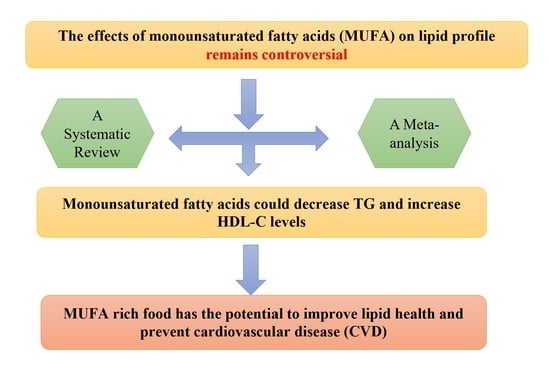
The Effect of MUFA-Rich Food on Lipid Profile: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Controlled-Feeding Trials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Study Characteristics
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Results of Meta-Analysis
3.4. Subgroup Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis
3.5. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, Y.; Robidoux, J. Dyslipidemia management update. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 33, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.C.; Tseng, C.H. Dyslipidemia, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease in diabetic patients. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2013, 10, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahinfar, H.; Bazshahi, E.; Amini, M.R.; Payandeh, N.; Pourreza, S.; Noruzi, Z.; Shab-Bidar, S. Effects of artichoke leaf extract supplementation or artichoke juice consumption on lipid profile: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6607–6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddei, C.; Zhou, B.; Bixby, H.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Danaei, G.; Jackson, R.T.; Farzadfar, F.; Sophiea, M.K.; Di Cesare, M.; Iurilli, M.L.C. Repositioning of the global epicentre of non-optimal cholesterol. Nature 2020, 582, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Opoku, S.; Gan, Y.; Fu, W.; Chen, D.; Addo-Yobo, E.; Trofimovitch, D.; Yue, W.; Yan, F.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z. Prevalence and risk factors for dyslipidemia among adults in rural and urban China: Findings from the China National Stroke Screening and prevention project (CNSSPP). BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koene, R.J.; Prizment, A.E.; Blaes, A.; Konety, S.H. Shared risk factors in cardiovascular disease and cancer. Circulation 2016, 133, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matey-Hernandez, M.L.; Williams, F.M.K.; Potter, T.; Valdes, A.M.; Spector, T.D.; Menni, C. Genetic and microbiome influence on lipid metabolism and dyslipidemia. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.M. Managing the spectrum of dyslipidemia in primary care. J. Vasc. Nurs. 2003, 21, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Ding, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Tan, L.; Mu, L.; Liu, J. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and availability of lipid-lowering medications among primary health care settings in china. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2127573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G. Monounsaturated fatty acids and risk of cardiovascular disease: Synopsis of the evidence available from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1989–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grundy, S.M. Monounsaturated fatty acids and cholesterol metabolism: Implications for dietary recommendations. J. Nutr. 1989, 119, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G. Monounsaturated fatty acids, olive oil and health status: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bos, M.B.; de Vries, J.H.; Feskens, E.J.; van Dijk, S.J.; Hoelen, D.W.; Siebelink, E.; Heijligenberg, R.; de Groot, L.C. Effect of a high monounsaturated fatty acids diet and a Mediterranean diet on serum lipids and insulin sensitivity in adults with mild abdominal obesity. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2010, 20, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, E.; Schulz, J.A.; Kaden, V.N.; Lawless, A.L.; Rotor, J.; Mantilla, L.B.; Liska, D.J. Cashew consumption reduces total and LDL cholesterol: A randomized, crossover, controlled-feeding trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohan, V.; Gayathri, R.; Jaacks, L.M.; Lakshmipriya, N.; Anjana, R.M.; Spiegelman, D.; Jeevan, R.G.; Balasubramaniam, K.K.; Shobana, S.; Jayanthan, M. Cashew nut consumption increases HDL cholesterol and reduces systolic blood pressure in Asian Indians with type 2 diabetes: A 12-week randomized controlled trial. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Strasser, B.; Hoffmann, G. Effects of monounsaturated fatty acids on cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 59, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Wang, J.; Shao, W. Monounsaturated fatty acid intake and stroke risk: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, F.; Micha, R.; Wu, J.H.Y.; Otto, M.C.d.O.; Otite, F.O.; Abioye, A.I.; Mozaffarian, D. Effects of saturated fat, polyunsaturated fat, monounsaturated fat, and carbohydrate on glucose-insulin homeostasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled feeding trials. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azad, B.; Daneshzad, E.; Azadbakht, L. Peanut and cardiovascular disease risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1123–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Sattar, N.; Toth, P.P.; Judd, S.; Blaha, M.; Hernandez, A.V.; Penson, P.E.; Banach, M. (International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP) & Lipid and Blood Pressure Meta-analysis Collaboration (LBPMC) Group). Association of types of dietary fats and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A prospective cohort study and meta-analysis of prospective studies with 1,164,029 participants. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3677–3686. [Google Scholar]
- Lotfi, K.; Salari-Moghaddam, A.; Yousefinia, M.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Dietary intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and risk of mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease and cancer: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 72, 101467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane. 20 February 2022. Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Mercanligil, S.M.; Arslan, P.; Alasalvar, C.; Okut, E.; Akgul, E.; Pinar, A.; Geyik, P.O.; Tokgozoglu, L.; Shahidi, F. Effects of hazelnut-enriched diet on plasma cholesterol and lipoprotein profiles in hypercholesterolemic adult men. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salar, A.; Faghih, S.; Pishdad, G.R. Rice bran oil and canola oil improve blood lipids compared to sunflower oil in women with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, single-blind, controlled trial. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2016, 10, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negele, L.; Schneider, B.; Ristl, R.; Stulnig, T.M.; Willfort-Ehringer, A.; Helk, O.; Widhalm, K. Effect of a low-fat diet enriched either with rapeseed oil or sunflower oil on plasma lipoproteins in children and adolescents with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Results of a pilot study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pieterse, Z.; Jerling, J.C.; Oosthuizen, W.; Kruger, H.S.; Hanekom, S.M.; Smuts, C.M.; Schutte, A.E. Substitution of high monounsaturated fatty acid avocado for mixed dietary fats during an energy-restricted diet: Effects on weight loss, serum lipids, fibrinogen, and vascular function. Nutrition 2005, 21, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonehouse, W.; Sergi, D.; Benassi-Evans, B.; James-Martin, G.; Johnson, N.; Thompson, C.H.; Abeywardena, M. Eucaloric diets enriched in palm olein, cocoa butter, and soybean oil did not differentially affect liver fat concentration in healthy participants: A 16-week randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griel, A.E.; Cao, Y.; Bagshaw, D.D.; Cifelli, A.M.; Holub, B.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. A macadamia nut-rich diet reduces total and LDL-cholesterol in mildly hypercholesterolemic men and women. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Bordi, P.L.; Fleming, J.A.; Hill, A.M.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Effect of a moderate fat diet with and without avocados on lipoprotein particle number, size and subclasses in overweight and obese adults: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ooi, E.M.; Watts, G.F.; Ng, T.W.; Barrett, P.H. Effect of dietary Fatty acids on human lipoprotein metabolism: A comprehensive update. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4416–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Pearson, T.A.; Wan, Y.; Hargrove, R.L.; Moriarty, K.; Fishell, V.; Etherton, T.D. High-monounsaturated fatty acid diets lower both plasma cholesterol and triacylglycerol concentrations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, S.; Burke, K.; Connell, B.; Myint, T.; Sabaté, J. A monounsaturated fatty acid-rich pecan-enriched diet favorably alters the serum lipid profile of healthy men and women. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, L.A.; Walzem, R.L.; Crouse, S.F.; Smith, D.R.; Adams, T.H.; Vaidyanathan, V.; Cao, X.; Smith, S.B. Consumption of high-oleic acid ground beef increases HDL-cholesterol concentration but both high- and low-oleic acid ground beef decrease HDL particle diameter in normocholesterolemic men. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilmore, L.A.; Crouse, S.F.; Carbuhn, A.; Klooster, J.; Calles, J.A.; Meade, T.; Smith, S.B. Exercise attenuates the increase in plasma monounsaturated fatty acids and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol but not high-density lipoprotein 2b cholesterol caused by high-oleic ground beef in women. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unhapipatpong, C.; Shantavasinkul, P.C.; Kasemsup, V.; Siriyotha, S.; Warodomwichit, D.; Maneesuwannarat, S.; Vathesatogkit, P.; Sritara, P.; Thakkinstian, A. Tropical oil consumption and cardiovascular disease: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta analyses. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López Ledesma, R.; Frati Munari, A.C.; Hernández Domínguez, B.C.; Cervantes Montalvo, S.; Hernández Luna, M.H.; Juárez, C.; Morán Lira, S. Monounsaturated fatty acid (avocado) rich diet for mild hypercholesterolemia. Arch. Med. Res. 1996, 27, 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, D.J. Dietary fatty acids, lipoproteins, and cardiovascular disease. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 1992, 36, 253–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Morgado, N.; Prada, J.L.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Muriana, F.J. Composition of human VLDL triacylglycerols after ingestion of olive oil and high oleic sunflower oil. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berry, E.M.; Eisenberg, S.; Haratz, D.; Friedlander, Y.; Norman, Y.; Kaufmann, N.A.; Stein, Y. Effects of diets rich in monounsaturated fatty acids on plasma lipoproteins--the Jerusalem Nutrition Study: High MUFAs vs high PUFAs. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Zhao, G.; Pelkman, C.L.; Fishell, V.K.; Coval, S.M. Beneficial effects of a diet high in monounsaturated fatty acids on risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 3, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbiner, B.; Low, C.C.; Reaven, P.D. Effects of a monounsaturated fatty acid-enriched hypocaloric diet on cardiovascular risk factors in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.S. Are n-3 fatty acids still cardioprotective? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.A. Dietary n-3 PUFA and CVD: A review of the evidence. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Wu, J.H. Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: Effects on risk factors, molecular pathways, and clinical events. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2047–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kromhout, D.; Yasuda, S.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Shimokawa, H. Fish oil and omega-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular disease: Do they really work? Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oswal, D.P.; Balanarasimha, M.; Loyer, J.K.; Bedi, S.; Soman, F.L.; Rider, S.D.; Hostetler, H.A. Divergence between human and murine peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha ligand specificities. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2354–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Literature | Year | Study Region | Mean Age (Years) | Number of Participants (M/C) | MUFA Source | Amount of MUFA (M/C) | Study Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salar-1 [23] | 2016 | Iran (Asia) | 51.42 | 24/23 | Canola oil | 6.9/6.5 a | Parallel |
| Salar-2 [23] | 2016 | Iran (Asia) | 51.42 | 25/23 | Rice bran oil | 7.63/6.5 a | Parallel |
| Negele [24] | 2015 | Austria | 11.1 | 12/9 | Rapeseed oil | NA | Parallel |
| Welma-1 [26] | 2021 | Australia | 32.66 | 20/22 | Palm olein | 25.65/9.42 b | Parallel |
| Welma-2 [26] | 2021 | Australia | 32.66 | 20/21 | Palm olein | 25.65/15.14 b | Parallel |
| Wang-1 [28] | 2015 | America | 45 | 42/43 | Avocado | 17/12 a | Crossover |
| Wang-2 [28] | 2015 | America | 45 | 43/43 | High oleic acid oils | 17/12 a | Crossover |
| Pieterse [25] | 2005 | South Africa | 40.8 | 28/27 | Avocado | 20/0 b | Parallel |
| Griel [27] | 2008 | America | 50.2 | 25/25 | Nut | 18/12 a | Crossover |
| Mercanligil [22] | 2007 | Turkey (Asia) | 48.0 | 15/15 | Hazelnut | 17–20/13–15 a | Crossover |
| Study | Random Sequence Generation | Allocation Concealment | Blinding of Participants and Personnel | Blinding of Outcome Assessment | Incomplete Outcome Data | Selective Reporting | Other Sources of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 Salar [24] | L | L | L | L | L | L | U |
| 2015 Negele [25] | H | L | L | L | L | L | U |
| 2021 Welma [27] | L | L | H | L | L | L | U |
| 2015 Wang [28] | U | U | H | L | L | L | U |
| 2005 Pieterse [26] | U | H | H | L | L | L | U |
| 2008 Griel [27] | U | U | U | L | L | L | U |
| 2007 Mercanlıgil [23] | U | U | H | L | L | L | U |
| Subgroups | TC | LDL-C | HDL-C | TG | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | WMD (95%CI) | Heterogeneity | N | WMD (95%CI) | Heterogeneity | N | WMD (95%CI) | Heterogeneity | N | WMD (95%CI) | Heterogeneity | |||||
| p | I2 (%) | p | I2 (%) | p | I2 (%) | p | I2 (%) | |||||||||
| MUFA source | 5 | 0.01 (−0.46, 0.48) | 0.001 | 79.4 | 5 | 0.15 (−0.02, 0.32) | 0.175 | 37.0 | 5 | 0.05 (0.01, 0.10) | 0.200 | 33.2 | 5 | −0.16 (−0.52, 0.20) | 0.002 | 76.6 |
| Canola oil | 2 | −0.2 (−0.67, 0.27) | 0.520 | 0 | 2 | 0.17 (−0.64, 0.30) | 0.638 | 0 | 2 | 0.01 (−0.09, 0.1) | 0.624 | 0 | 2 | −0.52 (−1.15, 0.11) | 0.627 | 0 |
| Palm olein | 2 | 0.42 (−0.07, 0.78) | 0.134 | 55.6 | 2 | 0.24 (0.04, 0.44) | 0.101 | 62.8 | 2 | 0.11 (0.04, 0.17) | 0.383 | 0 | 2 | 0.19 (0.06, 0.31) | 0.654 | 0 |
| Rice bran oil | 1 | −0.71 (−1.25, −0.17) | - | - | 1 | −0.08 (−0.57, 0.41) | - | - | 1 | −0.01 (−0.11, 0.09) | - | - | 1 | −1.21 (−1.97, −0.45) | - | - |
| Participant condition | 5 | 0.01 (−0.46, 0.48) | 0.001 | 79.4 | 5 | 0.15 (−0.02, 0.32) | 0.175 | 37.0 | 5 | 0.05 (0.01, 0.10) | 0.200 | 33.2 | 5 | −0.16 (−0.52, 0.20) | 0.002 | 76.6 |
| Patients | 3 | −0.41 (−0.80, −0.02) | 0.313 | 0 | 3 | −0.13 (−0.47, 0.21) | 0.864 | 0 | 3 | 0.00 (−0.07, 0.07) | 0.860 | 0 | 3 | −0.79 (−1.29, −0.29) | 0.346 | 5.7 |
| Healthy people | 2 | 0.42 (−0.07, 0.78) | 0.134 | 55.6 | 2 | 0.24 (0.04, 0.44) | 0.101 | 62.8 | 2 | 0.11 (0.04, 0.17) | 0.383 | 0 | 2 | 0.19 (0.06, 0.31) | 0.654 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Xia, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.; Liao, W.; Sun, G. The Effect of MUFA-Rich Food on Lipid Profile: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Controlled-Feeding Trials. Foods 2022, 11, 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131982
Cao X, Xia J, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Xia H, Wang S, Liao W, Sun G. The Effect of MUFA-Rich Food on Lipid Profile: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Controlled-Feeding Trials. Foods. 2022; 11(13):1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131982
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xinyi, Jiayue Xia, Yuhao Zhou, Yuanyuan Wang, Hui Xia, Shaokang Wang, Wang Liao, and Guiju Sun. 2022. "The Effect of MUFA-Rich Food on Lipid Profile: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Controlled-Feeding Trials" Foods 11, no. 13: 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131982
APA StyleCao, X., Xia, J., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Xia, H., Wang, S., Liao, W., & Sun, G. (2022). The Effect of MUFA-Rich Food on Lipid Profile: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Controlled-Feeding Trials. Foods, 11(13), 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131982