Just Suspended Speed Simulation in Torus Reactor Using Multiple Non-Linear Regression Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Sieve Particle Size Analysis
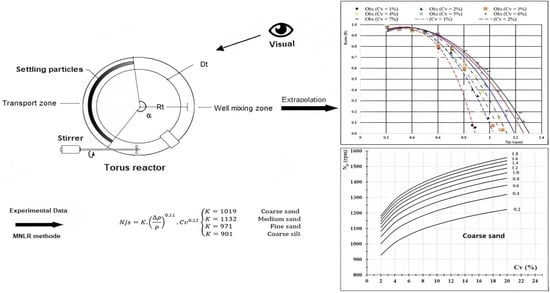
2.2. The Experimental Apparatus Description
2.3. Techniques and Methods for Measurement
2.4. Multiple Nonlinear Regression (MNLR) Model Optimization
2.5. Validation Criteria
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MNLR Simulation Results
3.2. Effect of Particle Concentration
3.3. The Effect of Particle Density
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teoman, B.; Sirasitthichoke, C.; Potanin, A.; Armenante, P.M. Determination of the just-suspended speed, Njs, in stirred tanks using electrical resistance tomography (ERT). AIChE J. 2021, 67, e17354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alouache, A.; Selatnia, A.; Lefkir, A.; Halet, F.; Sayah, H.E.; Nadjemi, B. Determination of the just suspended speed for solid particle in torus reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenante, P.M.; Kirwan, D.J. Mass transfer to microparticles in agitated systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1989, 44, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laederach, H.; Widmer, F. Le bioreacteur torique. Inf. Chim. 1984, 249, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Sendai, T.; Hosogai, K. Flowing characteristics in a circular loop reactor. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1989, 67, 423–427. [Google Scholar]
- Zwietering, T.N. Suspending of solid particles in liquid by agitators. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1958, 8, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienow, A.W. Suspension of solid particles in turbine agitated baffled vessels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1968, 23, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, G.; Conti, R.; Alaria, E. Complete suspension of particles in mechanically agitated vessels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1977, 33, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Raghava Rao, K.; Rewatkar, V.; Joshi, J. Critical impeller speed for solid suspension in mechanically agitated contactors. AIChE J. 1988, 34, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Teoman, B.; Shastry, S.; Abdelhamid, S.; Armenante, P.M. Imaging method for the determination of the minimum agitation speed, Njs, for solids suspension in stirred vessels and reactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 231, 116263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Sun, H.; Liu, W. Solid-liquid suspension in a stirred tank driven by an eccentric-shaft: Electrical resistance tomography measurement. Powder Technol. 2022, 411, 117943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.L.; Atiemo-Obeng, V.A.; Kresta, S.M. Handbook of Industrial Mixing: Science and Practice; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Hao, Z.; Gao, Z.; Shi, L.; Smith, J. Suspension of buoyant particles in a three phase stirred tank. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, A.; Dohi, N.; Kawase, Y. Dispersion of floating solid particles in aerated stirred tank reactors: Minimum impeller speeds for off-surface and ultimately homogeneous solid suspension and solids concentration profiles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwood, D. Reactors. Jpn. Pat. Showa 1962, 37, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Hirose, T.; Hashigushi, Y.; Ono, S.; Ichikawa, M. Flow pattern, circulation velocity and pressure loss in loop reactor. J Chem Eng Jpn 1979, 12, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Hirose, T.; Ono, S.; Eitoku, H.; Nishijima, T. Power Consumption and Pumping Characteristics in a Loop Reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1982, 21, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, L.; Legrand, J.; Popineau, Y.; Belleville, P. Enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat proteins Part 2: Comparison of performance of batch-stirred and torus reactors. Chem. Eng. J. 1997, 65, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ammar, S.; Farid, H.; Lefkir, A.; Sayah, H.; Boubekeur, N. Just Suspended Speed for Solid Particle Transport in TorusReactor. In Green Energy and Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, J.; Gue, J.; Berot, S.; Popineau, Y.; Nouri, L. Acetylation of Pea Isolate in a Torus Microreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 53, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annad, M.; Lefkir, A.; Mammar-Kouadri, M.; Bettahar, I. Development of a local scour prediction model clustered by soil class. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiguzel, D.; Bascetin, A. The investigation of effect of particle size distribution on flow behavior of paste tailings. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleville, P.; Nouri, L.; Legrand, J. Mixing characteristics in the torus reactor. Chem. Eng. Technol. 1992, 15, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, N.; Legrand, J.; Bensmaili, A.; Nouri, L. Effect of impeller type on the mixing in torus reactors. Chem. Eng. Process. 2008, 47, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, J.; Benmalek, N.; Imerzoukene, F.; Yeddou, A.-R.; Halet, F. Characterisation and comparison of the micromixing efficiency in torus and batch stirred reactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 142, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenante, P.M.; Huang, Y.T.; Li, T. Determination of the minimum agitation speed to attain the just dispersed state in solid-liquid and liquid-liquid reactors provided with multiples impellers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1992, 47, 2865–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucato, A.Ã.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G.; Scargiali, F.; Tamburini, A. Particle suspension in top-covered unbaffled tanks. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 3001–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirout, T.; Rieger, F. Impeller design for mixing of suspensions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmani, N.; Zaneti, R.; Akrap, M. Impact of floating suspended solids on the homogenisation of the liquid phasein dual-impeller agitated vessel. Chem. Eng. Process. 2008, 47, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelet, F.; Bakir, F.; Khelladi, S.; Rey, R. Experimental study of hydraulic transport of large particles in horizontal pipes. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2013, 45, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.; Arnold, J.; Van Liew, M.; Bingner, R.; Harmel, R.; Veith, T. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysingha, N.S.; Singh, M.; Sehgal, V.K.; Khanna, M.; Pathak, H.; Jayakody, P.; Srinivasan, R. Assessment of water yield and evapotranspiration over 1985 to 2010 in the Gomti River basin in India using the SWAT model. Curr. Sci. 2015, 108, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Tamburini, A.; Brucato, A.; Busciglio, A.; Cipollina, A.; Grisafi, F.; Micale, G.; Scargiali, F.; Vella, G. Solid-liquid suspensions in top-covered unbaffled vessels: Influence of particle size, liquid viscosity, impeller size, and clearance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9587–9599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| torus reactor | Dt (mm) | Lt (mm) | Rt (mm) |
| 50 | 1400 | 250 | |
| marine screw impeller | d1 (mm) | d2 (mm) | |
| 40 | 6 | 45° |
| Evaluation | R2 (%) | RSR (%) | PBIAS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Very good | |||
| Good | |||
| Satisfactory | |||
| Unsatisfactory |
| Type | D50 (mm) | Density (kg/m3) | Bulk Density (kg/m3) | Diameter Range (mm) | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| River Sand | 1.55 | 2400 | 1300 | 0.63 < dp < 2.00 | Coarse sand |
| Siporex | 0.6 | 1900 | 0635 | 0.2 < dp < 0.63 | Medium sand |
| Sea Sand | 0.62 | 2400 | 1464 | 0.2 < dp < 0.63 | Medium sand |
| Biomass | 0.18 | 1200 | 459 | 0.063 < dp < 0.2 | Fine sand |
| Fine Quartz | 0.05 | 2600 | 947 | 0.02 < dp < 0.063 | Coarse silt |
| Solid Classes | R2 (%) | RSR (%) | PBIAS (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Coarse sand | 97.97 | 25.92 | −0.34 |
| Medium sand | 90.66 | 32.09 | 0.18 | |
| Fine sand | 94.89 | 30.38 | 0.27 | |
| Coarse silt | 98.29 | 13.90 | −0.06 | |
| Global | 95.18 | 22.05 | 0.05 | |
| Validation | 98.47 | 20.38 | −0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayah, H.E.; Alouache, A.; Annad, M.; Lefkir, A.; Nouri, L.; Selatnia, A.; Messaoudi, M. Just Suspended Speed Simulation in Torus Reactor Using Multiple Non-Linear Regression Model. Separations 2023, 10, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020117
Sayah HE, Alouache A, Annad M, Lefkir A, Nouri L, Selatnia A, Messaoudi M. Just Suspended Speed Simulation in Torus Reactor Using Multiple Non-Linear Regression Model. Separations. 2023; 10(2):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020117
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayah, Houssem Eddine, Ali Alouache, Mohamed Annad, Abdelouahab Lefkir, L’hadi Nouri, Ammar Selatnia, and Mohammed Messaoudi. 2023. "Just Suspended Speed Simulation in Torus Reactor Using Multiple Non-Linear Regression Model" Separations 10, no. 2: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020117
APA StyleSayah, H. E., Alouache, A., Annad, M., Lefkir, A., Nouri, L., Selatnia, A., & Messaoudi, M. (2023). Just Suspended Speed Simulation in Torus Reactor Using Multiple Non-Linear Regression Model. Separations, 10(2), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020117