Searching for the Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Neuroprotective Potential of Natural Food and Nutritional Supplements for Ocular Health in the Mediterranean Population
Abstract
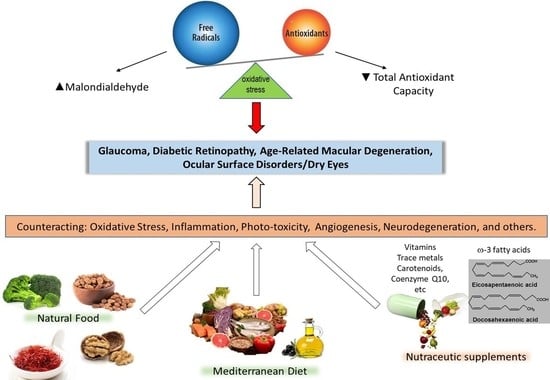
:1. Introduction
2. State of the Art
3. Material and Methods
Design
4. Natural Food and Ocular Health
4.1. Broccoli
4.2. Saffron
4.3. Tigernut-Chufa de Valencia
4.4. Walnuts
5. Mediterranean Diet—Current Knowledge on Eye Diseases
6. Nutritional Supplements
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. World Report on Vision; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/world-report-on-vision (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- GBD 2019 Blindness and Vision Impairment Collaborators; Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study. Causes of blindness and vision impairment in 2020 and trends over 30 years, and prevalence of avoidable blindness in relation to VISION 2020: The Right to Sight: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e144–e160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tuo, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, A.; Machalińska, A.; Long, Q. Pathogenesis of Common Ocular Diseases. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 734527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanzetta, P.; Sarao, V.; Scanlon, P.H.; Barratt, J.; Porta, M.; Bandello, F.; Loewenstein, A. Fundamental principles of an effective diabetic retinopathy screening program. Acta Diabetol. 2020, 57, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pondorfer, S.G.; Terheyden, J.H.; Heinemann, M.; Wintergerst, M.W.M.; Holz, F.G.; Finger, R.P. Association of Vision-related Quality of Life with Visual Function in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; García-Medina, J.J.; Arévalo, J.F.; Gallego-Pinazo, R.; Nucci, C. Eclectic Ocular Comorbidities and Systemic Diseases with Eye Involvement: A Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6215745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinazo-Duran, M.D.; Zanon-Moreno, V.; Garcıa-Medina, J.J.; Gallego-Pinazo, R. Evaluation of presumptive biomarkers of oxidative stress, immune response and apoptosis in primary open-angle glaucoma. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinazo-Durán, M.; Gallego-Pinazo, R.; García-Medina, J.J.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; Nucci, C.; Dolz-Marco, R.; Martínez-Castillo, S.; Galbis-Estrada, C.; Marco-Ramírez, C.; López-Gálvez, M.I.; et al. Oxidative stress in aging eyes. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nita, M.; Grzybowski, A. The Role of the Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in the Pathomechanism of the Age-Related Ocular Diseases and Other Pathologies of the Anterior and Posterior Eye Segments in Adults. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3164734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finkel, T. Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Muñoz-Negrete, F.J.; Sanz-González, S.M.; Benítez-Del-Castillo, J.; Giménez-Gómez, R.; Valero-Velló, M.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; García-Medina, J.J. The role of neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of glaucoma neurodegeneration. Prog. Brain Res. 2020, 256, 99–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Byzova, T.V. Oxidative stress in angiogenesis and vascular disease. Blood 2014, 5, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, A.; Xie, B.; Shen, J.; Yoshida, T.; Yokoi, K.; Hackett, S.F.; Campochiaro, P.A. Oxidative stress promotes ocular neovascularization. J. Cell Physiol. 2009, 219, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Przedborski, S.; Vila, M.; Jackson-Lewis, V. Neurodegeneration: What is it and where are we? J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maresca, A.; la Morgia, C.; Caporali, L.; Valentino, M.L.; Carelli, V. The optic nerve: A “mito-window” on mitochondrial neurodegeneration. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2013, 55, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinazo-Duran, M.D.; Zanon-Moreno, V.; Gallego-Pinazo, R.; Garcıa-Medina, J.J. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial failure in the pathogenesis of glaucoma neurodegeneration. Prog. Brain Res. 2015, 220, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia, K.C.; Adams, E.J. How the T cell receptor sees antigen—A structural view. Cell 2005, 122, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemke, H. Immune Response Regulation by Antigen Receptors’ Clone-Specific Nonself Parts. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, B.V.; Connors, T.J.; Farber, D.L. Human T Cell Development, Localization, and Function throughout Life. Immunity 2018, 48, 202–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benitez-Del-Castillo, J.; Cantu-Dibildox, J.; Sanz-González, S.M.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; Pinazo-Duran, M.D. Cytokine expression in tears of patients with glaucoma or dry eye disease: A prospective, observational cohort study. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 29, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Nakao, S.; Sonoda, K.H. Innate immune response in retinal homeostasis and inflammatory disorders. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 74, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooff, Y.; Man, S.M.; Aggio-Bruce, R.; Natoli, R.; Fernando, N. IL-1 family members mediate cell death, inflammation and angiogenesis in retinal degenerative diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindler, E.; Zipp, F. Neuronal injury in chronic CNS inflammation. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 24, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, N.N. Pathogenesis of ganglion “cell death” in glaucoma and neuroprotection: Focus on ganglion cell axonal mitochondria. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 173, 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Carelli, V.; La Morgia, C.; Ross-Cisneros, F.N.; Sadun, A.A. Optic neuropathies: The tip of the neurodegeneration iceberg. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, R139–R150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chitranshi, N.; Dheer, Y.; Abbasi, M.; You, Y.; Graham, S.L.; Gupta, V. Glaucoma pathogenesis and neurotrophins: Focus on the molecular and genetic basis for therapeutic prospects. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1018–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.D.; Newman-Casey, P.A.; Mrinalini, T.; Lee, P.P.; Hutton, D.W. Cost-effectiveness of bevacizumab and ranibizumab for newly diagnosed neovascular macular degeneration (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis). Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2013, 111, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niketeghad, S.; Pouratian, N. Brain Machine Interfaces for Vision Restoration: The Current State of Cortical Visual Prosthetics. Neurotherapeutics. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neuro Ther. 2019, 16, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Micera, A.; Balzamino, B.O.; Di Zazzo, A.; Dinice, L.; Bonini, S.; Coassin, M. Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration and Precision Therapy in Retinal Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 601647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, O.; Chi, G.; Brady, L.; Hippert, C.; Del Valle Rubido, M.; Daly, A.; Michaelides, M. The Impact of Inherited Retinal Diseases in the Republic of Ireland (ROI) and the United Kingdom (UK) from a Cost-of-Illness Perspective. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.K.; Nasonkin, I.O. Limitations and Promise of Retinal Tissue from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells for Developing Therapies of Blindness. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, K.L.; Harris, F.; Sioen, G.B.; Wannous, C.; Anyamba, A.; Bi, P.; Boeckmann, M.; Bowen, K.; Cissé, G.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. Transdisciplinary Research Priorities for Human and Planetary Health in the Context of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Banerjee, P.; Anas, M.; Singh, N.; Qamar, I. Traditional Nutritional and Health Practices Targeting Lifestyle Behavioral Changes in Humans. J. Lifestyle Med. 2020, 10, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.H.; Shin, D.S.; Lee, S.C.; Hwang, I.C. Sodium Intake and Socioeconomic Status as Risk Factors for Development of Age-Related Cataracts: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research Group. A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of high-dose supplementation with vitamins C and E, beta carotene, and zinc for age-related macular degeneration and vision loss: AREDS report no. 8. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2001, 119, 1417–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 Research Group. Lutein + zeaxanthin and omega-3 fatty acids for age-related macular degeneration: The Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrón, E.; Mares, J.; Clemons, T.E.; Swaroop, A.; Chew, E.Y.; Keenan, T.D.L.; AREDS and AREDS2 Research Groups. Dietary Nutrient Intake and Progression to Late Age-Related Macular Degeneration in the Age-Related Eye Disease Studies 1 and 2. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snodderly, D.M.; Mares, J.A.; Wooten, B.R.; Oxton, L.; Gruber, M.; Ficek, T.; CAREDS Macular Pigment Study Group. Macular pigment measurement by heterochromatic flicker photometry in older subjects: The carotenoids and age-related eye disease study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roig-Revert, M.J.; Lleó-Pérez, A.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; Vivar-Llopis, B.; Marín-Montiel, J.; Dolz-Marco, R.; Alonso-Muñoz, L.; Albert-Fort, M.; López-Gálvez, M.I.; Galarreta-Mira, D.; et al. Valencia Study On Diabetic Retinopathy (VSDR). Enhanced Oxidative Stress and Other Potential Biomarkers for Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetics: Beneficial Effects of the Nutraceutic Supplements. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 408180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, S.M.; Voland, R.; Tinker, L.; Blodi, B.A.; Klein, M.L.; Gehrs, K.M.; Johnson, E.J.; Snodderly, D.M.; Wallace, R.B.; Chappell, R.J.; et al. Associations between age-related nuclear cataract and lutein and zeaxanthin in the diet and serum in the Carotenoids in the Age-Related Eye Disease Study, an Ancillary Study of the Women’s Health Initiative. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008, 126, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, A.; Alassane, S.; Binquet, C.; Bretillon, L.; Acar, N.; Arnould, L.; Muselier-Mathieu, A.; Delcourt, C.; Bron, A.M.; Creuzot-Garcher, C. Dry eye disease in the elderly in a French population-based study (the Montrachet study: Maculopathy, Optic Nerve, nuTRition, neurovAsCular and HEarT diseases): Prevalence and associated factors. Ocul. Surf. 2018, 16, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, A.L.; Asbell, P.A. Nutritional supplements for dry eye syndrome. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2011, 22, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Galbis-Estrada, C.; Pons-Vázquez, S.; Cantú-Dibildox, J.; Marco-Ramírez, C.; Benítez-del-Castillo, J. Effects of a nutraceutical formulation based on the combination of antioxidants and ω-3 essential fatty acids in the expression of inflammation and immune response mediators in tears from patients with dry eye disorders. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galbis-Estrada, C.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Cantú-Dibildox, J.; Marco-Ramírez, C.; Díaz-Llópis, M.; Benítez-del-Castillo, J. Patients undergoing long-term treatment with antihypertensive eye drops responded positively with respect to their ocular surface disorder to oral supplementation with antioxidants and essential fatty acids. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Barabino, S.; Horwath-Winter, J.; Messmer, E.M.; Rolando, M.; Aragona, P.; Kinoshita, S. The role of systemic and topical fatty acids for dry eye treatment. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 61, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signes-Soler, I.; Javaloy Estañ, J. Nutrition and dry eye: A systematic review. Exp. Rev. Ophthalmol. 2019, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, S.G.; Smith, K.M.; Aragonès, G.; Whitcomb, E.A.; Weinberg, J.; Wang, X.; Bejarano, E.; Taylor, A.; Rowan, S. Dietary Patterns, Carbohydrates, and Age-Related Eye Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrone, L.A.; Rombolà, L.; Corasaniti, M.T.; Bagetta, G.; Nucci, C.; Russo, R. Natural compounds and retinal ganglion cell neuroprotection. Prog. Brain Res. 2015, 220, 257–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramdas, W.D. The relation between dietary intake and glaucoma: A systematic review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Owaifeer, A.M.; Al Taisan, A.A. The Role of Diet in Glaucoma: A Review of the Current Evidence. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2018, 7, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinazo-Duran, M.D.; Shoaie-Nia, K.; Zanon-Moreno, V.; Sanz-Gonzalez, S.M.; Del Castillo, J.B.; Garcia-Medina, J.J. Strategies to Reduce Oxidative Stress in Glaucoma Patients. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccà, S.C.; Corazza, P.; Gandolfi, S.; Ferrari, D.; Sukkar, S.; Iorio, E.L.; Traverso, C.E. Substances of Interest That Support Glaucoma Therapy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinazo-Duran, M.D.; Bendala Tufanisco, E. Guidelines for Nutrition in Retinal Diseases; Domenech Pujades: Barcelona, Spain, 2018; ISBN 978-84-697-4909-8. [Google Scholar]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Lee, C.H.; Estruch, R.; Clish, C.B.; Ros, E. Protective Effects of the Mediterranean Diet on Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. J. Nutr. 2015, 146, 920S–927S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merle, B.M.J.; Rosner, B.; Seddon, J.M. Genetic Susceptibility, Diet Quality, and Two-Step Progression in Drusen Size. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala-Vila, A.; Díaz-López, A.; Valls-Pedret, C.; Cofán, M.; García-Layana, A.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Castañer, O.; Zanon-Moreno, V.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Toledo, E.; et al. Dietary Marine ω-3 Fatty Acids and Incident Sight-Threatening Retinopathy in Middle-Aged and Older Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: Prospective Investigation From the PREDIMED Trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho-Barcia, L.; Bulló, M.; García-Gavilán, J.F.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Estruch, R.; Fitó, M.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Arós, F.; Fiol, M.; et al. Dairy products intake and the risk of incident cataracts surgery in an elderly Mediterranean population: Results from the PREDIMED study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viswanathan, M.; Patnode, C.; Berkman, N.D.; Bass, E.B.; Chang, S.; Hartling, L.; Murad, H.M.; Treadwell, J.R.; Kane, R.L. Assessing the Risk of Bias in Systematic Reviews of Health Care Interventions. Methods Guide for Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. (Prepared by the Scientific Resource Center under Contract No. 290-2012-0004-C); AHRQ Publication No. 17(18)-EHC036-EF; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2017; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann-Eßer, W.; Siering, U.; Neugebauer, E.A.; Brockhaus, A.C.; Lampert, U.; Eikermann, M. Guideline appraisal with AGREE II: Systematic review of the current evidence on how users handle the 2 overall assessments. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favela-González, K.M.; Hernández-Almanza, A.Y.; De la Fuente-Salcido, N.M. The value of bioactive compounds of cruciferous vegetables (Brassica) as antimicrobials and antioxidants: A review. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campas-Baypoli, O.N.; Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; Bueno-Solano, C.; Núñez-Gastélum, J.A.; Reyes-Moreno, C.; López-Cervantes, J. Biochemical composition and physicochemical properties of broccoli flours. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60 (Suppl. 4), 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.N.; Luong, H.Q.; Li, H.P.; Chiu, C.H.; Hsieh, P.C. Broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. var. italica) Sprouts as the Potential Food Source for Bioactive Properties: A Comprehensive Study on In Vitro Disease Models. Foods 2019, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, T.N.; Chiu, C.H.; Hsieh, P.C. Bioactive Compounds and Bioactivities of Brassica oleracea L. var. Italica Sprouts and Microgreens: An Updated Overview from a Nutraceutical Perspective. Plants 2020, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-H.; Lim, S.B. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Broccoli Florets in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 19, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalpana Deepa Priya, D.; Gayathri, R.; Gunassekaran, G.R.; Murugan, S.; Sakthisekaran, D. Apoptotic role of natural isothiocyanate from broccoli (Brassica oleracea italica) in experimental chemical lung carcinogenesis. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elkashty, O.A.; Tran, S.D. Broccoli extract increases drug-mediated cytotoxicity towards cancer stem cells of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente, B.; López-García, G.; Máñez, V.; Alegría, A.; Barberá, R.; Cilla, A. Antiproliferative Effect of Bioaccessible Fractions of Four Brassicaceae Microgreens on Human Colon Cancer Cells Linked to Their Phytochemical Composition. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbarzadeh Kaboli, P.; Afzalipour Khoshkbejari, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Abiri, A.; Mokhtarian, R.; Vazifemand, R.; Amanollahi, S.; Yazdi Sani, S.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Targets and mechanisms of sulforaphane derivatives obtained from cruciferous plants with special focus on breast cancer—Contradictory effects and future perspectives. BioMed Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacoppo, S.; Galuppo, M.; Montaut, S.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. An overview on neuroprotective effects of isothiocyanates for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Fitoterapia 2015, 106, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepici, G.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Efficacy of Sulforaphane in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, S.; Matsui, T. Protective role of sulphoraphane against vascular complications in diabetes. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rein, D.B.; Wittenborn, J.S.; Zhang, X.; Honeycutt, A.A.; Lesesne, S.B.; Saaddine, J. Vision Health Cost-Effectiveness Study Group. Forecasting age-related macular degeneration through the year 2050: The potential impact of new treatments. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bone, R.A.; Landrum, J.T.; Tarsis, S.L. Preliminary identification of the human macular pigment. Vis. Res. 1985, 25, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, R.; Calvo, C.M.; Conrady, C.D.; Bernstein, P.S. What do we know about the macular pigment in AMD: The past, the present, and the future. Eye 2018, 2, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research Group; SanGiovanni, J.P.; Chew, E.Y.; Clemons, T.E.; Ferris, F.L., 3rd; Gensler, G.; Lindblad, A.S.; Milton, R.C.; Seddon, J.M.; Sperduto, R.D. The relationship of dietary carotenoid and vitamin A, E, and C intake with age-related macular degeneration in a case-control study: AREDS Report No. 22. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2007, 125, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) Research Group; Chew, E.Y.; Clemons, T.E.; Sangiovanni, J.P.; Danis, R.P.; Ferris, F.L., 3rd; Elman, M.J.; Antoszyk, A.N.; Ruby, A.J.; Orth, D.; et al. Secondary analyses of the effects of lutein/zeaxanthin on age-related macular degeneration progression: AREDS2 report No. 3. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, P.S.; Delori, F.C.; Richer, S.; van Kuijk, F.J.; Wenzel, A.J. The value of measurement of macular carotenoid pigment optical densities and distributions in age-related macular degeneration and other retinal disorders. Vis. Res. 2010, 50, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolz-Marco, R.; Gallego-Pinazo, R.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Diaz-Llópis, M. Macular pigment optical density. In Thea Monographies of Information and Research in Ophthalmology; 2013; Volume 68, pp. 1–20. ISSN 84-1887-4096. Available online: https://www.laboratoriosthea.com/medias/thea_informacion_68.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Yu, L.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.T.Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.L. Home food preparation techniques impacted the availability of natural antioxidants and bioactivities in kale and broccoli. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Lim, S.B. Antioxidant and anticancer activities of broccoli by-products from different cultivars and maturity stages at harvest. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2015, 20, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsui, T.; Nakamura, N.; Ojima, A.; Nishino, Y.; Yamagishi, S.I. Sulforaphane reduces advanced glycation end products (AGEs)-induced inflammation in endothelial cells and rat aorta. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016, 26, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomparens, E.A.; Ding, Y. The neuroprotective mechanisms and effects of sulforaphane. Brain Circ. 2019, 5, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Vanduchova, A.; Anzenbacher, P.; Anzenbacherova, E. Isothiocyanate from Broccoli, Sulforaphane, and Its Properties. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basker, D.; Negbi, M. Uses of saffron. Econ. Bot. 1983, 37, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.; Oskoueian, E.; Hendra, R.; Jaafar, H.Z.E. Evaluation of Crocus sativus L. Stigma Phenolic and Flavonoid Compounds and Its Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2010, 15, 6244–6256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashemi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. A comprehensive review on biological activities and toxicology of crocetin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 130, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Qian, Z.; Du, P.; Fu, J. Pharmacokinetic properties of crocin (crocetin digentiobiose ester) following oral administration in rats. Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Saffron and its Active Components. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 43, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari, S.; Roshanravan, N. Saffron; An updated review on biological properties with special focus on cardiovascular effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Albarral, J.A.; De Hoz, R.; Ramírez, A.I.; López-Cuenca, I.; Salobrar-García, E.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Ramírez, J.M.; Salazar, J.J. Beneficial effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in ocular pathologies, particularly neurodegenerative retinal diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assimopoulou, A.N.; Sinakos, Z.; Papageorgiou, V.P. Radical scavenging activity of Crocus sativus L. extract and its bioactive constituents. Phyther. Res. 2005, 19, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeinali, M.; Zirak, M.R.; Rezaee, S.A.; Karimi, G.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Immunoregulatory and anti-inflammatory properties of Crocus sativus (Saffron) and its main active constituents: A review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khazdair, M.R.; Boskabady, M.H.; Hosseini, M.; Rezaee, R.; Tsatsakis, A.M. The effects of Crocus sativus (saffron) and its constituents on nervous system: A review. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akhondzadeh, S.; Sabet, M.S.; Harirchian, M.H.; Togha, M.; Cheraghmakani, H.; Razeghi, S.; Hejazi, S.S.; Yousefi, M.H.; Alimardani, R.; Jamshidi, A.; et al. Saffron in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A 16-week, randomized and placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardi, M.; Marangoni, D.; Minnella, A.M.; Savastano, M.C.; Valentini, P.; Ambrosio, L.; Capoluongo, E.; Maccarone, R.; Bisti, S.; Falsini, B. A longitudinal follow-up study of saffron supplementation in early age-related macular degeneration: Sustained benefits to central retinal function. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 429124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashay, A.; Sadough, G.; Ashrafi, E.; Lashay, M.; Movassat, M.; Akhondzadeh, S. Short-term Outcomes of Saffron Supplementation in Patients with Age-related Macular Degeneration: A Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Randomized Trial. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. J. 2016, 5, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Atkin, S.L.; Sahebkar, A. A review of the molecular mechanisms of hyperglycemia-induced free radical generation leading to oxidative stress. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1300–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepahi, S.; Mohajeri, S.A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Khodaverdi, E.; Shoeibi, N.; Namdari, M.; Tabassi, S.A.S. Effects of Crocin on Diabetic Maculopathy: A Placebo-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 190, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, I.; Achiron, A.; Bartov, E.; Maharshak, I.; Mendel, L.; Pe’er, L.; Bar, A.; Burgansky-Eliash, Z. Effects of dietary and lifestyle recommendations on patients with glaucoma: A randomized controlled pilot trial. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 25, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarpoor Bonyadi, M.H.; Yazdani, S.; Saadat, S. The ocular hypotensive effect of saffron extract in primary open angle glaucoma: A pilot study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Albarral, J.A.; Ramírez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; López-Villarín, N.; Salobrar-García, E.; López-Cuenca, I.; Licastro, E.; Inarejos-García, A.M.; Almodóvar, P.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; et al. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of a hydrophilic saffron extract in a model of glaucoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bixquert Jiménez, M. Horchata y Salud. Propiedades saludables y de prevención de enfermedades digestivas. In Jornada Chufa y Horchata, Tradición y Salud. Generalitat Valenciana; Conselleria de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación: Valencia, Spain, 2003; pp. 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Codina-Torrella, I.; Guamis, B.; Trujillo, A.J. Characterization and comparison of tiger nuts (Cyperus esculentus L.) from different geographical origin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, D.; Nunes, D.S.; Barba, F.J. An integrated strategy between food chemistry, biology, nutrition, pharmacology, and statistics in the development of functional foods: A proposal. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, A.A.M.; Awad, A.M.; Mohamed, H.H.; Iryna, S. Chemical composition, physicochemical properties and fatty acid profile of tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus L) seed oil as affected by different preparation methods. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Roselló-Soto, E.; Poojary, M.M.; Barba, F.J.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Mañes, J.; Moltó, J.C. Tiger nut and its by-products valorization: From extraction of oil and valuable compounds to development of new healthy products. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 45, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King Jaime II of Aragon. Letter to Ermengol Blasi about the Chufa Properties. (6 December 1297). Available online: http://www.chufadevalencia.org/ver/244/Historia.html (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Vilanova, A. Valencia Cathedral Archive. Manuscrito de la Biblioteca Capitular de Valencia, nº 123, 1307.
- Cavanilles, A.J. Observaciones Sobre la Historia Natural, Geografía, Agricultura, Población y Frutos del Reino de Valencia; Imprenta Real: Madrid, Spain, 1975; Available online: https://bivaldi.gva.es/es/consulta/registro.cmd?id=284 (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Denominación de Origen Chufa de Valencia. Available online: http://www.chufadevalencia.org/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Udefa, A.L.; Amama, E.A.; Archibong, E.A.; Nwangwa, J.N.; Adama, S.; Inyang, V.U.; Inyaka, G.U.; Aju, G.J.; Okpa, S.; Inah, I.O. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of hydro-ethanolic extract of Cyperus esculentus L. (tigernut) on lead acetate-induced testicular dysfunction in Wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguwike, F.N.; Nwosu, P.N.; Nwafor, C.; Onumonu, C.; Eluke, B.C.; Eze, R.I.; Asika, C.M. The effects of Cyperus esculentus (Tiger nut) on Haematological and Biochemical Profile of Male Hypercholesteremic Subjects in Uli, Anambra State Nigeria. Greener J. Med. Sci. 2017, 7, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zommara, M.; Imaizumi, K. Antiatherogenic effect of Tiger nut tubers (Cyperus esculentus L.) supplemented diet in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. J. Sustain. Agric. Sci. 2018, 43, 197–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahrani, A.A.; Greaves, R.F. Fat-Soluble Vitamins: Clinical Indications and Current Challenges for Chromatographic Measurement. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2016, 37, 27–47. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, V. Vitamin E. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinheiro-Sant’Ana, H.; Guinazi, M.; Oliveira, D.; Della Lucia, C.; Reis, B.; Brandão, S. Method for simultaneous analysis of eight vitamin E isomers in various foods by high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. 2011, 1218, 8496–8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, F.P.; Fernandes, R.S.; Bernardes, T.F.; Bonfioli, A.A.; Soares, E.J. Dry eye disease. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2010, 25, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubota, K.; Kawashima, M.; Inaba, T.; Dogru, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ishida, R.; Kaido, M.; Kojima, T.; Uchino, M.; Uchino, Y.; et al. The antiaging approach for the treatment of dry eye. Cornea 2012, 31 (Suppl. 1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Shibuya, M.; Nakashima, H.; Hisamura, R.; Masuda, N.; Imagawa, T.; Uehara, M.; Tsubota, K. Involvement of oxidative stress on corneal epithelial alterations in a blink-suppressed dry eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A.; Castellanos, E.; Stern, M.E.; Fernández, I.; Carreño, E.; García-Vázquez, C.; Herreras, J.M.; Calonge, M. Tear cytokine and chemokine analysis and clinical correlations in evaporative-type dry eye disease. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 862–873. [Google Scholar]
- Galbis-Estrada, C.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Martínez-Castillo, S.; Morales, J.M.; Monleón, D.; Zanon-Moreno, V. A metabolomic approach to dry eye disorders. The role of oral supplements with antioxidants and omega 3 fatty acids. Mol Vis. 2015, 21, 555–567. [Google Scholar]
- Saccà, S.C.; Cutolo, C.A.; Ferrari, D.; Corazza, P.; Traverso, C.E. The Eye, Oxidative Damage and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Nutrients 2018, 10, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ros, E.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Sala-Vila, A. Beneficial Effects of Walnut Consumption on Human Health: Role of Micronutrients. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulose, S.M.; Miller, M.G.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Role of Walnuts in Maintaining Brain Health with Age. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 561S–566S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chauhan, A.; Chauhan, V. Beneficial Effects of Walnuts on Cognition and Brain Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sala-Vila, A.; Valls-Pedret, C.; Rajaram, S.; Coll-Padrós, N.; Cofán, M.; Serra-Mir, M.; Pérez-Heras, A.M.; Roth, I.; Freitas-Simoes, T.M.; Doménech, M.; et al. Effect of a 2-Year Diet Intervention with Walnuts on Cognitive Decline. The Walnuts and Healthy Aging (WAHA) Study: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram, S.; Valls-Pedret, C.; Cofán, M.; Sabaté, J.; Serra-Mir, M.; Pérez-Heras, A.M.; Arechiga, A.; Casaroli-Marano, R.P.; Alforja, S.; Sala-Vila, A.; et al. The Walnuts and Healthy Aging Study (WAHA): Protocol for a Nutritional Intervention Trial with Walnuts on Brain Aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 8, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunes, S.; Alves, D.; Barreto, P.; Raimundo, M.; da Luz Cachulo, M.; Farinha, C.; Laíns, I.; Rodrigues, J.; Almeida, C.; Ribeiro, L.; et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet and Its Association with Age-Related Macular Degeneration. The Coimbra Eye Study–Report 4. Nutrition 2018, 51–52, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braakhuis, A.; Raman, R.; Vaghefi, E. The Association between Dietary Intake of Antioxidants and Ocular Disease. Diseases 2017, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rinninella, E.; Mele, M.; Merendino, N.; Cintoni, M.; Anselmi, G.; Caporossi, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Minnella, A. The Role of Diet, Micronutrients and the Gut Microbiota in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: New Perspectives from the Gut–Retina Axis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.S.L. Dietary Fatty Acids and the 10-Year Incidence of Age-Related Macular Degeneration: The Blue Mountains Eye Study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schleicher, M.; Weikel, K.; Garber, C.; Taylor, A. Diminishing Risk for Age-Related Macular Degeneration with Nutrition: A Current View. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2405–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walchuk, C.; Suh, M. Nutrition and the aging retina: A comprehensive review of the relationship between nutrients and their role in age-related macular degeneration and retina disease prevention. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 93, 293–332. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Medina, J.J.; Rubio-Velazquez, E.; Foulquie-Moreno, E.; Casaroli-Marano, R.P.; Pinazo-Duran, M.D.; Zanon-Moreno, V.; del-Rio-Vellosillo, M. Update on the Effects of Antioxidants on Diabetic Retinopathy: In Vitro Experiments, Animal Studies and Clinical Trials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryman, C.E.; Grieger, J.A.; West, S.G.; Chen, C.-Y.O.; Blumberg, J.B.; Rothblat, G.H.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Acute Consumption of Walnuts and Walnut Components Differentially Affect Postprandial Lipemia, Endothelial Function, Oxidative Stress, and Cholesterol Efflux in Humans with Mild Hypercholesterolemia. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Smith, L.E.H. Retinal Vasculature in Development and Diseases. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2018, 4, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.R.; Lawrenson, J.G. Antioxidant Vitamin and Mineral Supplements for Slowing the Progression of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD000254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, A.; Mienotti, A.; Karvonen, M.J.; Aravanis, C.; Blackburn, H.; Buzina, R.; Djordjevic, B.S.; Dontas, A.S.; Fidanza, F.; Keys, M.H.; et al. The diet and 15-year death rate in the seven countries study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 124, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Peláez, S.; Fito, M.; Castaner, O. Mediterranean Diet Effects on Type 2 Diabetes Prevention, Disease Progression, and Related Mechanisms. A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Maiorino, M.I.; Bellastella, G.; Chiodini, P.; Panagiotakos, D.; Giugliano, D. A journey into a Mediterranean diet and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analyses. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Innocenzo, S.; Biagi, C.; Lanari, M. Obesity and the Mediterranean Diet: A Review of Evidence of the Role and Sustainability of the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin-Calvo, N.; Chavarro, J.E.; Falbe, J.; Hu, F.B.; Field, A.E. Adherence to the Mediterranean dietary pattern and BMI change among US adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keenan, T.D.; Agrón, E.; Mares, J.; Clemons, T.E.; van Asten, F.; Swaroop, A.; Chew, E.Y.; Age-Related Eye Disease Studies (AREDS) 1 and 2 Research Groups. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Progression to Late Age-Related Macular Degeneration in the Age-Related Eye Disease Studies 1 and 2. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, R.; Sacanella, E.; Estruch, R. The immune protective effect of the Mediterranean diet against chronic low-grade inflammatory diseases. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 14, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karstens, A.J.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Zhan, L.; Rajendran, N.; Cohen, J.; Dion, C.; Zhou, X.J.; Lamar, M. Associations of the Mediterranean diet with cognitive and neuroimaging phenotypes of dementia in healthy older adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Barbagallo, M.; Muñoz-Garcia, M.; Godos, J.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. Dietary Patterns and Cognitive Decline: Key features for prevention. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2428–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, R.; Reutzel, M.; Dilberger, B.; Hein, H.; Zotzel, J.; Marx, S.; Tretzel, J.; Sarafeddinov, A.; Fuchs, C.; Eckert, G.P. Purified oleocanthal and ligstroside protect against mitochondrial dysfunction in models of early Alzheimer’s disease and brain ageing. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 328, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimundo, M.; Mira, F.; Cachulo, M.D.L.; Barreto, P.; Ribeiro, L.; Farinha, C.; Laíns, I.; Nunes, S.; Alves, D.; Figueira, J.; et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet, lifestyle and age-related macular degeneration: The Coimbra Eye Study—Report 3. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, e926–e932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-López, A.; Babio, N.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Amor, A.J.; Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Fiol, M.; et al. Mediterranean Diet, Retinopathy, Nephropathy, and Microvascular Diabetes Complications: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2134–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sala-Vila, A.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hu, F.B.; Sánchez-Tainta, A.; Bulló, M.; Serra-Mir, M.; López-Sabater, C.; Sorlí, J.V.; Arós, F.; Fiol, M.; et al. Dietary α-Linolenic Acid, Marine ω-3 Fatty Acids, and Mortality in a Population with High Fish Consumption: Findings From the PREvención con DIeta MEDiterránea (PREDIMED) Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abreu-Reyes, J.A.; Álvarez-Luis, D.; Arteaga-Hernández, V.; Sánchez-Mendez, M.; Abreu-González, R. Mediterranean diet adherence by patients with primary open angle glaucoma. Arch. Soc. Esp. Oftalmol. 2017, 92, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-González, S.M.; García-Medina, J.J.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; López-Gálvez, M.I.; Galarreta-Mira, D.; Duarte, L.; Valero-Velló, M.; Ramírez, A.I.; Arévalo, J.F.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D. On Behalf Of The Valencia Study Group On Diabetic Retinopathy VSDR. Report Number 5. Clinical and Molecular-Genetic Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Retinopathy: Antioxidant Strategies and Future Avenues. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Leyva, I.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Riquelme-Gallego, B.; Cano-Ibáñez, N.; García-Molina, L.; Bueno-Cavanillas, A. Effectiveness of Mediterranean Diet Implementation in Dry Eye Parameters: A Study of PREDIMED-PLUS Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, G. Ocular Pathology and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet: Scuola di Scienze della Salute Umana; Corso di Laurea/Laurea; Specialistica/Laurea Magistrale in Medicina e Chirurgia: Florence, Italy, 2016; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Castejón-Cervero, M.A.; Jiménez-Parras, R.; Fernandez-Arias, I.; Teus-Guezala, M.A.; IMCA Study Group. Evaluation of compliance with the EGS guidelines in Spain, using Achievable Benchmarks of Care (ABC®) methodology: The IMCA Study. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 21, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareja-Ríos, A.; Serrano-García, M.A.; Marrero-Saavedra, M.D.; Abraldes-López, V.M.; Reyes-Rodríguez, M.A.; Cabrera-López, F.; López-Gálvez, M.; Cardona-Guerra, P.; Abreu-Reyes, P.; Quijada-Fumero, E.; et al. Guías de práctica clínica de la SERV: Manejo de las complicaciones oculares de la diabetes. Retinopatía diabética y edema macular [Guidelines of clinical practice of the SERV (Spanish Retina and Vitreous Society): Management of ocular complications of diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy and macular oedema]. Arch. Soc. Esp. Oftalmol. 2009, 84, 429–450. [Google Scholar]
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group; Nathan, D.M.; Genuth, S.; Lachin, J.; Cleary, P.; Crofford, O.; Davis, M.; Rand, L.; Siebert, C. The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Bulló, M.; Babio, N.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Ibarrola-Jurado, N.; Basora, J.; Estruch, R.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; et al. Erratum. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with the Mediterranean diet: Results of the PREDIMED-Reus nutrition intervention randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coleman, A.L.; Stone, K.L.; Kodjebacheva, G.; Yu, F.; Pedula, K.L.; Ensrud, K.E.; Cauley, J.A.; Hochberg, M.C.; Topouzis, F.; Badala, F.; et al. Glaucoma Risk and the Consumption of Fruits and Vegetables among Older Women in the Study of Osteoporotic Fractures. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 145, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giaconi, J.A.; Yu, F.; Stone, K.L.; Pedula, K.L.; Ensrud, K.E.; Cauley, J.A.; Hochberg, M.C.; Coleman, A.L.; Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. The Association of Consumption of Fruits/Vegetables with Decreased Risk of Glaucoma among Older African-American Women in the Study of Osteoporotic Fractures. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 154, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramdas, W.D.; Schouten, J.S.A.G.; Webers, C.A.B. The Effect of Vitamins on Glaucoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2018, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bursell, S.E.; Clermont, A.C.; Aiello, L.P.; Aiello, L.M.; Schlossman, D.K.; Feener, E.P.; Laffel, L.; King, G.L. High-dose vitamin E supplementation normalizes retinal blood flow and creatinine clearance in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Medina, J.J.; Pinazo-Duran, M.D.; Garcia-Medina, M.; Zanon-Moreno, V.; Pons-Vazquez, S. A 5-year follow-up of antioxidant supplementation in type 2 diabetic retinopathy. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 21, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.J.; Hu, Y.N.; Lin, S.; Ma, W.J.; Li, X.R. Application of Lutein and Zeaxanthin in nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 4, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chous, A.P.; Richer, S.P.; Gerson, J.D.; Kowluru, R.A. The Diabetes Visual Function Supplement Study (DiVFuSS). Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohguro, H.; Ohguro, I.; Katai, M.; Tanaka, S. Two-Year Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of Black Currant Anthocyanins on Visual Field in Glaucoma. Ophthalmologica 2012, 228, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohguro, H.; Ohguro, I.; Yagi, S. Effects of Black Currant Anthocyanins on Intraocular Pressure in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Glaucoma. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 29, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Sohn, S.W.; Kee, C. Effect of Ginkgo Biloba Extract on Visual Field Progression in Normal Tension Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2013, 22, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Medina, J.J.; Garcia-Medina, M.; Garrido-Fernandez, P.; Galvan-Espinosa, J.; Garcia-Maturana, C.; Zanon-Moreno, V.; Pinazo-Duran, M.D. A Two-Year Follow-up of Oral Antioxidant Supplementation in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: An Open-Label, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutolo, M.G.; Albanese, G.; Rusciano, D.; Pescosolido, N. Oral administration of forskolin, homotaurine, carnosine, and folic acid in patients with primary open angle glaucoma: Changes in intraocular pressure, pattern electroretinogram amplitude, and foveal sensitivity. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 32, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo Villadóniga, S.; Rodríguez García, E.; Sagastagoia Epelde, O.; Álvarez Díaz, M.D.; Domingo Pedrol, J.C. Effects of Oral Supplementation with Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) plus Antioxidants in Pseudoexfoliative Glaucoma: A 6-Month Open-Label Randomized Trial. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 2018, 8259371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Downie, L.E.; Ng, S.M.; Lindsley, K.B.; Akpek, E.K. Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids for dry eye disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 12, CD011016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Ji, J. Omega-3 essential fatty acids therapy for dry eye syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galbis-Estrada, C.; Martinez-Castillo, S.; Morales, J.M.; Vivar-Llopis, B.; Monleón, D.; Díaz-Llopis, M.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D. Differential effects of dry eye disorders on metabolomic profile by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 542549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Raga-Cervera, J.; Sanz-González, S.M.; Salgado-Borges, J.; Benítez-Del-Castillo, J.; Ramírez, A.I.; Zanón-Moreno, V. Efficacy and safety study of an eyelid gel after repeated nocturnal application in healthy contact lens users and non-users. J. Optom. 2021, 14, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Walnuts (Juglans Californica) | |
|---|---|
| Content | Concentration/100 g |
| Polyphenols | 2500 mg |
| Phytosterols | 113 mg |
| α-linolenic acid | ~8000 mg |
| Υ-tocopherol | 21 mg |
| Sodium | 2 mg |
| Potassium | 441 mg |
| Magnesium | 158 mg |
| Calcium | 98 mg |
| Phytomelatonin | 350 ng |
| Type 2 Diabetics with DR | Type 2 Diabetics without DR | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poor Adherence MedDiet | Good Adherence MedDiet | Poor Adherence MedDiet | Good Adherence MedDiet | ||
| MDA/TBARS (mm/L) | 4 ± 1 | 3 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 | p < 0.001 |
| TAC (mM) | 2 ± 1 | 2 ± 2 | 3 ± 1 | 3 ± 2 | p < 0.051 |
| CG (n = 58) | Ocular Pathologies (n = 52) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cataracts (n = 16) | Glaucoma (n = 13) | DR (n = 23) | ||
| Adherence level | 8.4 ± 1.8 | 8.8 ± 2.3 | 8.9 ± 2.2 | 8.3 ± 2.1 |
| p value | Ref | 0.519 | 0.371 | 0.775 |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | |||||
| Oral Supplementation | Year | Authors | N | Follow-Up | Results of Intervention |
| Complex formula [DiVFuSS formula] | 2016 | Chous et al. [167] | 67 | 6 months | Improvement in visual function without macular thickness change. |
| Complex formula [Vitalux Forte®] | 2011 | Garcia-Medina et al. [165] | 105 | 5 years | Visual acuity unchanged. Slower progression of treated group. |
| Lutein and zeaxanthin | 2011 | Hu et al. [166] | 90 | 3 months | Better visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and decrease of foveal thickness. |
| Vitamin E | 1999 | Bursell et al. [164] | 45 | 8 months | Improvement of retinal blood flow after supplementation. |
| Antioxidants, Carotenoids, Trace metals and Omega 3 Fatty Acids [Nutrof Omega ® formula] | 2015 | Roig-Revert et al., VSDR group [40] | 360 | 18 months | Decreased plasmatic oxidative level and increased antioxidant activity was seen in T2DM patients. |
| Antioxidants, Carotenoids, Trace metals and Omega 3 Fatty Acids [Nutrof Omega ® formula] | 2020 | Sanz-González et al. VSDR group [154] | 575 | 38 months | Reduced oxidative load and dietary prophylaxis/adjunctive intervention for patients at risk of diabetic retinopathy. |
| Glaucoma | |||||
| Oral Supplementation | Year | Authors | N | Follow-Up | Results of Intervention |
| AREDS-based formulas | 2015 | Garcia-Medina et al. [171] | 117 | 2 years | No differences in visual field indexes, RGCl complex, peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer. |
| Black currant anthocyanins | 2012 | Ohguro et al. [168] | 38 | 24 months | Better mean deviation change (visual field index) in supplemented group. |
| Black currant anthocyanins | 2013 | Ohguro et al. [169] | 21 | 4 weeks | IOP decrease at 2 and 4 weeks in treated group but no change in placebo group. |
| Docosahexaenoic acid | 2018 | Romeo Villadoniga et al. [173] | 47 | 6 months | IOP decrease at 3 and 6 months in treated eyes. |
| Formula containing forskolin, homotaurine, carnosine, and folic acid | 2016 | Mutolo et al. [172] | 44 | 1 year | IOP lowering, ERG improvement and foveal sensitivity. |
| Antioxidants and Omega 3 fatty acids [Brudysec ® formula] | 2013 | Galbis-Estrada et al. [45] | 97 | 3 months | Reduced inflammation biomarkers in glaucomatous tears. |
| Ginkgo biloba extract | 2013 | Lee et al. [170] | 42 | 12 years | Slower progression of visual field damage in treated patients. |
| Ocular Surface Disorders/Dry Eyes | |||||
| Omega 3 and Omega 6 polyunsaturated fatty acids | 2019 | Downie et al. [174] | 4214 | Cochrane systematic review of clinical trials evidence uncertain/inconsistent for DEDs. | |
| Omega 3 and Omega 6 polyunsaturated fatty acids | 2014 | Liu and Ji, [175] | 790 | Meta-analyses of randomized, placebo-controlled studies. Improvement of clinical tests, individual-reported symptoms in DEDs. | |
| Antioxidants and Omega 3 fatty acids [Brudysec ® formula] | 2013 | Pinazo-Duran et al. [44] | 66 | Benefit DED patients. Improvement of dry eye-related quality of life. Ameliorating clinical tests and tear expression of inflammatory mediators. | |
| Antioxidants and Omega 3 fatty acids [Brudysec ® formula] | 2015 | Galbis-Estrada et al. [123] | 90 | Improvement of subjective dry-eye symptoms by changing the tear metabolomic profile | |
| Omega 3 fatty acids [Brudy Derm Dry Eye Gel ®] | 2021 | Pinazo-Durán et al. [177] | 72 | Ameliorating ocular surface relief and decreasing cytokine expression in tears from contact lenses users. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valero-Vello, M.; Peris-Martínez, C.; García-Medina, J.J.; Sanz-González, S.M.; Ramírez, A.I.; Fernández-Albarral, J.A.; Galarreta-Mira, D.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; Casaroli-Marano, R.P.; Pinazo-Duran, M.D. Searching for the Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Neuroprotective Potential of Natural Food and Nutritional Supplements for Ocular Health in the Mediterranean Population. Foods 2021, 10, 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061231
Valero-Vello M, Peris-Martínez C, García-Medina JJ, Sanz-González SM, Ramírez AI, Fernández-Albarral JA, Galarreta-Mira D, Zanón-Moreno V, Casaroli-Marano RP, Pinazo-Duran MD. Searching for the Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Neuroprotective Potential of Natural Food and Nutritional Supplements for Ocular Health in the Mediterranean Population. Foods. 2021; 10(6):1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061231
Chicago/Turabian StyleValero-Vello, Mar, Cristina Peris-Martínez, José J. García-Medina, Silvia M. Sanz-González, Ana I. Ramírez, José A. Fernández-Albarral, David Galarreta-Mira, Vicente Zanón-Moreno, Ricardo P. Casaroli-Marano, and María D. Pinazo-Duran. 2021. "Searching for the Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Neuroprotective Potential of Natural Food and Nutritional Supplements for Ocular Health in the Mediterranean Population" Foods 10, no. 6: 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061231
APA StyleValero-Vello, M., Peris-Martínez, C., García-Medina, J. J., Sanz-González, S. M., Ramírez, A. I., Fernández-Albarral, J. A., Galarreta-Mira, D., Zanón-Moreno, V., Casaroli-Marano, R. P., & Pinazo-Duran, M. D. (2021). Searching for the Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Neuroprotective Potential of Natural Food and Nutritional Supplements for Ocular Health in the Mediterranean Population. Foods, 10(6), 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061231