A Comparative Functional Analysis of Pea Protein and Grass Carp Protein Mixture via Blending and Co-Precipitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
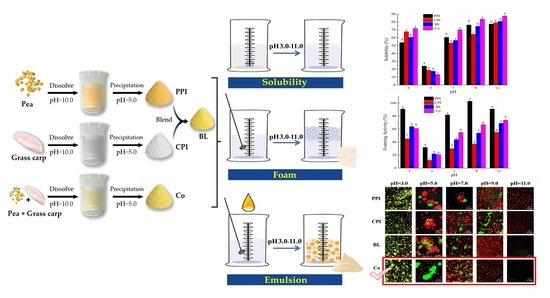
2.2. Preparation of PPI, CPI, Co, and BL
2.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.4. Solubility
2.5. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
2.6. Foaming Properties and Foaming Stability
2.7. Emulsion Preparation
2.8. Emulsifying Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsifying Stability Index (ESI)
2.9. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.10. Interface Protein Absorption (AP) and Interface Protein Content (Γ)
2.11. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.12. Rheological Properties
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protein Composition Analysis
3.2. Solubility and Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
3.3. Foaming Properties
3.4. Emulsifying Properties
3.4.1. EAI and ESI
3.4.2. Particle Size and Zeta-Potential Analysis
3.4.3. Interface Protein Adsorption (AP) and Interface Protein Content (Γ)
3.4.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
3.4.5. Rheological Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pimentel, D.; Pimentel, M. Sustainability of meat-based and plant-based diets and the environment. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 660S–663S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.H.; Yang, Y.; Bian, X.; Wang, B.; Ren, L.K.; Liu, L.L.; Yu, D.H.; Yang, J.; Guo, J.C.; Wang, L.; et al. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seed Protein–EGCG Conjugates: Covalent Bonding and Functional Research. Foods 2021, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.C.; Tavares, G.M. Mixing animal and plant proteins: Is this a way to improve protein techno-functionalities? Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, T.; Ren, C.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.S.; Du, M. Advancement of food-derived mixed protein systems: Interactions, aggregations, and functional properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 627–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, A.S.; Pires, C.; Batista, I.; Sousa, I.; Raymundo, A. Protein gels and emulsions from mixtures of Cape hake and pea proteins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Qi, B.K.; Xie, F.Y.; Hu, M.; Sun, Y.F.; Hu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Emulsion stability and dilatational rheological properties of soy/whey protein isolate complexes at the oil-water interface: Influence of pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.; Schroën, K.; Martín-González, M.; Berton-Carabin, C. Synergistic and antagonistic effects of plant and dairy protein blends on the physicochemical stability of lycopene-loaded emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yan, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, W.; Xu, X.; Du, M. A self-sorted gel network formed by heating a mixture of soy and cod proteins. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5140–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alu’datt, M.H.; Al-Rabadi, G.J.; Alli, I.; Ereifej, K.; Rababah, T.; Alhamad, M.N.; Torley, P.J. Protein co-precipitates: A review of their preparation and functional properties. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, H.T.; Christensen, M.; Hansen, M.S.; Hammershj, M.; Dalsgaard, T.K. Protein–protein interactions of a whey-pea protein co-precipitate. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 5777–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhallab, S.; Croguennec, T. Spontaneous Assembly and Induced Aggregation of Food Proteins. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2013, 256, 67–101. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, A.M.; Abu-Foul, N.S.; Moharram, Y.G. Preparation and characteristics of co-precipitate proteins from oil seeds and legumes seeds. Food Nahrung. 1995, 39, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alu’datt, M.H.; Alli, I.; Nagadi, M. Preparation, characterization and properties of whey-soy proteins co-precipitates. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Hong, P.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, D.; Zhong, T. Correlation between the Water Solubility and Secondary Structure of Tilapia-Soybean Protein Co-Precipitates. Molecules 2019, 24, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.Q.; Zhang, M.X.; Zheng, H.N.; Hong, P.Z.; Zhou, C.X. Emulsifying Properties Of Tilapia-Soybean Protein Co-Precipitates. Food Ferment. Ind. 2015, 41, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.H.; Zhou, C.X.; Zhu, P.H.; Li, T.; Hong, P.Z. Co-precipitated protein from tilapia muscle and soybean meal and its solubility and amino acid composition analysis. Food Ferment. Ind. 2018, 44, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- FAOSTAT. Production and prices statistics of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2019. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org (accessed on 26 October 2021).
- Ge, J.; Sun, C.X.; Corke, H.; Gul, K.; Gan, R.Y.; Fang, Y.P. The health benefits, functional properties, modifications, and applications of pea (Pisum sativum L.) protein: Current status, challenges, and perspectives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1835–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahergorabi, R.; Matak, K.E.; Jaczynski, J. Fish protein isolate: Development of functional foods with nutraceutical ingredients. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Peng, X.B.; Dong, Z.; You, Y.; Xu, H.P. Study on emulsifying properties of salt-soluble proteins from grass carp. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2013, 34, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Tu, S.; Ghosh, S.; Nickerson, M.T. Effect of pH on the inter-relationships between the physicochemical, interfacial and emulsifying properties for pea, soy, lentil and canola protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, H.G.; Hultin, H.O. Changes in Trout Hemoglobin Conformations and Solubility after Exposure to Acid and Alkali pH. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3633–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskard, C.A.; Li-Chan, E.C. Hydrophobicity of bovine serum albumin and ovalbumin determined using uncharged (PRODAN) and anionic (ANS-) fluorescent probes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2671–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekria, A.M.; Ahmed, I.; Ahmed, S.O.; Babiker, E.E. Nutritional and functional characterization of defatted seed cake of two Sudanese groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea) cultivars. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 629–637. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.N.; Tang, C.H. Pea protein exhibits a novel Pickering stabilization for oil-in-water emulsions at pH 3.0. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 58, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Wang, R.C.; He, S.H.; Chen, C.L.; Ma, Y. The stability and gastro-intestinal digestion of curcumin emulsion stabilized with soybean oil bodies. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 131, 109663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lu, J.; Fei, L.; Nsor-Atindana, J.; Fang, Z. Study on the emulsifying stability and interfacial adsorption of pea proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhao, J.M.; Li, X.P.; Yi, S.M.; Li, J.R.; Sun, X.T. Binding of aldehydes to myofibrillar proteins as affected by two-step heat treatments. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, H.; Hultin, H. Changes in conformation and subunit assembly of cod myosin at low and high pH and after subsequent refolding. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7187–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, R. Immunoaffinity chromatography as a means of purifying legumin from Pisum(pea) seeds. J. Biochem. 1979, 177, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barac, M.; Cabrilo, S.; Pesic, M.; Stanojevic, S.; Zilic, S.; Macej, O.; Ristic, N. Profile and functional properties of seed proteins from six pea (Pisum sativum) genotypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4973–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, M.; Adhikari, B.; Aldred, P.; Panozzo, J.F.; Kasapis, S.; Barrow, C.J. Interfacial and emulsifying properties of lentil protein isolate. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, A.C.Y.; Can Karaca, A.; Tyler, R.T.; Nickerson, M.T. Pea protein isolates: Structure, extraction, and functionality. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.Y.; Quillien, L.; Popineau, Y. Foaming and emulsifying properties of pea albumin fractions and partial characterisation of surface-active components. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1964–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Fukuda, T.; Zhang, M.; Motoyama, S.; Maruyama, N.; Utsumi, S. Comparison of physicochemical properties of 7S and 11S globulins from pea, fava bean, cowpea, and French bean with those of soybean-French bean 7S globulin exhibits excellent properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10273–10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Xie, J.; Gong, B.; Xin, X.; Wei, T.; Xuan, L.; Chang, L.; Xie, M. Extraction, physicochemical characteristics and functional properties of Mung bean protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 76, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Bandillo, N.; Wang, Y.; Ohm, J.B.; Rao, J. Functionality and structure of yellow pea protein isolate as affected by cultivars and extraction pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Song, J.; Yang, H.; Xiong, S.B.; Liu, Y.M.; Liu, R. Effects of Acid and Alkali Treatment on the Properties of Proteins Recovered from Whole Gutted Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) Using Isoelectric Solubilization/Precipitation. J. Food Qual. 2016, 39, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wihodo, M.; Moraru, C.I. Physical and chemical methods used to enhance the structure and mechanical properties of protein films: A review. J. Food Eng. 2013, 114, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity determination by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesch, R.; Juneja, M.; Monagle, C.; Corredig, M. Aggregation of soy/milk mixes during acidification. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.N.; Tang, C.H. pH-dependent emulsifying properties of pea [Pisum sativum (L.)] proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, E.Y.; Krishnan, S.; Randolph, T.W.; Carpenter, J.F. Physical stability of proteins in aqueous solution: Mechanism and driving forces in nonnative protein aggregation. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, L.; Silva, J.V.C.; Saffon, M.; Dombrowski, J. On the foaming properties of plant proteins: Current status and future opportunities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebiyi, A.P.; Aluko, R.E. Functional properties of protein fractions obtained from commercial yellow field pea (Pisum sativum L.) seed protein isolate. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.F.; Shen, C.; Wu, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.M. Comparison of wheat, soybean, rice, and pea protein properties for effective applications in food products. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, R.; Martínez, K.D.; Ruiz-Henestrosa, V.M.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Modification of foaming properties of soy protein isolate by high ultrasound intensity: Particle size effect. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 26, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J. Physicochemical and functional properties of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) myofibrillar protein glycated with konjac oligo-glucomannan. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 67, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.S.; Adebowale, K.O.; Ogunsanwo, B.M.; Sosanwo, O.A.; Bankole, S.A. On the fuctional properties of globulin and albumin protein fractions and flours of African locust bean (Parkia biglobossa). Food Chem. 2005, 92, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Structural and emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate subjected to acid and alka line pH-shifting processes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7576–7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeb, B.; Herz, E.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J. Impact of alcohols on the formation and stability of protein-stabilized nanoemulsions. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2014, 433, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Bui, T.H.; Dharmadana, D.; Zisu, B.; Chandrapala, J. Ultrasoundassisted formation of double emulsions stabilized by casein-whey protein mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Ma, L.; Li, T.Q.; Sun, D.X.; Hou, J.C.; Li, A.L.; Jiang, Z. Impact of ultrasonic power on the structure and emulsifying properties of whey protein isolate under various pH conditions. Process. Biochem. 2019, 81, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcclements, D.J. Critical review of techniques and methodologies for characterization of emulsion stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2007, 47, 611–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Avila, C.; Arranz, E.; Guri, A.; Trujillo, A.J.; Corredig, M. Vegetable protein isolate-stabilized emulsions for enhanced delivery of conjugated linoleic acid in Caco-2 cells. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, C.L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jiang, L.Z.; Qi, B.K.; Zhang, X.N.; Wang, Z.J.; Teng, F. Soy protein isolate-phosphatidylcholine nanoemulsions prepared using high-pressure homogenization. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Tang, C.H. Soy protein nanoparticle aggregates as pickering stabilizers for oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8888–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Cordobés, F.; Guerrero, A. Influence of pH on linear viscoelasticity and droplet size distribution of highly concentrated O/W crayfish flour-based emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriprablom, J.; Luangpituksa, P.; Wongkongkatep, J.; Pongtharangkul, T.; Suphantharika, M. Influence of pH and ionic strength on the physical and rheological properties and stability of whey protein stabilized o/w emulsions containing xanthan gum. J. Food Eng. 2019, 242, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Flocculation of protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Coupland, J.N. The effect of surfactants on the solubility, zeta potential, and viscosity of soy protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Samples | Aggregates | MHC | Convicilin | Leg α + β | Vicilin | AC | Leg α | TM | Leg β | Others | Vicilin/ Leg α + β |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | 11.61 | 15.90 | 4.60 | 9.98 | 7.22 | 19.31 | 10.63 | 5.31 | 9.98 | 5.45 | 0.72 |
| Co | 19.62 | 15.27 | 0.11 | 6.55 | 13.36 | 16.46 | 8.06 | 5.36 | 4.63 | 10.57 | 2.04 |
| pH | Samples | d4,3 (μm) | d3,2 (μm) | d′4,3 (μm) | d′3,2 (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | PPI | 10.66 ± 0.56 a | 6.75 ± 0.18 a | 3.68 ± 0.10 a | 2.63 ± 0.05 a |
| CPI | 3.53 ± 0.06 c | 2.58 ± 0.10 b | 1.08 ± 0.10 c | 1.29 ± 0.07 c | |
| BL | 6.91 ± 0.06 b | 3.23 ± 1.56 b | 1.84 ± 0.07 b | 1.63 ± 0.06 b | |
| Co | 3.29 ± 0.27 c | 2.10 ± 0.07 b | 0.90 ± 0.01 c | 0.87 ± 0.01 d | |
| 5.0 | PPI | 31.91 ± 3.23 a | 10.41 ± 1.01 a | 4.17 ± 0.13 b | 3.77 ± 0.19 a |
| CPI | 9.85 ± 0.10 d | 4.28 ± 0.06 c | 2.69 ± 0.22 c | 2.01 ± 0.24 b | |
| BL | 17.12 ± 1.46 c | 8.21 ± 0.36 b | 4.16 ± 0.13 b | 3.96 ± 0.34 a | |
| Co | 22.79 ± 2.75 b | 9.33 ± 0.23 ab | 7.76 ± 0.18 a | 3.73 ± 0.10 a | |
| 7.0 | PPI | 4.88 ± 0.19 a | 2.73 ± 0.05 a | 1.68 ± 0.03 a | 1.14 ± 0.07 a |
| CPI | 2.57 ± 0.18 c | 1.56 ± 0.09 c | 0.77 ± 0.08 c | 0.63 ± 0.02 d | |
| BL | 3.96 ± 0.09 b | 2.46 ± 0.17 b | 1.45 ± 0.07 b | 1.00 ± 0.02 b | |
| Co | 1.17 ± 0.07 d | 0.84 ± 0.07 d | 0.60 ± 0.03 d | 0.85 ± 0.00 c | |
| 9.0 | PPI | 3.20 ± 0.06 a | 2.89 ± 0.09 a | 1.28 ± 0.05 a | 1.16 ± 0.10 a |
| CPI | 2.01 ± 0.06 b | 1.85 ± 0.11 b | 0.89 ± 0.02 c | 0.72 ± 0.06 b | |
| BL | 3.02 ± 0.14 a | 2.75 ± 0.10 a | 1.12 ± 0.01 b | 1.02 ± 0.05 a | |
| Co | 0.95 ± 0.01 d | 0.86 ± 0.00 c | 0.68 ± 0.01 d | 0.39 ± 0.01 d | |
| 11.0 | PPI | 2.49 ± 0.05 a | 2.24 ± 0.19 a | 0.98 ± 0.03 a | 1.10 ± 0.07 a |
| CPI | 0.93 ± 0.02 c | 0.87 ± 0.02 b | 0.47 ± 0.00 b | 0.35 ± 0.00 c | |
| BL | 1.15 ± 0.05 b | 1.09 ± 0.03 b | 0.57 ± 0.02 c | 0.47 ± 0.02 b | |
| Co | 0.55 ± 0.01 d | 0.53 ± 0.02 c | 0.33 ± 0.01 d | 0.20 ± 0.00 d |
| Samples | pH = 3.0 | pH = 5 | pH = 7 | pH = 9 | pH = 11 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP/% | Γ/ (mg/m2) | AP% | Γ/ (mg/m2) | AP% | Γ/ (mg/m2) | AP% | Γ/ (mg/m2) | AP% | Γ/ (mg/m2) | |
| PPI | 33.43 ± 1.64 b | 13.61 ± 0.07 a | 2.96 ± 0.72 b | 2.73 ± 0.01 d | 22.94 ± 3.66 c | 4.04 ± 0.10 c | 38.39 ± 2.69 b | 6.60 ± 0.03 a | 48.11 ± 1.57 b | 7.75 ± 0.02 a |
| CPI | 38.91 ± 4.37 ab | 8.13 ± 0.23 c | 11.42 ± 1.12 a | 3.05 ± 0.02 c | 33.35 ± 0.88 b | 3.11 ± 0.00 d | 36.21 ± 2.87 b | 3.95 ± 0.02 c | 54.94 ± 4.08 b | 2.91 ± 0.09 c |
| BL | 36.19 ± 2.01 b | 9.18 ± 0.06 b | 9.42 ± 2.26 a | 5.30 ± 0.04 a | 32.50 ± 3.64 b | 4.56 ± 0.12 b | 37.33 ± 1.45 b | 5.66 ± 0.02 b | 54.29 ± 3.70 b | 3.81 ± 0.05 b |
| Co | 44.15 ± 0.87 a | 5.65 ± 0.03 d | 8.63 ± 0.51 a | 6.57 ± 0.00 b | 48.91 ± 4.31 a | 6.06 ± 0.26 a | 51.71 ± 4.89 a | 3.13 ± 0.11 d | 65.61 ± 4.49 a | 2.03 ± 0.21 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Cao, W.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, L. A Comparative Functional Analysis of Pea Protein and Grass Carp Protein Mixture via Blending and Co-Precipitation. Foods 2021, 10, 3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123037
Zhou X, Zhang C, Cao W, Zhou C, Zheng H, Zhao L. A Comparative Functional Analysis of Pea Protein and Grass Carp Protein Mixture via Blending and Co-Precipitation. Foods. 2021; 10(12):3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123037
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaohu, Chaohua Zhang, Wenhong Cao, Chunxia Zhou, Huina Zheng, and Liangzhong Zhao. 2021. "A Comparative Functional Analysis of Pea Protein and Grass Carp Protein Mixture via Blending and Co-Precipitation" Foods 10, no. 12: 3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123037
APA StyleZhou, X., Zhang, C., Cao, W., Zhou, C., Zheng, H., & Zhao, L. (2021). A Comparative Functional Analysis of Pea Protein and Grass Carp Protein Mixture via Blending and Co-Precipitation. Foods, 10(12), 3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123037