Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Silica Modified with Purpald and Its Application in the Preconcentration of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from Aqueous Samples through Solid-Phase Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solvents, Solutions, and Reactants
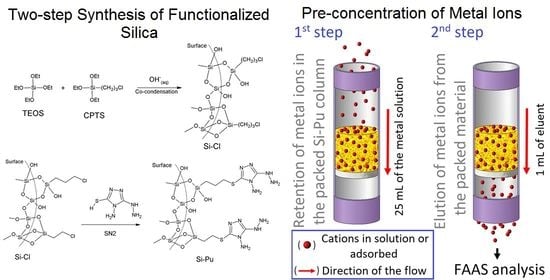
2.2. Synthesis of the Silica by Co-Condensation
2.3. Characterization of the Material
2.4. Functionalization of the Material
2.5. Point of Zero Charge (PZC) Experiment
2.6. Adsorption and Reutilization Experiments
2.7. Off-Line Flow Pre-Concentration System
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Materials
3.1.1. C and N Elemental Analysis
3.1.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
3.1.3. Determination of the Specific Surface Area by the BET Method
3.1.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.1.5. 29Si- and 13C-NMR Analysis
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
3.2.1. pH Effect
3.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.2.3. Determination of the Maximum Adsorption Capacity
3.3. Preconcentration Experiments
3.3.1. Optimization of the Parameters of the Preconcentration System for Cu(II) and Cd(II)
3.3.2. Effect of Potentially-Interfering Ions for the Preconcentration of Cu(II) and Cd(II)
3.3.3. Figure of Merit for the Cu(II) and Cd(II) Preconcentration System
3.3.4. Determination of Metal Ions in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of Heavy Metals on the Environment and Human Health: Novel Therapeutic Insights to Counter the Toxicity. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.d.A.; Arruda, M.A.Z.; Ferreira, S.L.C. Cloud Point Extraction as a Procedure of Separation and Pre-Concentration for Metal Determination Using Spectroanalytical Techniques: A Review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2005, 40, 269–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater: A Comprehensive and Critical Review. Npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodia, T.Z.; David, A.A.; Chesney, A.P.; Perri, J.N.; Gutierrez, G.E.; Nepple, C.M.; Isbell, S.M.; Cash, K.J. Nanoparticle-Based Liquid–Liquid Extraction for the Determination of Metal Ions. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 4408–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.A.; Arain, M.B.; Soylak, M. Nanomaterials-Based Solid Phase Extraction and Solid Phase Microextraction for Heavy Metals Food Toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Tehrani, A.A.; Shemirani, F.; Morsali, A. Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks as Selective Microporous Materials for Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions. Dalt. Trans. 2016, 45, 9193–9200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Show, P.-L.; Lau, B.F.; Chang, J.-S.; Ling, T.C. New Prospects for Modified Algae in Heavy Metal Adsorption. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Ge, X. Fabrication of Fibrous Amidoxime-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Microsphere and Its Selectively Adsorption Property for Pb2+ in Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Hou, G.; Li, J.; Wen, T.; Ren, X.; Wang, X. PANI/GO as a Super Adsorbent for the Selective Adsorption of Uranium(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Abdel-Latif, D.A.; Abou El-Reash, Y.G. Ion-Imprinted Modified Chitosan Resin for Selective Removal of Pd(II) Ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 469, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, E.; Yamini, Y. Polythiophene-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as a Selective Adsorbent for Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Silver(I), Gold(III), Copper(II) and Palladium(II). Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, H.A.; Marwani, H.M.; Soliman, E.M. Selective Solid Phase Extraction and Determination of Trace Pd(II) Using Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Modified with 8-Aminoquinoline. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 232, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-R.; Yu, K.; Ravi, S.; Ahn, W.-S. Selective Adsorption of Rare Earth Elements over Functionalized Cr-MIL-101. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 23918–23927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenawy, I.M.M.; Abou El-Reash, Y.G.; Hassanien, M.M.; Alnagar, N.R.; Mortada, W.I. Use of Microwave Irradiation for Modification of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Thioglycolic Acid for Removal of Cadmium and Mercury. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 258, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losev, V.N.; Buyko, O.V.; Trofimchuk, A.K.; Zuy, O.N. Silica Sequentially Modified with Polyhexamethylene Guanidine and Arsenazo I for Preconcentration and ICP–OES Determination of Metals in Natural Waters. Microchem. J. 2015, 123, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendil, D.; Demirci, Z.; Uluozlu, O.D.; Tuzen, M.; Soylak, M. A New Separation and Preconcentration Method for Selenium in Some Foods Using Modified Silica Gel with 2,6-Diamino-4-Phenil-1,3,5-Triazine. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Suzuki, T.; Sugita, T.; Nagai, D.; Hirayama, K.; Onozato, M.; Itabashi, H. Heavy Metal Adsorptivity of Calcium-Alginate-Modified Diethylenetriamine-Silica Gel and Its Application to a Flow Analytical System Using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 840, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Lu, S.; Liu, F.; Feng, X.; He, J.; Koopal, L.K. Determination Of The Point-of-Zero Charge of Manganese Oxides with Different Methods Including An Improved Salt Titration Method. Soil Sci. 2008, 173, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 9781118311653. [Google Scholar]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems. In Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008; pp. 1217–1230. ISBN 9783527610044. [Google Scholar]
- Sindorf, D.W.; Maciel, G.E. Cross-Polarization Magic-Angle-Spinning Silicon-29 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of Silica Gel Using Trimethylsilane Bonding as a Probe of Surface Geometry and Reactivity. J. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 5208–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökce, H.; Ceylan, S.; Öztürk, N.; Sert, Y. Tautomeric, Spectroscopic, Electronic and NLO Analyses of Purpald (4-Amino-3-Hydrazino-5-Mercapto-1,2,4-Triazole). Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 103862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revellame, E.D.; Fortela, D.L.; Sharp, W.; Hernandez, R.; Zappi, M.E. Adsorption Kinetic Modeling Using Pseudo-First Order and Pseudo-Second Order Rate Laws: A Review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Akhter, M.; Iqbal, M. Removal and Recovery of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution Using Papaya Wood as a New Biosorbent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 45, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y. Review of Second-Order Models for Adsorption Systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, N.; Guo, X.; Liang, S. Adsorption Study of Copper (II) by Chemically Modified Orange Peel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, V.A.; Laranjeira, M.C.M.; Fávere, V.T.; Kimura, I.Y. Cinética e Equilíbrio de Adsorção Dos Oxiânions Cr (VI), Mo (VI) e Se (VI) Pelo Sal de Amônio Quaternário de Quitosana. Polímeros 2005, 15, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.G. Hard and Soft Acids and Bases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3533–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Jorgetto, A.; Pereira, S.P.; Da Silva, R.I.V.; Saeki, M.J.; Martines, M.A.U.; De Albuquerque Pedrosa, V.; De Castro, G.R. Application of Mesoporous SBA-15 Silica Functionalized with 4-Amino-2-Mercaptopyrimidine for the Adsorption of Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(II), Ni(II), and Pb(II) from Water. Acta Chim. Slov. 2015, 62, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, F.N.; Ayyilidiz, H.F.; Kara, H.; Memon, S.; Kenar, A.; Leghari, M.K.; Topkafa, M.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Memon, N.A.; Durmaz, F.; et al. Application of Central Composite Design for the Optimization of On-Line Solid Phase Extraction of Cu2+ by Calix[4]Arene Bonded Silica Resin. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 146, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, M.; Feng, C.; Zeng, Q. Preparation and Characterization of Multi-Carboxyl-Functionalized Silica Gel for Removal of Cu (II), Cd (II), Ni (II) and Zn (II) from Aqueous Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ding, P.; Zhou, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Jiao, F. Preparation of Diamine Modified Mesoporous Silica on Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for the Adsorption of Heavy Metals in Aqueous Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 282, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Toni, A.M.; Habila, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Labis, J.P.; ALOthman, Z.A. Simple and Facile Synthesis of Amino Functionalized Hollow Core–Mesoporous Shell Silica Spheres Using Anionic Surfactant for Pb(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) Adsorption and Recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 251, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.W.; Song, K.; Kim, S.H. Synthesis of PPy/Silica Nanocomposites with Cratered Surfaces and Their Application in Heavy Metal Extraction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarley, C.R.T.; Corazza, M.Z.; de Oliveira, F.M.; Somera, B.F.; Nascentes, C.C.; Segatelli, M.G. On-Line Micro-Solid Phase Preconcentration of Cd2+ Coupled to TS-FF-AAS Using a Novel Ion-Selective Bifunctional Hybrid Imprinted Adsorbent. Microchem. J. 2017, 131, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, A.; Amjadi, M. Magnetic Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles Modified with 1-(2-Thiazolylazo)-2-Naphthol as a Novel Solid-Phase Extraction Sorbent for Preconcentration of Copper (II). Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durduran, E.; Altundag, H.; Imamoglu, M.; Yıldız, S.Z.; Tuzen, M. Simultaneous ICP-OES Determination of Trace Metals in Water and Food Samples after Their Preconcentration on Silica Gel Functionalized with N-(2-Aminoethyl)-2,3-Dihydroxybenzaldimine. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 27, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baytak, S.; Kasumov, V.T. Preconcentration and Determination of Copper(II) by Novel Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Resolution Continuum Source Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourreza, N.; Rastegarzadeh, S.; Larki, A. Simultaneous Preconcentration of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II) on Nano-TiO2 Modified with 2-Mercaptobenzothiazole Prior to Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Determination. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2680–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylak, M.; Erbas, Z. Vortex-Assisted Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II) on the Nitroso–R Salt Impregnated Magnetic Ambersorb 563 for Their Separation, Preconcentration and Determination by FAAS. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavid, M.R.; Arabieh, M.; Yousefi, S.R.; Akbari Sehat, A. Interference Free and Fast Determination of Manganese(II), Iron(III) and Copper(II) Ions in Different Real Samples by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy after Column Graphene Oxide-Based Solid Phase Extraction. Microchem. J. 2016, 129, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdes, D.; Duran, C. Preparation of Melon Peel Biochar/CoFe2O4 as a New Adsorbent for the Separation and Preconcentration of Cu(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) Ions by Solid-Phase Extraction in Water and Vegetable Samples. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, S.A.; Soleymanpour, A. Application of L-Cystine Modified Zeolite for Preconcentration and Determination of Ultra-Trace Levels of Cadmium by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1436, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabi, A.; Dalirandeh, Z.; Rad, A.S. Preparation of Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Sorbent for the Preconcentration and Determination of Cadmium Ions in Food and Environmental Water Samples Prior to Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 381, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkalkan, H.; Saygili Canlidinç, R. Investigation of the Conditions for Preconcentration of Cadmium Ions by Solid Phase Extraction Method Using Modified Juglans Regia L. Shells. J. AOAC Int. 2021, 104, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Sample | a SBET (m2 g−1) | b DBJH (nm) | c V (cm3 g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Si-Pucalcined | 489.24 ± 1.12 | 7.1 | 0.89 |
| Si-Pu | 369.84 ± 1.15 | 7.1 | 0.85 |
| Metal | Nf (exp) (mmol g−1) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min −1) | Ne (cal.) (mmol g−1) | R2 | k2 (mmol g−1 min−1) | Ne (cal.) (mmol g−1) | R2 | ||
| Cu(II) | 0.032 | −2.6 × 10−4 | 0.0304 | 0.708 | 10.1 | 0.0326 | 0.999 |
| Cd(II) | 0.0031 | −1.3 × 10−5 | 0.029 | 0.519 | 60.5 | 0.00305 | 0.992 |
| Metal | Nf (max) (exp.) (mmol g−1) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ns (mmol g−1) | b (L mmol−1) | R2 | Kf (mg g−1) | 1/n | R2 | ||
| Cu(II) | 0.057 | 0.064 | 3.334 | 0.993 | 0.382 | 0.549 | 0.946 |
| Cd(II) | 0.018 | 0.022 | 45.70 | 0.601 | 0.039 | 0.825 | 0.985 |
| Adsorbent | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mmol g−1) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu(II) | Cd(II) | ||
| Silica modified with 4-amino-2-mercaptopyrimidine | 0.0123 | 0.0006 | [29] |
| Silica modified with calix[4]arene | 0.026 | -------- | [30] |
| Silica gel modified with diethylenetriamine and calcium alginate | 0.123 | -------- | [17] |
| Multi-carboxyl-functionalized silica gel | 0.740 | 0.369 | [31] |
| Diamine modified mesoporous silica on multi-walled carbon nanotubes | 1.047 | -------- | [32] |
| Silica modified with polyhexamethylene guanidine and Arsenazo I | 0.06 | -------- | [15] |
| Amino-functionalized hollow core–mesoporous shell silica spheres | -------- | 1.69 | [33] |
| Silica-polypyrrole nanocomposite | 0.02 | 0.01 | [34] |
| Mesoporous silica modified with Purpald | 0.057 | 0.018 | This work |
| Variable | Abbreviation | Cu(II) | Cd(II) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−) | High (+) | Low (−) | High (+) | |||||
| pH | pH | 4.0 | 8.0 | 5.1 | 8.0 | |||
| Buffer concentration (mol L−1) | BC | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.1 | |||
| Eluent concentration (mol L−1) | EC | 0.5 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 2.0 | |||
| Sample flow (mL min−1) | SF | 2.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 5.0 | |||
| Abs./Time | ||||||||
| Experiment | pH | BC | EC | SF | Cu(II) | Cd(II) | ||
| 01 | − | − | − | − | 0.01 | 0.002096/0.002632 | ||
| 02 | + | − | − | − | 0.0097 | 0.0056/0.004224 | ||
| 03 | − | + | − | − | 0.0089 | 0.002088/0.003248 | ||
| 04 | + | + | − | − | 0.0087 | 0.003128/0.003144 | ||
| 05 | − | − | + | − | 0.0091 | 0.003232/0.003024 | ||
| 06 | + | − | + | − | 0.0094 | 0.005264/0.0056 | ||
| 07 | − | + | + | − | 0.0083 | 0.003824/0.004856 | ||
| 08 | + | + | + | − | 0.0088 | 0.004488/0.004848 | ||
| 09 | − | − | − | + | 0.0199 | 0.00712/0.00594 | ||
| 10 | + | − | − | + | 0.0231 | 0.0168/0.01526 | ||
| 11 | − | + | − | + | 0.0189 | 0.00642/0.00938 | ||
| 12 | + | + | − | + | 0.0177 | 0.01904/0.1486 | ||
| 13 | − | − | + | + | 0.0169 | 0.0053/0.0057 | ||
| 14 | + | − | + | + | 0.0202 | 0.01586/0.01604 | ||
| 15 | − | + | + | + | 0.0142 | 0.01152/0.01318 | ||
| 16 | + | + | + | + | 0.015 | 0.01574/0.01384 | ||
| Parameter | Magnitude of the Parameter | |
|---|---|---|
| Cu(II) | Cd(II) | |
| Sample volume (mL) | 25 | 25 |
| Adsorbent mass (mg) | 50 | 100 |
| Sample flow (mL min−1) | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Eluent type | HCl + thiourea | HNO3 |
| Eluent concentration (mol L−1) | 0.5 HCl + 0.2 thiourea | 2.0 |
| Buffer concentration (mol L−1) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| pH | 8.0 | 8.0 |
| Analyte | Interfering Ion | Recovery (%) for Distinct Analyte:Interfering Ion Ratios | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:5 | 1:10 | 1:25 | 1:50 | 1:100 | 1:500 | 1:1000 | 1:1500 | ||
| Cu(II) | Na+ | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 100.5 | ------- |
| K+ | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 102.4 | ------- | ------- | |
| Ca2+ | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 105.5 | ------- | |
| Mg2+ | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 98.0 | ------- | ------- | |
| Fe3+ | ------- | 101.7 | ------- | 92.3 | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | |
| Ba2+ | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 96.1 | ------- | ------- | |
| SO42− | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 99.4 | ------- | |
| H2PO4− | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 100.4 | ------- | ------- | |
| Cl− | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 100.5 | |
| Cd(II) | Na+ | 104.1 | 101.5 | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- |
| K+ | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 101.8 | ------- | ------- | |
| Ca2+ | 109.8 | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | |
| Mg2+ | ------- | ------- | 94.0 | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | |
| Fe3+ | 103.6 | 97.6 | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | |
| Ba2+ | ------- | ------- | 102.9 | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | |
| SO42− | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | 94.5 | ------- | ------- | ------- | |
| H2PO4− | ------- | ------- | 102.0 | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | ------- | |
| Analyte | Curve without Preconcentration + (Correlation Coefficient) | Curve with Preconcentration + (Correlation Coefficient) | PF | DL (µg L−1) | QL (µg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu(II) | Abs = 0.150 × [Cu2+] + 0.0033 (R2 = 0.999) | Abs = 2.722 × [Cu2+] + 0.0157 (R2 = 0.999) | 18.1 | 1.45 | 4.8 |
| Cd(II) | Abs = 0.335 × [Cd2+] + 0.0031 (R2 = 0.999) | Abs = 5.268 × [Cd2+] + 0.0032 (R2 = 0.999) | 15.8 | 0.38 | 1.27 |
| Material | Ion | DL (µg L−1) | PF | Sample Volume (mL) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@C nanoparticles modified with 1-(2-thiazolylazo)-2-naphtol | Cu(II) | 1.5 | 50 | 100 | [36] |
| Silica gel funcionalized with N-(2-aminoethyl)-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldimine | 0.098 | 100 | 500 | [37] | |
| Amberlite XAD-4 modified with N-para-anisidine-3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylaldimine | 0.56 | 125 | 50 | [38] | |
| Nano-TiO2 modified with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole | 0.15 | 83.3 | 250 | [39] | |
| Nitroso-R salt impregnated magnetic Ambersorb 563 | 5.8 | 15 | 30 | [40] | |
| Modified graphene | 0.06 | 280 | 1400 | [41] | |
| Mesoporous silica organofunctionalized with Purpald | 1.45 | 18.1 | 25 | This work | |
| Melon peel biochar modified with CoFe2O4 | Cd(II) | 1.82 | 50 | 250 | [42] |
| Nitroso-R salt impregnated magnetic Ambersorb 563 | 1.4 | 15 | 30 | [40] | |
| zeolite modified with l-cysteine | 0.04 | 400 | 800 | [43] | |
| Magnetic nanoparticles modified with surfactant | 3.71 | 100 | 100 | [44] | |
| Juglans regia L. shells modified with hydrazine hydrate | 0.18 | 30 | 150 | [45] | |
| Ion-imprinted nanoparticles | 0.3 | 14 | 10 | [35] | |
| Mesoporous silica organofunctionalized with Purpald | 0.38 | 15.8 | 25 | This work |
| Sample | Ion | Added | Found * | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River water 1 | Cu(II) | 0.0 | 19.79 ± 3.03 | ---------- |
| 50.0 | 67.86 ± 1.62 | 97.3 | ||
| Cd(II) | 0.0 | 5.42 ± 0.69 | ---------- | |
| 10 | 16.05 ± 0.91 | 104.1 | ||
| River water 2 | Cu(II) | 0.0 | 69.76 ± 1.77 | ---------- |
| 50.0 | 115.70 ± 1.94 | 96.6 | ||
| Cd(II) | 0.0 | 0.64 ± 0.21 | ---------- | |
| 10 | 11.24 ± 0.63 | 105.6 | ||
| Tap water | Cu(II) | 0.0 | <LD | ---------- |
| 100.0 | 105.37 ± 2.13 | 105.4 | ||
| Cd(II) | 0.0 | 1.91 ± 0.22 | ---------- | |
| 10 | 12.29 ± 0.57 | 103.2 | ||
| Mineral water | Cu(II) | 0.0 | <LD | ---------- |
| 100.0 | 105.83 ± 3.71 | 105.8 | ||
| Cd(II) | 0.0 | 0.55 ± 0.22 | ---------- | |
| 10 | 11.29 ± 0.61 | 103.2 | ||
| Underground water | Cd(II) | 0.0 | 3.18 ± 1.58 | ---------- |
| 10 | 13.24 ± 2.27 | 100.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wondracek, M.H.P.; Jorgetto, A.d.O.; da Silva, A.C.P.; Schneider, J.F.; Pedrosa, V.d.A.; Saeki, M.J.; de Castro, G.R. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Silica Modified with Purpald and Its Application in the Preconcentration of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from Aqueous Samples through Solid-Phase Extraction. Separations 2023, 10, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020108
Wondracek MHP, Jorgetto AdO, da Silva ACP, Schneider JF, Pedrosa VdA, Saeki MJ, de Castro GR. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Silica Modified with Purpald and Its Application in the Preconcentration of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from Aqueous Samples through Solid-Phase Extraction. Separations. 2023; 10(2):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020108
Chicago/Turabian StyleWondracek, Marcos Henrique Pereira, Alexandre de Oliveira Jorgetto, Adrielli Cristina Peres da Silva, José Fabián Schneider, Valber de Albuquerque Pedrosa, Margarida Juri Saeki, and Gustavo Rocha de Castro. 2023. "Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Silica Modified with Purpald and Its Application in the Preconcentration of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from Aqueous Samples through Solid-Phase Extraction" Separations 10, no. 2: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020108
APA StyleWondracek, M. H. P., Jorgetto, A. d. O., da Silva, A. C. P., Schneider, J. F., Pedrosa, V. d. A., Saeki, M. J., & de Castro, G. R. (2023). Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Silica Modified with Purpald and Its Application in the Preconcentration of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from Aqueous Samples through Solid-Phase Extraction. Separations, 10(2), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020108