Management of mining processes and monitoring of their performance is a basic prerequisite for continual improvement, elimination of waste, the introduction of innovations in mining, gaining competitive advantages, and application in the competitive environment of the mining industry by the view of sustainable development and economic growth. Jiskani et al. (2020) support the argument that improving the competitiveness of the mining industry aids in the promotion of its sustainable development by the SWOT analysis for the mining industry. Jiskani et al. (2021) [
1] comment that the performance indicators are evaluated in smart mining, but it is important to the importance of performance indicators framework should be highlighted. Cehlár et al. (2019) [
2] stated that the new mining machines mean improving mining operations, more efficiently boosting productivity and employee safety, and opportunities for future use of earth resources and new technologies in the mining industry [
3]. Optimization of the mining area and its layout means competitiveness in the market of mining industries (quality management). Jiskani et al. (2020) described the importance of mine optimization, safety, and green mining strategy as an essential pathway to achieving sustainable mining. The role of mining safety and green mining for sustainable mining is the base idea for future mining [
4]. Krupnik et al. (2020) stated that process and operation management and mining process improvement represent an approach that enables to ensure the maximum performance of mining processes, to fill in the strategic goals of the mining companies, and to ensure the competitiveness on the mining industry market [
5]. Sutoová et al. (2018) stated that the achievement of the performance in mining processes means focusing on innovation, developing knowledge, improving internal processes, eliminating waste, minimizing costs, improving technology, and using production factors effectively [
6]. Zhou et al. (2020) stated the concept of green mining is to improve the mining industry in a holistic way so that it is safe, efficient, and environmentally sustainable. They created an evaluation index system of green surface mining based on the theory of green grades. The evaluation model is comprised of three attributes (safety, efficiency, and environment), nine criteria, and 35 indicators [
7]. Chen et al. (2020) presented the idea of green mining was proposed as a practical approach to making the mining industry more sustainable than before. Green mining is a contemporary mining model centered on the sustainability of resources, environment, and socio-economic benefits. Its purpose is to develop and apply technologies and processes that increase environmental performance, while maintaining competitiveness throughout the entire mining cycle from exploration to post-closure [
8]. The main goal of the paper was to evaluate the performance indicators of mining processes after the implementation of strategic innovation—a new layout of the mining area focused on a combination of stationary and mobile mining equipment. Mining processes relate to negative environmental impacts (environmental management) and high energy consumption (energy management). Mirmozaffari et al. (2020) stated that it is important continually to evaluate ecological efficiency affected by CO2 consumption that is one part of the performance of mining processes [
9]. Negative impacts of mining processes to the adjacent territories create a base for evaluation. The contamination of territories is developed by active seepage of liquid waste of mining (waste management). Menshikova et al. (2020) commented particularly important is to evaluate water balance in the mining processes and a significant amount of wastewater (water management). The results of performance indicators are to substantiate the need to manage the seepage discharge process by means of enclosing dams to ensure environmentally safe operation of the tailings dump [
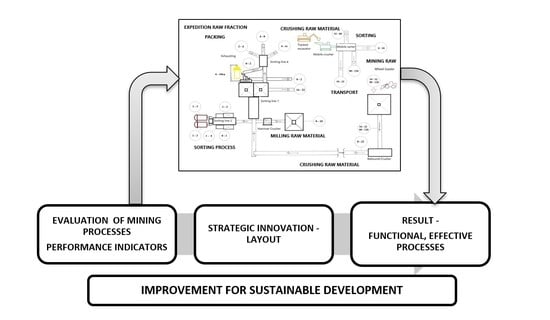
10]. The growing availability of information and data analysis capabilities provides new opportunities for improving the performance of mining operations. By using real-time measurements and artificial intelligence, it is possible to respond faster to changing conditions, while accurate and timely information permits rapid evaluation of changes and fast business improvement decisions (operation management). The base of the blueprint is a performance framework (
Figure 1) with a system of key performance indicators for mining control.
The synergy of all various forms of management creates the base of improvement in mining companies. Visser et al. (2020) commented that the introduction of the blueprint for operations management enables mines to leverage the developments in information and analysis capabilities to improve the performance of operations and prevention of risks (risk management) [
11]. An important part of performance evaluation in mining companies is effective risk management in mining. Jiskani et al. (2020) stated that the significance of risk identification, risk analysis, and risk management for sustainable development in the mining industry must be highlighted. Sustainability has always been a core concern in the mining industry because the exploitation of mineral resources poses adverse impacts on the environment and society. As a result, the industry is seeking spectacular progress to foster sustainable mining practices that can enable it to be financially viable, environmentally friendly, and socially responsible. Since mining is inevitably endemic with risks, risk assessment could enable the industry to deal with the risks that have significant impacts on its sustainable development [
12]. Risk needs to be properly identified before it may be estimated and later responded to adequately. Tworek et al. (2018) stated that prerequisite is an effective system of risk management in mining [
13]. One part of risk management in the mining area is the health and safety management system. Health risk management depends on mining technologies, mining areas, and mining processes (Risk management) [
14]. The best important part of management is financial and cost management in mining companies. Typical responses by mining companies are to cut costs or increase production what is presented as financial indicators—profit, revenues, and costs. Hall et al. (2003) stated that economic risk is important to know in mining companies. Most mineral deposits respond to increased production rates. Many mine failures can be prevented by a close examination of the tonnage grade curve and an understanding of how margins, net cash flows, and resulting business risk change with cut-off grades and rates of production. The synergy effect of cost and financial management is a base for improvement in mining companies [
15]. The economic situation of mining companies entails a strategic approach to cost reduction planning. The slowdown of the economy forces the business sector to restructure and reduction of cost, proceeding to rationalization processes which leads to optimization of mining processes, increasing of machine utilization, the use of materials, and people. Domaracká et al. (2013) commented that for the right decision-making it is necessary to have information about the financial situation and about critical areas in the mining process during risk management [
16]. Puzder et al. (2017) commented that one of the risks in mining companies is an economic indicator—cost ratio. The cost ratio indicator is the fundamental performance indicator of the mining companies and it is important to create a cost model for its evaluation orientated to minimize mining costs [
17]. The next problem for evaluation of the performance of mining is sustainable development and is it attracting new investment. Solving it requires access to international capital markets and preparing financial statements with international requirements based on the data generated by the accounting system. Tyuleneneva (2017) stated that the framework of international financial reporting standards is important to base for new investment in mining companies [
18]. Evaluation of the performance of mining must be introduced through the life cycle assessment (LCA). The mining industry is a potential field where sustainability and LCA can be implemented due to intense energy requirements and equipment utilization [
19]. LCA is beginning with the mining process. The rationalization of the transportation of raw material in a mining company creates a base for other processes for example sorting, milling, and crushing. The application of generally applicable logistics principles may result in the increased efficiency of the transportation process. The main input of the rationalization proposal is the analysis of technical parameters of belt conveyors and following their optimization [
20]. All mining processes would have to be managed effectively. Strategic development in mining companies is orientated to vertical integration. It means using outsourcing for the specific needs of the basic mining company during the IPO chain. The integration process may concern mining, processing, or mining–processing–metallurgical operations [
21]. Bye (2007) stated that in the frame of strategic development is important to evaluate mining areas not only for grade and tonnage predictions but also for predictions of rock mass quality. The development of 3D multi-parametric models facilitates the provision of resource information well in advance of the mining. This information can be used for overall mine planning and evaluation, costing, mining optimization, and slope design. This allows the full range of mining activities to be interconnected, thereby lowering costs and improving efficiencies [
22]. Mining companies using simulation modeling as an integral component in their development to determine which combination of infra-structure options, operating performance, and operating rules best achieve the goals of the mining process [
23]. Except for simulation, models are used, namely, the technical–economic model for calculating a suitable mining method with accepted technical and economic factors [
24]. The conventional discontinuity survey process in the mining industry to be a time-consuming one and it is technically challenging due to the limited accessibility of fresh rock exposures. A rapid and robust rock mass property quantification system is desirable for rock structure design during mining operations. An image-based and fully automatic rock mass geological strength index (GSI) rating system is used in praxis. The GSI system includes both structure rating (SR) and joint condition digital imaging (JCDI) to represent the bulk rock and discontinuity surface conditions of the rock mass [
25]. Information management is today part of mining processes. The raw material policy is focused on the performance of all mining processes. Performance indicators of mining processes show to efficiency and functionality of mining processes. In developed countries, support tools for process optimization are increasingly used, which ultimately affects the quality of the final product [
26]. Process management can be provided by managerial approaches (
Figure 2), which are focused on special areas of management.
In this paper, we used instruments of various forms of management and we showed how important a synergy of forms of management is in the mining companies. The main goal of the paper was to evaluate the performance indicators of mining processes after the implementation of strategic innovation—a new layout of the mining area focused on a combination of stationary and mobile mining equipment and their influence on the environment in a selected mining company in Slovakia in area of mining for limestone.
The most frequently implemented management approaches in mining companies include: facility management (FM), activity-based management (ABM), project management (PM), and human resource management (HRM), alongside other forms of management that are presented in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2. These managerial approaches focus on mining processes to shorten the time of product implementation, utilization of input resources in a particular process, sensitivity to the interconnection of activities in the process, risk documentation, and consistency and completeness in filling reports, records, and processed documentation. The orientation of process management is focused on measuring key performance indicators of mining processes, which are in the synergy of other management approaches.