Influence of Flour and Fat Type on Dough Rheology and Technological Characteristics of 3D-Printed Cookies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cookie Dough
2.3. The 3D Printing Process
2.4. Rheological Properties Measurements
2.5. Determination of Extrusion Rate
2.6. Baking
2.7. Analyses of Physical Properties of 3D-Printed Shapes
2.8. Determination of Total Dietary Fiber and Moisture Content
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Properties of Dough
3.2. Dough Utilization Rate and Repeatability of Printing Weight
3.3. Physical Properties of Cookies
3.4. Printing Repeatability and Accuracy
3.5. Dietary Fiber Content of Cookies
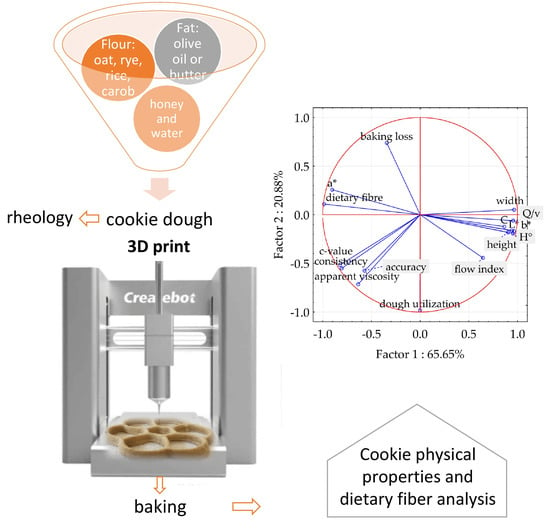
3.6. Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Saeed, A.; Lan, W.; Qin, W. Properties of 3D printed dough and optimization of printing parameters. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoi, F.C.; Prakash, S.; Bhandari, B. 3d printing technologies applied for food design: Status and prospects. J. Food Eng. 2016, 179, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le-Bail, A.; Maniglia, B.C.; Le-Bail, P. Recent advances and future perspective in additive manufacturing of foods based on 3D printing. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 35, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z.; Liu, Y. Impact of processing parameters and post-treatment on the shape accuracy of 3D-printed baking dough. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholamipour-Shirazi, A.; Kamlow, M.-A.; Norton, I.T.; Mills, T. How to Formulate for Structure and Texture via Medium of Additive Manufacturing-A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, M.; Prakash, S.; Liu, Y. Physical properties of 3D printed baking dough as affected by different compositions. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 49, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Monzó, J.; Cárdenas, J.; García-Segovia, P. Effect of Temperature on 3D Printing of Commercial Potato Puree. Food Biophys. 2019, 14, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zheng, L.; Zou, Y.; Tong, Z.; Han, S.; Wang, S. 3D food printing: Main components selection by considering rheological properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2335–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Walkowiak, K.; Masewicz, Ł.; Duda, A.; Poliszko, N.; Różańska, M.B.; Jeżowski, P.; Tomkowiak, A.; Mildner-Szkudlarz, S.; Baranowska, H.M. Wheat bread enriched with raspberry and strawberry oilcakes: Effects on proximate composition, texture and water properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob, J.; Leelavathi, K. Effect of fat-type on cookie dough and cookie quality. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulatsu, E.; Su, J.-W.; Lin, J.; Lin, M. Factors affecting 3D printing and post-processing capacity of cookie dough. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 61, 102316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, M. 3D Food Printing Technologies and Factors Affecting Printing Precision. In Fundamentals of 3D Food Printing and Applications; Godoi, F.C., Bhandari, B.R., Prakash, S., Zhang, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, W.; Yan, L.; Huang, D.; Lin, L.-Y. Extrusion-based food printing for digitalized food design and nutrition control. J. Food Eng. 2018, 220, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, J.; Arnold, D.; Nigl, F.; Lopez, N.; Cohen, D.; Norén, N.; Lipson, H. Multi-material food printing with complex internal structure suitable for conventional post-processing. In Proceedings of the Solid freeform fabrication symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 9–11 August 2010; pp. 809–815. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.W.; Lee, I.J.; Park, S.M.; Lee, J.H.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Park, H.J. Effect of hydrocolloid addition on dimensional stability in post-processing of 3D printable cookie dough. LWT 2019, 101, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantihal, S.; Prakash, S.; Godoi, F.C.; Bhandari, B. Optimization of chocolate 3D printing by correlating thermal and flow properties with 3D structure modeling. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 44, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.Y. Extrusion-Based 3D Printing and Characterization of Edible Materials. Master’s Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Igathinathane, C.; Pordesimo, L.O.; Batchelor, W. Major orthogonal dimensions measurement of food grains by machine vision using ImageJ. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosentrater, K.A.; Evers, A. Flour treatments, applications, quality, storage and transport. In Kent’s Technology of Cereals, 5th ed.; Rosentrater, K.A., Evers, A.S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 515–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miś, A. Interpretation of mechanical spectra of carob fibre and oat wholemeal-enriched wheat dough using non-linear regression models. J. Food Eng. 2011, 102, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, H.; Petkova, N.; Sapundzhieva, T.; Baeva, M.; Goranova, Z.; Slavov, A.; Krastev, L. Carob syrup and carob flour (Ceratonia siliqua L.) as functional ingredients in sponge cakes. Carpathian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 12, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsakidou, A.; Blekas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, A. Aroma and physical characteristics of cakes prepared by replacing margarine with extra virgin olive oil. LWT 2010, 43, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahi, S.; Alava, J.M. Functionality of emulsifiers in sponge cake production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathare, P.B.; Opara, U.L.; Al-Said, F.A.-J. Colour Measurement and Analysis in Fresh and Processed Foods: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derossi, A.; Caporizzi, R.; Ricci, I.; Severini, C. Critical variables in 3D food printing. In Fundamentals of 3D Food Printing and Applications; Godoi, F.C., Bhandari, B.R., Prakash, S., Zhang, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 41–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainakari, A.-I.; Rita, H.; Putkonen, T.; Pastell, H. New dietary fibre content results for cereals in the Nordic countries using AOAC 2011.25 method. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, N.; Petrova, I.; Ivanov, I.; Mihov, R.; Hadjikinova, R.; Ognyanov, M.; Nikolova, V. Nutritional and antioxidant potential of carob (Ceratonia siliqua) flour and evaluation of functional properties of its polysaccharide fraction. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 9, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar]
- Lille, M.; Kortekangas, A.; Heiniö, R.-L.; Sozer, N. Structural and Textural Characteristics of 3D-Printed Protein- and Dietary Fibre-Rich Snacks Made of Milk Powder and Wholegrain Rye Flour. Foods 2020, 9, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D. Locust bean gum: Processing, properties and food applications—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 66, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| MIXTURES | Oat Flour (g) | Rye Flour (g) | Carob Flour (g) | Rice Flour (g) | Olive Oil (g) | Butter (g) | Water (mL) | Honey (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A* | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 11 |
| 1B* | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 11 |
| 2A | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 12 | 11 |
| 2B | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 12 | 11 |
| 3A | 10 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 12 | 11 |
| 3B | 10 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 12 | 11 |
| Mixture | Apparent Viscosity (Pas) | Consistency Coefficient (Pasn) | Flow Behavior Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 63.2 c | 3.304 b | 0.659 a |
| 1B | 25.38 e | 2.434 a | 0.282 bc |
| 2A | 175.4 a | 16.559 e | 0.292 b |
| 2B | 61.49 c | 7.182 c | 0.160 c |
| 3A | 75.98 b | 9.498 d | 0.309 b |
| 3B | 32.04 d | 3.284 b | 0.380 b |
| Sample | Appearance | Baking Loss (%) | Moisture Content (%) | L* | a* | b* | C | H° | Height (mm) | c-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A |  | 18.90 a ± 0.48 | 4.76 a ± 0.03 | 72.04 a ± 0.41 | 1.00 a ± 0.07 | 16.09 a ± 0.27 | 16.12 a ± 0.28 | 86.45 a ± 0.21 | 5.48 a ± 0.22 | 0.85 ab ± 0.05 |
| 1B |  | 21.28 b ± 0.81 | 5.01 b ± 0.03 | 72.52 a ± 0.54 | 0.91 a ± 0.07 | 13.77 b ± 0.12 | 13.80 b ± 0.13 | 86.23 a ± 0.26 | 5.59 a ± 0.18 | 0.83 a ± 0.05 |
| 2A |  | 20.48 ab ± 0.44 | 5.29 c ± 0.02 | 49.88 b ± 0.26 | 5.02 b ± 0.15 | 10.75 e ± 0.28 | 11.85 c ± 0.32 | 65.03 c ± 0.15 | 4.91 a ± 0.09 | 0.91 b ± 0.08 |
| 2B |  | 24.44 c ± 0.31 | 5.17 bc ± 0.05 | 50.07 b ± 0.84 | 5.22 b± 0.33 | 11.32 de ± 0.64 | 12.46 bc ± 0.72 | 65.31 c ± 0.28 | 5.00 a ± 0.14 | 0.88 ab ± 0.06 |
| 3A |  | 20.22 ab ± 0.26 | 5.14 bc ± 0.07 | 51.25 bc ± 0.30 | 5.63 b ± 0.09 | 12.18 cd ± 0.21 | 13.41 b ± 0.22 | 65.18 c ± 0.19 | 5.01 a ± 0.12 | 0.87 ab ± 0.06 |
| 3B |  | 21.98 b ± 0.66 | 5.51 d ± 0.02 | 52.55 c ± 0.58 | 5.56 b ± 0.13 | 12.74 bc ± 0.33 | 13.90 b ± 0.35 | 66.40 b ± 0.30 | 4.87 a ± 0.20 | 0.84 ab ± 0.07 |
| Predictor | Variable | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flour | L* | 5630 | 2 | 2815 | 1209 | <0.001 * |
| Fat | 6 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 0.119 | |
| Flour × Fat | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.485 | |
| Flour | a* | 248.6 | 2 | 124.3 | 497.4 | <0.001 * |
| Fat | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.821 | |
| Flour × Fat | 0.3 | 2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.605 | |
| Flour | b* | 155.6 | 2 | 77.79 | 70.65 | <0.001 * |
| Fat | 2.3 | 1 | 2.33 | 2.11 | 0.152 | |
| Flour × Fat | 27.8 | 2 | 13.9 | 12.62 | <0.001 * | |
| Flour | C | 4.232 | 2 | 2.116 | 78.66 | <0.001 * |
| Fat | 78.62 | 2 | 39.31 | 29.65 | <0.001 * | |
| Flour × Fat | 2.45 | 1 | 2.45 | 1.85 | 0.18 | |
| Flour | H° | 27.56 | 2 | 13.78 | 10.39 | <0.001 * |
| Fat | 5779 | 2 | 2889 | 5225 | <0.001 * | |
| Flour × Fat | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 0.046 * | |
| Flour | height | 6 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0.007 * |
| Fat | 0.008 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.31 | 0.582 | |
| Flour × Fat | 0.188 | 2 | 0.094 | 3.49 | 0.038 * | |
| Flour | width | 3.715 | 2 | 1.858 | 24.34 | <0.001 * |
| Fat | 0.184 | 1 | 0.184 | 2.41 | 0.126 | |
| Flour × Fat | 0.059 | 2 | 0.029 | 0.39 | 0.682 | |
| Flour | weight | 0.057 | 2 | 0.029 | 0.862 | 0.428 |
| Fat | 0.049 | 1 | 0.049 | 1.484 | 0.229 | |
| Flour × Fat | 0.002 | 2 | 0.001 | 0.031 | 0.97 | |
| Flour | c-value | 0.036 | 2 | 0.018 | 4.729 | 0.013 * |
| Fat | 0.011 | 1 | 0.011 | 2.922 | 0.093 | |
| Flour × Fat | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0.045 | 0.956 | |
| Flour | baking loss | 45.6 | 2 | 22.8 | 8.73 | 0.001 * |
| Fat | 127.3 | 1 | 127.3 | 48.68 | <0.001 * | |
| Flour × Fat | 9.9 | 2 | 5 | 1.9 | 0.159 | |
| Flour | % shape accuracy | 16.29 | 2 | 8.14 | 2.033 | 0.141 |
| Fat | 14.48 | 1 | 14.48 | 3.616 | 0.063 | |
| Flour × Fat | 13.07 | 2 | 6.54 | 1.632 | 0.205 | |
| Flour | 1.873 | 2 | 0.937 | 43.21 | <0.001 * | |
| Fat | 0.032 | 1 | 0.032 | 1.46 | 0.233 | |
| Flour × Fat | 0.04 | 2 | 0.02 | 0.92 | 0.405 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vukušić Pavičić, T.; Grgić, T.; Ivanov, M.; Novotni, D.; Herceg, Z. Influence of Flour and Fat Type on Dough Rheology and Technological Characteristics of 3D-Printed Cookies. Foods 2021, 10, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010193
Vukušić Pavičić T, Grgić T, Ivanov M, Novotni D, Herceg Z. Influence of Flour and Fat Type on Dough Rheology and Technological Characteristics of 3D-Printed Cookies. Foods. 2021; 10(1):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010193
Chicago/Turabian StyleVukušić Pavičić, Tomislava, Tomislava Grgić, Mia Ivanov, Dubravka Novotni, and Zoran Herceg. 2021. "Influence of Flour and Fat Type on Dough Rheology and Technological Characteristics of 3D-Printed Cookies" Foods 10, no. 1: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010193
APA StyleVukušić Pavičić, T., Grgić, T., Ivanov, M., Novotni, D., & Herceg, Z. (2021). Influence of Flour and Fat Type on Dough Rheology and Technological Characteristics of 3D-Printed Cookies. Foods, 10(1), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010193