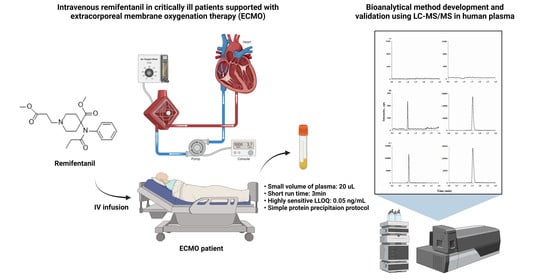
A Sensitive, Simple, and Fast LC–MS/MS Method for Quantification of Remifentanil in Human Plasma: Applications in Critically Ill Patients’ Plasma during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. LC–MS/MS System
2.3. Calibration Standard and Quality Control (QC) Samples
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. Validation of the Method
2.5.1. Selectivity
2.5.2. Linearity and Sensitivity
2.5.3. Carry-Over
2.5.4. Accuracy and Precision
2.5.5. Extraction Recovery and Absolute Matrix Effects
2.5.6. Stability
2.5.7. Incurred Sample Analysis (ISR)
2.6. Clinical Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. LC–MS/MS Condition
3.2. Validation of the Method
3.2.1. Selectivity
3.2.2. Linearity and Sensitivity
3.2.3. Carry-Over
3.2.4. Precision and Accuracy
3.2.5. Extraction Recovery and Absolute Matrix Effects
3.2.6. Stability
3.3. Application to Clinical Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stroumpos, C.; Manolaraki, M.; Paspatis, G.A. Remifentanil, a different opioid: Potential clinical applications and safety aspects. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2010, 9, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beers, R.; Camporesi, E. Remifentanil Update: Clinical science and utility. CNS Drugs 2004, 18, 1085–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapila, A.; Glass, P.S.A.; Jacobs, J.R.; Muir, K.T.; Hermann, D.J.; Shiraishi, M.; Howell, S.; Smith, R.L. Measured Context-sensitive Half-times of Remifentanil and Alfentanil. Anesthesiology 1995, 83, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, L.G.; Hug, C.C., Jr. The pharmacokinetics of remifentanil. J. Clin. Anesth. 1996, 8, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westmoreland, C.L.; Hoke, J.F.; Sebel, P.S.; Hug, C.C.; Muir, K.T. Pharmacokinetics of Remifentanil (GI87084B) and Its Major Metabolite (GI90291) in Patients Undergoing Elective Inpatient Surgery. Anesthesiology 1993, 79, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dershwitz, M.; Hoke, J.F.; Rosow, C.E.; Michalowski, P.; Connors, P.M.; Muir, K.T.; Dienstag, J. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Remifentanil in Volunteer Subjects with Severe Liver Disease. Anesthesiology 1996, 84, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dershwitz, M.; Rosow, C.E. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of remifentanil in volunteers with severe hepatic or renal dysfunction. J. Clin. Anesth. 1996, 8, S88–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoke, J.F.; Cunningham, F.; James, M.K.; Muir, K.T.; Hoffman, W.E. Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of remifentanil, its principle metabolite (GR90291) and alfentanil in dogs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 281, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Breen, D.; Wilmer, A.; Bodenham, A.; Bach, V.; Bonde, J.; Kessler, P.; Albrecht, S.; Shaikh, S. Offset of pharmacodynamic effects and safety of remifentanil in intensive care unit patients with various degrees of renal impairment. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R21–R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitsiu, M.; Wilmer, A.; Bodenham, A.; Breen, D.; Bach, V.; Bonde, J.; Kessler, P.; Albrecht, S.; Fisher, G.; Kirkham, A. Pharmacokinetics of remifentanil and its major metabolite, remifentanil acid, in ICU patients with renal impairment. Br. J. Anaesth. 2004, 92, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egan, T.D. Remifentanil Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1995, 29, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, R.A.; Vereecke, H.E.M.; Greijdanus, B.; Touw, D.J.; Struys, M.M.R.F.; Alffenaar, J.W.C. Analysis of Remifentanil with Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry and an Extensive Stability Investigation in EDTA Whole Blood and Acidified EDTA Plasma. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 120, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’hara, K.; Schneider, J.J.; Jones, A.L.; Wright, I.M.R.; Martin, J.; Galettis, P. Development of an UHPLC-MS/MS method for remifentanil quantification in a small plasma volume. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2019, 42, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, J.; Elshout, J.V.D.; Selinger, K.; Broeders, G.; Dankers, J.; van der Heiden, C. Determination of remifentanil in human heparinised whole blood by tandem mass spectrometry with short-column separation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergov, M.; Nokua, P.; Vuori, E.; Ojanperä, I. Simultaneous screening and quantification of 25 opioid drugs in post-mortem blood and urine by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 2009, 186, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooreman, S.; Deprez, C.; Martens, F.; Van Bocxlaer, J.; Croes, K. A comprehensive LC-MS-based quantitative analysis of fentanyl-like drugs in plasma and urine. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hamd, M.A.; Wada, M.; Ikeda, R.; Kawakami, S.; Kuroda, N.; Nakashima, K. Simultaneous determination of propofol and remifentanil in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Application to preclinical pharmacokinetic drug-drug interaction analysis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.C.; Abe, E.; Etting, I.; Le Guen, M.; Devillier, P.; Grassin-Delyle, S. Quantification of remifentanil and propofol in human plasma: A LC–MS/MS assay validated according to the EMA guideline. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, R.; Pohanka, A.; Andersson, M.; Beck, O.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Determination of remifentanil in human plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry utilizing micro extraction in packed syringe (MEPS) as sample preparation. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckart, K.; Röhrich, J.; Breitmeier, D.; Ferner, M.; Laufenberg-Feldmann, R.; Urban, R. Development of a new multi-analyte assay for the simultaneous detection of opioids in serum and other body fluids using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 1001, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selinger, K.; Lanzo, C.; Sekut, A. Determination of remifentanil in human and dog blood by HPLC with UV detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1994, 12, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidar, S.H.; Liang, Z.; Selinger, K.; Hamlett, L.; Eddington, N.D. Determination of remifentanil, an ultra-short-acting opioid anesthetic, in rat blood by high performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1996, 14, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorksten, A.R.; Chan, C.; Crankshaw, D.P. Determination of remifentanil in human blood by capillary gas chromatography with nitrogen-selective detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 775, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, C.; Davis, I.; Arrendale, R.; Jersey, J.; Amin, J. Determination of remifentanil in human blood by liquid-liquid extraction and capillary GC-HRMS-SIM using a deuterated internal standard. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1994, 12, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Noh, H.; Hahn, J.; Jin, B.H.; Min, K.L.; Bae, S.K.; Kim, J.; Park, M.S.; Hong, T.; Wi, J.; et al. Population pharmacokinetics of remifentanil in critically ill patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Center of Drug Evaluation and Research; US Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry-Bioanalytical Method Validation. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70858/download (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the Assessment of Matrix Effect in Quantitative Bioanalytical Methods Based on HPLC−MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Sun, J.; Fu, S. A small dose of remifentanil pretreatment suppresses sufentanil-induced cough during general anesthesia induction: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019, 19, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Huang, H.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Lin, P.-L. Efficacy and safety of remifentanil for endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition: A single center retrospective study. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 6516–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneyd, J.; Whaley, A.; Dimpel, H.L.; Andrews, C.J. An open, randomized comparison of alfentanil, remifentanil and alfentanil followed by remifentanil in anaesthesia for craniotomy. Br. J. Anaesth. 1998, 81, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Instrument | Sample Preparation | Matrices | Stabilizing Agent | Internal Standard | Volume (μL) | Calibration Range (ng/mL) | Run Time (min) | Retention Time (min) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC–MS/MS | Protein precipitation | Human plasma | Formic acid (1.5 μL/1 mL plasma) | Chlorpropamide | 20 | 0.05–50 | 3 | 0.93 | PM |
| 13C6-remifentanil | 100 | 0.2–250 | 2.6 | 1.2 | [12] | ||||
| 50% citric acid (10 μL/1 mL plasma) | Sufentanil | 100 | 0.25–50 | 3 | 1.93 | [13] | |||
| LLE | Human blood | 50% citric acid (20 μL/1 mL blood) | D4-remifentanil | 500 | 0.1–50 | 3 | 1.27 | [14] | |
| Bovine whole blood/ Human urine | N/A | Fentanyl-d5 | 1000 | 0.2–30 | 33 | 8.5 | [15] | ||
| Human plasma/urine | Fentanyl-d5 | 500 | 0.1–50 | 13.5 | 4.05 | [16] | |||
| Rat plasma | Carbamazepine | 200 | 0.17–50 | N/A | N/A | [17] | |||
| Human plasma | 50% citric acid (25 μL/1 mL plasma) | 13C6-remifentanil | 500 | 0.1–20 | 10 | 2 | [18] | ||
| MEPS | Human plasma | 0.1% formic acid 160 μL/20 μL of plasma | 13C6-remifentanil | 20 | 0.05–50 | 5 | 2.2 | [19] | |
| SPE | Human plasma/serum | pH 6.0 phosphate buffer | Fentanyl-d5 | 200 | 1–100 | 30 | 15.6 | [20] | |
| HPLC | LLE | Human blood/ Dog blood | 50% citric acid (20 μL/1 mL blood) | GI97559 | 1000/ 200 | 1–200 | 15 | 8.5 | [21] |
| Rat blood | N/A | GI97559 | 400 | 2.5–50 | N/A | 6 | [22] | ||
| GC | LLE | Human blood | 10 mg/mL citric acid (20 μL/1 mL blood) | Fentanyl | 1000 | 0.2–100 | 15 | 9.1 | [23] |
| GC–MS | LLE | Human blood | Acetonitrile-methylene | 2H4-remifentanil | 1000 | 0.1–25 | N/A | N/A | [24] |
| Spiked (ng/mL) | Intra-Day (n = 6) | Inter-Day (n = 5) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated ± SD (ng/mL) | Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy (RE, %) | Calculated ± SD (ng/mL) | Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy (RE, %) | |
| 0.05 | 0.0493 ± 0.00427 | 8.66 | −1.33 | 0.0530 ± 0.00278 | 5.27 | 5.60 |
| 0.15 | 0.145 ± 0.00725 | 5.01 | −3.44 | 0.151 ± 0.0127 | 8.47 | 0.333 |
| 3 | 2.93 ± 0.0917 | 3.13 | −2.46 | 3.06 ± 0.200 | 6.53 | 2.16 |
| 40 | 42.0 ± 1.98 | 4.72 | 4.89 | 42.8 ± 2.19 | 5.11 | 6.89 |
| Analytes | Spiked (ng/mL) | Extraction Recoveries | Matrix Effects | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated ± SD (%) | RSD (%) | Mean (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Remifentanil | 0.15 | 101 ± 3.99 | 3.95 | 103 ± 7.95 | 7.72 |
| 3 | 103 ± 3.59 | 3.49 | 101 ± 5.99 | 5.53 | |
| 40 | 102 ± 5.01 | 4.91 | 107 ± 4.01 | 3.75 | |
| Chlorpropamide | 1000 | 104 ± 4.29 | 4.13 | 100 ± 2.47 | 2.47 |
| Spiked (ng/mL) | Bench-Top (3 h, RT) | Long-Term (4 Months, –80 °C) | Freeze–Thaw (Three Cycles) | Processed Sample (24 h, 4 °C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | |
| 0.15 | 10.5 | 8.07 | 3.70 | −6.53 | 3.79 | −4.13 | 11.1 | 13.9 |
| 3 | 2.21 | −12.0 | 5.03 | 2.69 | 1.96 | −7.23 | 2.85 | −12.6 |
| 40 | 5.92 | −10.6 | 8.43 | −7.18 | 2.11 | 0.169 | 3.89 | −9.39 |
| Infusion Rate (mg/h) | Time Points (h) | Original Conc. (ng/mL) | Incurred Sample Conc. (ng/mL) | Difference (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient A | 0.35 | 8 | 1.39 | 1.26 | 9.35 |
| 24 | 0.772 | 0.770 | 0.259 | ||
| 48 | 0.0920 | 0.100 | 8.70 | ||
| Patient B | 0.35 | 8 | 1.16 | 0.979 | 15.6 |
| 24 | 1.98 | 1.75 | 11.6 | ||
| 48 | 1.61 | 1.50 | 6.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chae, S.U.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, C.B.; Jo, S.J.; Min, K.L.; Chang, M.J.; Bae, S.K. A Sensitive, Simple, and Fast LC–MS/MS Method for Quantification of Remifentanil in Human Plasma: Applications in Critically Ill Patients’ Plasma during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Separations 2023, 10, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060359
Chae SU, Kim JS, Lee CB, Jo SJ, Min KL, Chang MJ, Bae SK. A Sensitive, Simple, and Fast LC–MS/MS Method for Quantification of Remifentanil in Human Plasma: Applications in Critically Ill Patients’ Plasma during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Separations. 2023; 10(6):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060359
Chicago/Turabian StyleChae, Soon Uk, Ji Seon Kim, Chae Bin Lee, Seong Jun Jo, Kyung Lok Min, Min Jung Chang, and Soo Kyung Bae. 2023. "A Sensitive, Simple, and Fast LC–MS/MS Method for Quantification of Remifentanil in Human Plasma: Applications in Critically Ill Patients’ Plasma during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation" Separations 10, no. 6: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060359
APA StyleChae, S. U., Kim, J. S., Lee, C. B., Jo, S. J., Min, K. L., Chang, M. J., & Bae, S. K. (2023). A Sensitive, Simple, and Fast LC–MS/MS Method for Quantification of Remifentanil in Human Plasma: Applications in Critically Ill Patients’ Plasma during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Separations, 10(6), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060359