021, 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynes, S.G.; Riley, A.E.; Milbee, S.; Bastin, M.R.; Price, M.E.; Ladson, A. Evaluating complications of local anesthesia administration and reversal with phentolamine mesylate in a portable pediatric dental clinic. Gen. Dent. 2013, 61, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Aquilanti, L.; Mascitti, M.; Togni, L.; Contaldo, M.; Rappelli, G.; Santarelli, A. A systematic review on nerve-related adverse effects following mandibular nerve block anesthesia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrel, M.A. Broken local anesthetic needles: A case series of 16 patients, with recommendations. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2009, 140, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.J.; Hochman, M.N. A 21st century computerized injection system for local pain control. Comp. Contin. Educ. Dent. 1997, 18, 995–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Pozos-Guillén, A.; Loredo-Cruz, E.; Esparza-Villalpando, V.; Martínez-Rider, R.; Noyola-Frías, M.; Garrocho-Rangel, A. Pain and Anxiety Levels Using Conventional versus Computer-Controlled Local Anesthetic Systems in Pediatric Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2020, 44, 371–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.J.; Pang, N.S.; Cho, J.H.; Jung, B.Y.; Kim, K.D.; Park, W. Computer-controlled local anesthetic delivery for painless anesthesia: A literature review. J. Dent. Anesth. Pain Med. 2016, 16, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, J.K. Adjuncts to local anesthesia: Separating fact from fiction. J. Can Dent. Assoc. 2001, 67, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Sixou, J.L.; Barbosa-Rogier, M.E. Efficacy of intraosseous injections of anesthetic in children and adolescents. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2008, 106, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Trials 2010, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankl, S.N.; Shire, F.R.; Fogels, H.R. Should the parent remain with the child in the dental operatory? J. Dent. Child. 1962, 29, 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, D.L.; Baker, C.M. Pain in children: Comparison of assessment scales. Pediatr. Nurs. 1988, 14, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merkel, S.I.; Voepel-Lewis, T.; Shayevitz, J.R.; Malviya, S. The FLACC: A behavioral scale for scoring postoperative pain in young children. Pediatr. Nurs. 1997, 23, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sixou, J.L.; Marie-Cousin, A.; Huet, A.; Hingant, B.; Robert, J.C. Pain assessment by children and adolescents during intraosseous anaesthesia using a computerized system (QuickSleeper). Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2009, 19, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Smaïl-Faugeron, V.; Muller-Bolla, M.; Sixou, J.L.; Courson, F. Split-mouth and parallel-arm trials to compare pain with intraosseous anaesthesia delivered by the computerised Quicksleeper system and conventional infiltration anaesthesia in paediatric oral healthcare: Protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ. Open. 2015, 5, e007724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteiro, J.; Tanday, A.; Ashley, P.F.; Parekh, S.; Alamri, H. Interventions for increasing acceptance of local anaesthetic in children and adolescents having dental treatment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2, CD011024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandiah, P.; Tahmassebi, J.F. Comparing the onset of maxillary infiltration local anaesthesia and pain experience using the conventional technique vs. the Wand in children. Br. Dent. J. 2012, 213, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Chopra, R.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, D. Comparison of Pain perception using conventional versus computer-controlled intraligamentary local anesthetic injection for extraction of primary molars. Anesth. Prog. 2019, 66, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghlaf, K.; Alamoudi, N.; Elashiry, E.; Farsi, N.; El Derwi, D.A.; Abdullah, A.M. The pain-related behavior and pain perception associated with computerized anesthesia in pulpotomies of mandibular primary molars: A randomized controlled trial. Quintessence Int. 2015, 46, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoppe-Dhamodhara, Y.K.; Asokan, S.; John, B.J.; Pollachi-Ramakrishnan, G.; Ramachandran, P.; Vilvanathan, P. Cartridge syringe vs computer controlled local anesthetic delivery system: Pain related behaviour over two sequential visits—A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2015, 7, e513–e518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langthasa, M.; Yeluri, R.; Jain, A.A.; Munshi, A.K. Comparison of the pain perception in children using comfort control syringe and a conventional injection technique during pediatric dental procedures. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2012, 30, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carugo, N.; Paglia, L.; Re, D. Pain perception using a computer-controlled anaesthetic delivery system in paediatric dentistry: A review. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2020, 21, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garret-Bernardin, A.; Cantile, T.; D'Antò, V.; Galanakis, A.; Fauxpoint, G.; Ferrazzano, G.F.; De Rosa, S.; Vallogini, G.; Romeo, U.; Galeotti, A. Pain Experience and Behavior Management in Pediatric Dentistry: A Comparison between Traditional Local Anesthesia and the Wand Computerized Delivery System. Pain Res. Manag. 2017, 2017, 7941238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patini, R.; Staderini, E.; Cantiani, M.; Camodeca, A.; Guglielmi, F.; Gallenzi, P. Dental anaesthesia for children—Effects of a computer-controlled delivery system on pain and heart rate: A randomised clinical trial. Br. J. Oral. Maxillofac Surg. 2018, 56, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetti, L.; Forabosco, E.; Spinas, E.; Re, D.; Murri Dello Diago, A. Single tooth anaesthesia: A new approach to the paediatric patient. A clinical experimental study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2018, 19, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolarek, P.C.; Wambier, L.M.; Siqueira Silva, L.; Chibinski, A.C.R. Does computerized anaesthesia reduce pain during local anaesthesia in paediatric patients for dental treatment? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2020, 30, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, V.; Libonati, A.; Nardi, R.; Angotti, V.; Gallusi, G.; Montemurro, E.; D'Amario, M.; Marzo, G. Single tooth anesthesia versus conventional anesthesia: A cross-over study. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2018, 22, 3205–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Hachem, C.; Kaloustian, M.K.; Cerutti, F.; Chedid, N.R. Metallic syringe versus electronically assisted injection system: A comparative clinical study in children. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2019, 20, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.L.; von Baeyer, C.L.; Spafford, P.A.; van Korlaar, I.; Goodenough, B. The Faces Pain Scale-Revised: Toward a common metric in pediatric pain measurement. Pain 2001, 93, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, K.E.; Freeman, R. Reliability and validity of a faces version of the Modified Child Dental Anxiety Scale. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2007, 17, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrololoomi, Z.; Maghsoudi, N. Articaine use does not routinely eliminate the need for palatal injections for primary maxillary molar extractions: A randomized cross-over clinical trial. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 26, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamoudi, N.M.; Baghlaf, K.K.; Elashiry, E.A.; Farsi, N.M.; El Derwi, D.A.; Bayoumi, A.M. The effectiveness of computerized anesthesia in primary mandibular molar pulpotomy: A randomized controlled trial. Quintessence Int. 2016, 47, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugia, C.; Bartolino, M.; Docimo, R. Comparison of single tooth anaesthesia by computer-controlled local anaesthetic delivery system (C-CLADS) with a supraperiosteal traditional syringe injection in paediatric dentistry. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2017, 18, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Gabka, J.; Taubenheim, L. Intraligamentary anesthesia: Benefits and limitations. Quintessence Int. 2008, 39, e15–e25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Obaida, M.I.; Haider, M.; Hashim, R.; AlGheriri, W.; Celur, S.L.; Al-Saleh, S.A.; Al-Madi, E.M. Comparison of perceived pain and patients' satisfaction with traditional local anesthesia and single tooth anesthesia: A randomized clinical trial. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 2986–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztaş, N.; Ulusu, T.; Bodur, H.; Doğan, C. The wand in pulp therapy: An alternative to inferior alveolar nerve block. Quintessence Int. 2005, 36, 559–564. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, U.B.; Joshi, A.V. Efficacy of Intraosseous Local Anesthesia for Restorative Procedures in Molar Incisor Hypomineralization-Affected Teeth in Children. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9, S272–S277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaïl-Faugeron, V.; Muller-Bolla, M.; Sixou, J.L.; Courson, F. Evaluation of intraosseous computerized injection system (QuickSleeper™) vs conventional infiltration anaesthesia in paediatric oral health care: A multicentre, single-blind, combined split-mouth and parallel-arm randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2019, 29, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovichetti, F.S.; Zuccon, A.; Zambon, G.; Pellegrino, G.; Signoriello, A.G.; Milia, E.; Bortone, A.; Gracco, A.; Mazzoleni, S. Pain perception in paediatric patients: Evaluation of computerised anaesthesia delivery system vs conventional infiltration anaesthesia in paediatric patients. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2022, 23, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laux, M.; Schmidlin, P.R. Parodontale Komplikationen nach intraossärer Anästhesie [Periodontal complications with intrabony anesthesia]. Swiss Dent. J. 2020, 130, 995–999. [Google Scholar]
- Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Ata-Ali, J.; Oltra-Moscardó, M.J.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Peñarrocha, M. Side effects and complications of intraosseous anesthesia and conventional oral anesthesia. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2012, 17, e430–e434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodmansey, K.F.; White, R.K.; He, J. Osteonecrosis related to intraosseous anesthesia: Report of a case. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, J.C.; Witherspoon, D.E.; Regan, J.D.; Hall, E. Procedural mishaps with trephine-based intraosseous anesthesia. Tex. Dent. J. 2011, 128, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kuşcu, O.O.; Akyuz, S. Children's preferences concerning the physical appearance of dental injectors. J. Dent. Child. 2006, 73, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kuscu, O.O.; Akyuz, S. Is it the injection device or the anxiety experienced that causes pain during dental local anaesthesia? Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2008, 18, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melwani, A.M.; Srinivasan, I.; Setty, J.V.; Krishna, D.R.M.; Pamnani, S.S.; Lalitya, D. A clinical comparative study between conventional and camouflaged syringes to evaluate behavior and anxiety in 6-11-year-old children during local anesthesia administration-a novel approach. J. Dent. Anesth. Pain Med. 2018, 18, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beneito-Brotons, R.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Ata-Ali, J.; Peñarrocha, M. Intraosseous anesthesia with solution injection controlled by a computerized system versus conventional oral anesthesia: A preliminary study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2012, 17, e426–e429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, U.; Hunzeker, C.; Hutfless, S.; Galloway, A. Quality of anesthesia for the maxillary primary anterior segment in pediatric patients: Comparison of the P-ASA nerve block using CompuMed delivery system vs traditional supraperiosteal injections. J. Dent. Child. 2005, 72, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhruddin, K.S.; Hisham, E.B.; Gorduysus, M.O. Effectiveness of audiovisual distraction eyewear and computerized delivery of anesthesia during pulp therapy of primary molars in phobic child patients. Eur. J. Dent. 2015, 9, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, A.; Singh, B.D.; Pagaria, S.; Avinash, A. The Wand: A mini review of an advanced technique for local anesthesia delivery in Dentistry. AJADD. 2014, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi, M.; Blumer, S.; Eli, I. Effectiveness of computerized delivery of intrasulcular anesthetic in primary molars. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2005, 136, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortoluzzi, M.C.; de Camargo Smolarek, P.; Cecato, R.; Pochapski, M.T.; Chibinski, A.C.R. Anaesthetic efficacy of 4% articaine compared with 2% mepivacaine: A randomized, double-blind, crossover clinical trial. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| IANB (n = 100) | CDS-ILA (n = 50) | CDS-IOA (n = 50) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain by anesthesia injection (Wong–Baker score) | Score 0 | 7% | 36% | 28% |
| Score 1 | 49% | 54% | 52% | |
| Score 2 | 34% | 10% | 16% | |
| Score 3 | 10% | 0% | 4% | |
| Physical reaction during the anesthesia injection (FLACC score) | 4.4 ± 2.8 points (range 0–10.0) | 2.4 ± 1.7 points (range 0–9.0) | 3.8± 2.1 points (range 0–8.0) | |
| Anesthetic reinforcement | 17% | 14% | 8% | |
| Pain during the therapeutic procedure (Wong–Baker score) | Score 0 | 50% | 58% | 56% |
| Score 1 | 36% | 36% | 28% | |
| Score 2 | 11% | 0% | 16% | |
| Score 3 | 3% | 6% | 0% | |
| Overall behavior during the visit (Frankl scale) | Score 1 | 1% | 2% | 0% |
| Score 2 | 8% | 14% | 8% | |
| Score 3 | 35% | 22% | 28% | |
| Score 4 | 56% | 62% | 64% | |
| Postoperative morbidity | Total | 52% | 12% | 28% |
| Type of postoperative complication | Discomfort | 28% | 12% | 12% |
| Pain | 12% | 0% | 16% | |
| Nibbling injury | 12% | 0% | 0% |
| CDS-ILA vs. IANB | CDS-IOA vs. IANB | |
|---|---|---|
| Pain by anesthesia injection (Wong–Baker score) | p < 0.001 a | p = 0.005 a |
| Pain due to the anesthesia injection (recoded) | p = 0.004 b | p = 0.003 b |
| Physical reaction during the anesthesia injection (FLACC score) | p < 0.001 c | p = 0.103 c |
| Anesthetic reinforcement | p = 0.248 b | p = 0.157 b |
| Pain during the therapeutic procedure (Wong–Baker score) | p = 0.859 a | p = 0.969 a |
| Pain during the therapeutic procedure (recoded) | p = 0.803 b | p = 0.987 a |
| Overall behavior during the visit (Frankl scale) | p = 1.000 a | p = 0.564 a |
| Behavior during the anesthesia injection (recoded) | p = 0.773 b | p = 0.439 b |
| Postoperative morbidity | p < 0.001 b | p = 0.009 b |
| Type of postoperative complication | p < 0.001 a | p = 0.014 a |
| Pain Due to the Anesthesia Injection a | Physical Reaction during the Anesthesia Injection b | Anesthetic Reinforcement | Pain during the Therapeutic Procedure a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDS-ILA versus IANB | OR = 6.410 CI = 1.723–23.817 p = 0.010 | EC = 1.125 SE = 0.222 p < 0.001 | ns | ns |
| CDS-IOA versus IANB | OR = 0.107 CI = 0.012–0.950 p = 0.045 | EC = −1.680 SE = 0.639 p = 0.011 | ns | ns |
| Overall behavior during the visit c,d | Postoperative morbidity | Type of postoperative complication e | ||
| CDS-ILA versus IANB | ns | OR = 14.661 CI = 2.697–79.903 p < 0.001 | OR = 3.980 CI = 0.991–15.957 p = 0.021 | |
| CDS-IOA versus IANB | ns | OR = 0.306 CI = 0.094–0.992 p = 0.048 | OR = 1.473 CI = 0.658–1.894 p = 0.043 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prol Castelo, A.; García Mato, E.; Varela Aneiros, I.; Sande López, L.; Outumuro Rial, M.; Abeleira Pazos, M.T.; Rivas Mundiña, B.; Limeres Posse, J. Evaluation of Intraligamentous and Intraosseous Computer-Controlled Anesthetic Delivery Systems in Pediatric Dentistry: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Children 2023, 10, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10010079
Prol Castelo A, García Mato E, Varela Aneiros I, Sande López L, Outumuro Rial M, Abeleira Pazos MT, Rivas Mundiña B, Limeres Posse J. Evaluation of Intraligamentous and Intraosseous Computer-Controlled Anesthetic Delivery Systems in Pediatric Dentistry: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Children. 2023; 10(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleProl Castelo, Andrea, Eliane García Mato, Iván Varela Aneiros, Lucía Sande López, Mercedes Outumuro Rial, María Teresa Abeleira Pazos, Berta Rivas Mundiña, and Jacobo Limeres Posse. 2023. "Evaluation of Intraligamentous and Intraosseous Computer-Controlled Anesthetic Delivery Systems in Pediatric Dentistry: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Children 10, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10010079
APA StyleProl Castelo, A., García Mato, E., Varela Aneiros, I., Sande López, L., Outumuro Rial, M., Abeleira Pazos, M. T., Rivas Mundiña, B., & Limeres Posse, J. (2023). Evaluation of Intraligamentous and Intraosseous Computer-Controlled Anesthetic Delivery Systems in Pediatric Dentistry: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Children, 10(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10010079