HPLC-DAD-MS and Antioxidant Profile of Fractions from Amontillado Sherry Wine Obtained Using High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography
Abstract
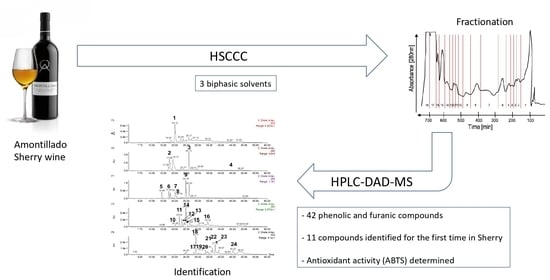
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Wine Samples
2.3. Preparation of the Extracts
2.4. Selection of Two-Phases HSCCC Solvents Systems
2.5. Separation by Means of High-Speed Countercurrent Chromatography (HSCCC)
2.6. Characterisation of the Fractions Separated by HSCCC
2.7. Antioxidant Activity Determination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. HSCCC Fractionation Using Different Solvent Systems
3.2. Identification of the Compounds in the Different Fractions Obtained by HSCCC
3.3. Prevalence of the Identified Phenolic and Furanic Compounds in Wines
3.4. Antioxidant Activity of the Fractions Obtained
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, V.; Pereira, A.C.; Marques, J.C. Emerging Trends in Fortified Wines: A Scientific Perspective; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128152690. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, J.; Villani, T.S.; Guo, Y.; Qi, Y.; Chin, K.; Pan, M.H.; Ho, C.T.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q. Phytochemistry, antioxidant capacity, total phenolic content and anti-inflammatory activity of Hibiscus sabdariffa leaves. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrella, M.I.; Hernández, M.T.; Olano, A. Changes in polyalcohol and phenol compound contents in the ageing of sherry wines. Food Chem. 1986, 20, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, D.A.; Barroso, C.G.; Pérez-Bustamante, J.A. Automation of sample preparation as a preliminary stage in the high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of polyphenolic compounds in sherry wines. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 730, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valme García Moreno, M.; García Barroso, C. Comparison of the evolution of low molecular weight phenolic compounds in typical sherry wines: Fino, amontillado, and oloroso. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7556–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, A.F.; Lopez-Toledano, A.; Mayen, M.; Merida, J.; Medina, M. Changes in color and phenolic compounds during oxidative aging of sherry white wine. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Bayón, M.Á.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. Sherry wines: Manufacture, composition and analysis. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- López de Lerma, M.N.; Bellincontro, A.; García-Martínez, T.; Mencarelli, F.; Moreno, J.J. Feasibility of an electronic nose to differentiate commercial Spanish wines elaborated from the same grape variety. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yang, C.; Pei, H.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ito, Y. Application of counter-current chromatography as a new pretreatment method for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, S.; Ito, Y. Isolation and purification of nootkatone from the essential oil of fruits of Alpinia oxyphylla Miquel by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Pei, D.; Duan, W.D.a.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Di, D.L. The applicability of high-speed counter current chromatography to the separation of natural antioxidants. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1623, 461150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surup, F.; Minh Thi Tran, T.; Pfütze, S.; Budde, J.; Moussa-Ayoub, T.E.; Rohn, S.; Jerz, G. Opuntisines, 14-membered cyclopeptide alkaloids from fruits of Opuntia stricta var. dillenii isolated by high-performance countercurrent chromatography. Food Chem. 2021, 334, 127552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Wray, V.; Winterhalter, P. Isolation of dimeric, trimeric, tetrameric and pentameric procyanidins from unroasted cocoa beans (Theobroma cacao L.) using countercurrent chromatography. Food Chem. 2015, 179, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rivera, M.P.; Lugo-Cervantes, E.; Winterhalter, P.; Jerz, G. Metabolite profiling of polyphenols in peels of citrus limetta risso by combination of preparative high-speed countercurrent chromatography and LC-ESI-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, B. Separation and purification of polyphenols from red wine extracts using high speed counter current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1054, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, F.; Winterhalter, P. Synthesis and structure elucidation of ethyliden-linked anthocyanin—Flavan-3-ol oligomers. Food Res. Int. 2014, 65, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguer, M.; Cerezo, A.B.; Rentzsch, M.; Winterhalter, P.; Troncoso, A.M.; García-Parrilla, M.C. Simulated digestion and antioxidant activity of red wine fractions separated by high speed countercurrent chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8879–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, P.; Sun, B. Preparative separation of grape skin polyphenols by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawel, R.; Schulkin, A.; Smith, P.A.; Waters, E.J. Taste and textural characters of mixtures of caftaric acid and grape reaction product in model wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2014, 20, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baderschneider, B.; Winterhalter, P. Isolation and characterization of novel benzoates, cinnamates, flavonoids, and lignans from Riesling wine and screening for antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2788–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalado, E.L.; Tolle, S.; Pino, J.A.; Winterhalter, P.; Menendez, R.; Morales, A.R.; Rodríguez, J.L. Isolation and identification of phenolic compounds from rum aged in oak barrels by high-speed countercurrent chromatography/high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and screening for antioxidan. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 7358–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, N.; Wray, V.; Winterhalter, P. Preparative isolation of procyanidins from grape seed extracts by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1177, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, E.; Dueñas, M.; Schwarz, M.; Winterhalter, P.; Cheynier, V.; Fulcrand, H. Characterization of pigments from differents high speed countercurrent chromatography wine fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4536–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, N.; Winterhalter, P. Large-scale isolation of flavan-3-ol phloroglucinol adducts by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1172, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y. Golden rules and pitfalls in selecting optimum conditions for high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1065, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, Á.M.; Guillén, D.A.; Barroso, C.G. Development of an electrochemical method for the determination of antioxidant activity. Application to grape-derived products. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 216, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, A.; Ruiz-Angel, M.J.; Carda-Broch, S. Elution-extrusion countercurrent chromatography. Use of the liquid nature of the stationary phase to extend the hydrophobicity window. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5886–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.; Câmara, J.S.; Cacho, J.; Marques, J.C. HPLC-DAD methodology for the quantification of organic acids, furans and polyphenols by direct injection of wine samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega, A.F.; Mayen, M.; Medina, M. Study of colour and phenolic compounds in two models of oxidative ageing for sherry type white wines. Food Control. 2008, 19, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcari, S.G.; Chaves, E.S.; Vanderlinde, R.; Rosier, J.P.; Bordignon-Luiz, M.T. Brazilian fortified wines: Chemical composition, chromatic properties and antioxidant activity. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.; Hogg, T.A.; Silva, M.C.M. Application of a liquid chromatographic method for the determination of phenolic compounds and furans in fortified wines. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pachón, M.S.; Villaño, D.; Troncoso, A.M.; García-Parrilla, M.C. Determination of the phenolic composition of sherry and table white wines by liquid chromatography and their relation with antioxidant activity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 563, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canas, S. Phenolic composition and related properties of aged wine spirits: Influence of barrel characteristics. A review. Beverages 2017, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarni, F.; Moutounet, M.; Puech, J.L.; Rabier, P. Effect of heat treatment of oak wood extractable compounds. Holzforschung 1990, 44, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, J.S.; Alves, M.A.; Marques, J.C. Changes in volatile composition of Madeira wines during their oxidative ageing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 563, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, D.M.; Hoffman, B.; Yang, J.; Soleas, G.J. Phenolic constituents, furans, and total antioxidant status of distilled spirits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3978–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Mar, M.I.; Mateos, R.; García-Parrilla, M.C.; Puertas, B.; Cantos-Villar, E. Bioactive compounds in wine: Resveratrol, hydroxytyrosol and melatonin: A review. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcenilla, J.; Estrella, I.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Hernández, T.; Hernández, L. The influence of yeasts on certain non-volatile components of wine. Food Chem. 1989, 31, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordiga, M.; Lorenzo, C.; Pardo, F.; Salinas, M.R.; Travaglia, F.; Arlorio, M.; Coïsson, J.D.; Garde-Cerdán, T. Factors influencing the formation of histaminol, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and tryptophol in wine: Temperature, alcoholic degree, and amino acids concentration. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, H.; Curiel, J.A.; Landete, J.M.; de las Rivas, B.; de Felipe, F.L.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Mancheño, J.M.; Muñoz, R. Food phenolics and lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 132, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerezo, A.B.; Álvarez-Fernández, M.A.; Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Troncoso, A.M.; García-Parrilla, M.C. Phenolic composition of vinegars over an accelerated aging process using different wood species (acacia, cherry, chestnut, and oak): Effect of wood toasting. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4369–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, M.C.; Barroso, C.G.; Pérez-Bustamante, J.A. Analysis of polyphenolic compounds of different vinegar samples. Z. Lebensm. Unters. 1994, 199, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, M.; Piñeiro, Z.; Barroso, C.G. Stability of phenolic compounds during extraction with superheated solvents. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 921, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, A.R.; Delgado, A.M.; Issaoui, M.; Chammem, N.; Fiorino, M.; Pellerito, A.; Natalello, S. Review of the role of fluid dairy in delivery of polyphenolic compounds in the diet: Chocolate milk, coffee beverages, matcha green tea, and beyond. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, G.C.; Minatel, I.O.; Junior, A.P.; Gomez-Gomez, H.A.; de Camargo, J.P.C.; Diamante, M.S.; Pereira Basílio, L.S.; Tecchio, M.A.; Pereira Lima, G.P. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity of grape pomace flours. LWT 2021, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotoras, M.; Vivanco, H.; Melo, R.; Aguirre, M.; Silva, E.; Mendoza, L. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the antioxidant and prooxidant activity of phenolic compounds obtained from grape (Vitis vinifera) pomace. Molecules 2014, 19, 21154–21167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso, Á.M.; Castro, R.; Rodríguez, M.C.; Guillén, D.A.; Barroso, C.G. Study of the antioxidant power of brandies and vinegars derived from Sherry wines and correlation with their content in polyphenols. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciano, R.P.; Bravo, M.N.; Pires, M.M.; Serra, A.T.; Duarte, C.M.; Boas, L.V.; Bronze, M.R. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of moscatel dessert wines from the setúbal region in portugal. Food Anal. Methods 2009, 2, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, G.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H. Bin Antioxidant activities, phenolic profiles, and organic acid contents of fruit vinegars. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odabasoglu, F.; Aslan, A.; Cakir, A.; Suleyman, H.; Karagoz, Y.; Bayir, Y.; Halici, M. Antioxidant activity, reducing power and total phenolic content of some lichen species. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, T.L.; Miller, S.A.; Myers, L.E.; Miguez, F.E.; Engeseth, N.J. Evaluation of synergistic antioxidant potential of complex mixtures using oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudnic, I.; Modun, D.; Rastija, V.; Vukovic, J.; Brizic, I.; Katalinic, V.; Kozina, B.; Medic-Saric, M.; Boban, M. Antioxidative and vasodilatory effects of phenolic acids in wine. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, C.A.; Bonesi, C.D.M.; Marzarotto, V.; Barnabé, D.; Spinelli, F.R.; Webber, V.; Vanderlinde, R. Phenolic composition and antioxidant activity in sparkling wines: Modulation by the ageing on lees. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, M.; Rodríguez, M.C.; Guillén, D.A.; Barroso, C.G. Evolution of the colour, antioxidant activity and polyphenols in unusually aged sherry wines. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.T.; Le, J.; Peng, R.; Li, Y. Efficient extraction and sensitive LC-MS quantification of hydroxytyrosol in wine, oil and plasma. Food Chem. 2020, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| System I | System II | System III | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fractions | Weight (mg) | Fractions | Weight (mg) | Fractions | Weight (mg) |
| F1 | 56 | F1 | 75.3 | F1 | 30 |
| F2 | 32 | F2 | 20.5 | F2 | 13 |
| F3 | 30 | F3 | 8 | F3 | 33 |
| F4 | 22 | F4 | 7.1 | F4 | 14 |
| F5 | 56.6 | F5 | 8.4 | F5 | 20 |
| F6 | 20.9 | F6 | 8 | F6 | 30 |
| F7 | 34.2 | F7 | 7.2 | F7 | 12.3 |
| F8 | 52 | F8 | 9.2 | F8 | 50 |
| F9 | 101.6 | F9 | 5.9 | F9 | 80 |
| Total | 405.3 | F10 | 12.2 | F10 | 24 |
| F11 | 8.5 | F11 | 12.9 | ||
| F12 | 19.2 | F12 | 58.5 | ||
| F13 | 12.5 | Total | 377.7 | ||
| F14 | 27 | ||||
| F15 | 17.3 | ||||
| F16 | 8.6 | ||||
| F17 | 112.5 | ||||
| F18 | 36.9 | ||||
| Total | 404.3 | ||||
| N. | Compounds | Fraction | RetentionTime (min) | UV Bands (nm) | Mass Weight | Molecular Formula | [M + H]+ | [M − H]− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | cis-Caftaric acid a | F5 S_I | 20.1 | 327 | 312.23 | C13H12O9 | 231 | 179/229/311 |
| 2 | Tyrosol a | F6 S_I | 17.7 | 274 | 138.16 | C8H10O2 | 121 | 137 |
| 3 | Syringaldehyde a | F6 S_I | 26.1 | 309 | 182.17 | C9H10O4 | 183 | 181 |
| 4 | 3-Feruloylquinic acid b | F6 S_I | 43.9 | 332 | 368.30 | C17H20O9 | 164/370 | 163/206/368 |
| 5 | Protocatechuic acid a | F7 S_I | 14.4 | 260, 290 | 154.12 | C7H6O4 | 153 | 155 |
| 6 | Protocatechualdehyde a | F7 S_I | 17.4 | 280, 311 | 138.12 | C7H6O3 | 139 | 137 |
| 7 | trans-Caftaric acid a | F7 S_I | 20.2 | 328 | 312.23 | C13H12O9 | 179/311 | |
| 8 | Isovanillin a | F7 S_I | 20.8 | 277, 310 | 152.15 | C8H8O3 | 151 | |
| 9 | Syringic acid a | F7 S_I | 24.8 | 275 | 198.17 | C9H10O5 | 197 | |
| 10 | p-Hydroxybenzoic acid a | F8 S_I | 20.2 | 255 | 138.12 | C7H6O3 | 137 | |
| 11 | p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde a | F8 S_I | 22.0 | 284 | 122.12 | C7H6O2 | 121 | |
| 12 | Vanillic acid a | F8 S_I | 23.1 | 260, 290 | 168.15 | C8H8O4 | 167 | |
| 13 | Cis-p-Coutaric acid b | F8 S_I | 23.9 | 312 | 296.23 | C13H12O8 | 150/163/295 | |
| 14 | Caffeic acid a | F8 S_I | 24.8 | 323 | 180.16 | C9H8O4 | 135/179 | |
| 15 | trans-p-Coutaric acid b | F8 S_I | 24.9 | 313 | 296.23 | C13H12O8 | 150/163/295 | |
| 16 | Caffeic acid-C-hexoside 1 b | F8 S_I | 34.3 | 330 | 342.30 | C15H18O9 | 179/341 | |
| 17 | cis-p-Coumaric acid b | F9 S_I | 28.3 | 297 | 164.16 | C9H8O3 | 119/ 163 | |
| 18 | trans-p-Coumaric acid a | F9 S_I | 29.2 | 310 | 164.16 | C9H8O3 | 119/163 | |
| 19 | trans-Ferulic acid a | F9 S_I | 30.3 | 323 | 194.18 | C10H10O4 | 194 | |
| 20 | Caffeic acid-C-hexoside 2 b | F9 S_I | 33.3 | 332 | 342.30 | C15H18O9 | 179/341 | |
| 21 | Derivative Caffeic acid 1 b | F9 S_I | 35.8 | 313 | 326.00 | C15H18O8 | 178/324 | |
| 22 | Derivative Caffeic acid 2 b | F9 S_I | 36.4 | 315 | 326.00 | C15H18O8 | 178/324 | |
| 23 | Coumaroyl hexoside b | F9 S_I | 37.5 | 315 | 326.30 | C15H18O8 | 162/178/325 | |
| 24 | cis-Ferulic acid b | F9 S_I | 45.2 | 310 | 194.18 | C10H10O4 | 192/193 | |
| 25 | Ethyl vanillate b | F7 S_II | 17.9 | 281, 320 | 196.20 | C10H12O4 | 123/195 | |
| 26 | Hydroxymethylfurfural a | F9 S_II | 9.9 | 284 | 126.11 | C6H6O3 | 127 | |
| 27 | Fertaric acid b | F13 S_II | 26.1 | 326 | 326.25 | C14H14O9 | 193/325 | |
| 28 | Gallic acid a | F14 S_II | 8.6 | 271 | 170.12 | C7H6O5 | 171 | 169 |
| 29 | Furoic acid b | F14 S_II | 14.2 | 151 | 112.08 | C5H4O3 | 113 | 111 |
| 30 | Dihydro-p-coumaric acid b | F17 S_II | 27.8 | 278 | 166,17 | C9H10O3 | 167 | |
| 31 | 6-O-Feruloylglucose b | F17 S_II | 33.5 | 307 | 356,32 | C16H20O9 | 193/323/355 | |
| 32 | Ethyl gallate b | F18 S_II | 26.2 | 272 | 198.17 | C9H10O5 | 199 | 197 |
| 33 | Veratric acid a | F18 S_II | 32.9 | 260, 294 | 182.17 | C9H10O4 | 183 | 181 |
| 34 | 4-O-beta-D-Glucosyl-4-coumaric acid b | F4 S_III | 29.7 | 290, 329 | 326.30 | C15H18O8 | 163/246/325 | |
| 35 | Hydroxytyrosol b | F6 S_III | 18.2 | 275 | 154.16 | C8H10O3 | 154 | |
| 36 | Methyl protocatechuate b | F9 S_III | 20.2 | 307 | 168.15 | C8H8O4 | 145/167 | |
| 37 | Esculetin a | F9 S_III | 22.8 | 300, 346 | 178.14 | C9H6O4 | 129/179 | 131/177 |
| 38 | Homoveratric acid b | F10 S_III | 26.7 | 279 | 196.20 | C10H12O4 | 156/195 | |
| 39 | Scopoletin a | F10 S_III | 28.3 | 300, 344 | 192.17 | C10H8O4 | 194 | 192 |
| 40 | Vanillin a | F11 S_III | 24.8 | 280, 310 | 152.15 | C8H8O3 | 153 | 151 |
| 41 | Veratraldehyde a | F11 S_III | 27.3 | 278, 315 | 166.17 | C9H10O3 | 168 | 165 |
| 42 | Ethyl caffeate b | F12 S_III | 38.6 | 326 | 208.21 | C11H12O4 | 207 |
| XAD-7 Extract | Ethyl Acetate Extract | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fractions | Antioxidant Activity * (mM Trolox) | Standard Deviation | Fractions | Antioxidant Activity * (mM Trolox) | Standard Deviation |
| F1 | 0.000 a | 0.000 | F1 | 2.712 bc | 0.740 |
| F2 | 0.704 abc | 0.823 | F2 | 2.768 bc | 1.041 |
| F3 | 1.963 cd | 0.183 | F3 | 6.680 d | 0.250 |
| F4 | 2.250 d | 0.535 | F4 | 2.214 b | 0.256 |
| F5 | 0.000 a | 0.000 | F5 | 2.720 bc | 0.336 |
| F6 | 1.451 bcd | 0.469 | F6 | 3.631 bc | 0.952 |
| F7 | 4.320 e | 0.864 | F7 | 2.749 bc | 0.183 |
| F8 | 2.180 d | 0.333 | F8 | 4.142 c | 0.536 |
| F9 | 0.220 ab | 0.249 | F9 | 2.790 bc | 0.205 |
| F10 | 2.918 bc | 0.048 | |||
| F11 | 3.846 c | 0.521 | |||
| F12 | 0.236 a | 0.239 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwarz, M.; Weber, F.; Durán-Guerrero, E.; Castro, R.; Rodríguez-Dodero, M.d.C.; García-Moreno, M.V.; Winterhalter, P.; Guillén-Sánchez, D. HPLC-DAD-MS and Antioxidant Profile of Fractions from Amontillado Sherry Wine Obtained Using High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. Foods 2021, 10, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010131
Schwarz M, Weber F, Durán-Guerrero E, Castro R, Rodríguez-Dodero MdC, García-Moreno MV, Winterhalter P, Guillén-Sánchez D. HPLC-DAD-MS and Antioxidant Profile of Fractions from Amontillado Sherry Wine Obtained Using High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. Foods. 2021; 10(1):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010131
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwarz, Mónica, Fabian Weber, Enrique Durán-Guerrero, Remedios Castro, María del Carmen Rodríguez-Dodero, Maria Valme García-Moreno, Peter Winterhalter, and Dominico Guillén-Sánchez. 2021. "HPLC-DAD-MS and Antioxidant Profile of Fractions from Amontillado Sherry Wine Obtained Using High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography" Foods 10, no. 1: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010131
APA StyleSchwarz, M., Weber, F., Durán-Guerrero, E., Castro, R., Rodríguez-Dodero, M. d. C., García-Moreno, M. V., Winterhalter, P., & Guillén-Sánchez, D. (2021). HPLC-DAD-MS and Antioxidant Profile of Fractions from Amontillado Sherry Wine Obtained Using High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. Foods, 10(1), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010131