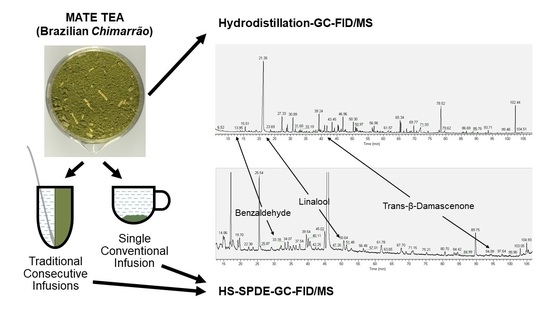
Screening of Volatile Compounds in Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Tea—Brazilian Chimarrão Type—By HS-SPDE and Hydrodistillation Coupled to GC-MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Volatiles in Different Mate Tea Types
1.2. Analytical Approaches and Instrumentation
1.3. Mate Tea Infusions: Traditional Consecutive Infusions and Single Infusions
1.4. Mate Tea Types
1.5. Aims of This Research
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Hydrodistillation: Extraction of Volatiles in the Mate Tea Samples
2.3. Preparation of Popular Mate Tea Infusions: Single Infusion and Traditional Consecutive Infusions
2.4. HS-SPDE: Extraction of Volatiles in Infusions
2.5. HS-SPDE: Extraction of Volatiles in the Mate Tea Samples
2.6. GC, FID, and MS Parameters
2.7. Identification and Semi-Quantification of Compounds
2.8. Replicates
2.9. Compilation of Odor Thresholds of the Identified Volatiles
3. Results
3.1. Compounds Obtained by Hydrodistillation and SPDE
3.2. Odor Thresholds
4. Discussion
4.1. Compounds Obtained by Hydrodistillation and SPDE
4.2. Odor Thresholds
4.3. Potential Key Odorants in the Brazilian Chimarrão Type
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawakami, M.; Kobayashi, A. Volatile Constituents of Green Mate and Roasted Mate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, D.H.M.; Ishimoto, E.Y.; Ortiz MMarques, M.; Fernando Ferri, A.; Torres, E.A.F.S. Essential oil and antioxidant activity of green mate and mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis) infusions. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, P.R.; Cadwallader, K.R.; González de Mejia, E. Identification of Characteristic Aroma Components of Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Tea. ACS Symp. Ser. 2007, 946, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lasekan, O.; Lasekan, A. Flavour chemistry of mate and some common herbal teas. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 27, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcaro, G.; Tranchida, P.Q.; Jacques, R.; Caramão, E.B.; Moret, S.; Conte, L.; Dugo, P.; Dugo, G.; Mondello, L. Characterization of the yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) volatile fraction using solid-phase microextraction-comprehensive 2-D GC-MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 3755–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, I.; Muroi, H.; Himejima, M. Antibacterial Activity against Streptococcus mutans of Mate Tea Flavor Components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, V.; Martínez, N.; Guerra, M.; Fariña, L.; Boido, E.; Dellacassa, E. Characterization of aroma-impact compounds in yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) using GC-olfactometry and GC-MS. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.C.B.; Bastos, D.H.M.; Janzantti, N.S.; Facanali, R.; Marques, M.O.M.; Franco, M.R.B. Determinação do perfil de compostos voláteis e avaliação do sabor e aroma de bebidas produzidas a partir da erva-mate (Ilex paraguariensis). Quim Nova 2007, 30, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, K.G.; Kim, M.K. Volatile and non-volatile compounds in green tea affected in harvesting time and their correlation to consumer preference. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3735–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, L.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Xiao, D. Characterization of volatile compounds of pu-erh tea using solid-phase microextraction and simultaneous distillation-extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2014, 57, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilgaard, M.C.; Civille, G.V.; Carr, B.T. Sensory Evaluation Techniques, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Heck, C.I.; De Mejia, E.G. Yerba mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis): A comprehensive review on chemistry, health implications, and technological considerations. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinhart, A.D.; Bizzotto, C.S.; Ballus, C.A.; Poloni Rybka, A.C.; Sobrinho, M.R.; Cerro-Quintana, R.S.; Teixeira-Filho, J.; Godoy, H.T. Methylxanthines and phenolics content extracted during the consumption of mate (IIex paraguariensis St. HiI) beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2188–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, D.; Barrios, E.; Zanetti, R. Cancer and yerba mate consumption: A review of possible associations. Rev. Panam Salud Pública 2009, 25, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Juaristi, M.; Martínez-López, S.; Sarria, B.; Bravo, L.; Mateos, R. Absorption and metabolism of yerba mate phenolic compounds in humans. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butiuk, A.P.; Martos, M.A.; Adachi, O.; Hours, R.A. Study of the chlorogenic acid content in yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil.): Effect of plant fraction, processing step and harvesting season. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat Plants 2016, 3, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, A.N.N.; Amboni, R.D.D.M.C.; Prudencio, E.S.; Amante, E.R.; Fritzen-Freire, C.B.; Boaventura, B.C.B.; Muñoz, I.; Branco, C.D.S.; Salvador, M.; Maraschin, M. Concentration of biologically active compounds extracted from Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil. by nanofiltration. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolón, P.A.; Castellsagué, X.; Benz, M.; Muñoz, N. Hot and Cold Mate Drinking and Esophageal Cancer in Paraguay. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 1995, 4, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bates, M.N.; Hopenhayn, C.; Rey, O.A.; Moore, L.E. Bladder cancer and mate consumption in Argentina: A case-control study. Cancer Lett. 2007, 246, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of Europe. European Pharmacopoeia 9.0; European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and Health Care of the Council of Europe (EDQM): Strasbourg, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bicchi, C.; Cordero, C.; Liberto, E.; Rubiolo, P.; Sgorbini, B. Automated headspace solid-phase dynamic extraction to analyse the volatile fraction of food matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1024, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L.; Meng, Q. Comparative analysis of Pu-erh and Fuzhuan teas by fully automatic headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and chemometric methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Quadrupole Mass Spectroscopy, 4th ed.; Allured Publishing: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Linstrom, P.J.; Mallard, W.G. (Eds.) NIST Chemistry webBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018.
- Van Gemert, L.J. Odour Thresholds—Compilations of Odour Thresholds in Air, Water and Other Media, 2nd ed.; Oliemans Punter and Partners: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pherobase. The Pherobase: Database of Pheromones and Semiochemicals. 2019. Available online: http://www.pherobase.com/ (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- Smelindro, A.Q.E.; Os, J.O.D.; Irardi, S.A.G.; Ossi, A.L.M.; Osa, R. Influence of Agronomic Variables on the Composition of Mate Tea Leaves (Ilex paraguariensis) Extracts Obtained from CO2 Extraction at 30 °C and 175 bar. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, R.A.; Freitas, L.S.; Pérez, V.F.; Dariva, C.; Oliveira, A.P.; Oliveira, J.V.; Caramão, E.B. The use of ultrasound in the extraction of Ilex paraguariensis leaves: A comparison with maceration. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Injected volume | 1 µL |
| Carrier gas | Helium |
| Carrier gas flow | 1 mL/min (constant) |
| Injection | PTV, splitless |
| Injection temperature | 250 °C |
| Temperature program | 60 °C 2 °C/min  230 °C 3 °C /min 230 °C 3 °C /min  300 °C 300 °C |
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Desorption volume | 1000 µL of Helium |
| Pre-desorption time | 45 s |
| Pre-desorption temperature | 250 °C |
| Desorption speed | 10 µL/s |
| Desorption temperature | 250 °C |
| Carrier gas | Helium |
| Carrier gas flow | 1 mL/min (constant) |
| Injection | PTV, splitless |
| Injection temperature | 250 °C |
| Temperature program | 40 °C (5 min hold time) 5 °C/min  70 °C 95 °C 70 °C 95 °C  0.5 °C/min 95 0.7 °C/min 0.5 °C/min 95 0.7 °C/min  105 °C 1 °C/min 105 °C 1 °C/min  140 °C/min 5 °C 140 °C/min 5 °C  160 °C at 5 °C, 160–250 at 7 °C/min, and 250 °C (2 min hold time) 160 °C at 5 °C, 160–250 at 7 °C/min, and 250 °C (2 min hold time) |
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Base temperature | 300 °C |
| Ignition threshold | 0.5 pA |
| Flow (air) | 350 mL/min |
| Flow (H2) | 35 mL/min |
| Flow (Makeup): | 30 mL/min |
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Scan mode | Full scan |
| Detector gain | 1 × 105 (Multiplier voltage 1340 V) |
| Ionization | Positive |
| Mass range | 1–650 Da |
| Start of the scan | 0 min (‘on’ during the whole GC program) |
| Rates | Scans/s: 2.0833 Scan rate (amu/s): 1411.6 |
| Compound | Retention Index | Retention Time (min) | CAS- Number | Identification Confirmed by Standard | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Literature a | Essential Oils | Infusions | Essential Oils | Infusions | |||
| Hexanal | 801 | - | 803 | - | 19.39 | 66-25-1 | x |
| Oxime–metoxy–phenyl | - | - | 891 | - | 25.31 | - | |
| Pinene <α–> | 932 | - | 931 | - | 29.19 | 80-56-8 | x |
| Camphene | 946 | - | 948 | - | 30.93 | 79-92-5 | x |
| Benzaldehyde | 952 | 954 | 959 | 12.91 | 32.06 | 100-52-7 | x |
| Pinene <β–> | 974 | - | 977 | - | 33.97 | 127-91-3 | x |
| 5–Hepten–2–one <6–methyl–5> | 981 | 975 | 979 | 13.94 | 34.15 | 110-93-0 | x |
| Myrcene <β–> | 988 | - | 985 | - | 34.84 | 123-35-3 | x |
| Pentyl furan <2–> | 988 | - | 986 | - | 34.84 | 3777-69-3 | |
| Heptadienal <(2E,4Z)–> | 990 n | 992 | - | 14.63 | - | 4313-02-4 | |
| Octanal | 998 | - | 1001 | - | 36.52 | 124-13-0 | x |
| Heptadienal <(2E,4E)–> | 1005 | 1006 | 1008 | 15.47 | 37.64 | 4313-03-5 | |
| Cymene <p–> | 1020 | 1020 | 1021 | 16.31 | 39.62 | 99-87-6 | x |
| Limonene | 1024 | 1024 | 1025 | 16.58 | 40.25 | 5989-27-5 | x |
| Eucalyptol | 1026 | 1028 | 1029 | 16.81 | 40.76 | 470-82-6 | x |
| Ocimene <(E)–β–> | 1044 | 1039 | 1039 | 17.47 | 42.35 | 3779-61-1 | x |
| 2–octenal <(E)–> | 1049 | 1052 | - | 18.21 | - | 2548-87-0 | |
| Terpinene <γ–> | 1054 | - | 1052 | - | 44.3 | 99-85-4 | x |
| 1–octanol (internal standard) | 1063 | - | 1063 | - | 45.86 | 11-87-5 | x |
| Octadien–2–one <(3E,5E)–> | 1066 n | 1063 | - | 18.89 | - | 30086-02-3 | |
| Linalooloxide <(Z)–> | 1067 | 1065 | - | 19.02 | - | 5989-33-3 | |
| Linalooloxide <(E)–> | 1084 | 1082 | - | 19.98 | - | 34995-77-2 | |
| Fenchone | 1083 | - | 1085 | - | 49.27 | 1195-79-5 | x |
| Linalool | 1095 | 1100 | 1095 | 21.09 | 50.71 | 78-70-6 | x |
| Unknown | - | - | 1101 | - | 51.58 | - | |
| Perillene (?) | 1102 | - | 1109 | - | 52.99 | 539-52-6 | |
| Pinocarveol <(E)–> | 1135 | 1138 | - | 23.57 | - | 547-61-5 | |
| Verbenol <(E)–> | 1140 | 1142 | - | 23.82 | - | 1820-09-3 | |
| Camphor | 1141 | 1145 | - | 24.00 | - | 76-212 | x |
| Nonadienal <(2E,6Z)–> | 1150 | 1148 | - | 24.20 | - | 557-48-2 | |
| Menthone | 1148 | 1153 | - | 24.53 | - | 89-80-5 | x |
| Isoborneol | 1155 | - | 1159 | - | 61.91 | 124-76-5 | x |
| Menthol | 1167 | - | 1173 | - | 64.26 | 15356-60-2 | x |
| Menthol <iso–> | 1179 | 1175 | - | 25.93 | - | 3623-52-7 | x |
| Terpinen–4–ol | 1174 | 1178 | - | 26.14 | - | 562-74-3 | x |
| Naphtalene | 1178 | 1182 | - | 26.40 | - | 91-20-3 | |
| MethylSalicylate | 1190 | 1188 | - | 26.83 | - | 119-36-8 | |
| Estragole | 1195 | - | 1193 | - | 67.75 | 140-67-0 | x |
| Terpineol <α–> | 1186 | 1194 | - | 27.18 | - | 98-55-5 | x |
| Safranal | 1197 | 1196 | - | 27.35 | - | 116-26-7 | |
| Decanal <n> | 1201 | 1203 | 1203 | 27.75 | 69.5 | 112-31-2 | x |
| Cyclocitral <β–> | 1217 | 1217 | 1214 | 28.67 | 71.19 | 432-25-7 | |
| Nerol | 1227 | 1222 | - | 29.00 | - | 106-25-2 | x |
| 166;136;120;108;93;86;79;69 | - | 1227 | - | 29.32 | - | - | |
| Carvone | 1239 | 1242 | - | 30.27 | - | 99-49-0 | x |
| Geraniol | 1249 | 1249 | - | 30.73 | - | 106-24-1 | |
| Ionene, <α–> | 1266 n | 1253 | - | 30.95 | - | 475-03-6 | |
| 2–Decenal <(E)– > | 1260 | 1261 | - | 31.46 | - | 3913-81-3 | |
| 1H–2–Indenone,2,4,5,6,7,7a–hexahydro–3–(1–methylethyl)–7a–methyl | - | 1279 | 1276 | 32.67 | 80.63 | - | |
| Anethole <(E)–> | 1282 | 1285 | 1282 | 33.05 | 81.65 | 4180-23-8 | x |
| Safrole | 1285 | 1289 | - | 33.28 | - | 94-59-7 | |
| Carvacrol | 1298 | - | 1293 | 83.36 | 499-75-2 | x | |
| Edulan I <dihydro–> (?) | 1273 n | 1294 | - | 33.59 | - | 63335-66-0 | |
| 172;157;142;128;115;91;77;69;57 | - | 1356 | - | 37.42 | - | - | |
| Undecenal <(2E)–> (?) | 1357 | 1367 | - | 38.10 | - | 53448-07-0 | |
| Copaene <α–> | 1374 | 1379 | - | 38.84 | - | 3856-25-5 | |
| Damascenone <(Z)–β–> | 1383 | 1383 | 1376 | 39.10 | 94.41 | 59739-63-8 | x |
| 192;147;144;131;119;105;93;91;79;69;55 | - | 1389 | - | 39.41 | - | - | |
| Elemene <β–> | 1389 | 1394 | - | 39.72 | - | 515-13-9 | |
| Damascone <(E)–β–> | 1413 | 1412 | - | 40.88 | - | 23726-91-2 | |
| 192;174;159;144;131;119;105;91;82;77;71 | - | 1414 | - | 40.98 | - | - | |
| Caryophyllene <(E)–β–> | 1417 | 1425 | - | 41.65 | - | 87-44-5 | x |
| Ionone <(E)–α–> | 1428 | 1426 | - | 41.75 | - | 127-41-3 | |
| Merged peaks | - | 1434 | - | 42.20 | - | - | |
| Aromadendrene | 1439 | 1443 | - | 42.77 | - | 489-39-4 | |
| Geranylacetone <(E)–> | 1453 | 1452 | 1451 | 43.33 | 102.9 | 3796-70-1 | |
| 204;178;163;161;150;135;121;107;91;79;71 | - | 1465 | - | 44.13 | - | - | |
| Muurolene <γ–> | 1478 | 1479 | - | 45.01 | - | 30021-74-0 | |
| Ionone <(E)–β–> | 1487 | 1483 | 1487 | 45.23 | 105.3 | 79-77-6 | x |
| Muurola–4(14),5–diene <trans–> | 1493 | 1486 | - | 45.41 | - | 54324-03-7 | |
| Unknown | - | 1494 | - | 45.92 | - | - | |
| Bicyclogermacrene (?) | 1500 | 1499 | - | 46.24 | - | 24703-35-3 | |
| Farnesene <α–> | 1505 | 1509 | - | 46.85 | - | 502-61-4 | x |
| Cadinene <γ–> | 1513 | 1522 | - | 47.62 | - | 39029-41-9 | |
| Unknown | - | 1529 | - | 48.04 | - | - | |
| Nerolidol <(E)–> | 1561 | 1565 | - | 50.22 | - | 40716-66-3 | |
| Dendrolasin | 1570 | 1577 | - | 50.89 | - | 23262-34-2 | |
| Spathulenol | 1577 | 1582 | - | 51.20 | - | 6750-60-3 | |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 1582 | 1586 | - | 51.43 | - | 1139-30-6 | |
| Merged peaks | - | 1587 | - | 51.61 | - | - | |
| Guaiol | 1600 | 1597 | - | 52.15 | - | 489-86-1 | |
| Hexadecane <n–> | - | 1602 | - | 52.42 | - | 544-76-3 | |
| Merged peaks | - | 1615 | - | 53.10 | - | - | |
| Merged peaks | - | 1631 | - | 53.99 | - | - | |
| Cadinol <α–> | 1652 | 1659 | - | 55.50 | - | 481-34-5 | |
| 6,9–Heptadecadiene (?) | 1668 n * | 1674 | - | 56.29 | - | - | |
| Unknown | 1677 | - | 56.45 | - | - | ||
| 3–Heptadecene <(Z)–> (?) | 1687 n * | 1684 | - | 56.84 | - | - | |
| 236;258;189;161;145;133;123;119;109;95;81;69;67;57 | - | 1690 | - | 57.16 | - | - | |
| Pentadecanone <2–> | 1697 | 1702 | - | 57.81 | - | 2345-28-0 | |
| Merged peaks | - | 1720 | - | 58.78 | - | - | |
| Tetradecanoic acid | 1770 | 1768 | - | 61.30 | - | 544-63-8 | |
| 122;196;166;138;123;109;96;82;69;57 | - | 1785 | - | 62.23 | - | - | |
| 278;263;249;236;222;208;193;179;165;151;137;123;109;95;82;71;68;57 | - | 1844 | - | 65.26 | - | - | |
| Hexahydrofarnesylacetone | 1847 n | 1849 | - | 65.51 | - | 502-69-2 | |
| 278;263;249;236;222;208;193;179;165;151;137;123;109;95;82;71;68;57 | - | 1886 | - | 67.40 | - | - | |
| Farnesylacetone <(5E,9E)–> | 1913 | 1915 | - | 68.83 | - | 1117-52-8 | |
| Methyl hexadecanoate | 1927 b | 1933 | - | 69.69 | - | 112-39-0 | |
| Isophytol(?) | 1952 | - | 70.62 | - | - | ||
| Palmitic acid | 1970 n | 1985 | - | 72.19 | - | 57-10-3 | x |
| 272;257;229;215;203;189;175;161;147;136;121;107;93;81;69 | - | 2029 | - | 74.28 | - | - | |
| Methyl linolenate | 2108 n | 2105 | - | 77.78 | - | 301-00-8 | |
| 296;264;236;222;180;166;152;137;123;110;96;83;74 | - | - | - | 77.85 | - | - | |
| Phytol | 2128n | 2122 | - | 78.57 | - | 150-86-7 | |
| Merged peaks | - | 2146 | - | 79.64 | - | - | |
| Merged peaks | - | 2151 | - | 79.85 | - | - | |
| 9–Tricosene <(Z)–> | 2271 n | 2281 | - | 85.46 | - | 27519-02-4 | |
| Tricosane | 2300 | 2310 | - | 86.64 | - | 638-67-5 | |
| 242;299;273;257;231;217;203;191;185;161;149;136;121;1007;95;81;69 | - | 2366 | - | 88.70 | - | - | |
| Squalene | 2847 n * | 2832 | - | 102.47 | - | 111-02-4 | x |
| Compound | Average Odor Threshold (ppm) a | Minimum Odor Threshold (ppm) a | Odor Characteristics b |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damascenone, <(Z)–β–> | 0.000002 | 0.00000075 | Honey, sweet, fruity, apple, tobacco, canned peach |
| Damascone, <(E)–β–> | 0.000002 | 0.000002 | Fruity, floral, berry, honey, rose, tobacco |
| Ionone <(E)–β–> | 0.000007 | 0.000007 | Violets, floral, raspberry, woody |
| 2–Decenal, <(E)–> | 0.0004 | 0.0003 | Green, fatty, tallowy, orange |
| Octanal | 0.0008 | 0.00032 | Lemon, stewed, boiled meat, rancid, soapy, orange |
| Ionene, <α–> | 0.002 | 0.002 | - |
| Hexanal | 0.0024 | 0.00032 | Green, fruity, tallowy, fishy, grassy, herbal, leafy |
| Decanal <n> | 0.003 | 0.00008 | Stewed, burnt, green, waxy, floral, lemon, herbal |
| Ionone <(E)–α–> | 0.00378 | 0.0004 | Floral, violet, woody, fruity |
| 2–octenal, <(E)–> | 0.004 | 0.00034 | Fatty, nutty, sweet, waxy, green, burnt, mushroom |
| Cyclocitral <β–> | 0.005 | 0.003 | Sweet, mild, green, grassy, floral, hay |
| Linalool | 0.006 | 0.00001 | Lavender, muscat, sweet, green, floral, lemon |
| Naphtalene | 0.006 | 0.0068 | Medicinal |
| Geraniol | 0.0066 | 0.001 | Rose, geranium, floral, sweet, fruity, citrus |
| Cymene <p–> | 0.0114 | 0.0062 | Lemon, fruity, fuel-like, sweet, herbal, spicy |
| Pinene <α–> | 0.014 | 0.0025 | Terpeny, fruity, sweet, green, woody, pine, citrus |
| Pentyl furan <2–> | 0.0145 | 0.0058 | Buttery, green bean |
| (β)–Myrcene | 0.015 | 0.0012 | Metallic, musty, geranium, sweet, fruity |
| Estragole | 0.016 | 0.006 | Liquorice, sweet, herbal, anise, spicy |
| Eucalyptol | 0.023 | 0.0011 | Camphor, minty, sweet, liquorice, pine |
| Safrole | 0.033 | 0.01 | Sweet, warm, spicy, woody, floral |
| Ocimene <(E)–β–> | 0.034 | 0.034 | Herbal, mild, citrus, sweet, orange, lemon |
| MethylSalicylate | 0.04 | 0.0349 | Wine, berry, warm, sweet, wintergreen |
| Heptadienal <(2E,4E)–> | 0.056 | 0.0154 | Orange oil, oily, fatty, rancid |
| 2.4–Heptadienal, <(E,Z)–> | 0.056 | 0.0154 | Orange oil, oily, fatty, rancid |
| Anethole <(E)–> | 0.086 | 0.0015 | Herbal, anise, sweet, spicy |
| Farnesene <α–> | 0.087 | 0.087 | Woody |
| Linalooloxide <(Z)–> | 0.1 | 0.1 | Sweet, woody, floral, creamy, slightly earthy |
| 3,5–Octadien–2–one <(E,E)–> | 0.125 | 0.1 | Fresh, sweet, woody, mushroom |
| Pinene <β–> | 0.14 | 0.006 | Musty, green, sweet, pine, resin, turpentine |
| Caryophyllene <(E)–> | 0.15 | 0.064 | Oily, fruity, woody |
| 5–Hepten–2–one <6–methyl–5> | 0.16 | 0.05 | Mushroom, earthy, vinyl, rubbery, blackcurrant |
| Carvone | 0.16 | 0.0067 | Caraway, herbal minty |
| Geranylacetone, <(E)–> | 0.186 | 0.06 | Fresh, floral, rose, green, fruity |
| Limonene | 0.2 | 0.034 | Licorice, green, citrus, ethereal, fruity |
| Nerolidol <(E)–> | 0.25 | 0.25 | Waxy, floral |
| Terpinene <γ–> | 0.26 | 0.065 | Citrus, terpeny, herbal, fruity, sweet |
| Linalooloxide <(E)–> | 0.32 | 0.19 | Sweet, floral creamy, leafy, earthy, green |
| Terpineol <α–> | 0.35 | 0.0046 | Peach, anise, oily, minty, toothpaste |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 0.41 | 0.2 | Sweet, fruity, sawdust, fruity, herbal |
| Fenchone | 0.44 | 0.44 | Camphor |
| Phytol | 0.64 | 0.64 | Herbal, delicate, floral, balsamic |
| Nerol | 0.68 | 0.29 | Floral, rose, citrus, marine |
| Benzaldehyde | 0.75 | 0.024 | Burnt sugar, almond, woody |
| Carvacrol | 0.8 | 0.07 | Yuzu, caraway |
| Camphor | 0.83 | 0.25 | Camphor, green, dry, leafy |
| Isoborneol | 0.9 | 0.001 | Musty, dusty |
| Menthol, <iso–> | 0.95 | 0.1 | Fresh, green, cool, herbal |
| Terpinen–4–ol | 1.2 | 0.34 | Terpeny, woody, sweet, herbal, pine, musty |
| Camphene | 1.98 | 1.86 | Sweet, fruity, camphor, pine, oily, herbal |
| Methyl hexadecanoate | 2 | 2 | Oily, faint, waxy, sweet |
| Menthol | 2.1 | 0.9 | Fresh, green, cool, herbal |
| Menthone | 2.4 | 0.17 | Herbal, minty, sweet, earthy |
| Pinocarveol <(E)–> | - | - | Floral, herbal, camphor, woody, pine |
| Verbenol <(E)–> | - | - | Balsamic, pine |
| Safranal | - | - | Powerful saffron aroma, tobacco, camphor |
| Spathulenol | - | - | Fruity, herbal |
| Palmitic acid | - | - | Oily |
| Perillene (?) | - | - | Woody |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaltbach, P.; Gillmeister, M.; Kabrodt, K.; Schellenberg, I. Screening of Volatile Compounds in Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Tea—Brazilian Chimarrão Type—By HS-SPDE and Hydrodistillation Coupled to GC-MS. Separations 2021, 8, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090131
Kaltbach P, Gillmeister M, Kabrodt K, Schellenberg I. Screening of Volatile Compounds in Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Tea—Brazilian Chimarrão Type—By HS-SPDE and Hydrodistillation Coupled to GC-MS. Separations. 2021; 8(9):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090131
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaltbach, Pedro, Marit Gillmeister, Kathrin Kabrodt, and Ingo Schellenberg. 2021. "Screening of Volatile Compounds in Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Tea—Brazilian Chimarrão Type—By HS-SPDE and Hydrodistillation Coupled to GC-MS" Separations 8, no. 9: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090131
APA StyleKaltbach, P., Gillmeister, M., Kabrodt, K., & Schellenberg, I. (2021). Screening of Volatile Compounds in Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Tea—Brazilian Chimarrão Type—By HS-SPDE and Hydrodistillation Coupled to GC-MS. Separations, 8(9), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090131