Plant-Based Cheeses: A Systematic Review of Sensory Evaluation Studies and Strategies to Increase Consumer Acceptance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Search Criteria
3. Literature Review
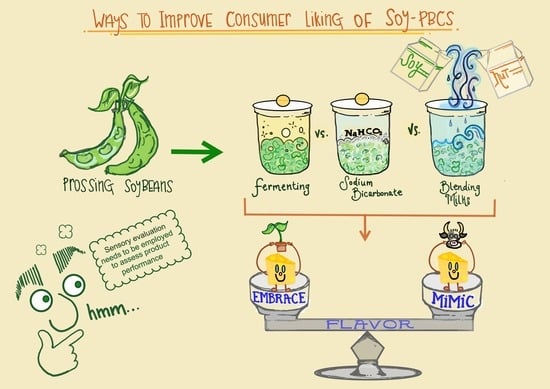
3.1. Strategies to Improve Consumer Liking
3.1.1. Modified Fermentation
3.1.2. Blending Milks
3.1.3. Modified Processing of Soybeans
3.2. Sensory Profile of Coconut-Based Cheese Products
4. Review of the Sensory Methods
4.1. Limitations and Considerations for Current Literature
4.2. Consumers and Future Considerations for Segmentation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nathan, C.; Garnett, T.; Lorimer, J. Dairy intensification: Drivers, impacts and alternatives. Ambio 2020, 49, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- SPINS. New Data Shows Plant-Based Food Outpacing Total Food Sales during COVID-19; SPINS Headquarters: Chicago, IL, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.spins.com/new-data-shows-plant-based-food-outpacing-total-food-sales-during-covid-19/ (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- GFI. Plant-Based Market (2020 Release); The Good Food Institute (GFI): Washington, DC, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.gfi.org/marketresearch (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Mintel Group Ltd. Cheese: Incl Impact of COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://store.mintel.com/report/cheese-incl-impact-of-covid-19-us-november-2020 (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Jeske, S.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Past, present and future: The strength of plant-based dairy substitutes based on gluten-free raw materials. Food Rest Int. 2018, 110, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeewanthi, R.; Paik, H. Modifications of nutritional, structural, and sensory characteristics of non-dairy soy cheese analogs to improve their quality attributes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 4384–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintel Group Ltd. Taste is Top Reason Americans Eat Plant-Based Proteins. 2018. Available online: https://www.mintel.com/press-centre/food-and-drink/taste-is-the-top-reason-us-consumers-eat-plant-based-proteins (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- McClements, D.J. Development of next-generation nutritionally fortified plant-based milk substitutes: Structural design principles. Foods 2020, 9, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mintel Group Ltd. GNPD. Ingredient Watch: Vegan Cheese Formulations; Mintel. UMass Library: Amherst, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://clients-mintel-com.silk.library.umass.edu/insight/ingredient-watch-vegan-cheese-formulations?fromSearch=%3Ffreetext%3DIngredient%2520Watch%253A%2520Vegan%2520Cheese%2520Formulations (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- Saraco, M.N.; Blaxland, J. Dairy-free imitation cheese: Is further development required? Br. Food J. 2020, 122, 3727–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IFT. Beyond Soy: Formulating Vegan and Vegetarian Foods; Institute of Food Technologists (IFT): Chicago, IL, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.ift.org/news-and-publications/food-technology-magazine/issues/2020/july/columns/ingredients-beyond-soy-formulating-vegan-and-vegetarian-foods (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Xu, X.; Duncan, A.M.; Wangen, K.E.; Kurzer, M.S. Soy consumption alters endogenous estrogen metabolism in postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2000, 9, 781–786. [Google Scholar]
- Bohrer, B.M. An investigation of the formulation and nutritional composition of modern meat analogue products. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, H. Cheese analogues: A review. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; McSweeney, P.L. Processed cheese and substitute/imitation cheese products. In Fundamentals of Cheese Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 589–627. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xie, J. Evaluation of the rheological, textural, microstructural and sensory properties of soy cheese spreads. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butool, M.; Butool, S. Studies on carrot incorporated soy paneer. Int. J. Dev. Res. 2015, 5, 4124–4130. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, X.; Jia, X.; Du, P.; Li, A. Influence of the addition of Geotrichum candidum on the microbial, chemical, textural, and sensory features of soft soy cheese. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumchuere, S.; MacDougall, D.B.; Robinson, R.K. Production and Properties of a Semi-Hard Cheese Made from Soya Milk. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adejuyitan, J.A.; Olanipekun, B.F.; Moyinwin, O.A. Production and evaluation of cheese-like product from the blend of soy milk and coconut milk. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2014, 6, 263–266. [Google Scholar]
- Khodke, S.; Pardhi, M.; Pramodini, M.; Kakade, A. Characteristic evaluation of soy-groundnut paneer. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2014, 8, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, M.A.; Oyeyinka, S.A.; Kolawole, F.L.; Joseph, J.K.; Olajobi, G.E. Chemical composition and sensory properties of soy-tiger nut cheese. Ceylon J. Sci. 2019, 48, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadbhane, V.S.; Shelke, G.N.; Thorat, S.L. Preparation of non-dairy cheese analogue enriched with coconut milk. Pharma Innov. 2019, 8, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- James, S.; Nwokocha, L.; Tsebam, B.; Amuga, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Audu, Y. Effects of different coagulants on the physico-chemical, microbial and sensory properties of Wara, a Nigerian soft soy-cheese. Agro-Science 2017, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyeyinka, A.T.; Odukoya, J.; Adebayo, Y.S. Nutritional composition and consumer acceptability of cheese analog from soy and cashew nut milk. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arise, A.; Opaleke, D.; Salami, K.; Awolola, G.; Akinboro, D. Physico-chemical and sensory properties of a cheese-like product from the blend of soymilk and almond milk. Agrosearch 2020, 19, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Khan, K.Y.; Majeed, H.; Xu, L.; Wu, F.; Tao, H.; Xu, X. Imitation of soymilk–cow’s milk mixed enzyme modified cheese: Their composition, proteolysis, lipolysis and sensory properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borhan, M. Lipoxygenase Activity and Protein Solubility in Extracts from Soybeans Treated with Heat and Ethanol. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Endres, J.G. Soy Protein Products: Characteristics, Nutritional Aspects, and Utilization; The American Oil Chemists Society: Urbana, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jianming, W.; Qiuqian, L.; Yiyun, W.; Xi, C. Research on Soybean Curd Coagulated by Lactic Acid Bacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 2, p. 250. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena, V.; Khu, W.S. NASAR-ABBAS SM. The development and sensory acceptability of lupin-based tofu. J. Food Qual. 2010, 33, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IFIC. Food and Health Survey; The International Food Information Council (IFIC) Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: https://foodinsight.org/2019-food-and-health-survey/ (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hough, G.; Wakeling, I.; Mucci, A.; Chambers, I.V.E.; Gallardo, I.M.; Alves, L.R. Number of consumers necessary for sensory acceptability tests. Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.E.; Sarah, C.; Merrigan, J.M. Sensory evaluation. In Food Science: An Ecological Approach; Jones & Bartlett Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 84–113. [Google Scholar]
- Adise, S.; Gavdanovich, I.; Zellner, D.A. Looks like chicken: Exploring the law of similarity in evaluation of foods of animal origin and their vegan substitutes. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 41, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.; Bleibaum, R.N.; Thomas, H.A. Sensory Evaluation Practices; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aini, N.; Sumarmono, J.; Sustriawan, B.; Prihananto, V.; Priscillia, E. The quality of corn milk-based cheese analogue made with virgin coconut oil as a fat substitute and with various emulsifiers. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 443, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattice, K.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Physical properties of plant-based cheese products produced with zein. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Strategy | Ingredient | Sensory Method | Described Sample Size | Solution | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Fermentation | soy | H/D | 10 panelists | Ferm/SB | Li, Q. et al., 2013 [16] |
| soy | H/D | 10 panelists | Ferm/SB | Li, Y. et al., 2020 [18] | |
| soy | H/D | 14 participants | Ferm | Chumchuere et al., 2020 [19] | |
| Blending Milks | soy/coconut | Hedonic | 10 participants | Ferm/BM | Adejuyitan et al., 2014 [20] |
| soy/groundnut | Hedonic | 10 panelists | Ferm/BM | Khodke et al., 2014 [21] | |
| soy/tigernut | Hedonic | 20 participants | Ferm/BM | Balogun et al., 2005 [22] | |
| soy | Hedonic | 20 panelists | B* | Butool et al., 2015 [17] | |
| Modified Processing | soy/coconut | Hedonic | not reported | Blanching/BM/SB | Kadbhane et al., 2019 [23] |
| soy | Hedonic | 20 participants | Acidification | James et al., 2016 [24] | |
| soy/cashew | Hedonic | 30 participants | Blanching/BM | Oyeyinka et al., 2019 [25] | |
| soy/almond | Hedonic | 50 participants | Ferm/BM | Arise et al., 2020 [26] | |
| Commercial ProductsA | coconut | H/D | 4 panelists | N/A | Saraco et al., 2020 [10] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Short, E.C.; Kinchla, A.J.; Nolden, A.A. Plant-Based Cheeses: A Systematic Review of Sensory Evaluation Studies and Strategies to Increase Consumer Acceptance. Foods 2021, 10, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040725
Short EC, Kinchla AJ, Nolden AA. Plant-Based Cheeses: A Systematic Review of Sensory Evaluation Studies and Strategies to Increase Consumer Acceptance. Foods. 2021; 10(4):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040725
Chicago/Turabian StyleShort, Erin C., Amanda J. Kinchla, and Alissa A. Nolden. 2021. "Plant-Based Cheeses: A Systematic Review of Sensory Evaluation Studies and Strategies to Increase Consumer Acceptance" Foods 10, no. 4: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040725
APA StyleShort, E. C., Kinchla, A. J., & Nolden, A. A. (2021). Plant-Based Cheeses: A Systematic Review of Sensory Evaluation Studies and Strategies to Increase Consumer Acceptance. Foods, 10(4), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040725