Processing, Characteristics and Composition of Umqombothi (a South African Traditional Beer)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Umqombothi: Its Origins and Processing
2.1. The Socioeconomic, Cultural and Spiritual Significance of Umqombothi
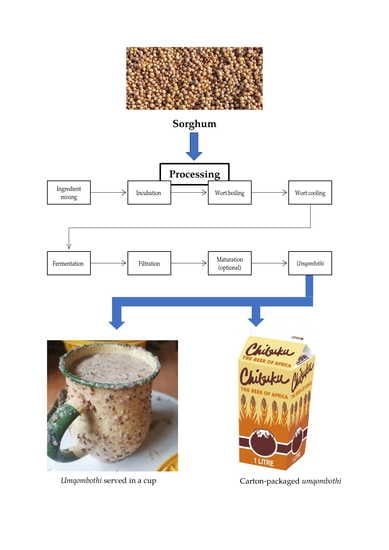
2.2. Processing Steps Involved in Brewing Practices of Umqombothi
2.3. Early Industrialisation Attempts for Umqombothi Processing
3. Composition of Umqombothi and Benefits
3.1. Physicochemical Constituents
3.2. Nutritional Content and Health Benefits
3.3. Microbiota
4. Safety Challenges with Umqombothi Processing
5. Bioprocessing Approaches
5.1. Classical Bioprocessing Optimisation Approaches
5.2. Bioprocess Optimisation Approaches Using the Concepts of the 4th Industrial Revolution
6. Future Directions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konfo, C.T.R.; Chabi, N.W.; Dahouenon-Ahoussi, E.; Cakpo-Chichi, M.; Soumanou, M.M.; Sohounhloue, D.C.K. Improvement of african traditional sorghum beers quality and potential applications of plants extracts for their stabilization: A review. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2015, 5, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lues, J.; Ikalafeng, B.; Maharasoa, M.; Shale, K. Brewing and Consumptions Practices of Indigenous Traditional Beer in A Typical South African Semi-Urban Area. Indilinga Afr. J. Indig. Knowl. Syst. 2009, 8, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabvandi, S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Razavi, S.H.; Mortazavian, A.M. Application of Advanced Instrumental Techniques for Analysis of Physical and Physicochemical Properties of Beer: A Review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2010, 13, 744–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madella, M.; García-Granero, J.J.; Out, W.A.; Ryan, P.; Usai, D. Microbotanical Evidence of Domestic Cereals in Africa 7000 Years Ago. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood-Sichra, U. Cereal Crops, 1st ed.; International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI): Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Evera, E.; Abedin Abdallah, S.H.; Shuang, Z.; Sainan, W.; Yu, H. Shelf life and nutritional quality of sorghum beer: Potentials of phytogenic-based extracts. J. Agric. Food. Tech. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Adebo, O.A. African Sorghum-Based Fermented Foods: Past, Current and Future Prospects. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyumugabe, F.; Gros, J.; Nzungize, J.; Bajyana, E.; Thonart, P. Characteristics of African traditional beers brewed with sorghum malt: A review. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2012, 16, 509–530. [Google Scholar]
- Gadaga, T.; Mutukumira, A.; Narvhus, J.; Feresu, S. A review of traditional fermented foods and beverages of Zimbabwe. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekoya, I.; Obadina, A.; Adaku, C.C.; De Boevre, M.; Okoth, S.; De Saeger, S.; Njobeh, P.B. Mycobiota and co-occurrence of mycotoxins in South African maize-based opaque beer. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 270, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mboti, N. Song and genocide: Investigating the function of Yvonne Chaka Chaka’s ‘Umqombothi’ inHotel Rwanda. South-North Cult. Media Stud. 2012, 26, 728–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikalafeng, B.K. Microbiota and Mycotoxins in Traditional Beer of The Greater Kimberley Area and Associated Brewing and Consumption Practices; Central University of Technology: Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Choma, S.S.R.; Alberts, M.; Urdal, P. Effect of traditional beer consumption on the iron status of a rural South African population. S. Afr. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 20, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katongole, J. The Microbial Succession in Indigenous Fermented Maize Products; University of Free State: Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 3 More Dead in EC After Drinking Home-Brewed Beer Mixed with Methylated Spirits. Available online: https://www.news24.com/news24/southafrica/news/3-more-dead-in-ec-after-drinking-home-brewed-beer-mixed-with-methylated-spirits-20200524 (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Mawonike, R.; Chigunyeni, B.; Chipumuro, M. Process improvement of opaque beer (chibuku) based on multivariate cumulative sum control chart. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 124, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shackelton, S.E. The Informal Marula Beer Traders of Bushbuckridge; Rhodes University: Grahamstown, South Africa, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Umoja Adds Innovation to SA’s Umqombothi Heritage. Available online: https://transformsa.co.za/2019/10/umoja-adds-innovation-to-sas-umqombothi-heritage/ (accessed on 17 August 2020).
- Sorgho Looks to Modernise Umqombothi With Umoja Beer Powder. Available online: https://retailbriefafrica.co.za/sorgho-looks-to-modernise-umqombothi-with-umoja-beer-powder/ (accessed on 17 August 2020).
- Mandishona, E.; Moyo, V.; Gordeuk, V.; Khumalo, H.; Saungweme, T.; Gangaidzo, I.; Gomo, Z.; Rouault, T.; MacPhail, A. A traditional beverage prevents iron deficiency in African women of child bearing age. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aloys, N.; Angeline, N. Traditional fermented foods and beverages in Burundi. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achi, O. The potential for upgrading traditional fermented foods through biotechnology. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lyumugabe, F.; Uyisenga, J.P.; Songa, E.B.; Thonart, P. Production of Traditional Sorghum Beer “Ikigage” Using Saccharomyces cerevisae, Lactobacillus fermentum and Issatckenkia orientalis as Starter Cultures. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moodley, S.S.; Dlamini, N.R.; Steenkamp, L.; Buys, E.M. Bacteria and yeast isolation and characterisation from a South African fermented beverage. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2019, 115, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, C.M. African traditional beer: Changing organization and spaces of South Africa’s sorghum beer industry. Afr. Geogr. Rev. 2019, 38, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquest-Ross, L.-C.; Vink, N.; Sigge, G. Food consumption changes in South Africa since 1994. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2015, 111, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanadoum, M.; Pourquie, J. Sorghum Beer: Production, Nutritional Value and Impact upon Human Health. In Beer in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- The Oxford Companion to Beer Definition of Africa, Traditional Brewing In. Available online: https://beerandbrewing.com/dictionary/izd8yFIQEc/ (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- How to Make Umqombothi (Zulu Beer). Available online: https://www.thesouthafrican.com/food/recipes/how-to-make-umqombothi/ (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- United National Breweries—About Beer. Available online: http://www.unbreweries.co.za/view/unb/en/page59.html (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- How Beer Is Made. Available online: http://www.sab.co.za/post/beer-culture/how-beer-is-made (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- Ingredients to the Perfect Umqombothi. Available online: https://www.jacarandafm.com/shows/the-complimentary-breakfast-with-rian-van-heerden/5-ingredients-perfect-umqombothi/ (accessed on 3 September 2020).
- Lukinac, J.; Habschied, K.; Mastanjević, K.; Nakov, G.; Jukić, M. Computer Vision Method in Beer Quality Evaluation—A Review. Beverages 2019, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdoul-latif, F.; Bassolé, I.; Dicko, M. Proximate composition of traditional local sorghum beer “dolo” manufactured in Ouagadougou. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Xu, X. Sprouted grains-based fermented products. Sprouted Grains 2019, 7, 143–173. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, D.O. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy—A Review. Nutrients 2016, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yolmeh, M.; Jafari, S.M. Applications of Response Surface Methodology in the Food Industry Processes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; Daari, K.; O’Sullivan, O.; Martin, J.C.; Arthur, C.T.; Claesson, M.J.; Scott, K.P.; Cotter, P.D. Strain-Level Metagenomic Analysis of the Fermented Dairy Beverage Nunu Highlights Potential Food Safety Risks. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wu, G. Dietary essentiality of “nutritionally non-essential amino acids” for animals and humans. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Wu, G. Nutritionally Essential Amino Acids. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-H.; Coloff, J.L. The Diverse Functions of Non-Essential Amino Acids in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romano, C.; Corsetti, G.; Flati, V.; Pasini, E.; Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Marzetti, E.; Dioguardi, F.S. Influence of Diets with Varying Essential/Nonessential Amino Acid Ratios on Mouse Lifespan. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokoena, M.P.; Mutanda, T.; Olaniran, A.O. Perspectives on the probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria from African traditional fermented foods and beverages. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 29630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Heerden, I. Nutrient content of sorghum beer strainings. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 1987, 17, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Van Heerden, I.V. The nutritive content of african beers brewed with maize grits or sorghum adjunct. J. Inst. Brew. 1989, 95, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.W.; Baird, P.; Davis, R., Jr.; Ferreri, S.; Knudtson, M.; Koraym, A.; Waters, V.; Williams, C.L. Health benefits of dietary fiber. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarczyk, M.M.; Miller, M.J.; Freund, G.G. The health benefits of dietary fiber: Beyond the usual suspects of type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and colon cancer. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ötles, S.; Ozgoz, S. Health effects of dietary fiber. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2014, 13, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selhub, E.M.; Logan, A.C.; Bested, A.C. Fermented foods, microbiota, and mental health: Ancient practice meets nutritional psychiatry. J. Physiol. Anthr. 2014, 33, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.; Hong, V.M.; Yang, J.; Hyun, H.; Im, J.J.; Hwang, J.; Yoon, S.; Kim, J.E. A Review of Fermented Foods with Beneficial Effects on Brain and Cognitive Function. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 21, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şanlier, N.; Gökcen, B.B.; Sezgin, A.C. Health benefits of fermented foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 506–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, H.; Green, J.; Jacka, F.N.; Collier, F.; Berk, M.; Pasco, J.; Dawson, S.L. Fermented foods, the gut and mental health: A mechanistic overview with implications for depression and anxiety. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Chaiyasut, C. Impact of Fermented Foods on Human Cognitive Function—A Review of Outcome of Clinical Trials. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 86, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Walt, J.P. Kaffircorn malting and brewing studies. II.—Studies on the microbiology of Kaffir beer. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1956, 7, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Walt, J. Better Kaffir beer. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1954, 50, 221. [Google Scholar]
- Capozzi, V.; Fragasso, M.; Romaniello, R.; Berbegal, C.; Russo, P.; Spano, G. Spontaneous Food Fermentations and Potential Risks for Human Health. Fermentation 2017, 3, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbegal, C.; Khomenko, I.; Russo, P.; Spano, G.; Fragasso, M.; Biasioli, F.; Capozzi, V. PTR-ToF-MS for the Online Monitoring of Alcoholic Fermentation in Wine: Assessment of VOCs Variability Associated with Different Combinations of Saccharomyces/Non-Saccharomyces as a Case-Study. Fermentation 2020, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, V.; Fragasso, M.; Russo, P. Microbiological Safety and the Management of Microbial Resources in Artisanal Foods and Beverages: The Need for a Transdisciplinary Assessment to Conciliate Actual Trends and Risks Avoidance. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyanzi, R.; Jooste, P. Cereal-Based Functional Foods. Probiotics 2012, 161–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shephard, G.S.; Van Der Westhuizen, L.; Gatyeni, P.M.; Somdyala, N.I.M.; Burger, H.-M.; Marasas, W.F.O. Fumonisin Mycotoxins in Traditional Xhosa Maize Beer in South Africa. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9634–9637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hijum, S.A.; Vaughan, E.E.; Vogel, R.F. Application of state-of-art sequencing technologies to indigenous food fermentations. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.M.; Pipingas, A.; White, D.; Gauci, S.; Scholey, A.B. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of B Vitamin Supplementation on Depressive Symptoms, Anxiety, and Stress: Effects on Healthy and ‘At-Risk’ Individuals. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behera, S.S.; Ray, R.C.; Zdolec, N. Lactobacillus plantarum with Functional Properties: An Approach to Increase Safety and Shelf-Life of Fermented Foods. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9361614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, F.; Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Xia, X.; Du, G. Characterization of a Lactobacillus brevis strain with potential oral probiotic properties. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghmouchi, K.; Belguesmia, Y.; Bendali, F.; Spano, G.; Seal, B.S.; Drider, D. Lactobacillus fermentum: A bacterial species with potential for food preservation and biomedical applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercolini, D. High-Throughput Sequencing and Metagenomics: Moving Forward in the Culture-Independent Analysis of Food Microbial Ecology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3148–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staley, C.; Sadowsky, M.J. Application of metagenomics to assess microbial communities in water and other environmental matrices. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2015, 96, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbegal, C.; Borruso, L.; Fragasso, M.; Tufariello, M.; Russo, P.; Tognetti, R.; Spano, G.; Capozzi, V. A Metagenomic-Based Approach for the Characterization of Bacterial Diversity Associated with Spontaneous Malolactic Fermentations in Wine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, P.; Fiocco, D.; Albenzio, M.; Spano, G.; Capozzi, V. Microbial Populations of Fresh and Cold Stored Donkey Milk by High-Throughput Sequencing Provide Indication for A Correct Management of This High-Value Product. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makinde, O.M.; Ayeni, K.I.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R.; Adeleke, R.A.; Ezekiel, C.N. Microbiological safety of ready-to-eat foods in low-and middle-income countries: A comprehensive 10-year (2009 to 2018) review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 703–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, S.R.; Mammel, M.K.; Lacher, D.W.; Elkins, C.A. Application of Metagenomic Sequencing to Food Safety: Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli on Fresh Bagged Spinach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 8183–8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, M.B.; De Oliveira, H.C.; Núñez, E.G.F.; Rocha, J.C. Brewing process optimization by artificial neural network and evolutionary algorithm approach. J. Food Process. Eng. 2019, 42, e13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibundu, N.E.; Kolawole, I.A.; Jane, M.M.; Yinka, M.S.; Ihuoma, E.C.; Oluwawapelumi, A.O.; Wilfred, A.A.; Michael, S.; Gordon, S.S.; Rudolf, K. Traditionally Processed Beverages in Africa: A Review of the Mycotoxin Occurrence Patterns and Exposure Assessment. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 334–351. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, H.-M.; Lombard, M.; Shephard, G.S.; Rheeder, J.; Van Der Westhuizen, L.; Gelderblom, W. Dietary fumonisin exposure in a rural population of South Africa. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsheka, M.; Magwamba, C.; Mpuchane, S.; Gashe, B. Biogenic amine producing bacteria associated with three different commercially fermented beverages in Botswana. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magwamba, C.; Matsheka, M.I.; Mpuchane, S.; Gashe, B.A. Detection and Quantification of Biogenic Amines in Fermented Food Products Sold in Botswana. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasekan, O. Biogenic amines in traditional alcoholic beverages produced in Nigeria. Food Chem. 2000, 69, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, C. The change of the staple diet of black South Africans from sorghum to maize (corn) is the cause of the epidemic of squamous carcinoma of the oesophagus. Med. Hypotheses 2005, 64, 658–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, C.; Mothobi, P.; Hale, M.; Tomar, L.K.; Tyagi, C.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Altini, M.; Pillay, V. Carcinogenic nitrosamines in traditional beer as the cause of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma in black South Africans. S. Afr. Med J. 2015, 105, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sate Wants A Say in How to Make Beer. Available online: https://www.news24.com/news24/southafrica/news/state-wants-a-say-in-how-to-make-beer-20170722 (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Kana, E.B.G.; Oloke, J.K.; Lateef, A.; Oyebanji, A. Comparative evaluation of artificial neural network coupled genetic algorithm and response surface methodology for modeling and optimization of citric acid production by Aspergillus niger MCBN297. Chem. Eng. 2012, 27, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Basheer, I.; Hajmeer, M. Artificial neural networks: Fundamentals, computing, design, and application. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 43, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewsynker-Sukai, Y.; Faloye, F.; Kana, E.B.G. Artificial neural networks: An efficient tool for modelling and optimization of biofuel production (a mini review). Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2017, 31, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madamba, P. The Response Surface Methodology: An Application to Optimize Dehydration Operations of Selected Agricultural Crops. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 2002, 37, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwabueze, T.U. Review article: Basic steps in adapting response surface methodology as mathematical modelling for bioprocess optimisation in the food systems. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, R.; Travaglioni, M.; Piscitelli, G.; Petrillo, A.; De Felice, F. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications in Smart Production: Progress, Trends, and Directions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simeone, O. A Very Brief Introduction to Machine Learning With Applications to Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 648–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatiha, B.; Sameh, B.; Youcef, S.; Zeineddine, D.; Nacer, R. Comparison of artificial neural network (ann) and response surface methodology (rsm) in optimization of the immobilization conditions for lipase from Candida rugosa ON AMBERJET® 4200-Cl. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 43, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyed, R. Computational Biotechnology: An Approach in Silico Based Modeling Bioprocess. Int. J. Res. Stud. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, Y.; Wilson, R.; Weber, S. Methods of Measuring Enzysme Activity Ex Vivo and In Vivo. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 11, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. AI, big data, and robots for the evolution of biotechnology. Genom. Inform. 2019, 17, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, A.L. Biotechnology, Big Data and Artificial Intelligence. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 14, e1800613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salam, O.; Okwu, M. Comparison of Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) in modelling of waste coconut oil ethyl esters production. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2018, 41, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A. Machine learning algorithms: A review. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2016, 7, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Littmann, M.; Selig, K.; Cohen-Lavi, L.; Frank, Y.; Hönigschmid, P.; Kataka, E.; Mösch, A.; Qian, K.; Ron, A.; Schmid, S.; et al. Validity of machine learning in biology and medicine increased through collaborations across fields of expertise. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsh, K.; Bharath, N.; Siddesh, C.; Kuldeep, S. An Introduction to Artificial Neural Network. Int. J. Adv. Res. Innov. Ideas Educ. 2016, 1, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mewa-Ngongang, M.; Du Plessis, H.W.; Ntwampe, S.; Chidi, B.S.; Hutchinson, U.F.; Mekuto, L.; Jolly, N.P. Grape Pomace Extracts as Fermentation Medium for the Production of Potential Biopreservation Compounds. Foods 2019, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mewa-Ngongang, M.; Du Plessis, H.W.; Hlangwani, E.; Ntwampe, S.; Chidi, B.S.; Hutchinson, U.F.; Jolly, N.P. Activity Interactions of Crude Biopreservatives against Spoilage Yeast Consortia. Fermentation 2019, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, S.; Panda, A.; Bisht, S.; Kumar, N. Microbial Ecology in the Era of Next Generation Sequencing. J. Next Gener. Seq. Appl. 2015, 1, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulas, A.; Pavloudi, C.; Polymenakou, P.; Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Papanikolaou, N.; Kotoulas, G.; Arvanitidis, C.; Iliopoulos, L. Metagenomics: Tools and Insights for Analyzing Next-Generation Sequencing Data Derived from Biodiversity Studies. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2015, 9, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adebo, O.A.; Oyeyinka, S.A.; Adebiyi, J.A.; Feng, X.; Wilkin, J.D.; Kewuyemi, Y.O.; Abrahams, A.M.; Tugizimana, F. Application of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS)-based metabolomics for the study of fermented cereal and legume foods: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Day | Ingredients | Utensil(s) | Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 L lukewarm water, 1 kg sorghum malt, 1 kg mealie meal, and 1 kg wheat malt | 20 L bucket, blanket (optional) | Mix ingredients together in a 20 L bucket. Place lid on top without sealing it and allow fermentation to proceeded overnight in a warm area or covered with a blanket and/or placed next to a fire (in winter times). |
| 2 | - | Large container, iron-cast pot | Resuspended ingredients by stirring. Fill a large pot with between 1/5 and 3/5 of water and heat to boiling point. Add the fermented mixture to the boiling water until a slurry is formed. The cooked slurry is left on a large container and allowed to cool throughout the rest of the day and overnight. |
| 3 | Wheat malt and previously cooked slurry | Blanket (optional) | A sufficient amount (1–3 kg) of wheat malt is added to the porridge. The mixture is gently stirred and allowed to ferment overnight in a warm area or covered with a blanket and/or placed next to a fire (in winter times). |
| 4 | - | Woven sieve (ivovo), a traditional beer-drinking vessel (ukhamba) | The fermented mixture is stirred and the beer strained using a woven sieve (ivovo) to remove unwanted suspended solids. The desired beer can then be served on ukhamba and stored in large plastic drum (gogogo). |
| Fermentation Time (h) | Fermentation Temperature (°C) | Mash Cooking Time (h) | Mash Cooking Temperature (°C) | Secondary Fermentation Time (h) | Secondary Fermentation Temperature (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 72 | 25–30 | 3–5 | NR | 120–168 | 25–30 | [9] |
| 10–12 | RT | 3 | NR | 12–24 | 25 | [8] |
| 8 | 28–29 | 2.5 | 106 | NR | NR | [1] |
| 24 | 25–30 | NR | NR | 24–48 | 25–30 | [12] |
| 24 | NR | NR | NR | 18 | NR | [10] |
| 14 | 30 | 0.3 | 90 | NR | 4 | [24] |
| 12–48 | NR | 0.8 | NR | 24 | NR | [21] |
| 24–72 | NR | 4 | NR | 24–72 | NR | [22] |
| 24 | NR | 2 | NR | 24 | 50 | [14] |
| 18–20 | 48–50 | 1.5–2 | 50–60 | 25 | 25 | [23] |
| NR | 48–50 | 1.5–3 | 98 | 25 | 25 | [16] |
| Nutritional Parameters | Nutrient per 100 g | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Calories (kJ) | 130.12–394 | [8,27,34,44] |
| Dietary fibre (g) | 5–14.5 | [45] |
| Protein (g) | 0.5–8.7 | [8,27,34] |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 3.6–4.8 | [8,34] |
| Thiamine—B1 (mg) | 0.1–3.4 | [8,27] |
| Riboflavin—B2 (mg) | 0.05–0.76 | [8,27] |
| Niacin—B3 (mg) | 0.008–0.4 | [8,27] |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) (mg) | 0.09 | [8] |
| Pyridoxin—B6 (mg) | 0.17–0.59 | [7] |
| Folic acid—B9 (mg) | 0.2 | [7] |
| Cyanocobalamin—B12 (µg) | 0.03 | [8] |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 0.04 | [8] |
| Leucine (g) | 11.74–14.8 | [7] |
| Lysine (g) | 7.2 | [27] |
| Phenylalanine (g) | 4.03–5.62 | [7] |
| Tryptophan (g) | 0.9–1.16 | [7] |
| Valine (g) | 4.22–6.86 | [7] |
| Aspartic acid (g) | 4.83–7.06 | [7] |
| Glutamic acid (g) | 17.50–28.12 | [7] |
| Alanine (g) | 7.34–9.62 | [7] |
| Calcium (mg) | 2.2–20.7 | [8,27] |
| Magnesium (mg) | 144 | [45] |
| Zinc (mg) | 2.84 | [45] |
| Sodium (mg) | 1.1–26.7 | [8,27] |
| Manganese (mg) | 1.91 | [45] |
| Potassium(mg) | 84–1101 | [8,27] |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 39 | [8] |
| Iron (mg) | 2.55–6.08 | [8,20,45] |
| Concentration (mg) | RDA (mg) | % Contribution/L of Beer to RDA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | 178 | 350 | 51 |
| Mn | 1.83 | 4 | 46 |
| P | 305 | 800 | 38 |
| Fe | 3.44 | 10 | 34 |
| Zn | 1.94 | 15 | 13 |
| K | 407 | 3760 | 11 |
| Cu | 0.27 | 3 | 9 |
| Ca | 52 | 800 | 7 |
| Na | 18 | 2300 | 1 |
| Bacteria | aNo | BGA Content (mg/100 mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| His | Put | Cad | Tyr | ||
| Endospore formers | |||||
| Bacillus subtilis | 80 | 1.86 | 0.10 | 0.122 | 0.1 |
| B. thermoglucosidasius | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| B. cereus | 20 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 19.8 | 3.45 |
| B. laevolacticus | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| B. halodurans | 48 | 1.05 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 1.772 |
| B. megaterium | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| B. coagulans | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Paenibacillus azotofixans | 39 | ND | 4.04 | 2.36 | 1.88 |
| Clostridium spp. | 67 | 1.11 | 0.23 | 0.42 | 1.01 |
| Enterobacteriaceae | |||||
| Enterobacter aerogenes | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| E. intermedius | 64 | ND | 7.50 | ND | 2.02 |
| C. freundii | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| C. braakii | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Hafnia alvei | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Escherichia coli | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Pantoea citrea | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Pseudomonads | |||||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens/putida | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| P. seudomonas spp. | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Staphylococcus | |||||
| Staphylococcus epidermis | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| S. auricularis | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| S. arlettae | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| S. aureus | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Lactic acid bacteria | |||||
| Enterococcus faecium | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Ent. faecalis | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Ent. gallinarum | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Lactobacillus spp. | 67 | ND | ND | ND | NR |
| Carnobacterium gallinarum | 52 | ND | ND | ND | NR |
| Streptococcus oralis | 35 | 2.34 | 4.20 | 3.81 | NR |
| Lactococcus raffinolacticus | 29 | ND | ND | ND | NR |
| Pediococcus dextrinicus | 23 | ND | ND | ND | NR |
| Leuconostoc mesenteroides | ND | ND | ND | ND | NR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hlangwani, E.; Adebiyi, J.A.; Doorsamy, W.; Adebo, O.A. Processing, Characteristics and Composition of Umqombothi (a South African Traditional Beer). Processes 2020, 8, 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111451
Hlangwani E, Adebiyi JA, Doorsamy W, Adebo OA. Processing, Characteristics and Composition of Umqombothi (a South African Traditional Beer). Processes. 2020; 8(11):1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111451
Chicago/Turabian StyleHlangwani, Edwin, Janet Adeyinka Adebiyi, Wesley Doorsamy, and Oluwafemi Ayodeji Adebo. 2020. "Processing, Characteristics and Composition of Umqombothi (a South African Traditional Beer)" Processes 8, no. 11: 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111451
APA StyleHlangwani, E., Adebiyi, J. A., Doorsamy, W., & Adebo, O. A. (2020). Processing, Characteristics and Composition of Umqombothi (a South African Traditional Beer). Processes, 8(11), 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111451