Loss of Health Promoting Bacteria in the Gastrointestinal Microbiome of PICU Infants with Bronchiolitis: A Single-Center Feasibility Study
Abstract
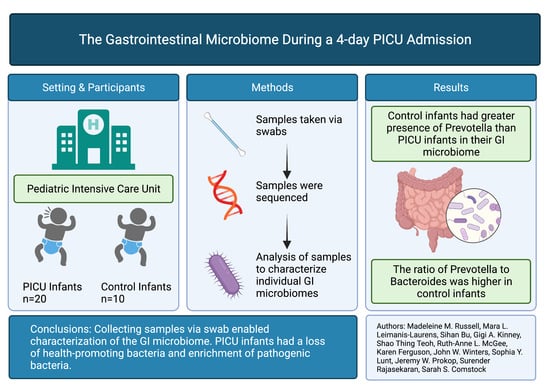
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Population, Site and Sample Collection
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction, 16S Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Vaishampayan, P.A.; Kuehl, J.V.; Froula, J.L.; Morgan, J.L.; Ochman, H.; Francino, M.P. Comparative Metagenomics and Population Dynamics of the Gut Microbiota in Mother and Infant. Genome Biol. Evol. 2010, 2, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hills, R.D.; Pontefract, B.A.; Mishcon, H.R.; Black, C.A.; Sutton, S.C.; Theberge, C.R. Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taft, D.H.; Ambalavanan, N.; Schibler, K.R.; Yu, Z.; Newburg, D.S.; Ward, D.V.; Morrow, A.L. Intestinal microbiota of preterm infants differ over time and between hospitals. Microbiome 2014, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, M.; Klingensmith, N.J.; Coopersmith, C.M. New insights into the gut as the driver of critical illness and organ failure. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2017, 23, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Ackermann, G.; Khailova, L.; Baird, C.; Heyland, D.; Kozar, R.; Lemieux, M.; Derenski, K.; King, J.; Vis-Kampen, C.; et al. Extreme dysbiosis of the microbiome in critical illness. Msphere 2016, 1, e00199-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojima, M.; Motooka, D.; Shimizu, K.; Gotoh, K.; Shintani, A.; Yoshiya, K.; Nakamura, S.; Ogura, H.; Iida, T.; Shimazu, T. Metagenomic Analysis Reveals Dynamic Changes of Whole Gut Microbiota in the Acute Phase of Intensive Care Unit Patients. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 61, 1628–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickson, R.P.; Singer, B.; Newstead, M.W.; Falkowski, N.R.; Erb-Downward, J.R.; Standiford, T.J.; Huffnagle, G.B. Enrichment of the lung microbiome with gut bacteria in sepsis and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y. The Cross-Talk between Gut Microbiota and Lungs in Common Lung Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krezalek, M.A.; Yeh, A.; Alverdy, J.C.; Morowitz, M. Influence of nutrition therapy on the intestinal microbiome. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papan, C.; Willersinn, M.; Weiß, C.; Karremann, M.; Schroten, H.; Tenenbaum, T. Antibiotic utilization in hospitalized children under 2 years of age with influenza or respiratory syncytial virus infection—A comparative, retrospective analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Leimanis, M.L.; Adams, M.; Bachmann, A.S.; Uhl, K.L.; Bupp, C.P.; Hartog, N.L.; Kort, E.J.; Olivero, R.; Comstock, S.S.; et al. Balancing precision versus cohort transcriptomic analysis of acute and recovery phase of viral bronchiolitis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L1147–L1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, W.N. Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 39 (Suppl. 1), 5–41. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine (IOM). Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirement; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; p. 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Moreno, A.; Comstock, S.S.; Sugino, K.Y.; Ma, T.F.; Paneth, N.; Davis, Y.; Olivero, R.; Schein, R.; Maurer, J.; Zhang, L. Perinatal risk factors for fecal antibiotic resistance gene patterns in pregnant women and their infants. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.; Wagner, H.; et al. Package “vegan” Title Community Ecology Package Version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: https://cran.ism.ac.jp/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.; Venables, B.; Bates, D.M.; Hornik, K.; Gebhardt, A.; Firth, D.; Ripley, M.B. Package “MASS”. Support Functions and Datasets for Venables and Ripley’s MASS. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MASS/MASS.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2021).
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S-PLUS; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Drell, T.; Lutsar, I.; Štšepetova, J.; Parm, Ü.; Metsvaht, T.; Ilmoja, M.-L.; Simm, J.; Sepp, E. The development of gut microbiota in critically ill extremely low birth weight infants assessed with 16S rRNA gene based sequencing. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 304–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, M.B.; Firek, B.; Shi, M.; Yeh, A.; Brower-Sinning, R.; Aveson, V.; Kohl, B.L.; Fabio, A.; Carcillo, J.A.; Morowitz, M.J. Disruption of the microbiota across multiple body sites in critically ill children. Microbiome 2016, 4, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akrami, K.; Sweeney, D.A. The microbiome of the critically ill patient. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2018, 24, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precup, G.; Vodnar, D.-C. Gut Prevotella as a possible biomarker of diet and its eubiotic versus dysbiotic roles: A comprehensive literature review. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, C.E.; Caseiro, C.; Martins, M.; Monteiro, R.; Brandão, I. Gut Microbiota, in the Halfway between Nutrition and Lung Function. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Gamallat, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Meyiah, A.; Yan, C.; Shang, D.; Xin, Y. The distribution characteristics of intestinal microbiota in children with community-acquired pneumonia under five Years of age. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Mande, S.S. Diet, Microbiota and Gut-Lung Connection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.M. The immune response to Prevotella bacteria in chronic inflammatory disease. Immunology 2017, 151, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iljazovic, A.; Roy, U.; Gálvez, E.J.; Lesker, T.R.; Zhao, B.; Gronow, A.; Amend, L.; Will, S.E.; Hofmann, J.D.; Pils, M.C.; et al. Perturbation of the gut microbiome by Prevotella spp. enhances host susceptibility to mucosal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 14, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Ma, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Yan, G.; Lu, G. Altered Gut Microbiota Taxonomic Compositions of Patients With Sepsis in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 645060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenbach, E.; Harris, A.D.; Perencevich, E.N.; Nachamkin, I.; Tolomeo, P.; Metlay, J.P. Test Characteristics of Perirectal and Rectal Swab Compared to Stool Sample for Detection of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Escherichia coli in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyman, M.; Van Houten, M.A.; Arp, K.; Sanders, E.A.M.; Bogaert, D. Rectal swabs are a reliable proxy for faecal samples in infant gut microbiota research based on 16S-rRNA sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.; Jin, G.; Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Cao, H. Current Sampling Methods for Gut Microbiota: A Call for More Precise Devices. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Bottacini, F.; Casey, E.; Turroni, F.; Mahony, J.; Belzer, C.; Delgado Palacio, S.; Arboleya Montes, S.; Mancabelli, L.; et al. The first microbial colonizers of the human gut: Composition, activities, and health implications of the infant gut microbiota. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00036-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurens, M.L.L.; Jaji, A.M.; Montgomery, J.; Jess, J.; Ferguson, K.; Parker, J.; Sanfilippo, D.; Rajasekaran, S. Preadmission Diet and Zip Code Influences the Pediatric Critical Care Clinical Course for Infants with Severe Respiratory Illness (N = 187). J. Pediatr. Intensive Care 2020, 09, 277–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Typpo, K. Nutrition: A primary therapy in pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome. Front. Pediatr. 2016, 4, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| 24 h Timepoint | 72 h Timepoint | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Age (mo) | Sex | Admit Weight (kg) | Sequenced (Yes/No) | Abx a (Yes/No) | Mode of Feeding b | Diet b | % Calories b,c | % Protein b,c | Sequenced (Yes/No) | Abx a (Yes/No) | Mode of Feeding b | Diet b | % Calories b,c | % Protein b,c |
| 1 | 2–4 | M | 5.8 | No | No | N/A e | MD | N/A | N/A | Yes | Yes | NG | MD | 100 | 100 |
| 2 | 2–4 | M | 6.5 | Yes | No | PO | FF | <33 | <33 | Yes | Yes | NG | FF | 94 | 100 |
| 3 | 2–4 | M | 5.7 | No | No | BF | BM | <33 | <33 | Yes | No | NG | BM | 99 | 70 |
| 4 | >4 | F | 8.5 | Yes | Yes | NG | FF | 74 | 67 | No | Yes | PO/NG | FF | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | <2 | F | 3.8 | No | No | NG | FF | 20 | 24 | Yes | Yes | NG | FF | 95 | 100 |
| 6 | <2 | M | 3.9 | No | Yes | None | BM | 0 | 0 | Yes | No | NG | BM | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | <2 | F | 3.2 | Yes | Yes | None | FF | 0 | 0 | No | No | NG | FF | 44 | 63 |
| 8 | 2–4 | F | 6.3 | No | No | BF | MD | <33 | <33 | No | Yes | None | MD | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | <2 | F | 2.9 | Yes | Yes | NG | FF | 67 | 79 | Yes | No | NG | FF | 100 | 100 |
| 10 | 2–4 | F | 2.3 | Yes | No | NG | FF | 43 | 65 | Yes | Yes | NG | FF | 100 | 100 |
| 11 | 2–4 | F | 2.8 | Yes | No | NG | FF | 40 | 93 | Yes | No | NG | FF | 99 | 100 |
| 12 | <2 | M | 4.2 | No | N/A | N/A | BM | N/A | N/A | Yes | No | NJ | MD | 100 | 100 |
| 13 | 2–4 | F | 5.0 kg | Yes | No | OG | MDBM + Beneprotein | 76 | 71 | Yes | No | OG | MD | 100 | 72 |
| 14 | <2 | F | 2.7 | Yes | Yes | NG | BM | 10 | 10 | Yes | Yes | NG | BM | 77 | 80 |
| 15 | 2–4 | F | 4.9 | Yes | No | PO | FF | 13 | 14 | Yes | No | PO | FF | 77 | 84 |
| 16 | <2 | F | 4.2 | No | No | NG | MD: BM + Enf Inf | 96 | 81 | Yes | No | NG | FF | 100 | 98 |
| 17 | 2–4 | F | 3.3 | Yes | Yes | None | FF | 0 | 0 | Yes | Yes | NG | FF | 97 | 100 |
| 18 | <2 | M | 3.1 | Yes | Yes | PO 85% NG 15% | FF | 16 | 23 | Yes | No | NG | FF | 100 | 100 |
| 19 d | 2–4 | F | 6.0 | No | Yes | NG | BM | 32 | 17 | Yes | Yes | NG | MD:BM + Beneprtein | 100 | 100 |
| 20 | 2–4 | M | 6.4 | Yes | No | NPO | NPO | 0 | 0 | No | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Taxa | Controls (Mean ± SD) | RSV (Mean ± SD) | p-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lachnospiraceae_unclassified | 1.9 ± 2.2 | 4.3 ± 3 | 0.071 |
| Bifidobacterium | 7.3 ± 9.4 | 20.8 ± 11.7 | 0.011 |
| Enterobacteriaceae_unclassified | 9.5 ± 7.2 | 23.7 ± 18.7 | 0.005 |
| Veillonella | 11.6 ± 5.9 | 10.9 ± 8.1 | 0.888 |
| Bacteroides | 10.1 ± 6.5 | 9.2 ± 11.2 | 0.888 |
| Prevotella | 10.9 ± 9.5 | 3.1 ± 4.9 | 0.019 |
| Clostridium_sensu_stricto | 8.3 ± 12.4 | 3.6 ± 4.6 | 0.079 |
| Clostridiales_unclassified | 2.4 ± 3.7 | 0.6 ± 1.5 | 0.019 |
| Clostridium_XlVa | 1.7 ± 1 | 1.1 ± 2.5 | 0.556 |
| Lachnospiracea_incertae_sedis | 2.1 ± 2.2 | 5.7 ± 4.3 | 0.025 |
| Porphyromonas | 4.6 ± 7.4 | 0.1 ± 0.3 | 0.015 |
| Enterococcus | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 2.6 | <0.001 |
| Megasphaera | 1.5 ± 1.7 | 1.1 ± 3.2 | 0.773 |
| Salmonella | 3 ± 3.2 | 3.1 ± 7.9 | 0.973 |
| Measures | Controls | RSV | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (min, max) | Median (min, max) | ||
| Chao1 | 106.2 (84.2, 200.1) | 87.3 (42.0, 189.0) | 0.02 |
| Shannon | 2.8 (2.2, 3.2) | 2.1 (0.8, 3.0) | 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russell, M.M.; Leimanis-Laurens, M.L.; Bu, S.; Kinney, G.A.; Teoh, S.T.; McKee, R.-A.L.; Ferguson, K.; Winters, J.W.; Lunt, S.Y.; Prokop, J.W.; et al. Loss of Health Promoting Bacteria in the Gastrointestinal Microbiome of PICU Infants with Bronchiolitis: A Single-Center Feasibility Study. Children 2022, 9, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010114
Russell MM, Leimanis-Laurens ML, Bu S, Kinney GA, Teoh ST, McKee R-AL, Ferguson K, Winters JW, Lunt SY, Prokop JW, et al. Loss of Health Promoting Bacteria in the Gastrointestinal Microbiome of PICU Infants with Bronchiolitis: A Single-Center Feasibility Study. Children. 2022; 9(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleRussell, Madeleine M., Mara L. Leimanis-Laurens, Sihan Bu, Gigi A. Kinney, Shao Thing Teoh, Ruth-Anne L. McKee, Karen Ferguson, John W. Winters, Sophia Y. Lunt, Jeremy W. Prokop, and et al. 2022. "Loss of Health Promoting Bacteria in the Gastrointestinal Microbiome of PICU Infants with Bronchiolitis: A Single-Center Feasibility Study" Children 9, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010114
APA StyleRussell, M. M., Leimanis-Laurens, M. L., Bu, S., Kinney, G. A., Teoh, S. T., McKee, R. -A. L., Ferguson, K., Winters, J. W., Lunt, S. Y., Prokop, J. W., Rajasekaran, S., & Comstock, S. S. (2022). Loss of Health Promoting Bacteria in the Gastrointestinal Microbiome of PICU Infants with Bronchiolitis: A Single-Center Feasibility Study. Children, 9(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010114